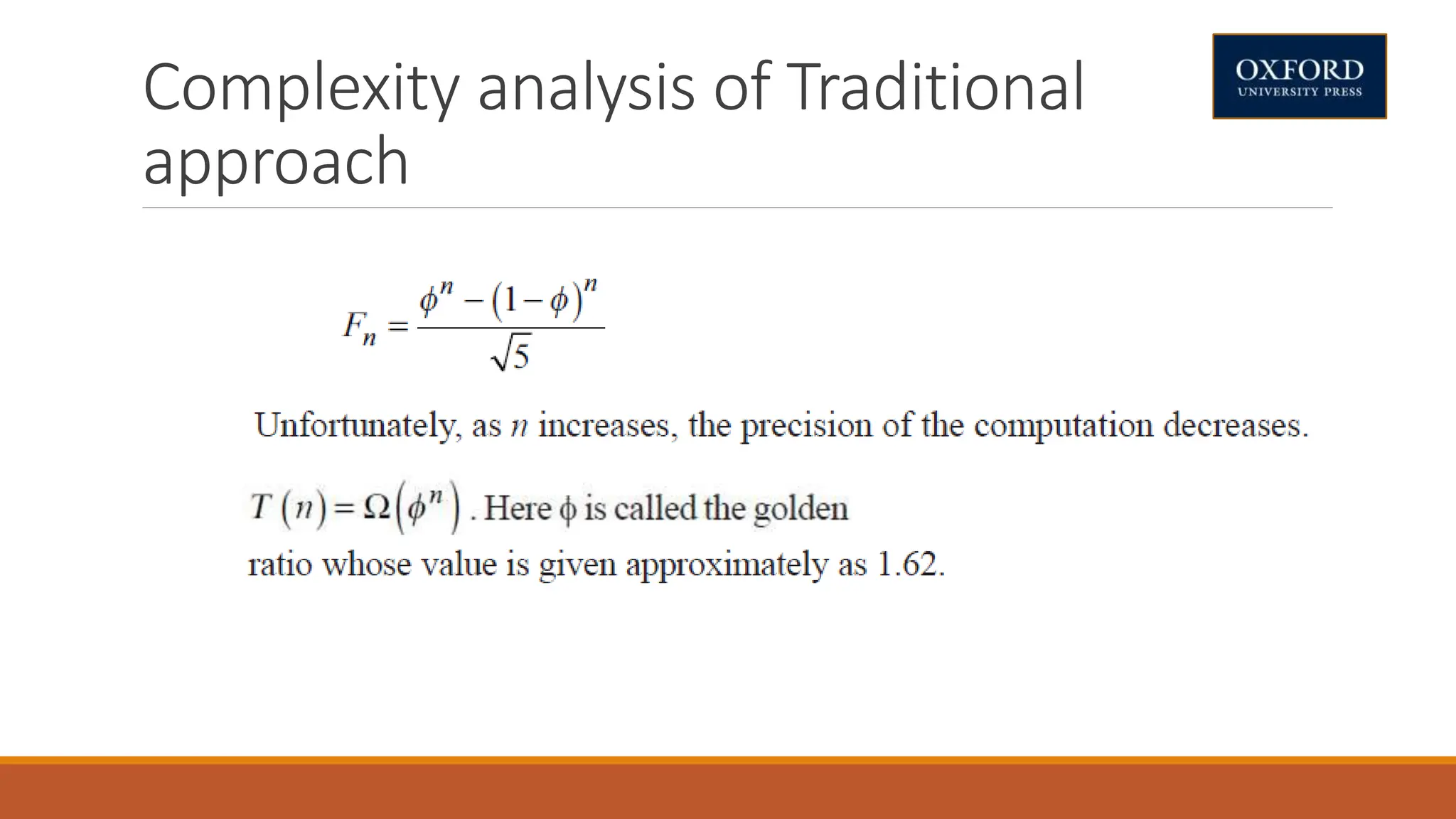
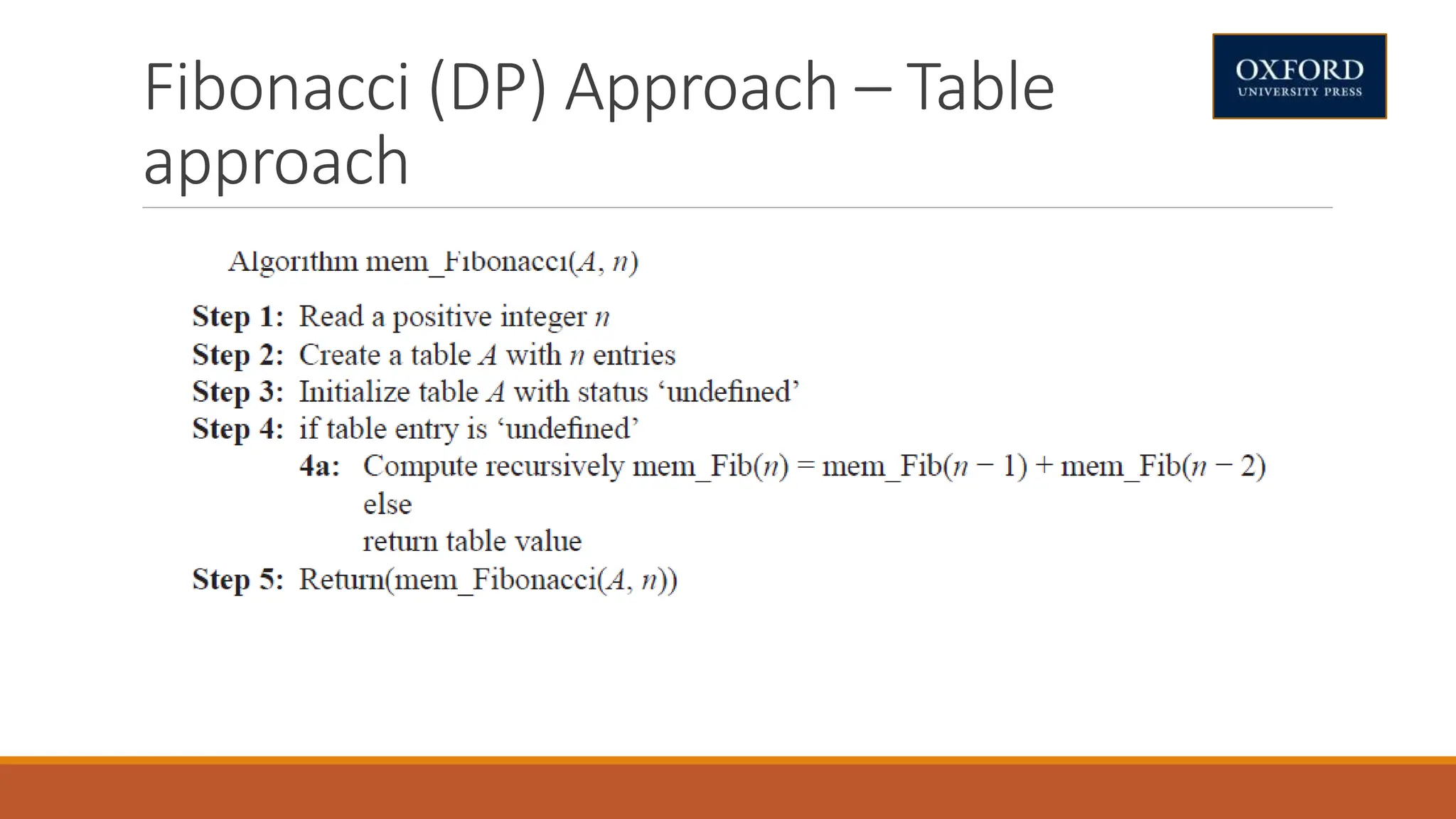
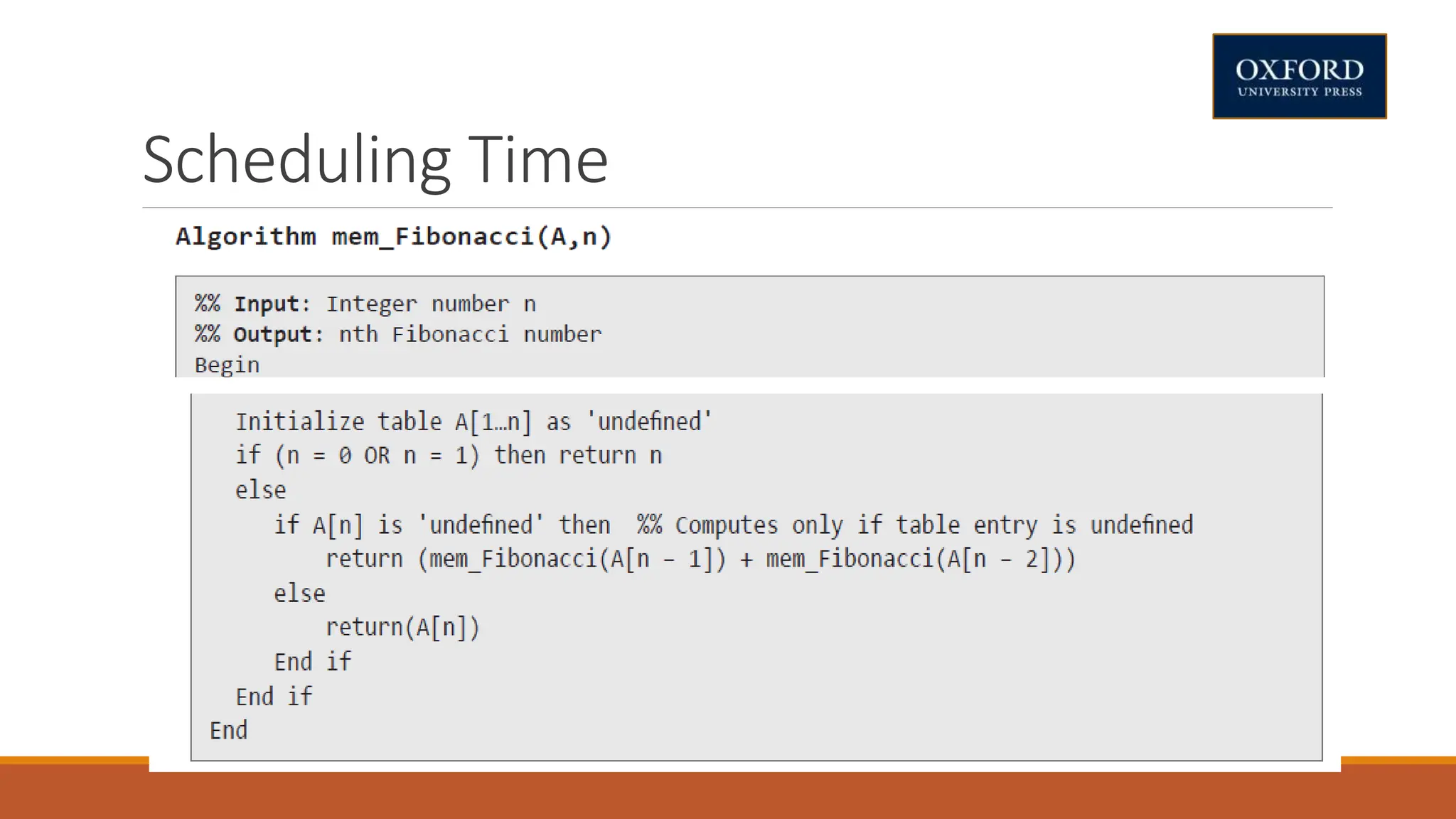
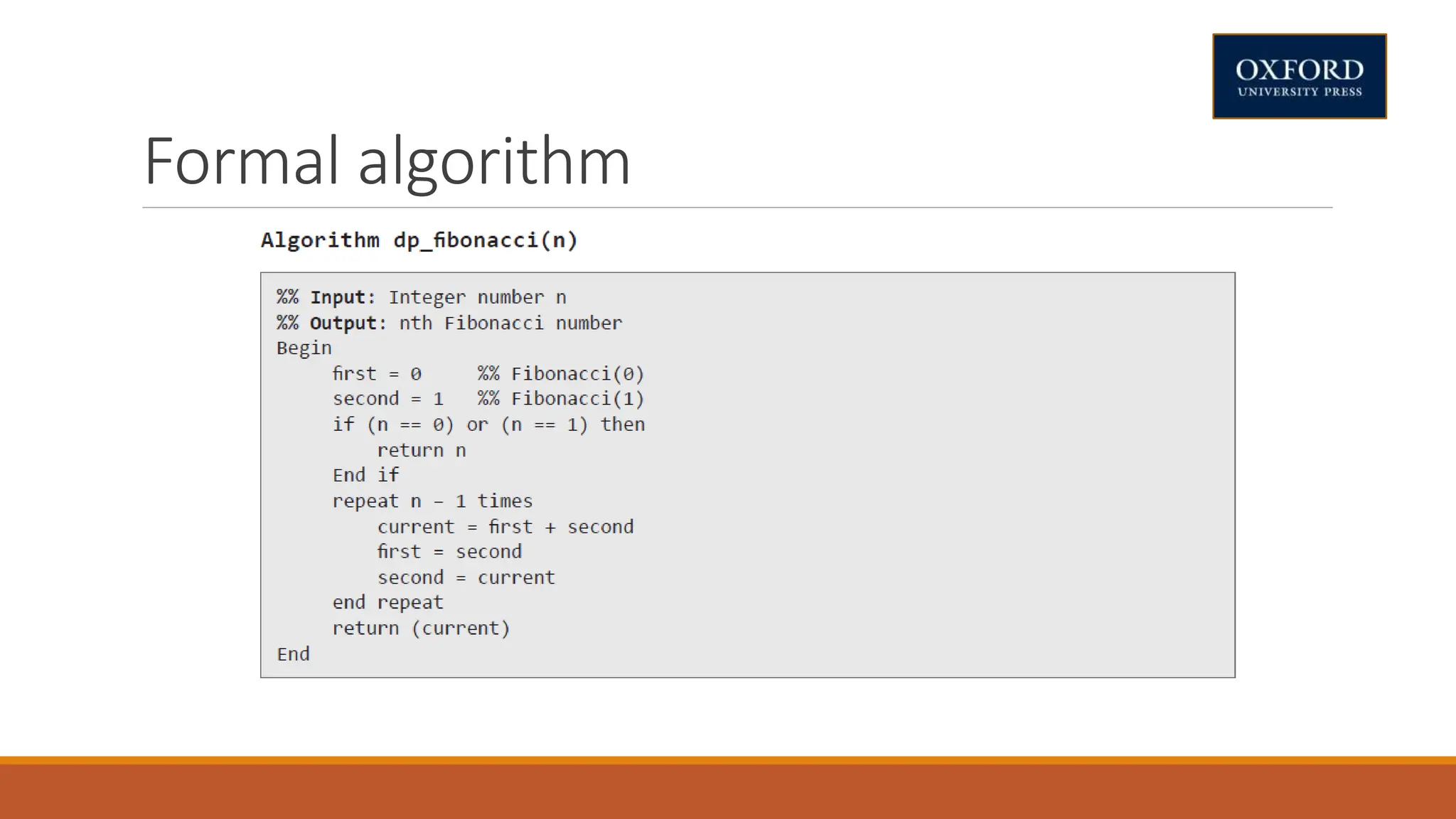
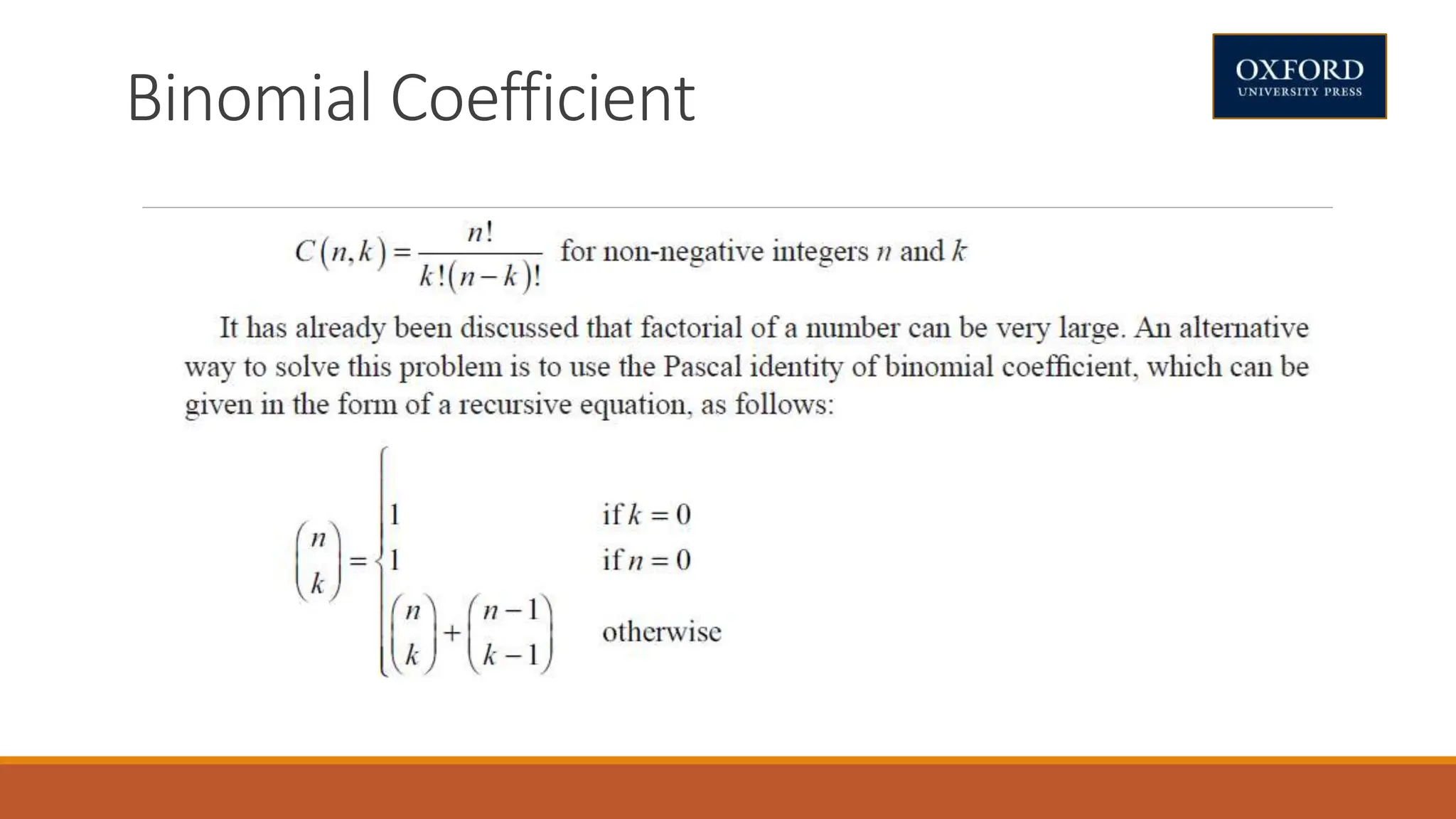
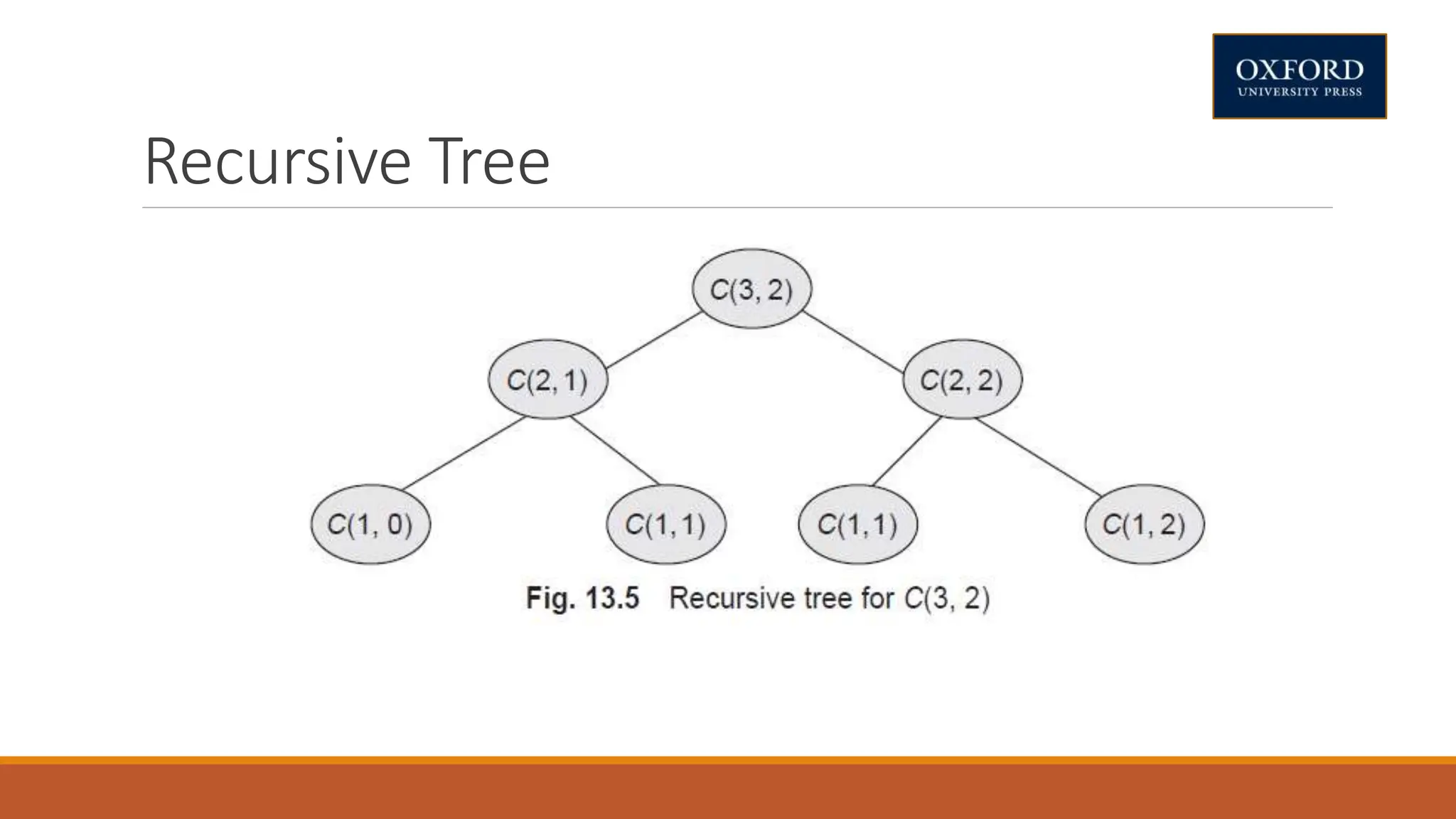
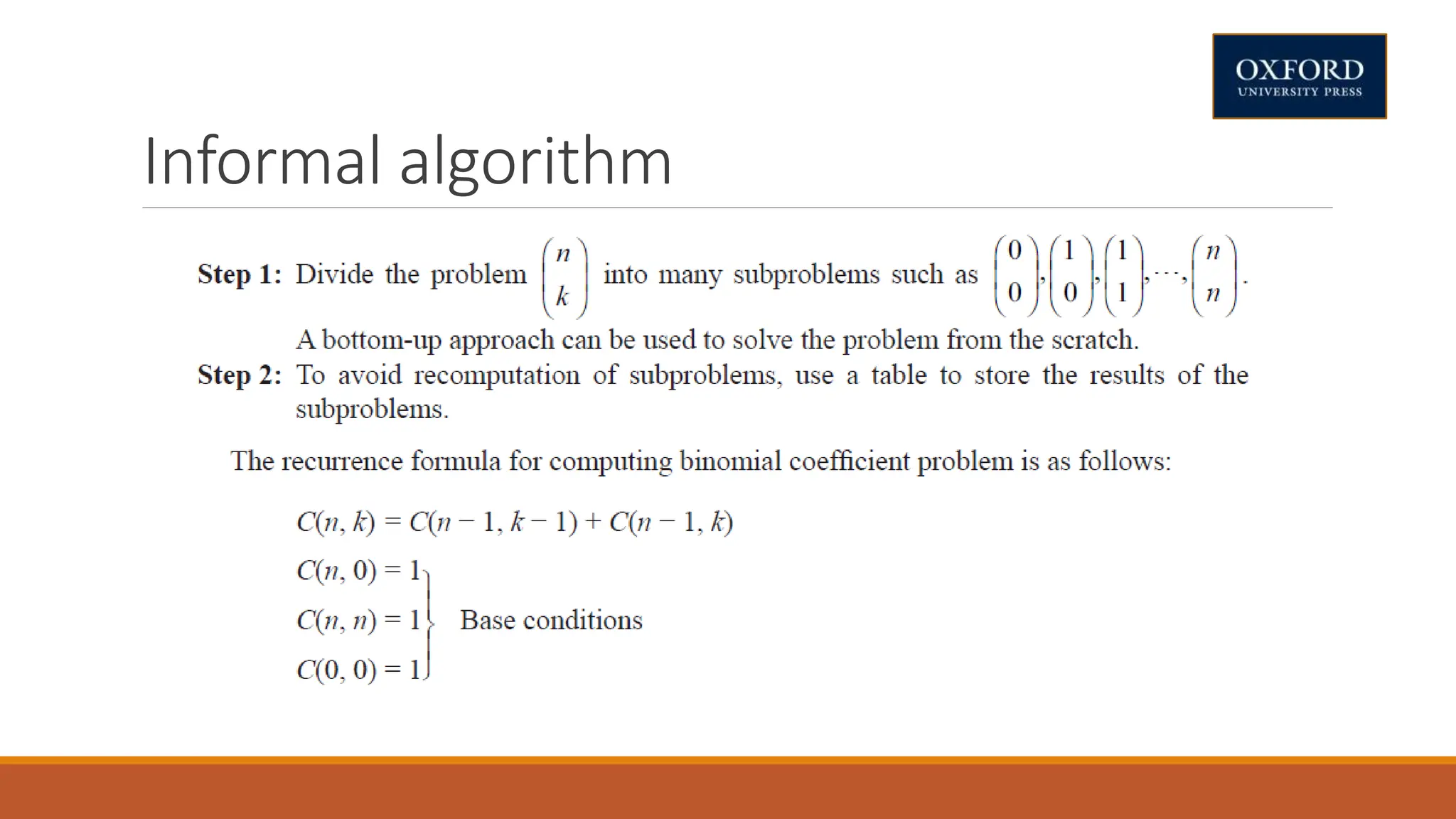
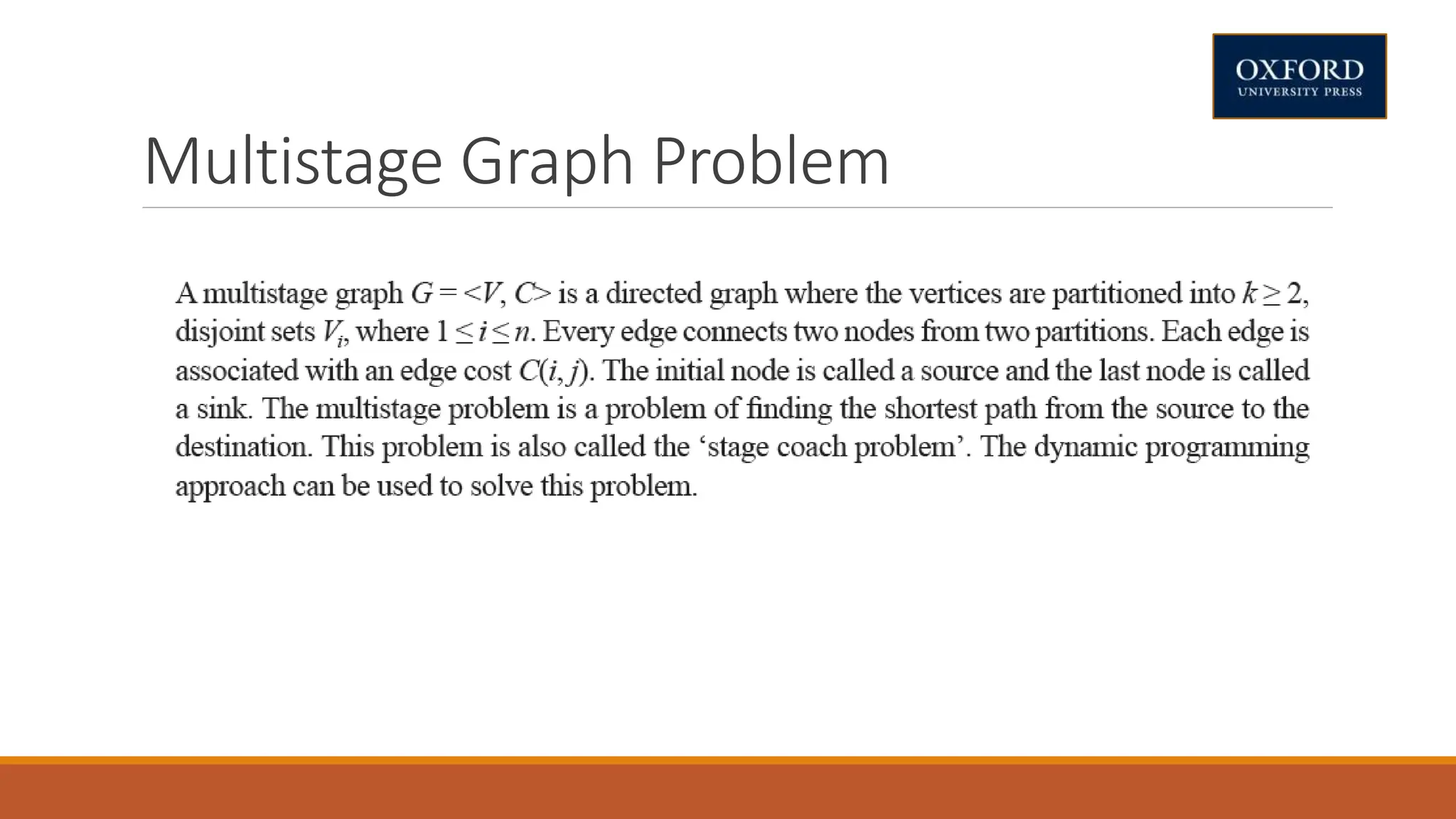
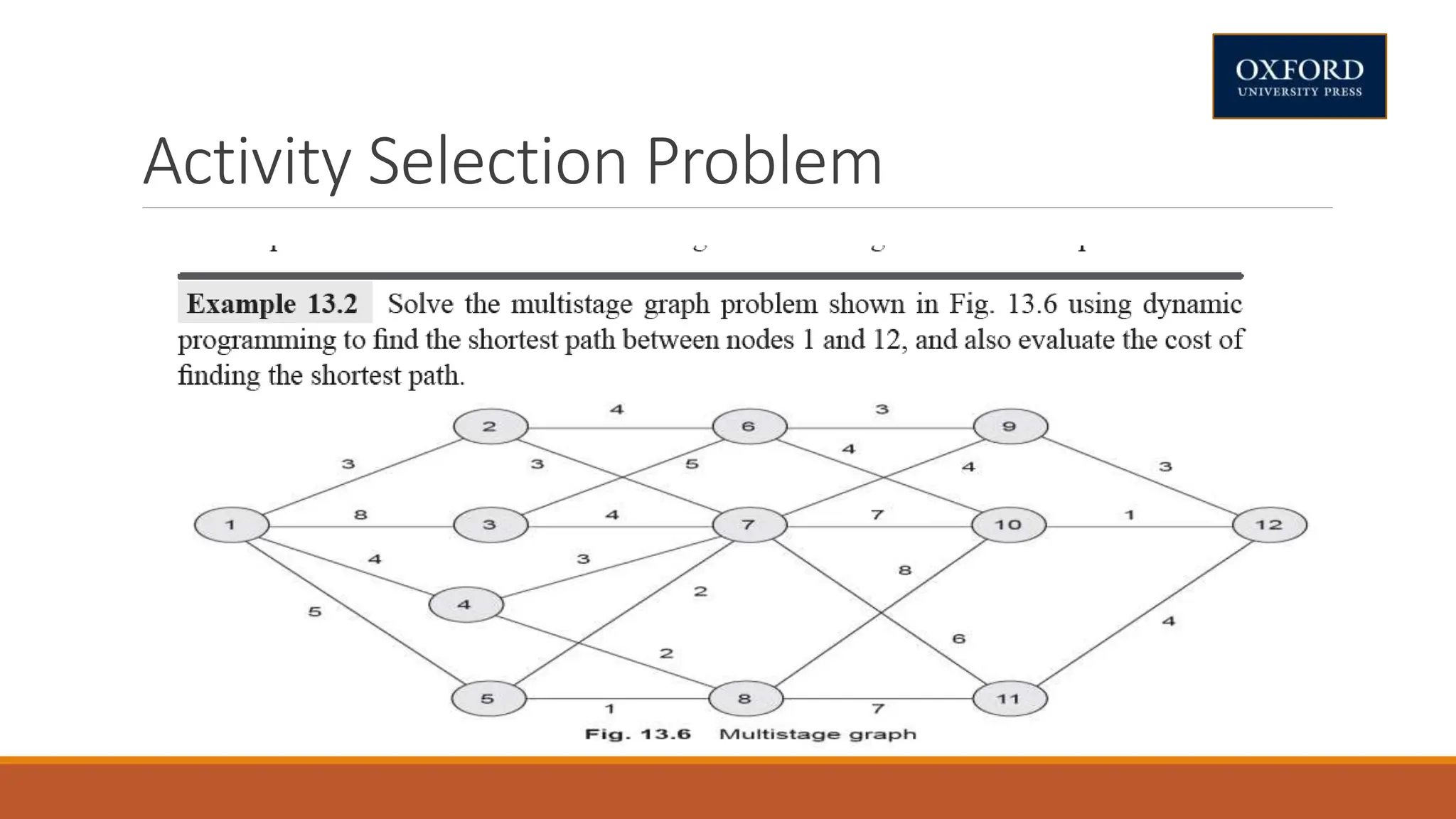
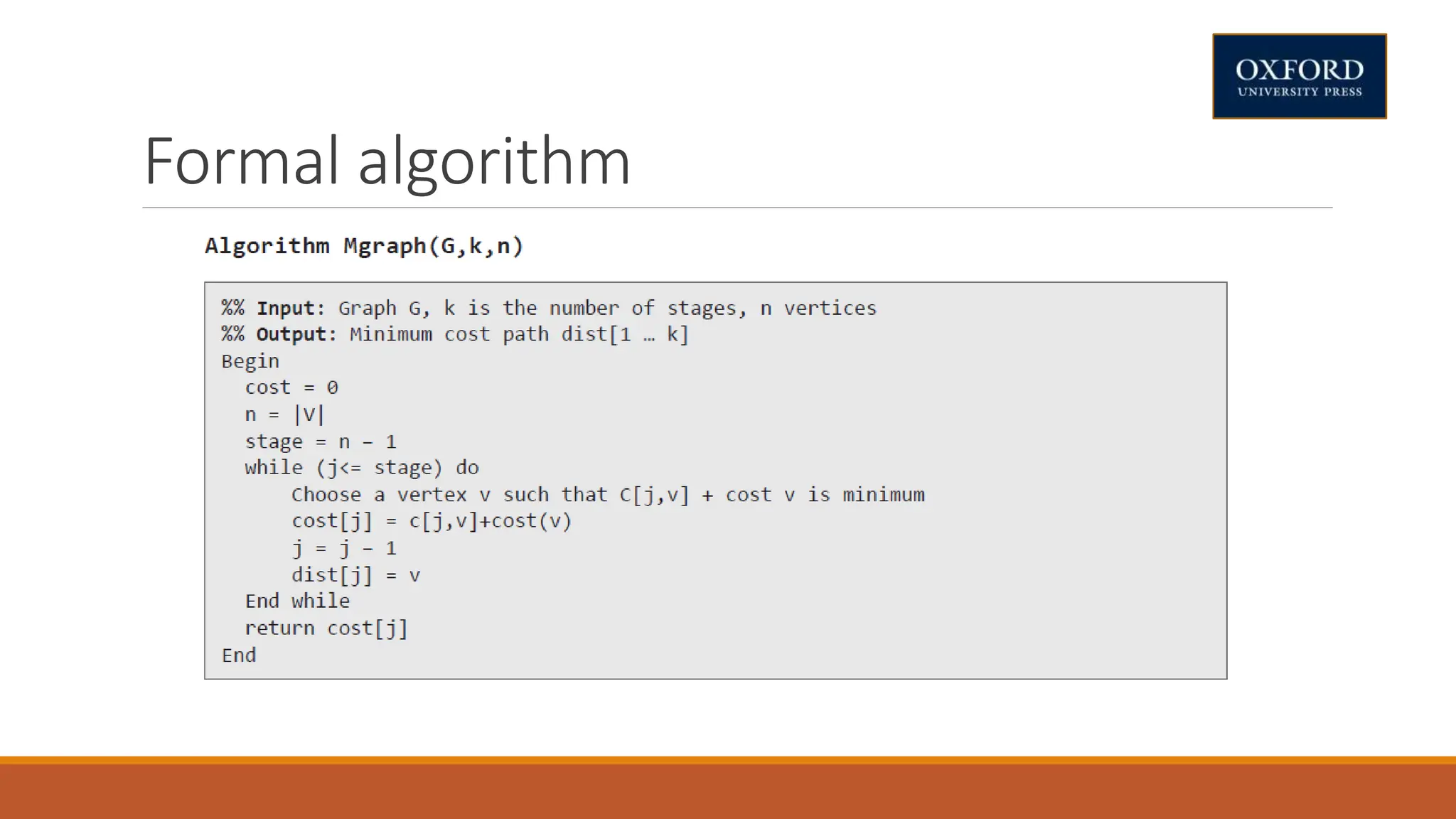
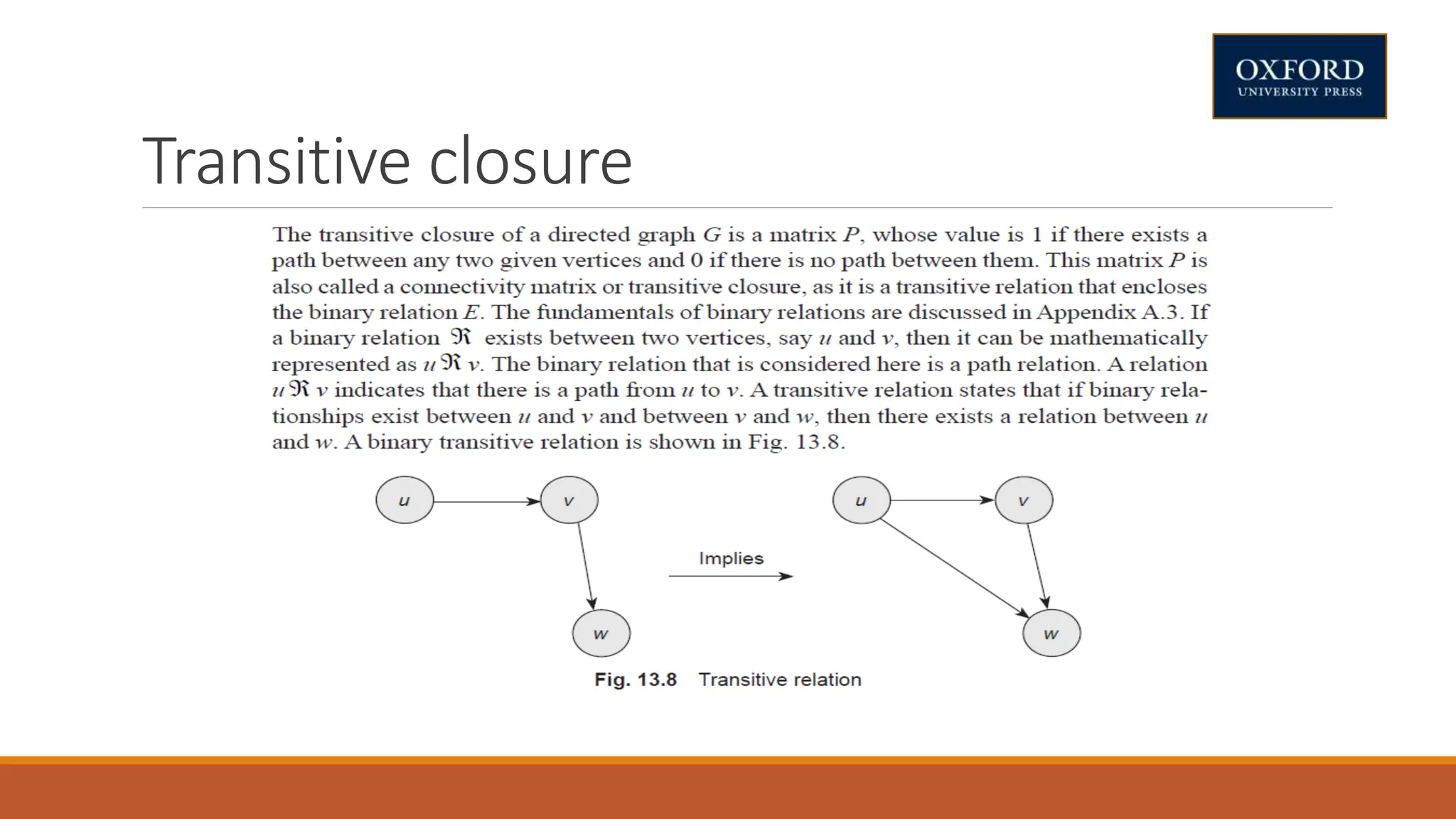
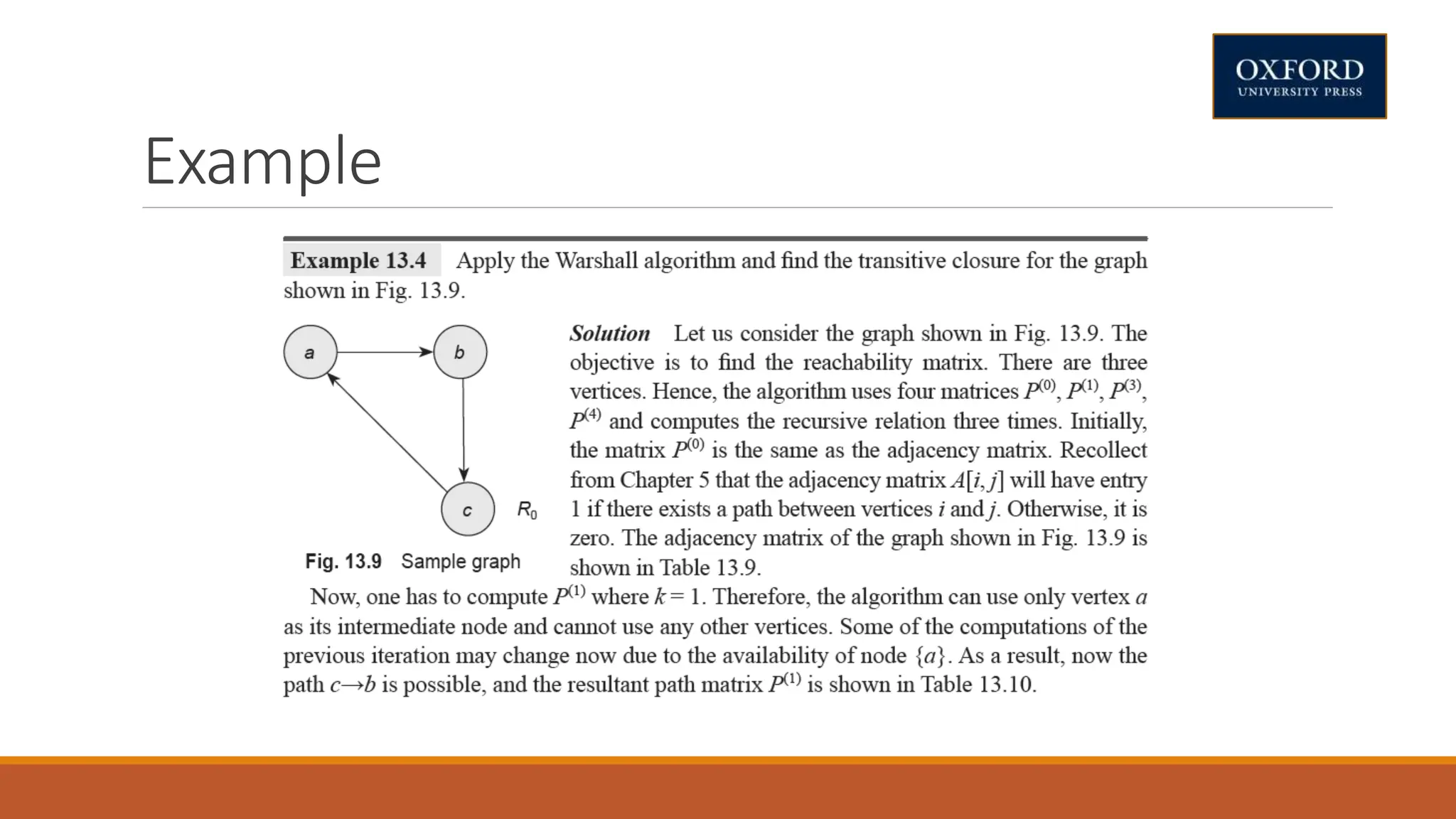
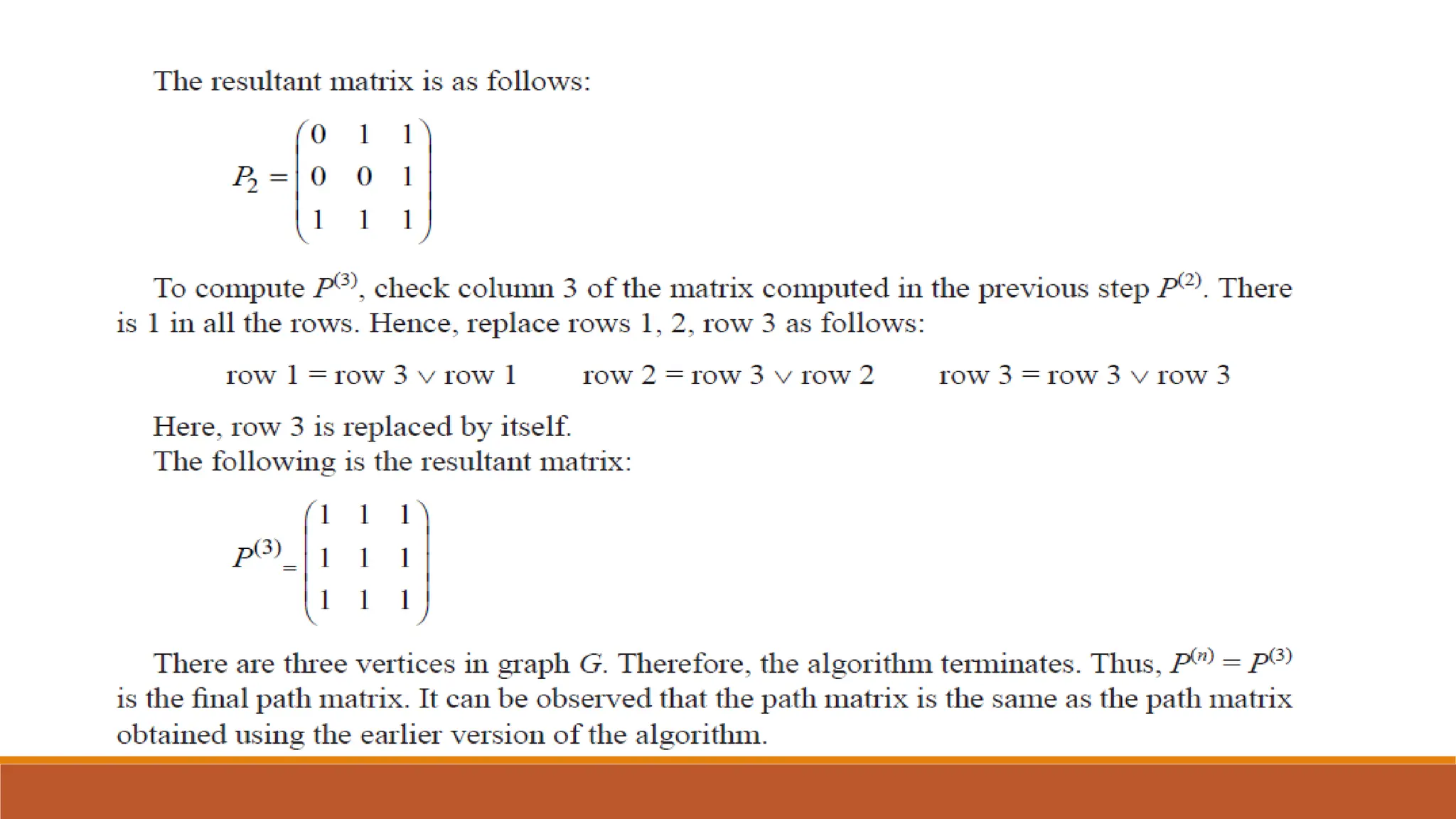
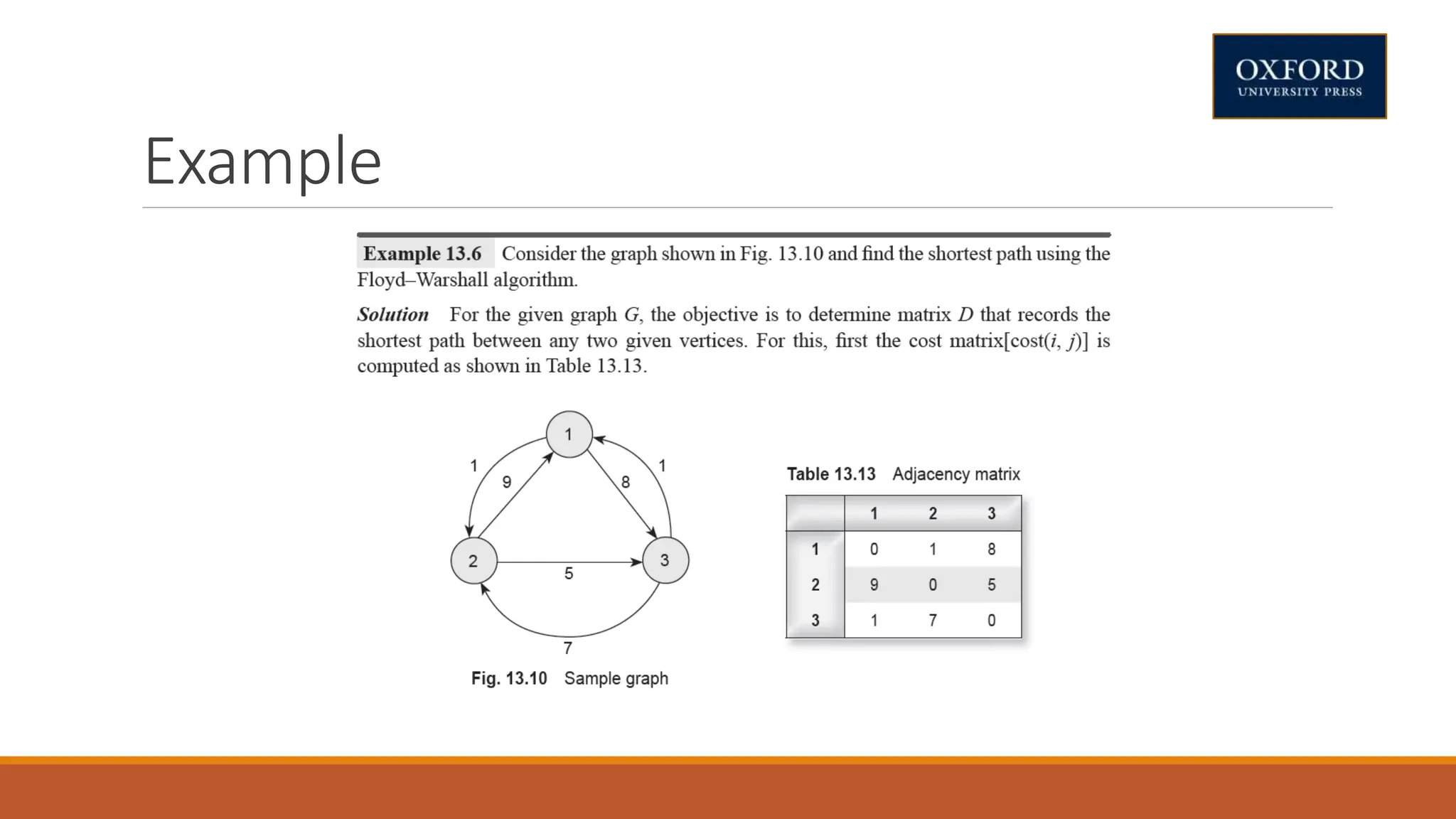
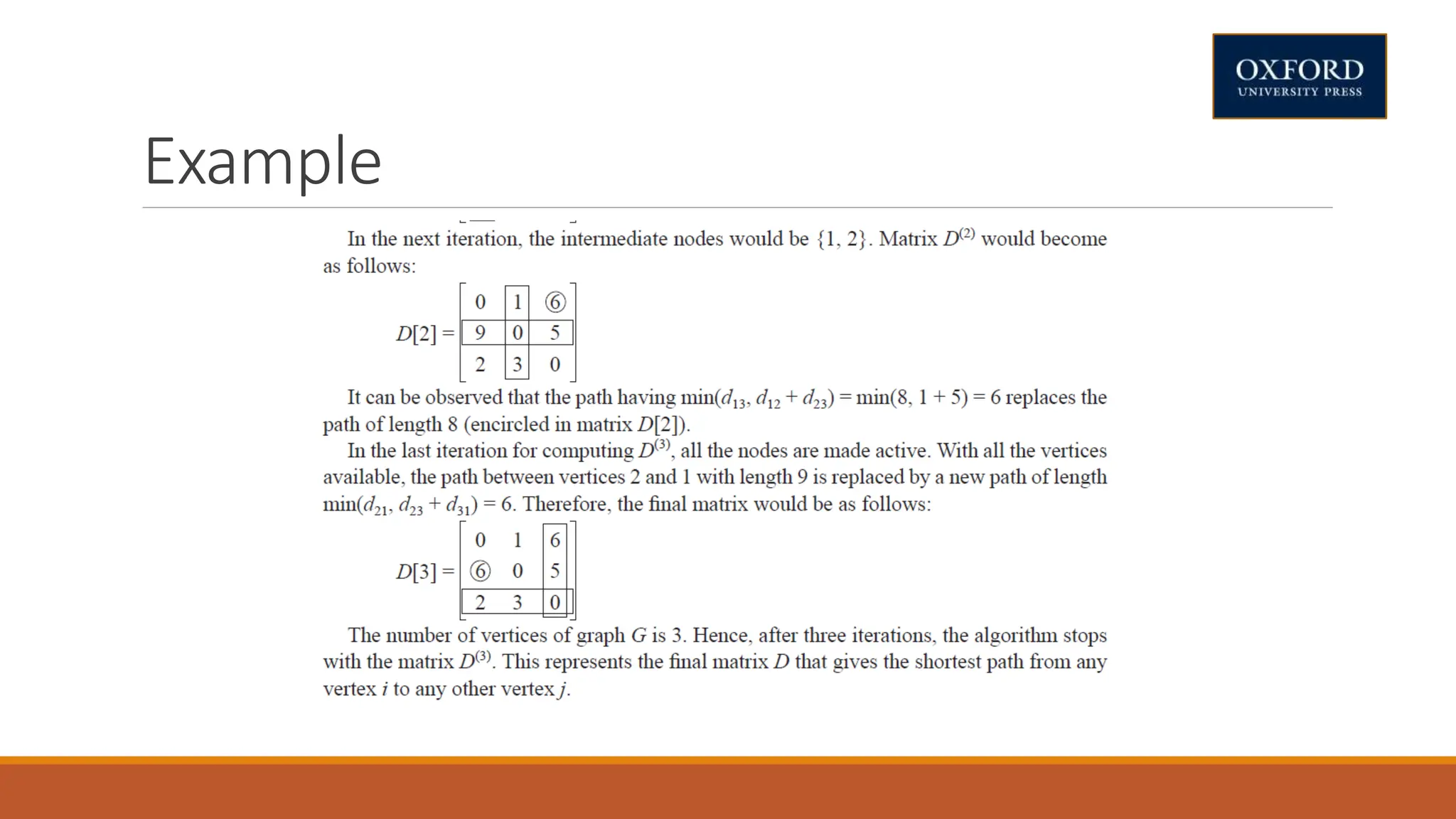
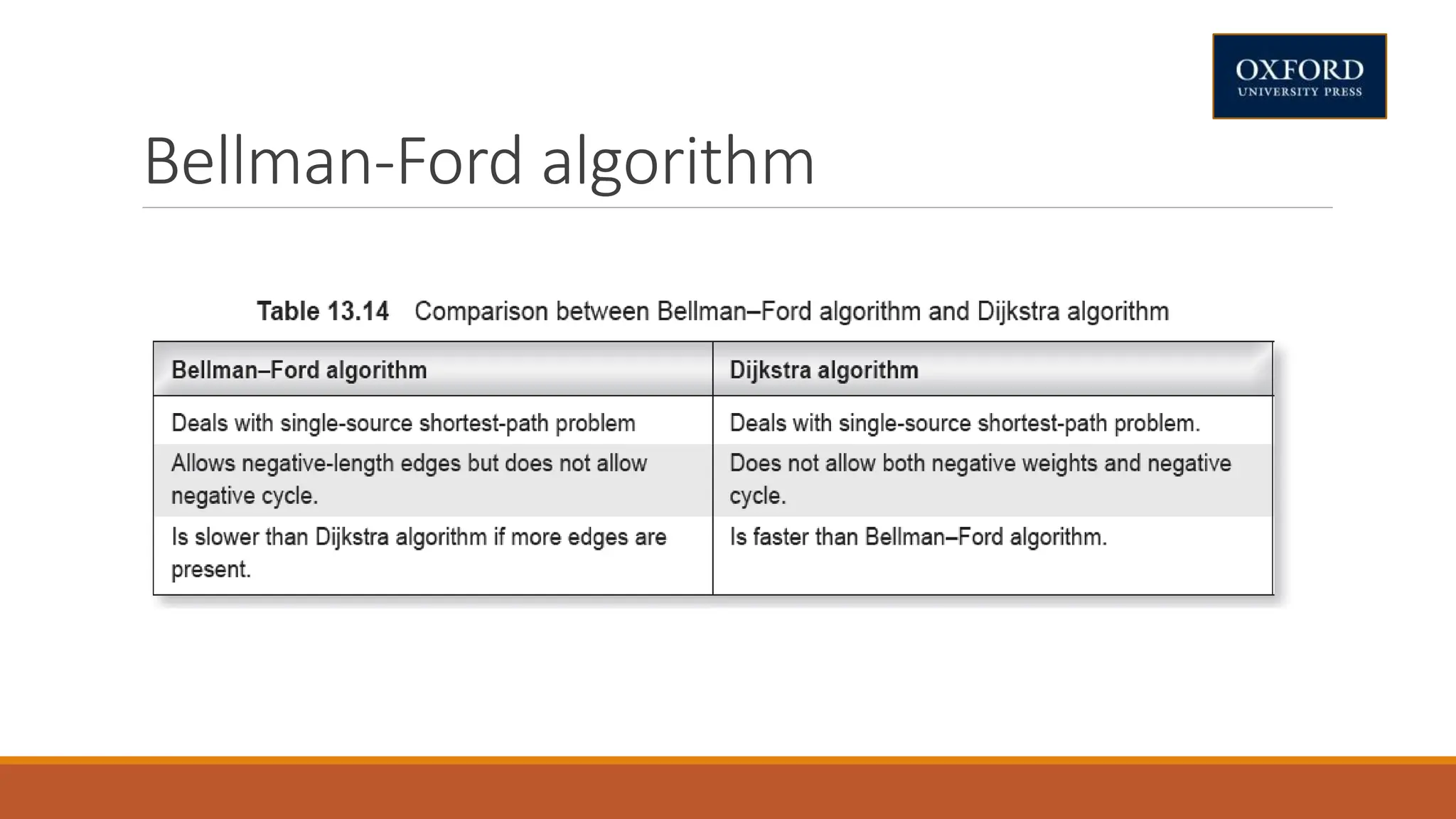
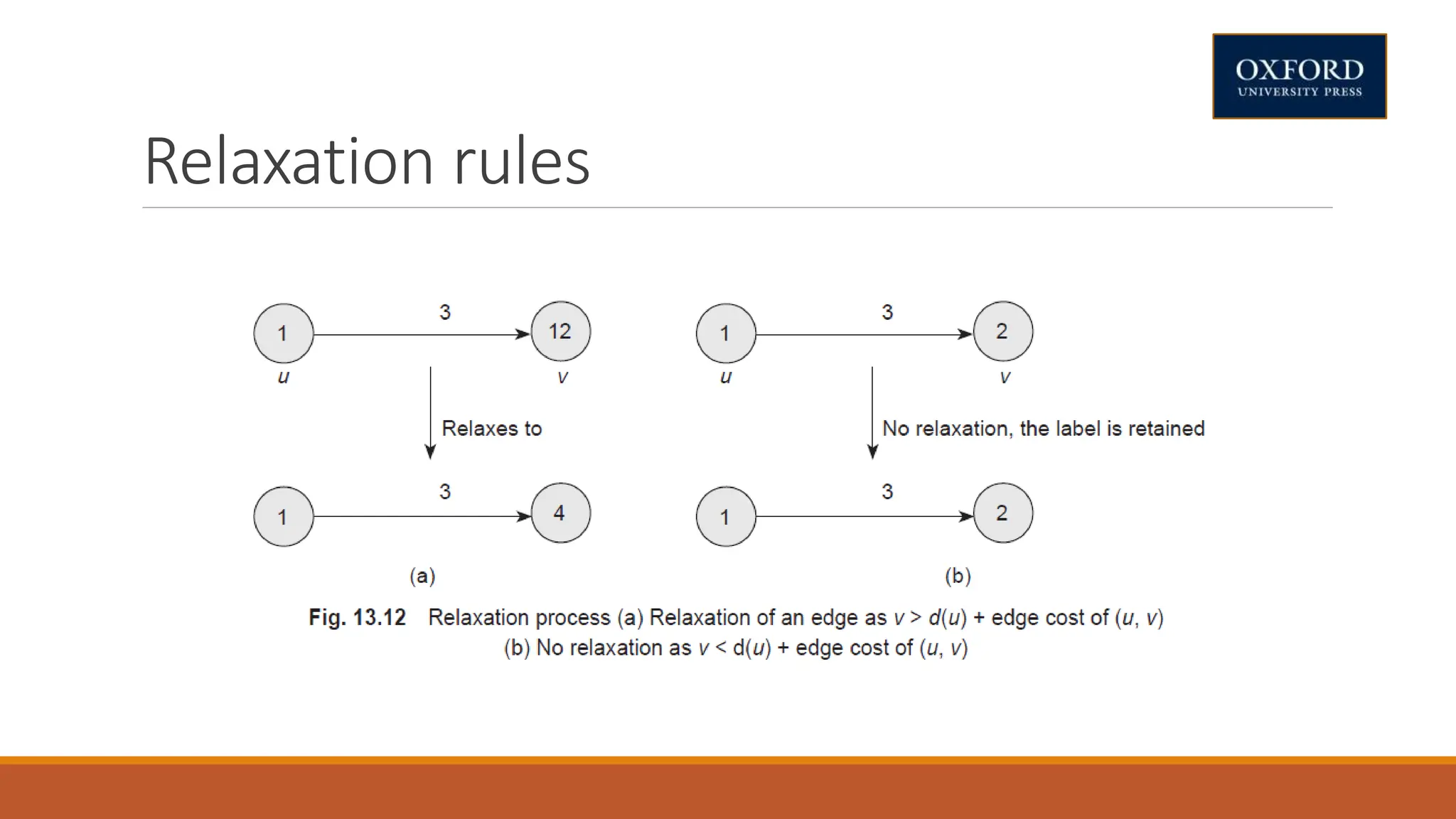
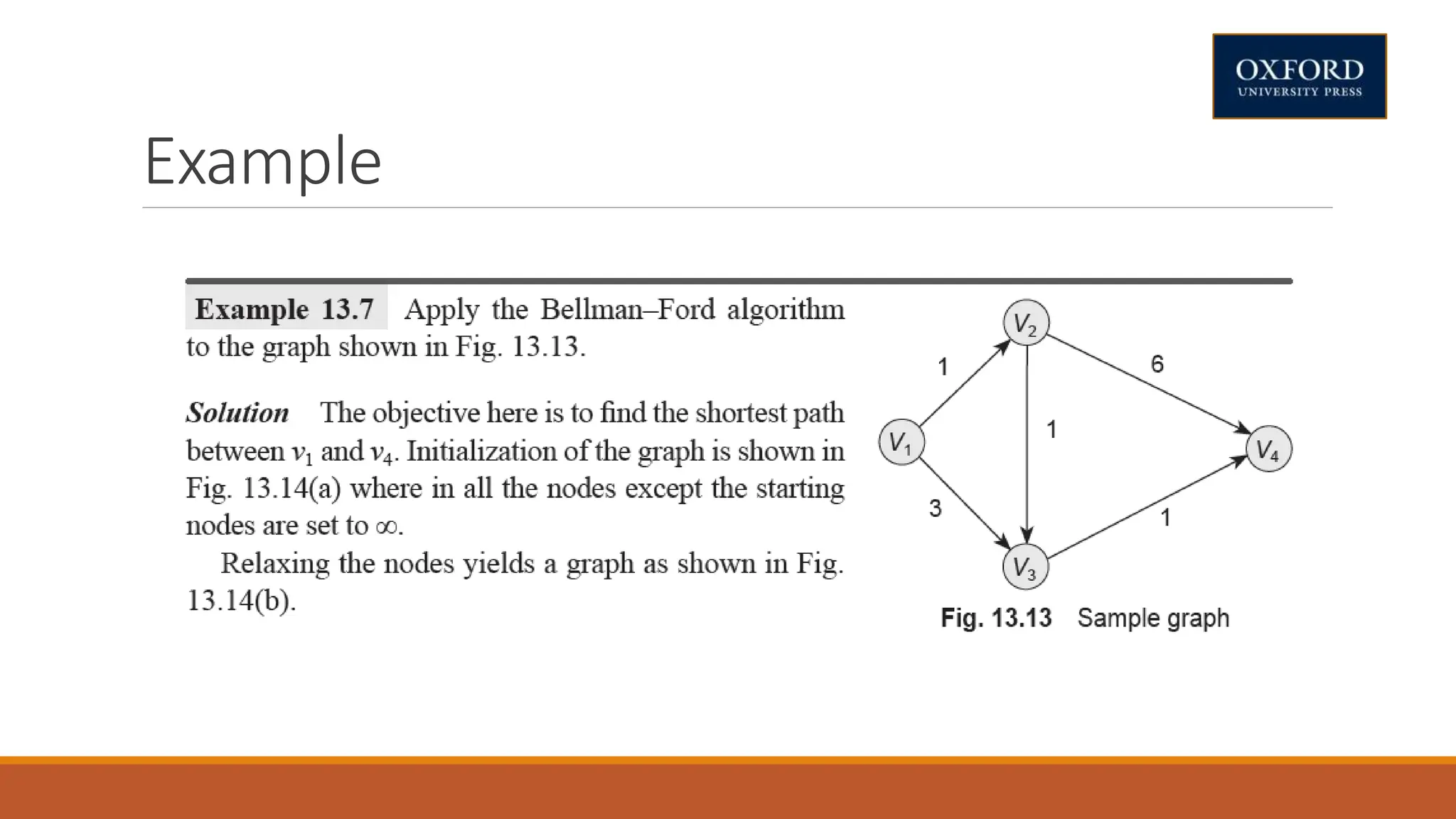
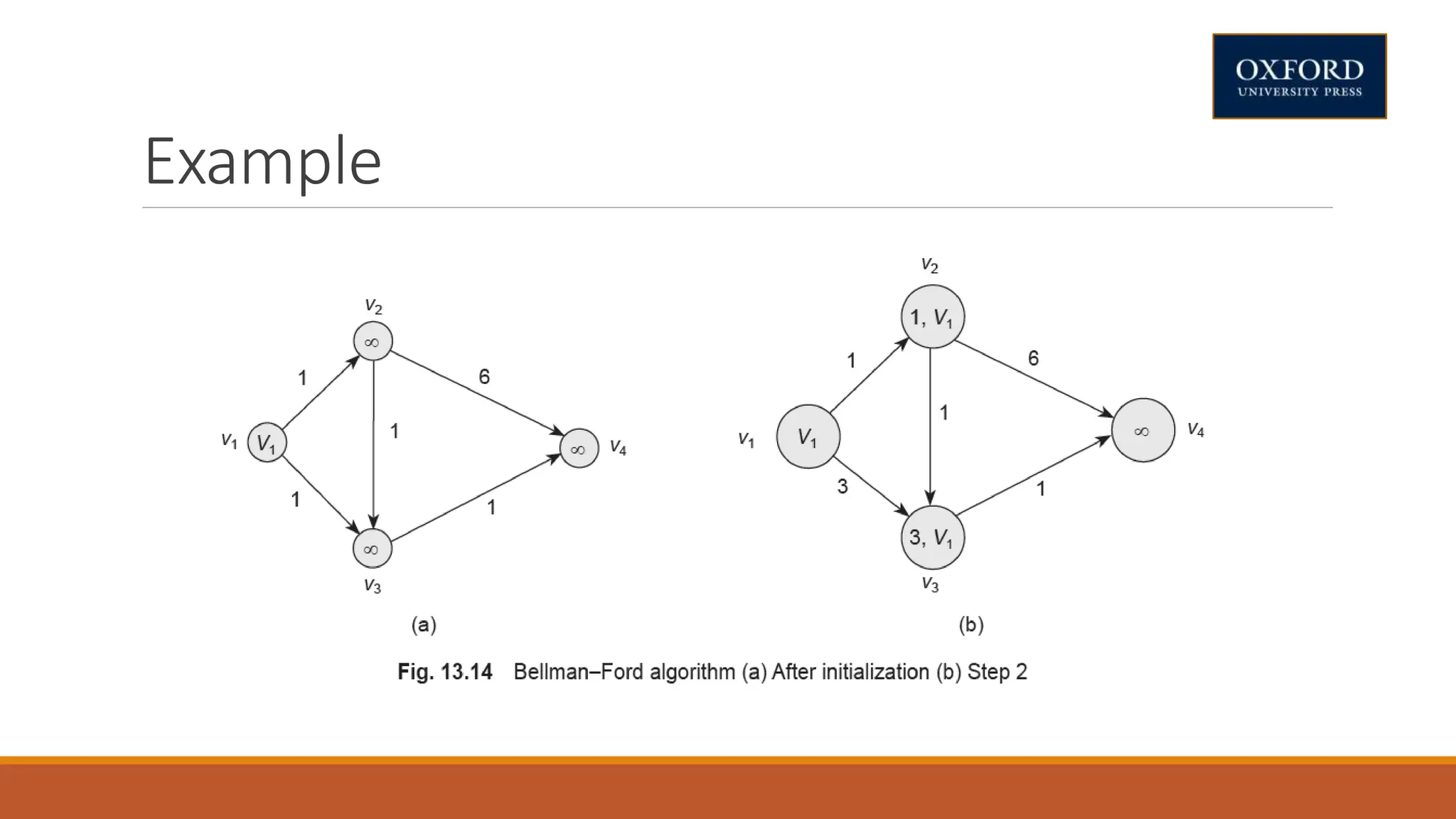
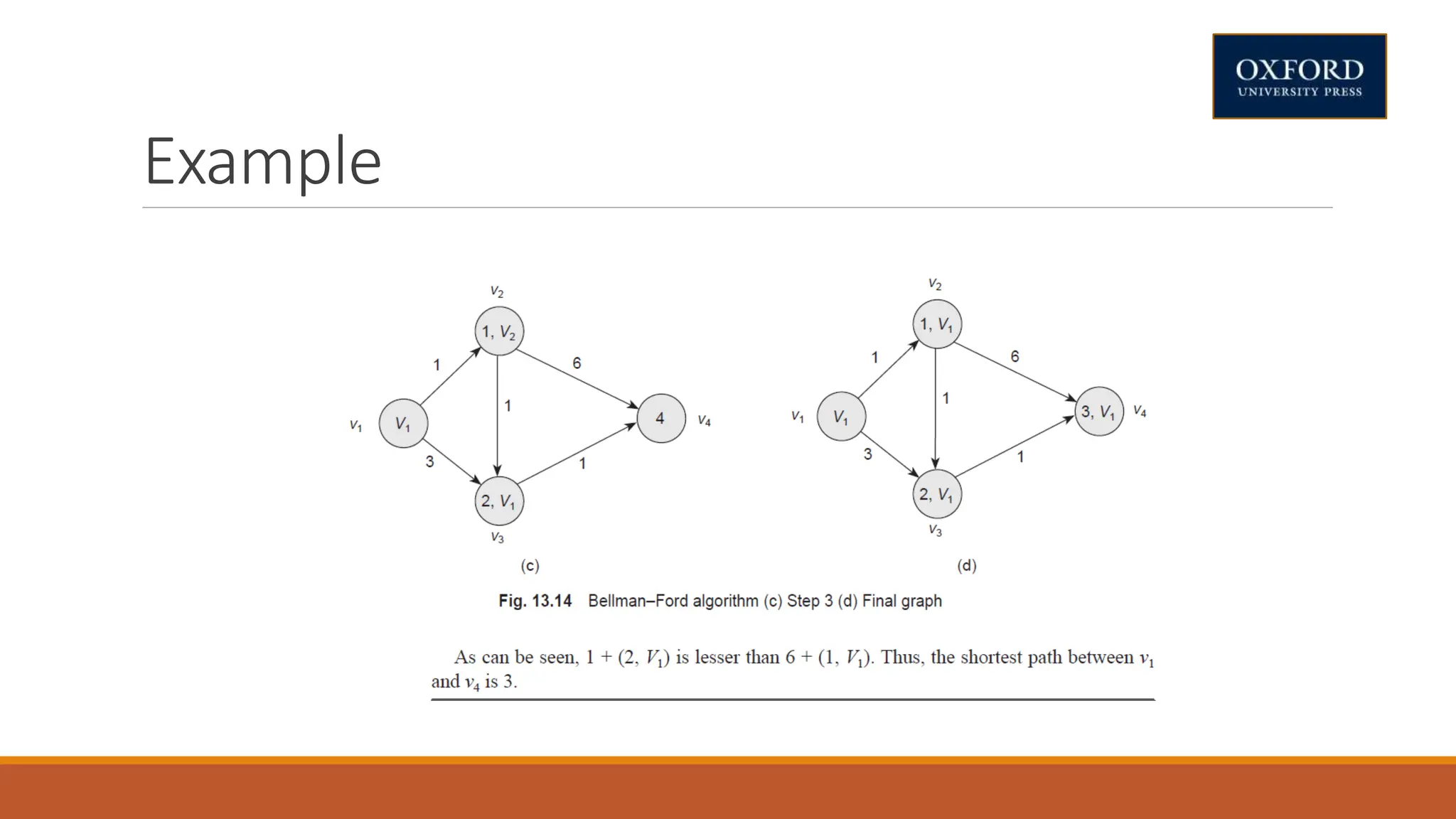
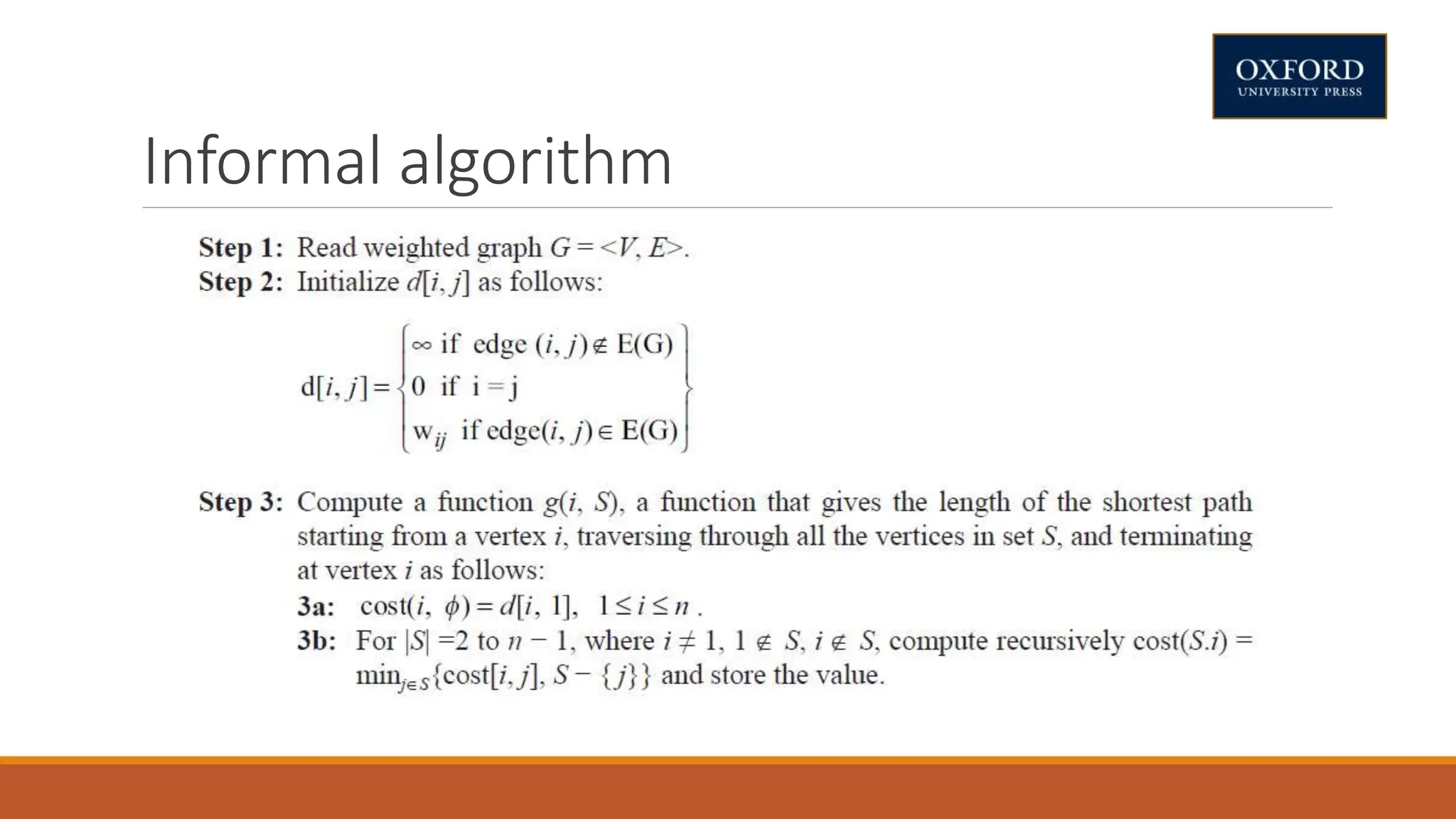
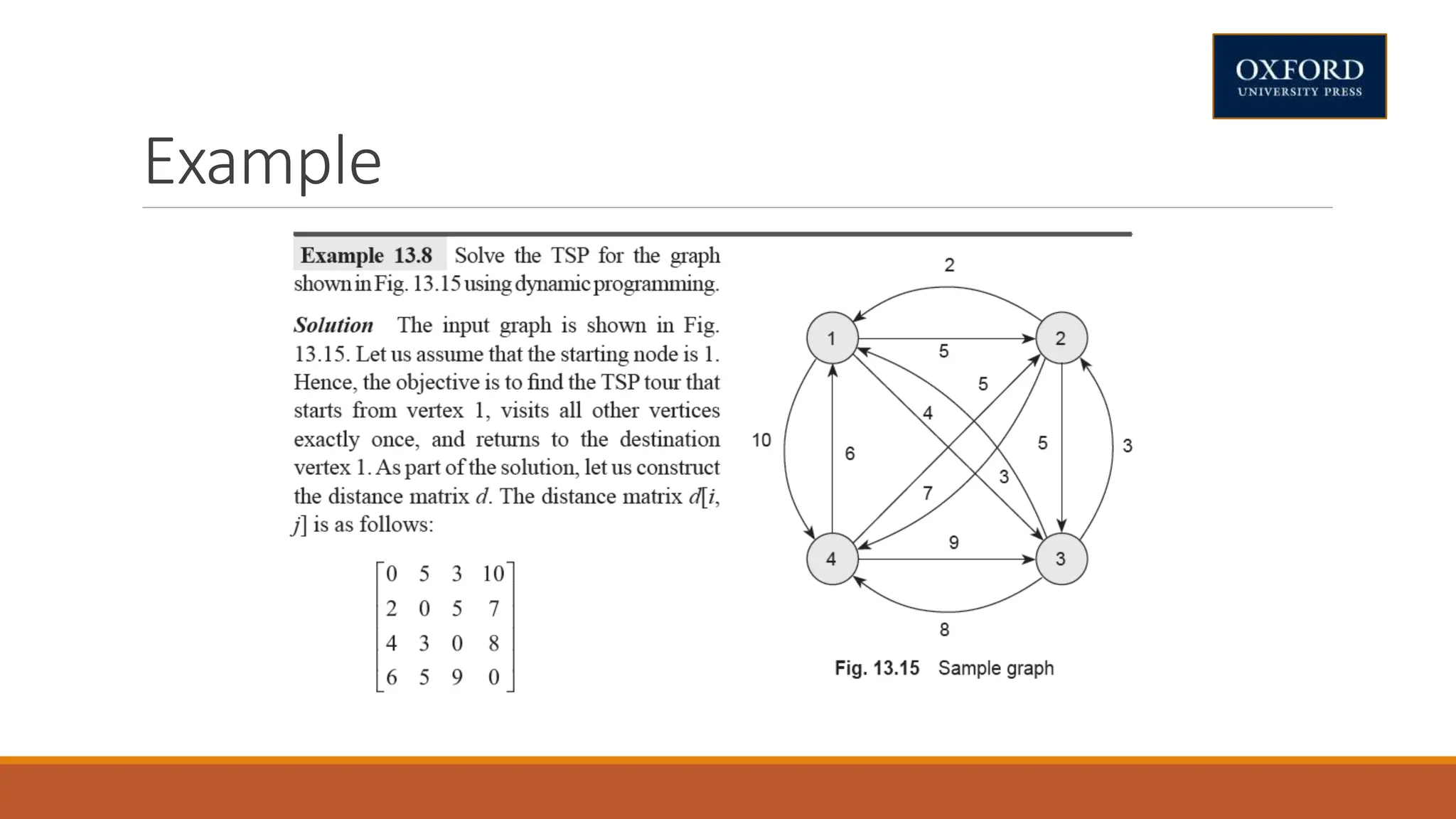
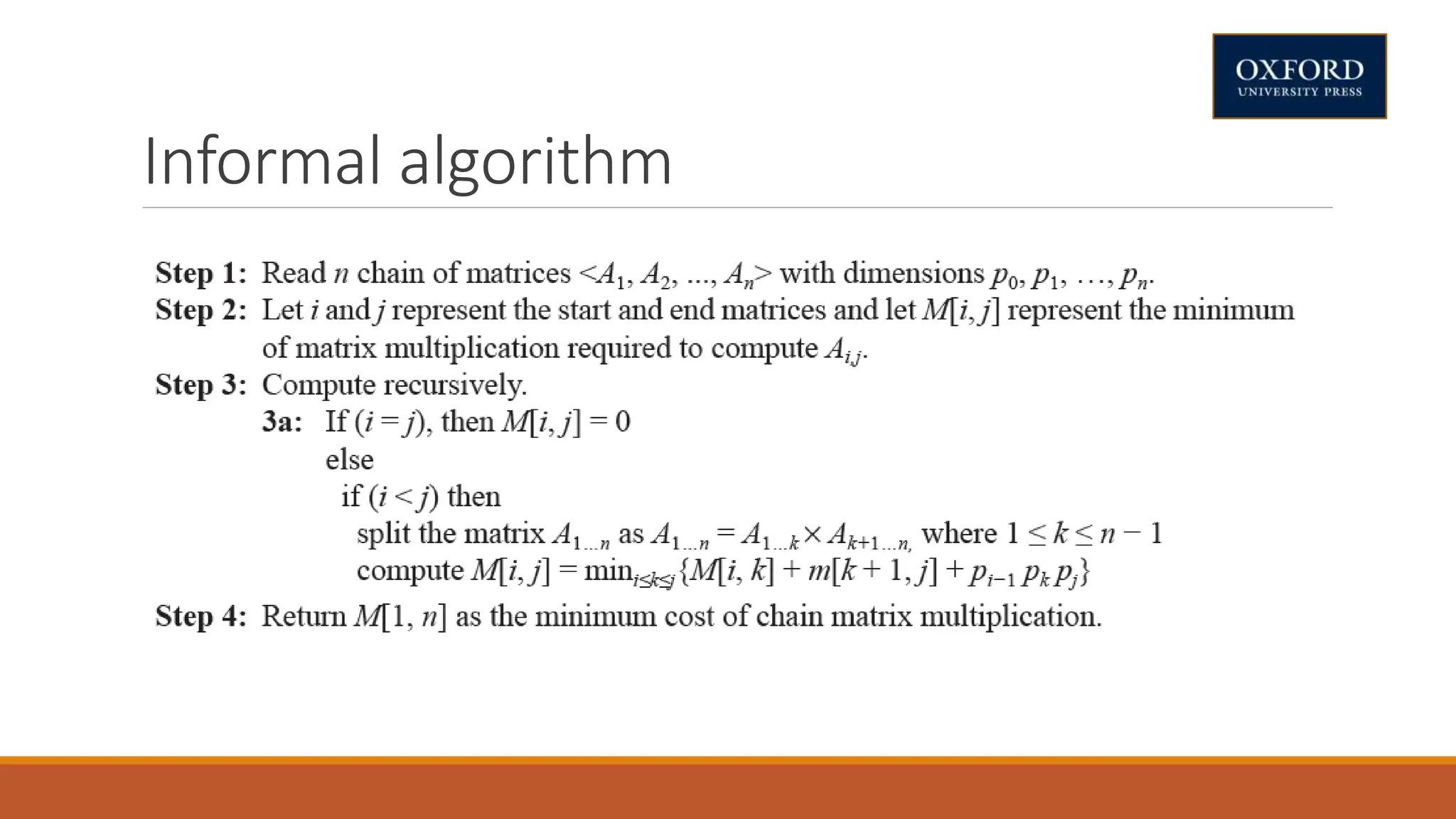
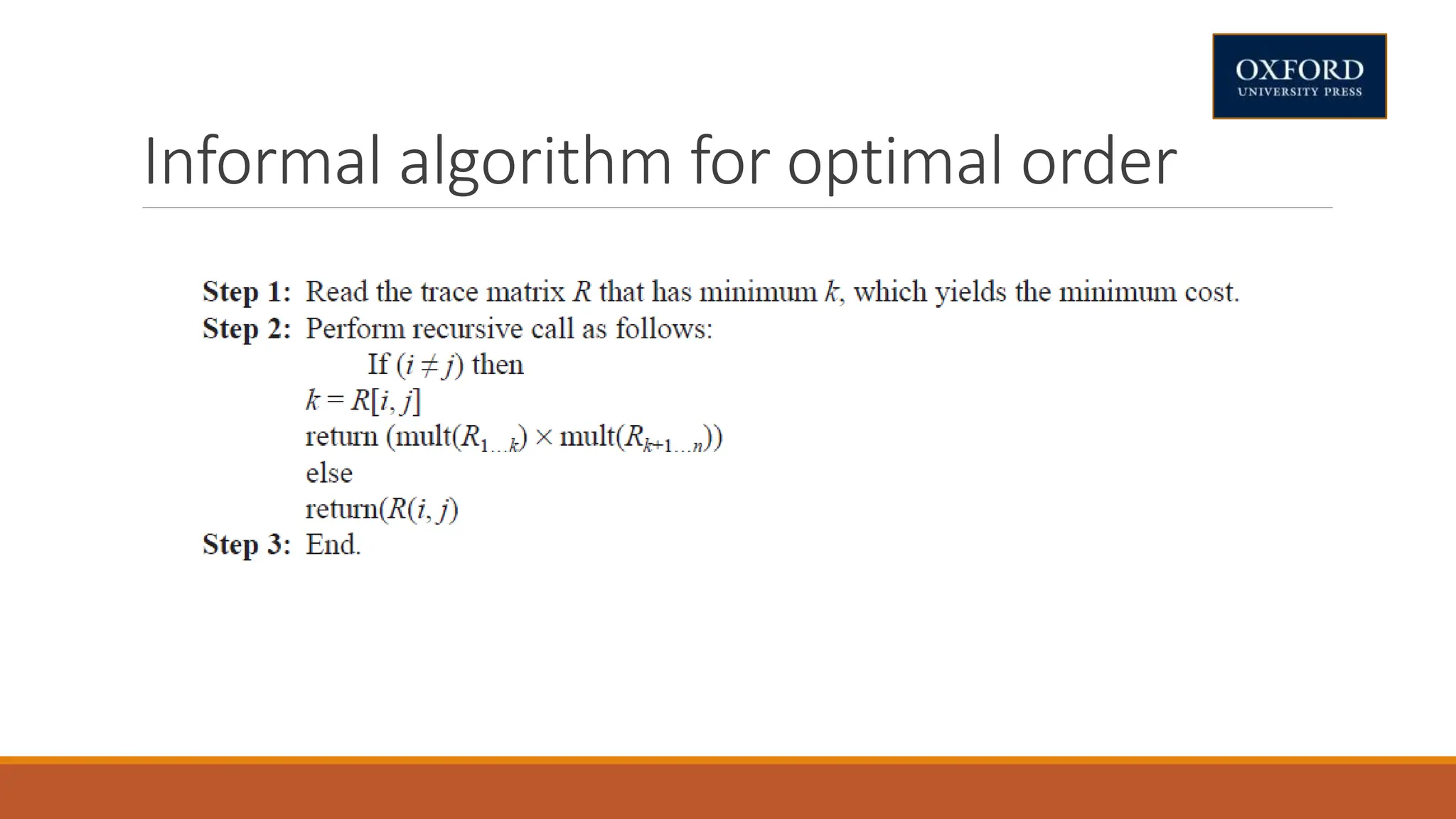
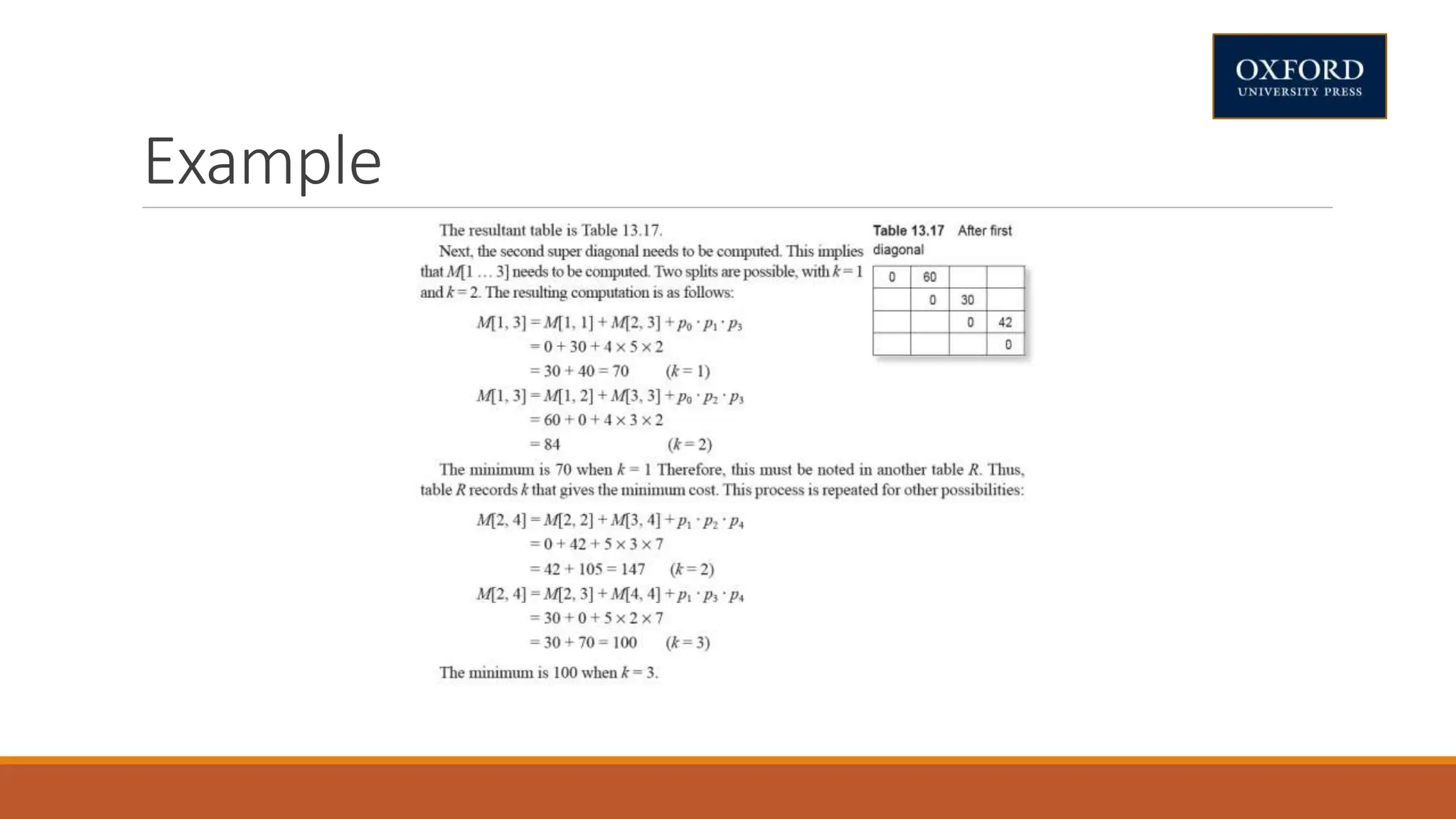
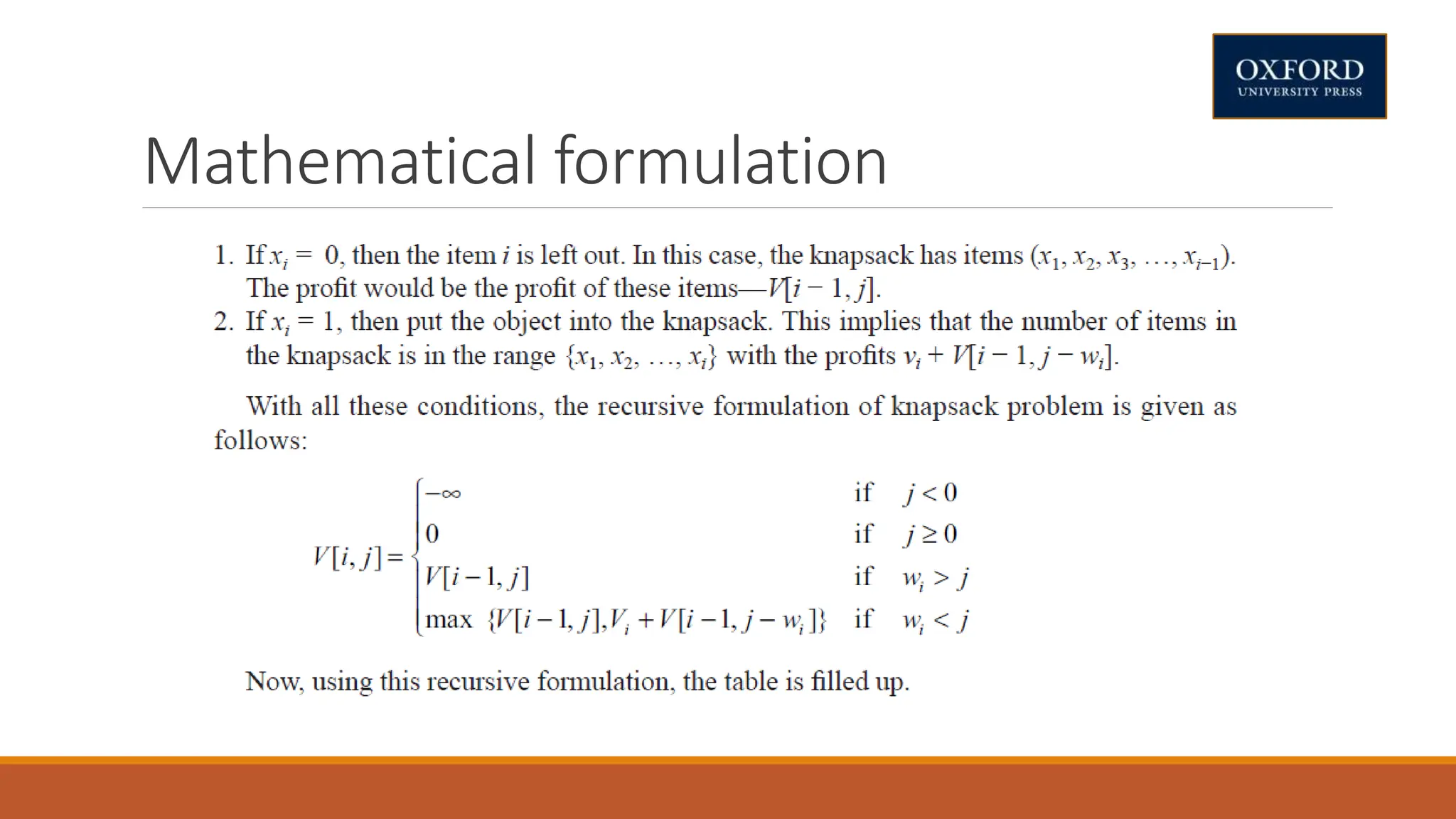
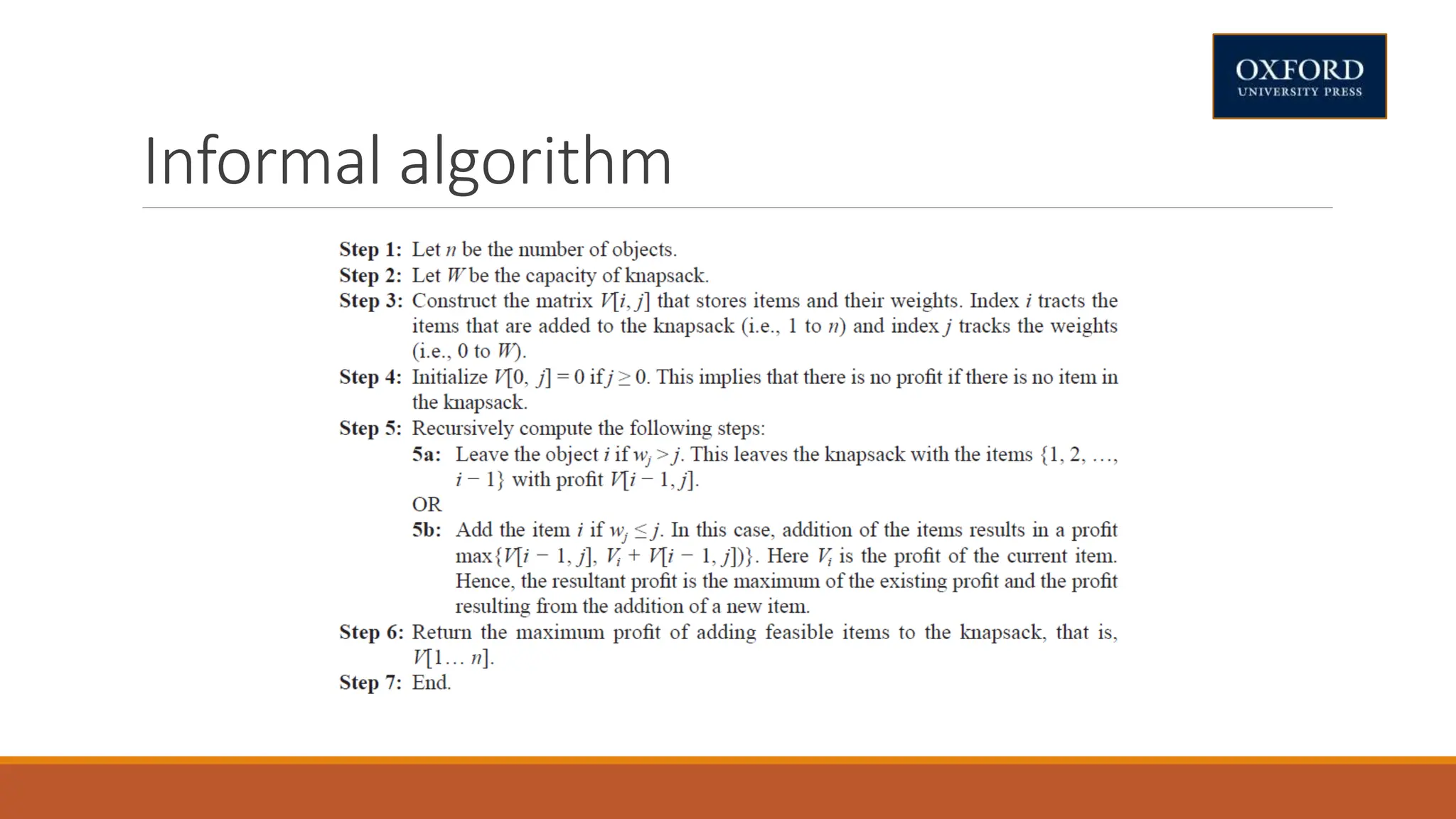
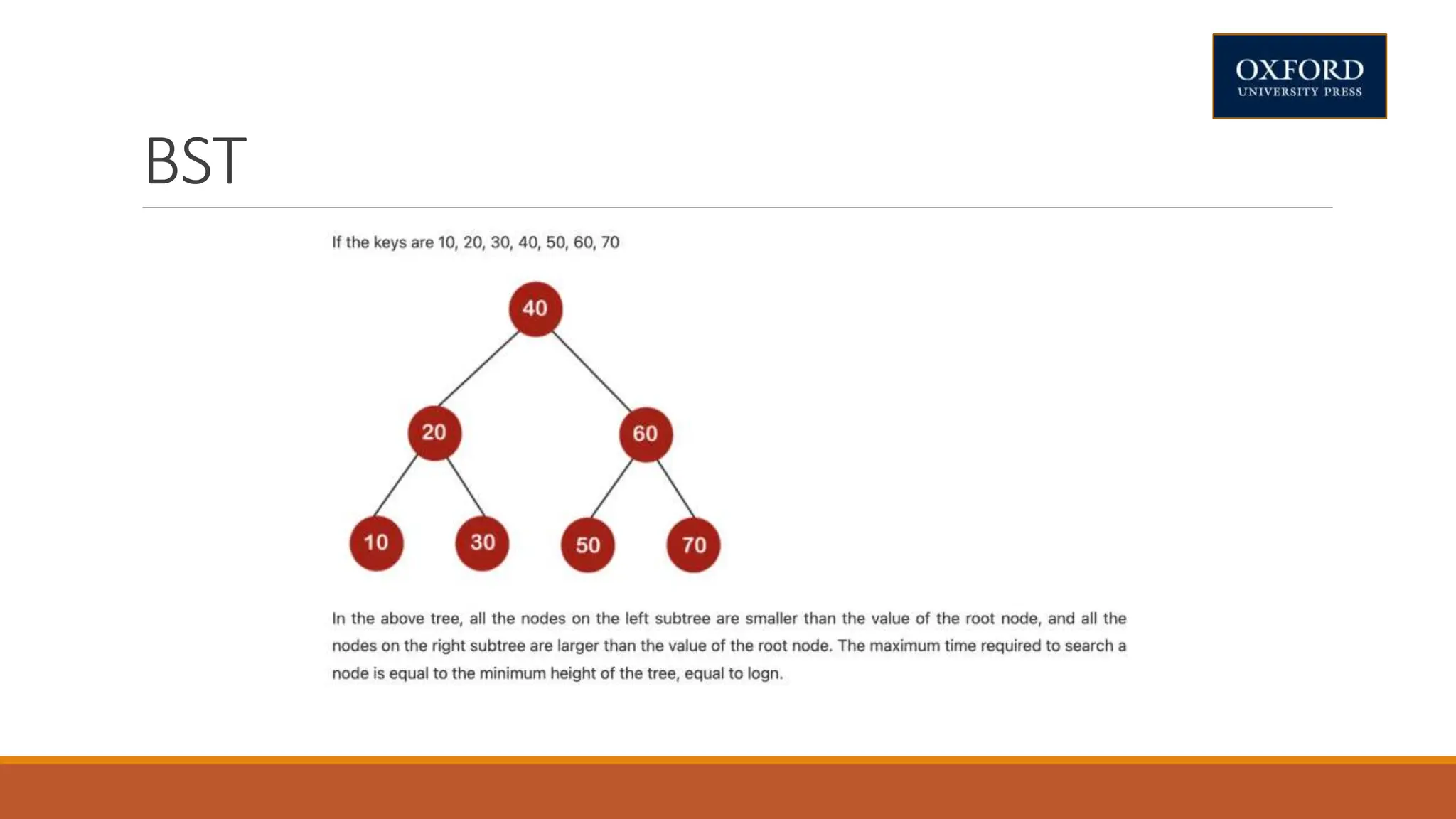
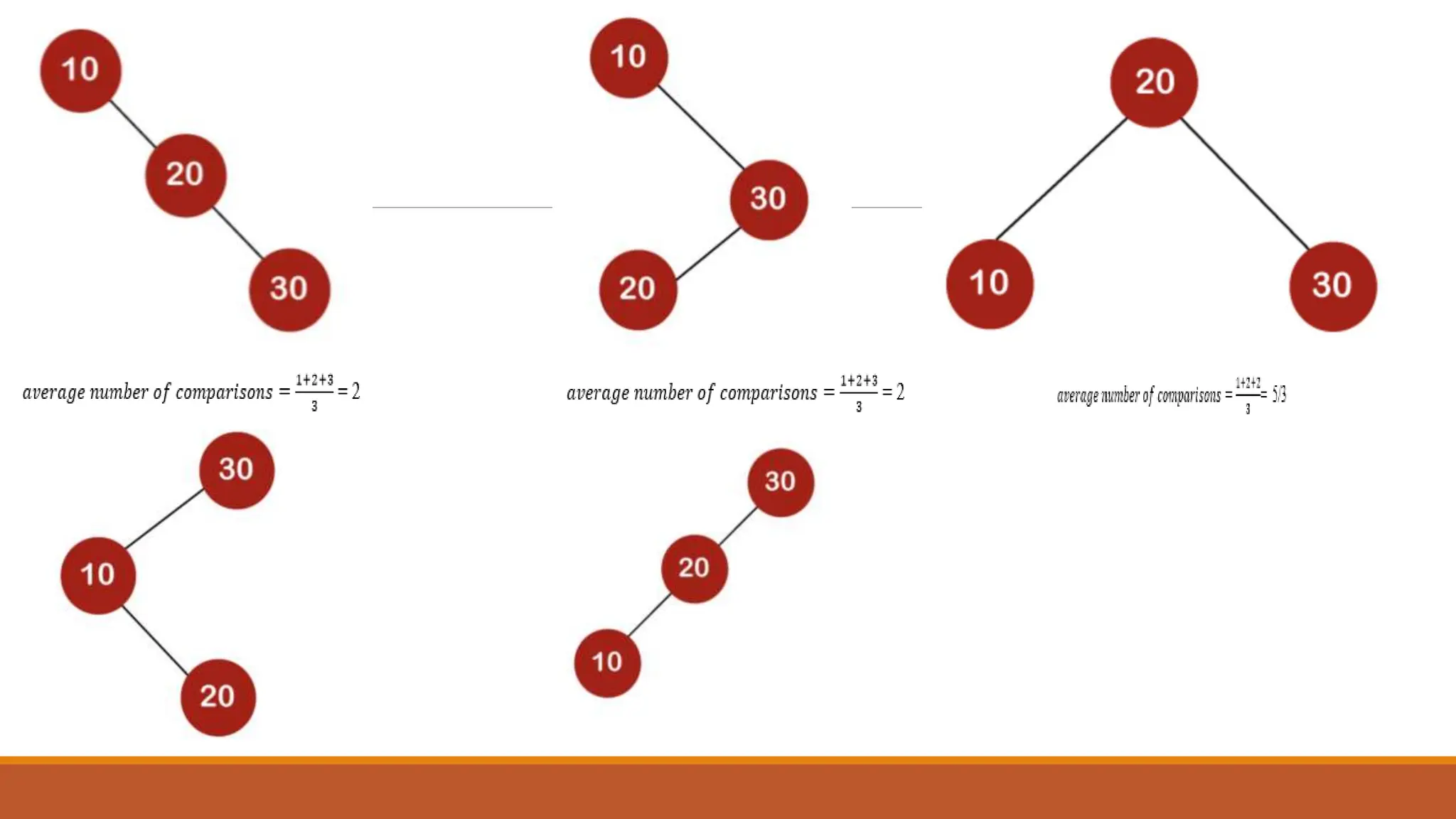
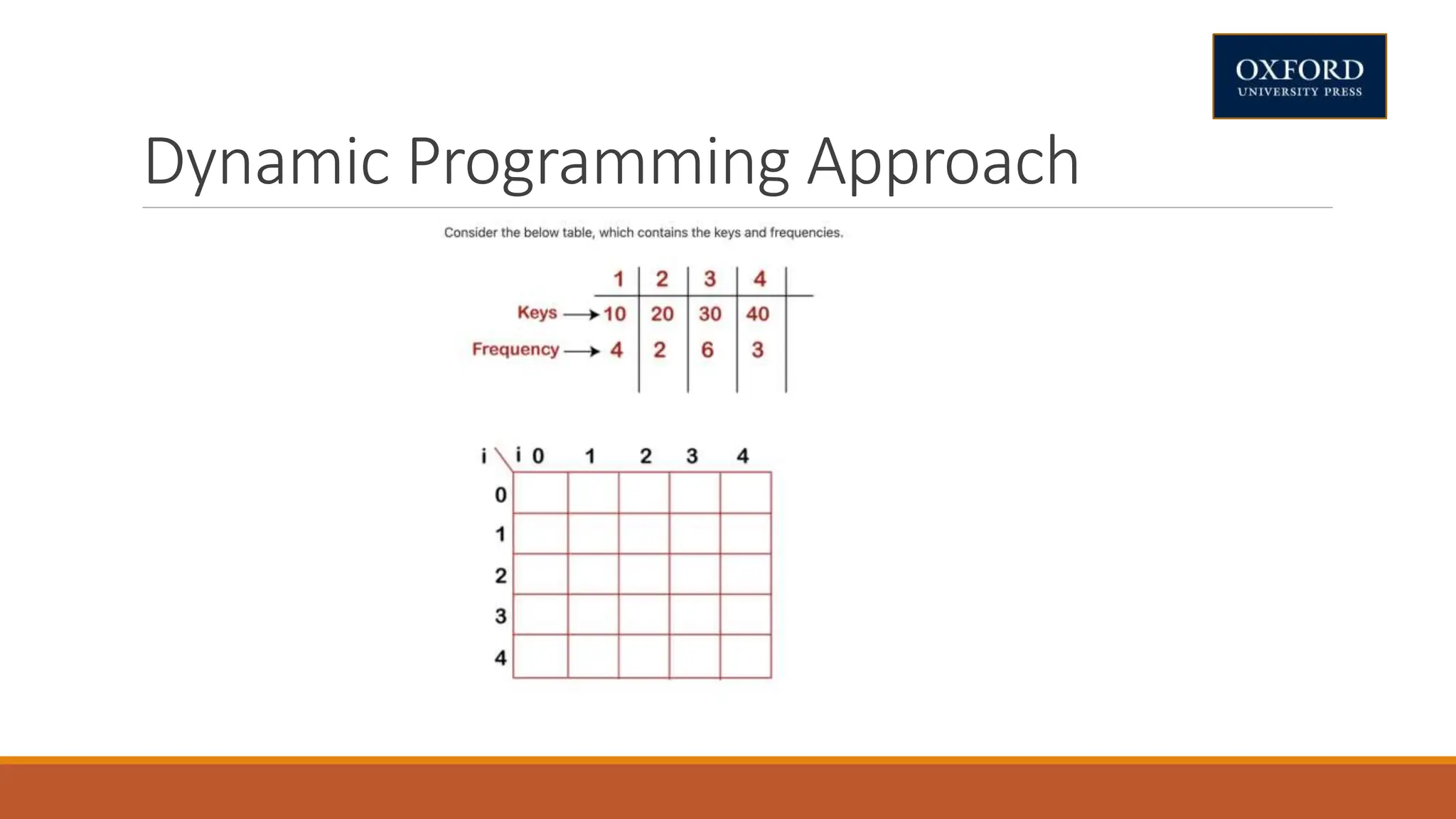
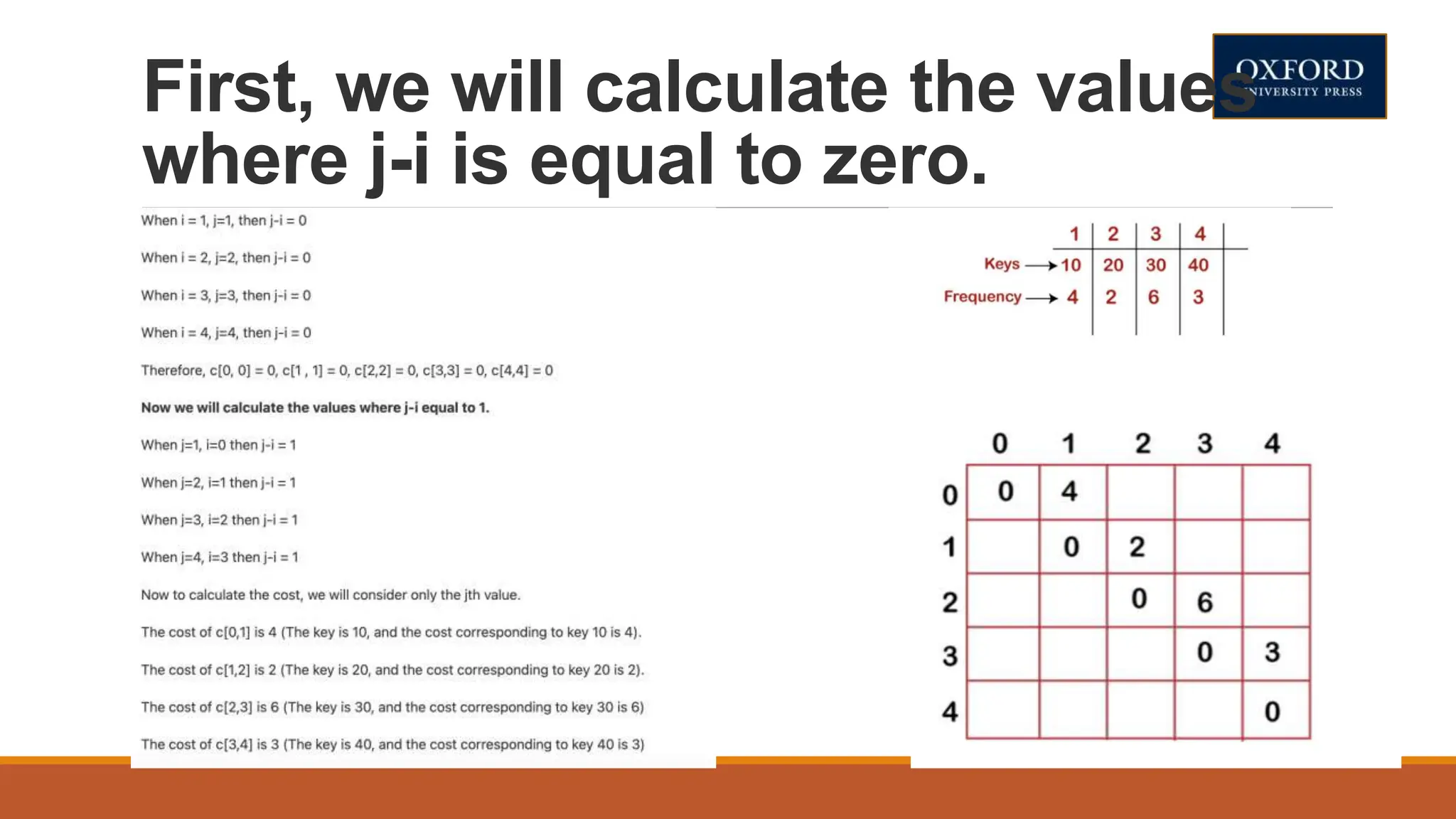
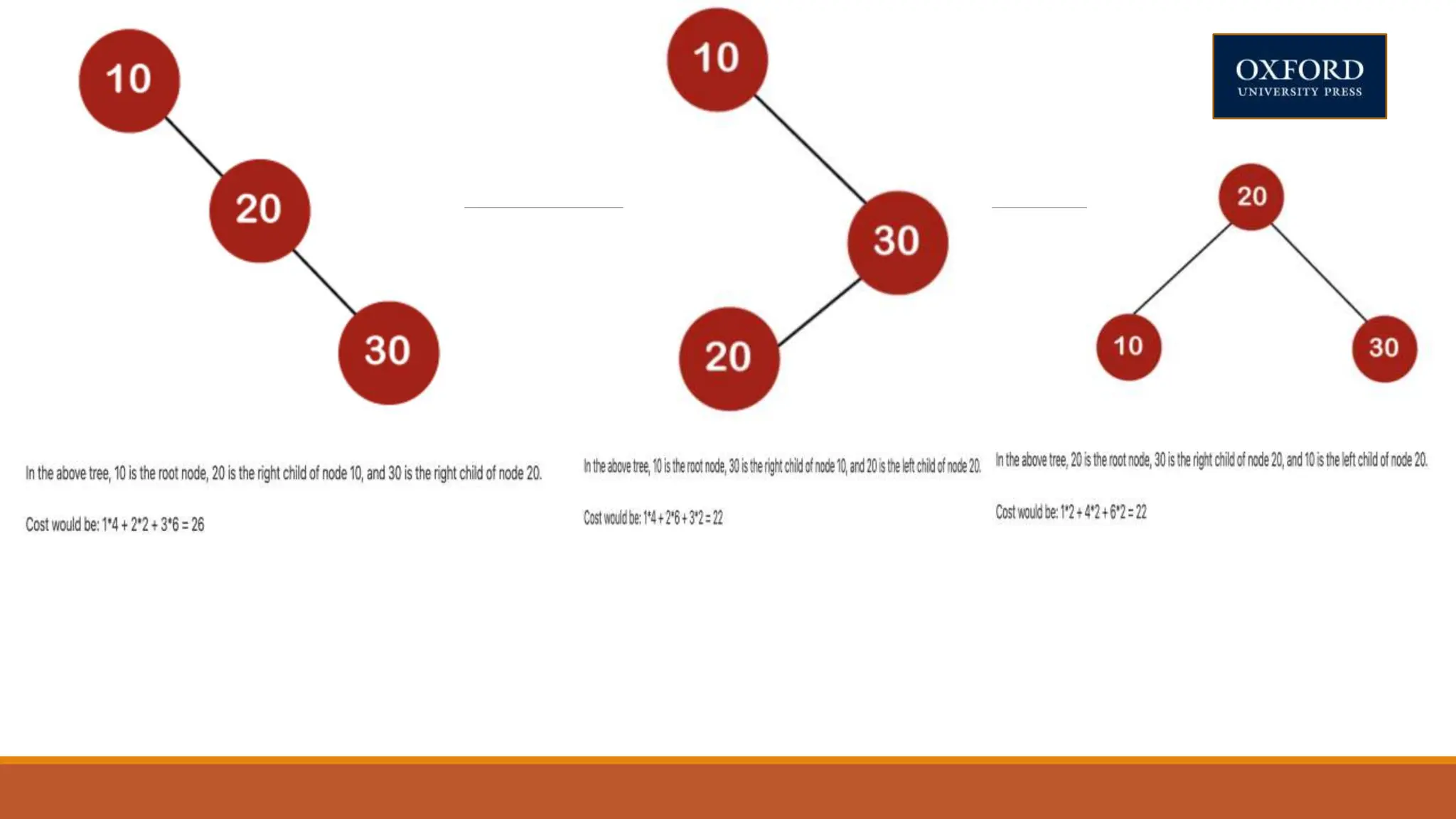
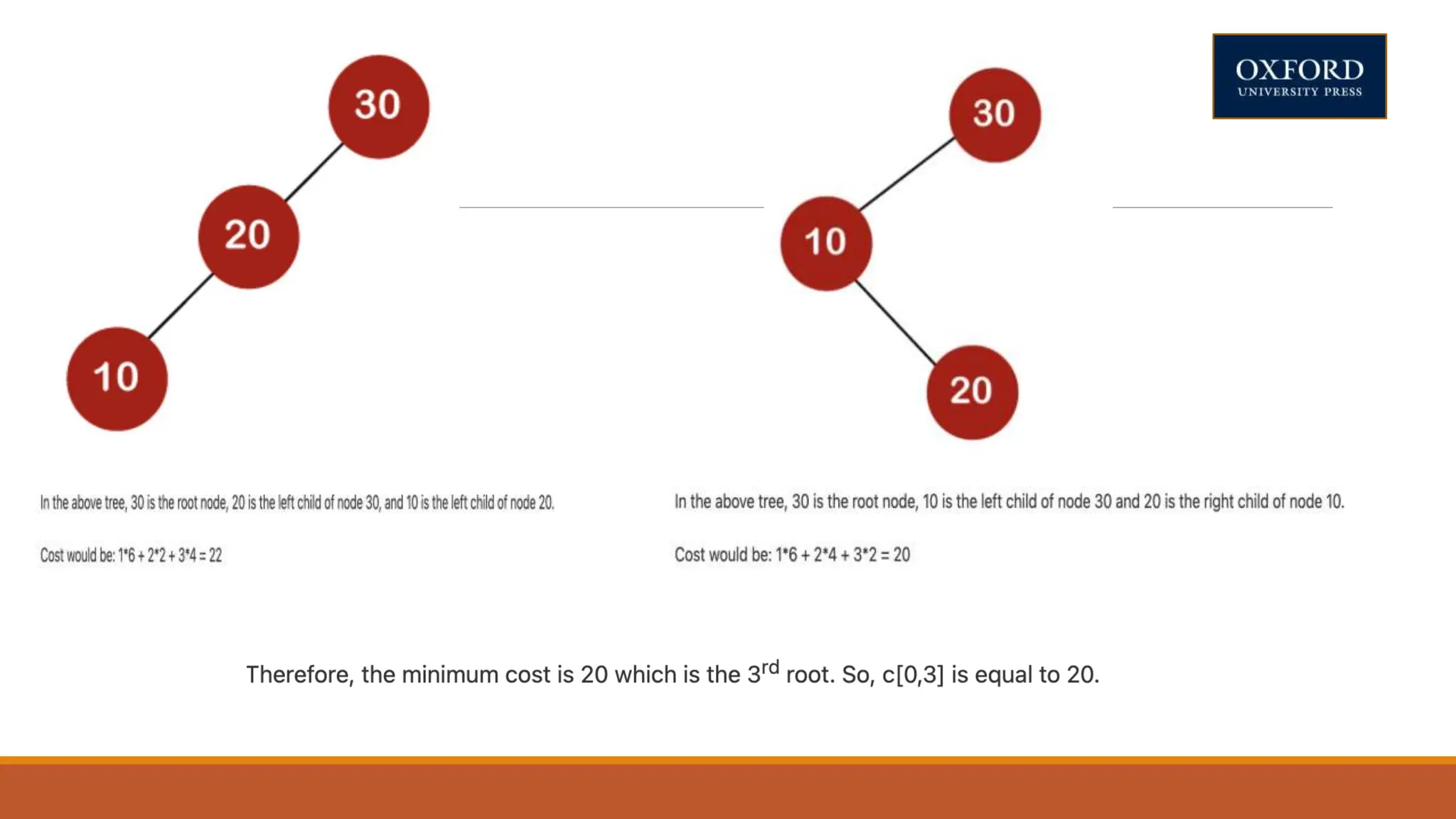
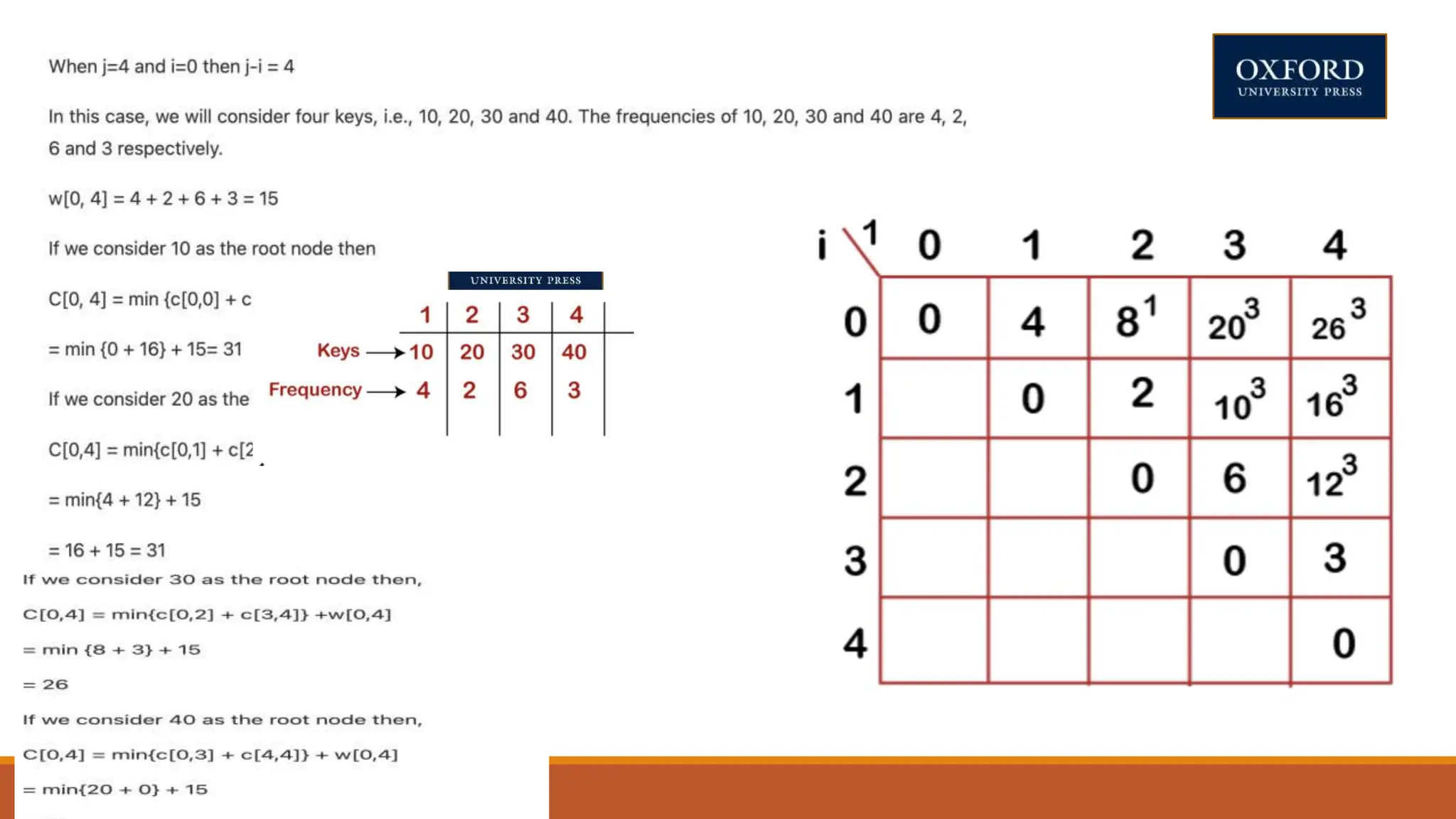
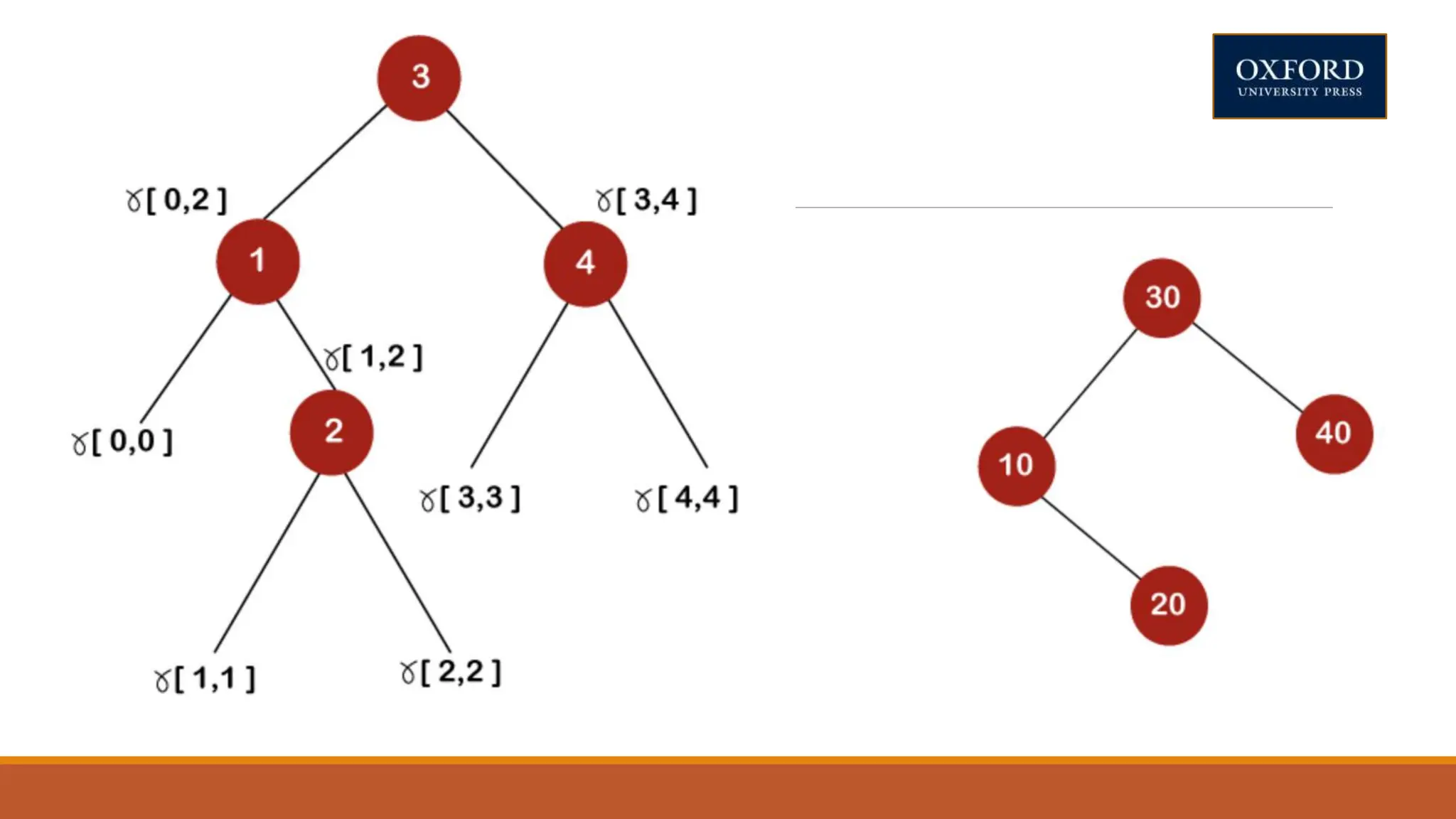
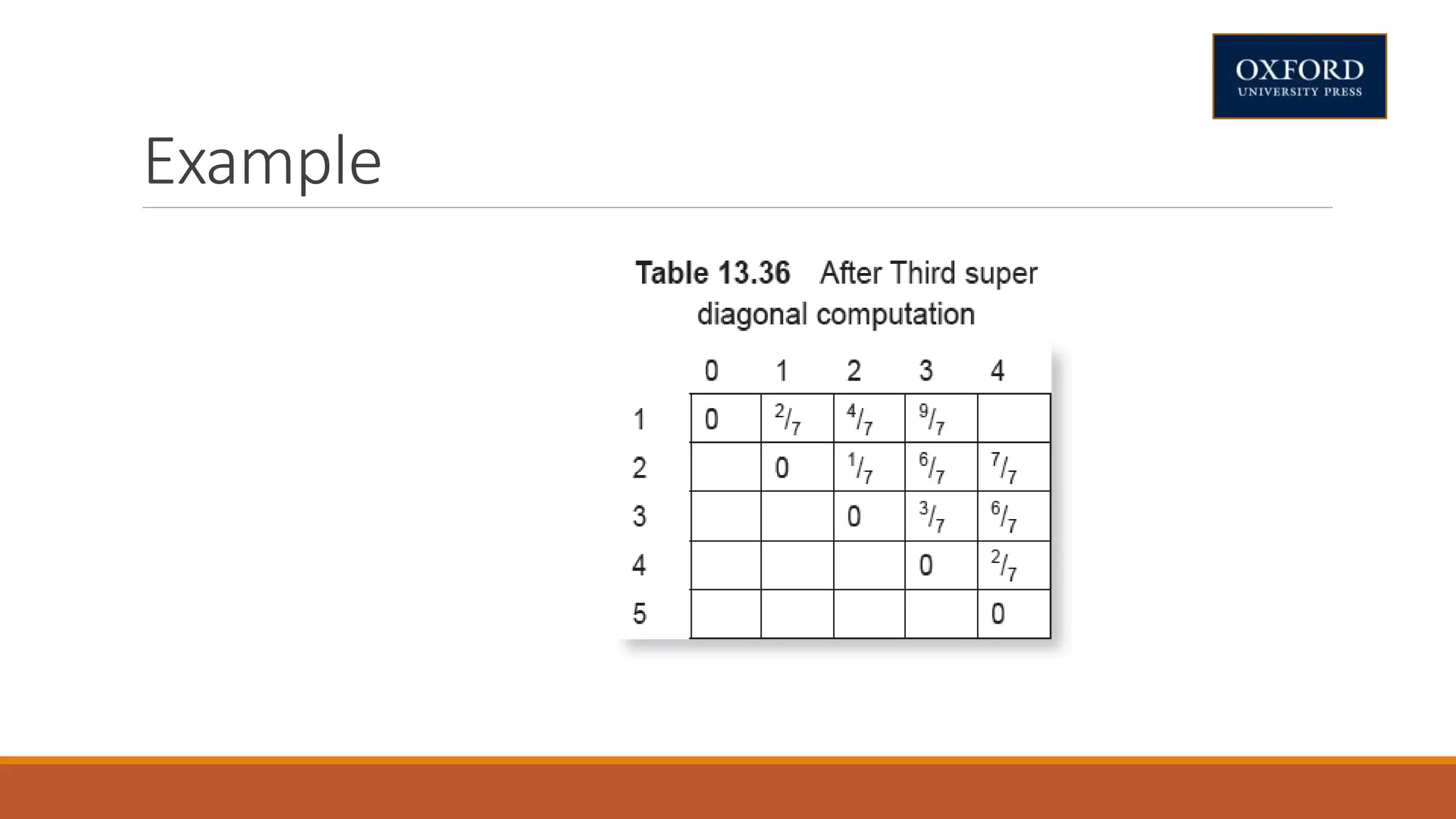
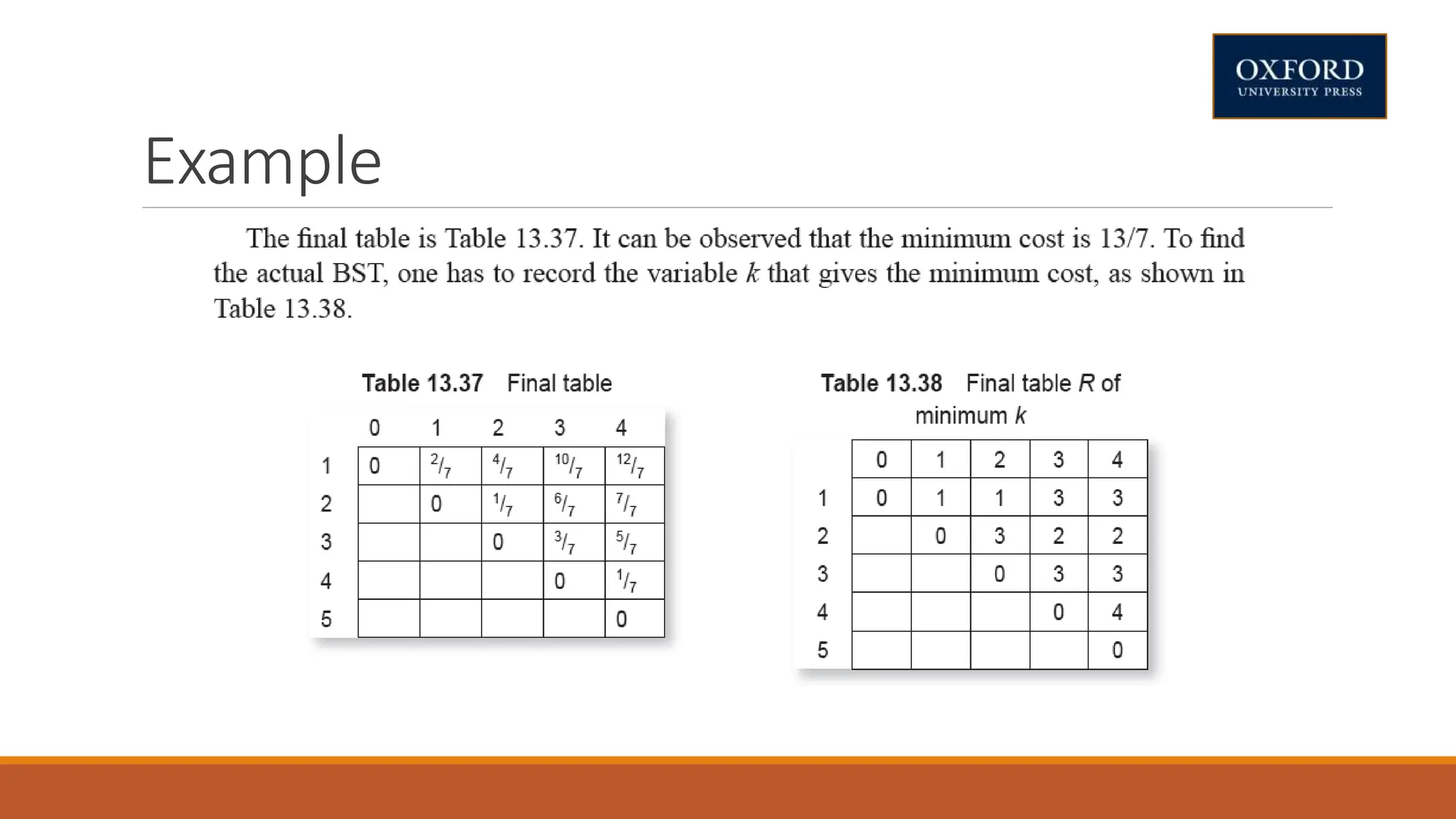
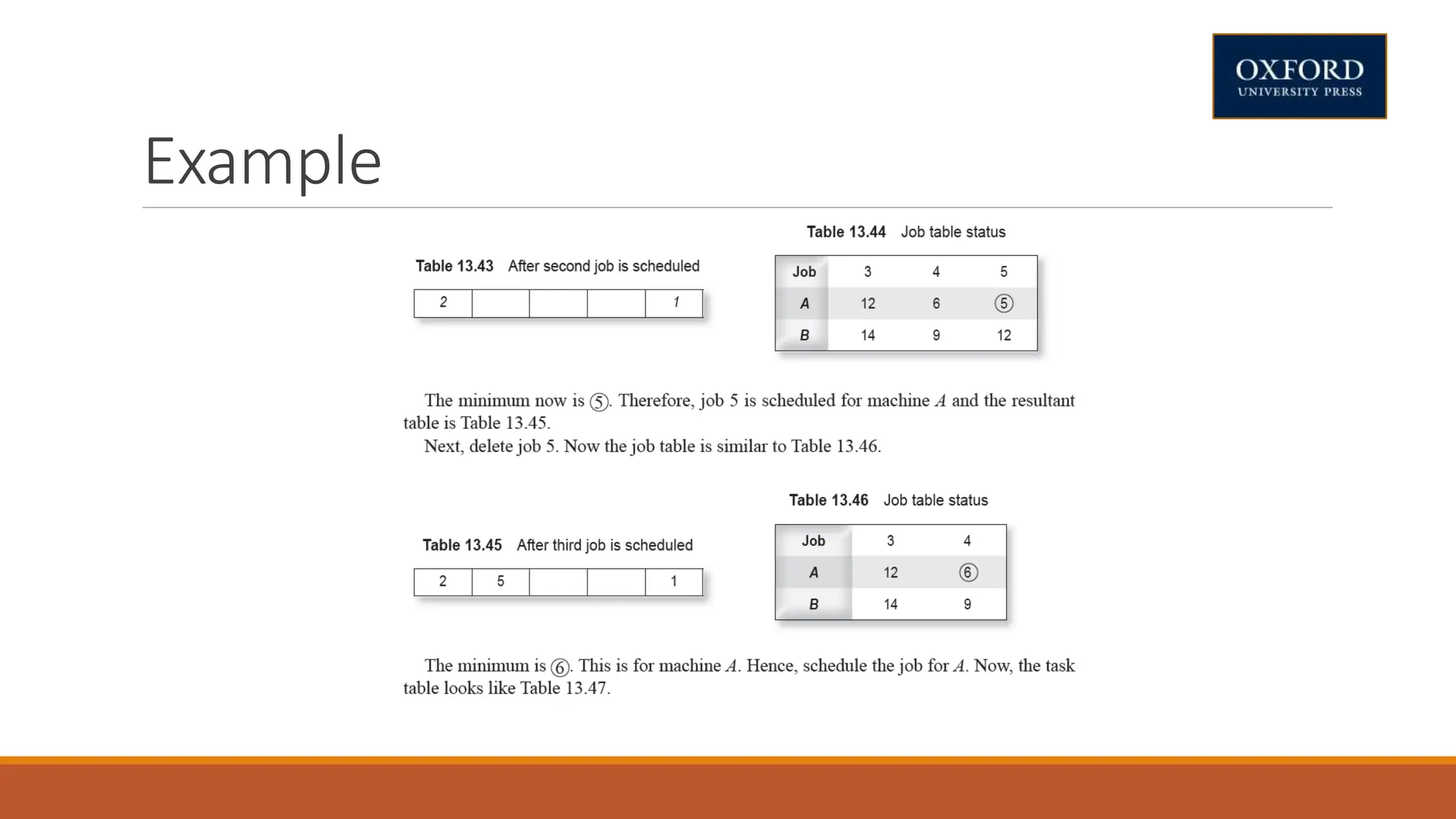
This document covers dynamic programming techniques and algorithms. It discusses topics like the principle of optimality, components of dynamic programming, properties, advantages and disadvantages. It provides algorithms and examples for problems like Fibonacci numbers, binomial coefficients, activity selection, shortest paths, transitive closure, optimal storage, traveling salesperson, chain matrix multiplication, knapsack problem, optimal binary search trees, and flow shop scheduling.