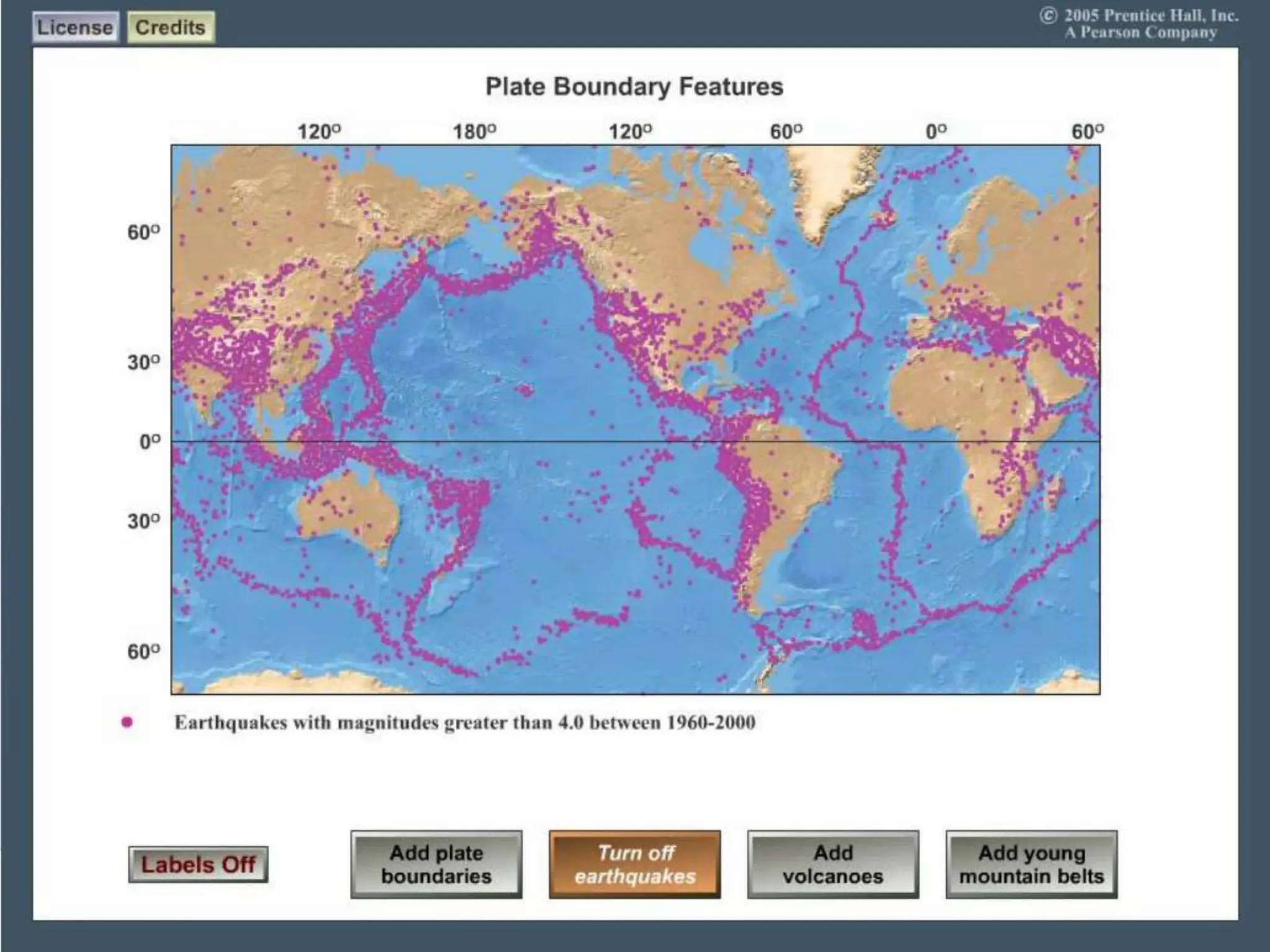
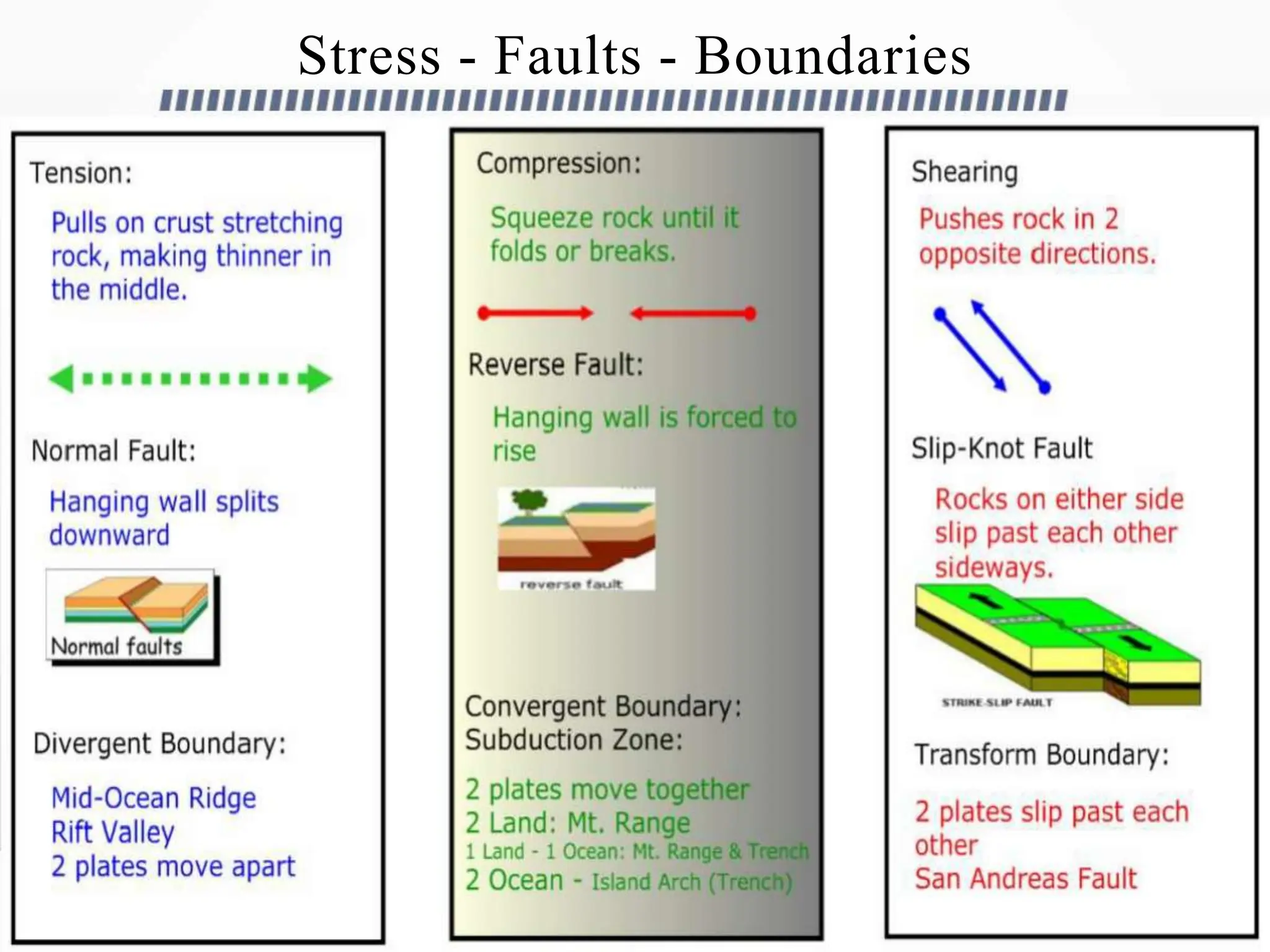
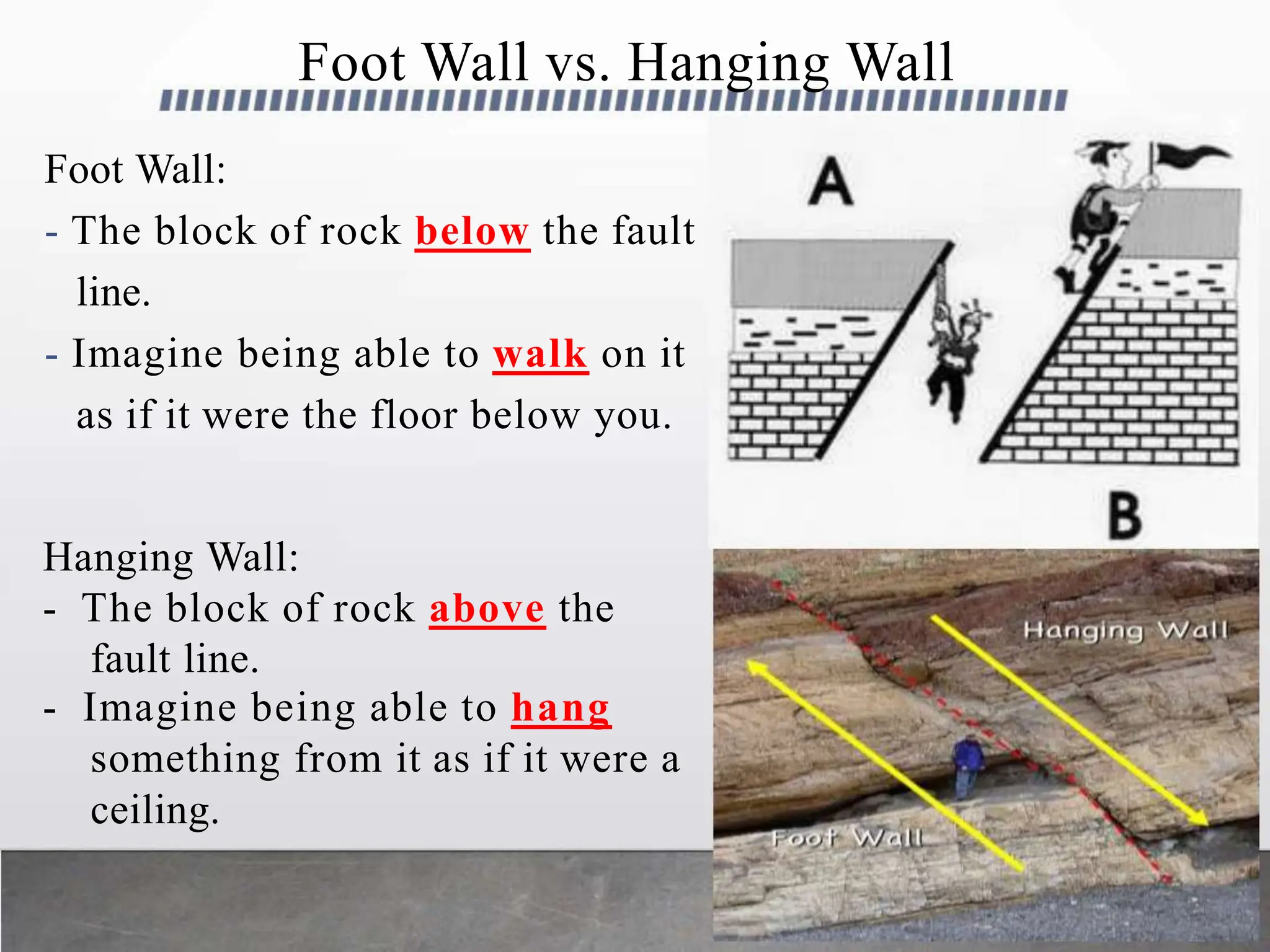
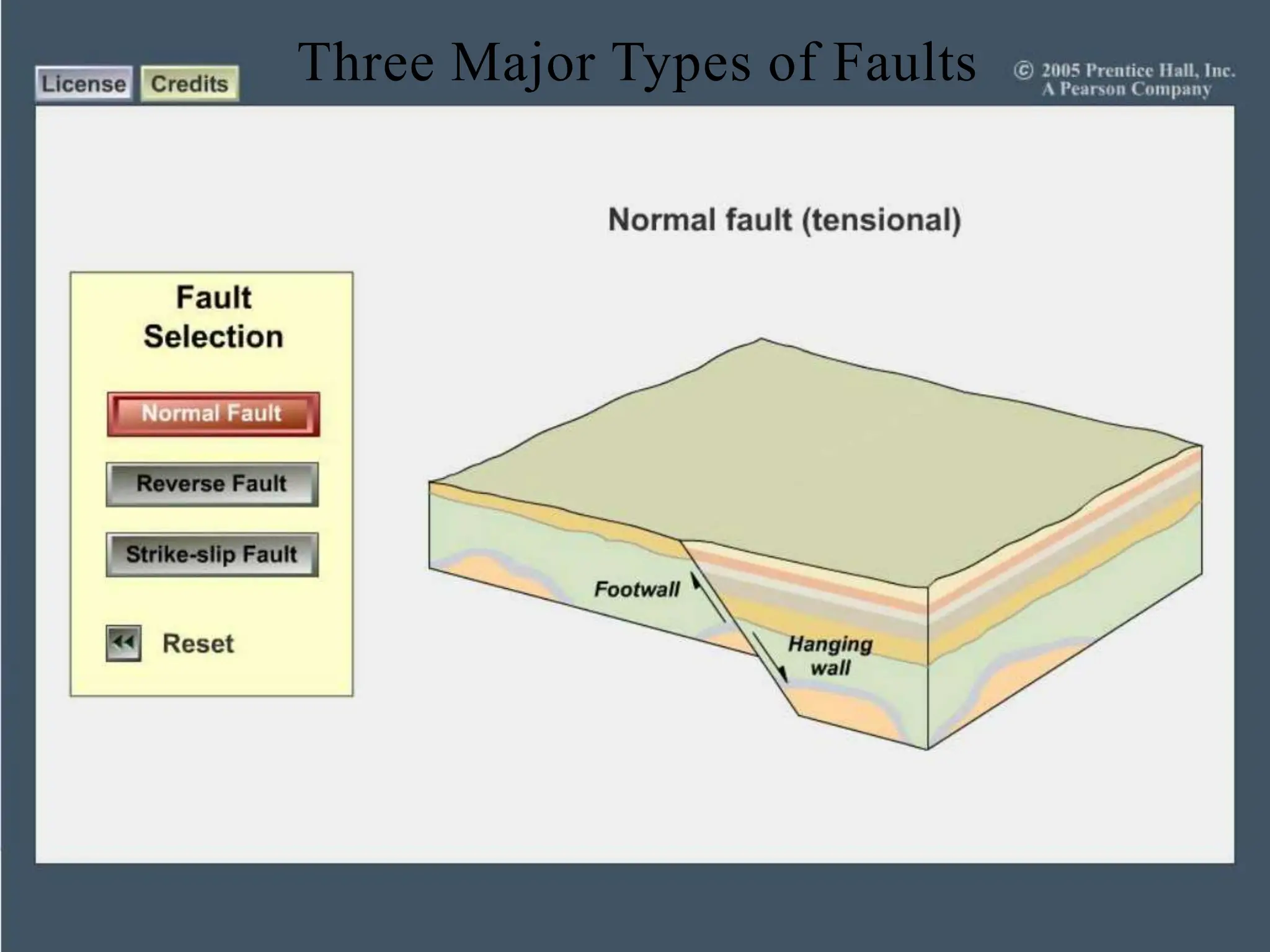
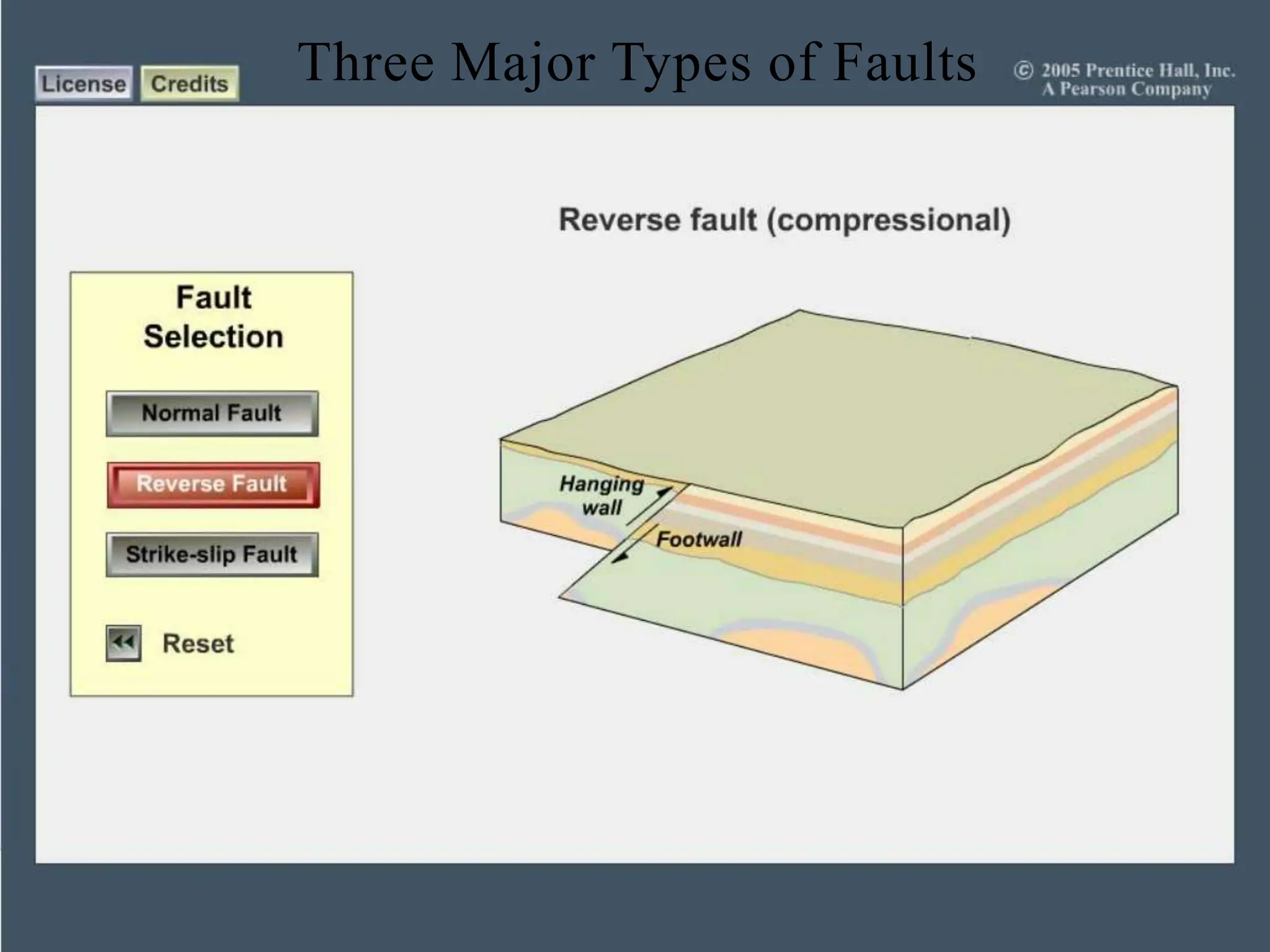
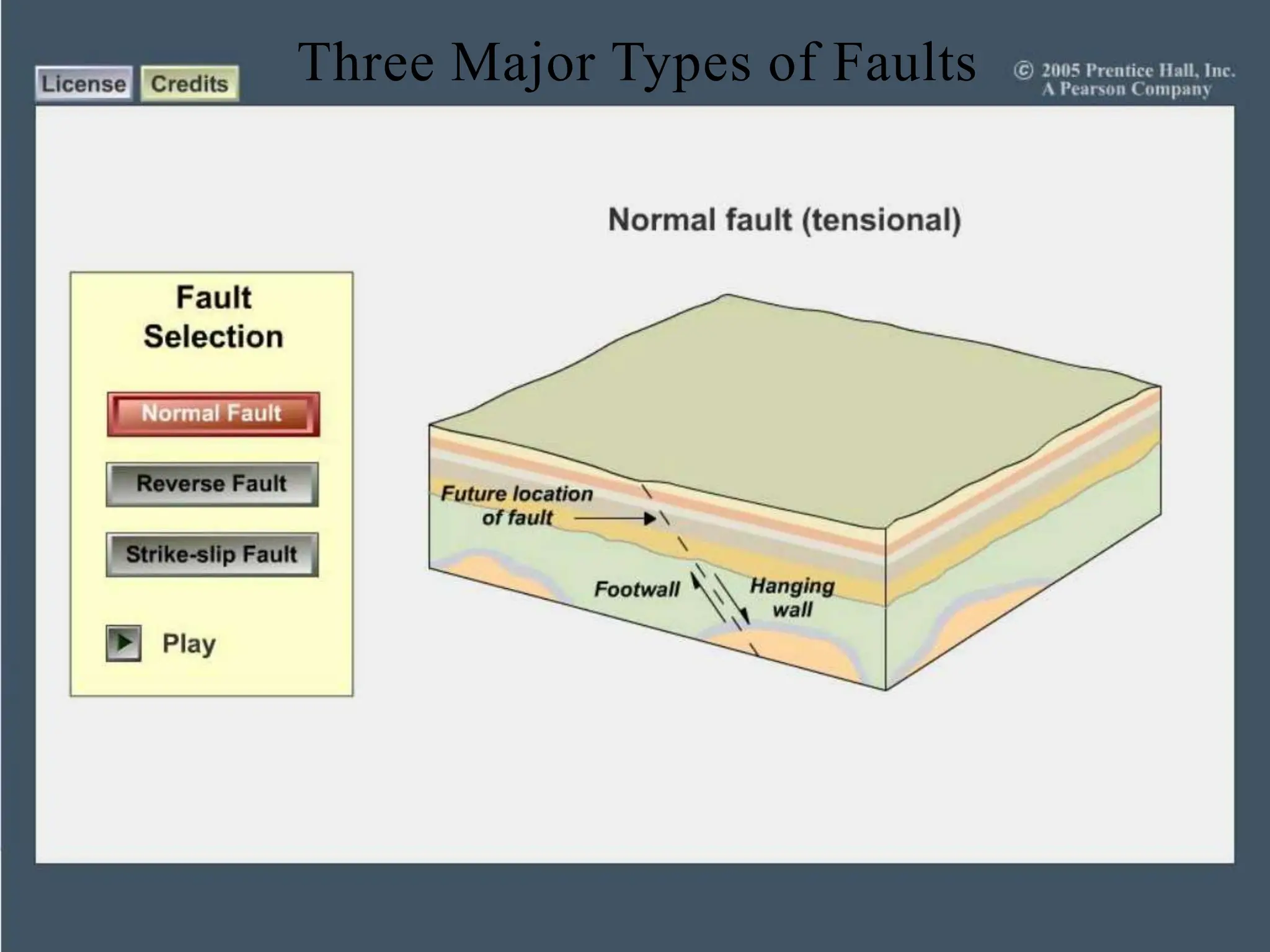
Earthquakes occur when built-up stress causes rocks beneath the earth's surface to suddenly break along faults. Rocks experience stress as the tectonic plates they reside in slowly move and push against each other over long periods of time. This stress eventually exceeds the rocks' elastic limit, resulting in an earthquake as the rocks snap back to their original positions. The three major types of faults that cause earthquakes are normal faults formed by tension between plates, reverse faults caused by compression, and strike-slip faults driven by horizontal shearing movements between plates.