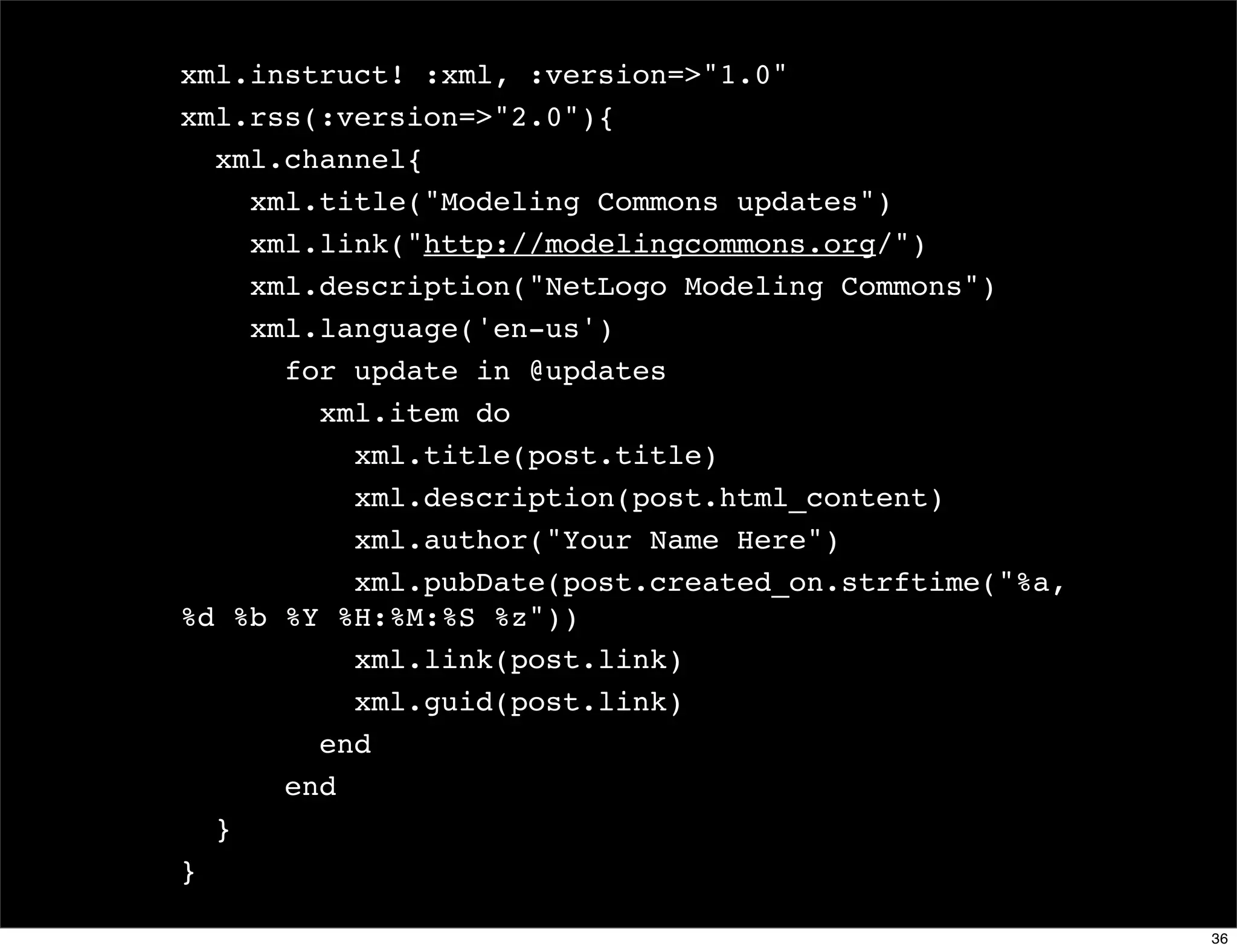
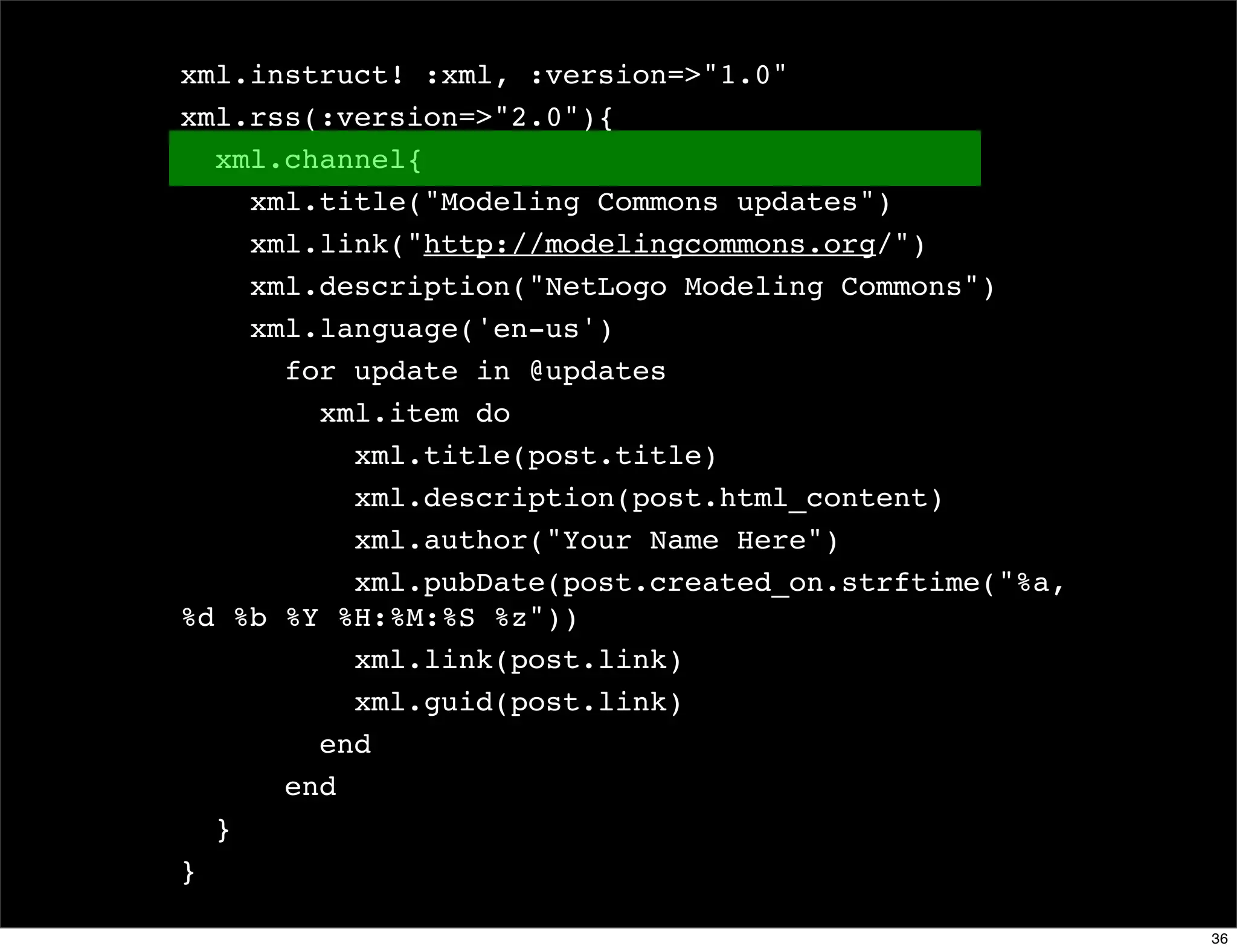
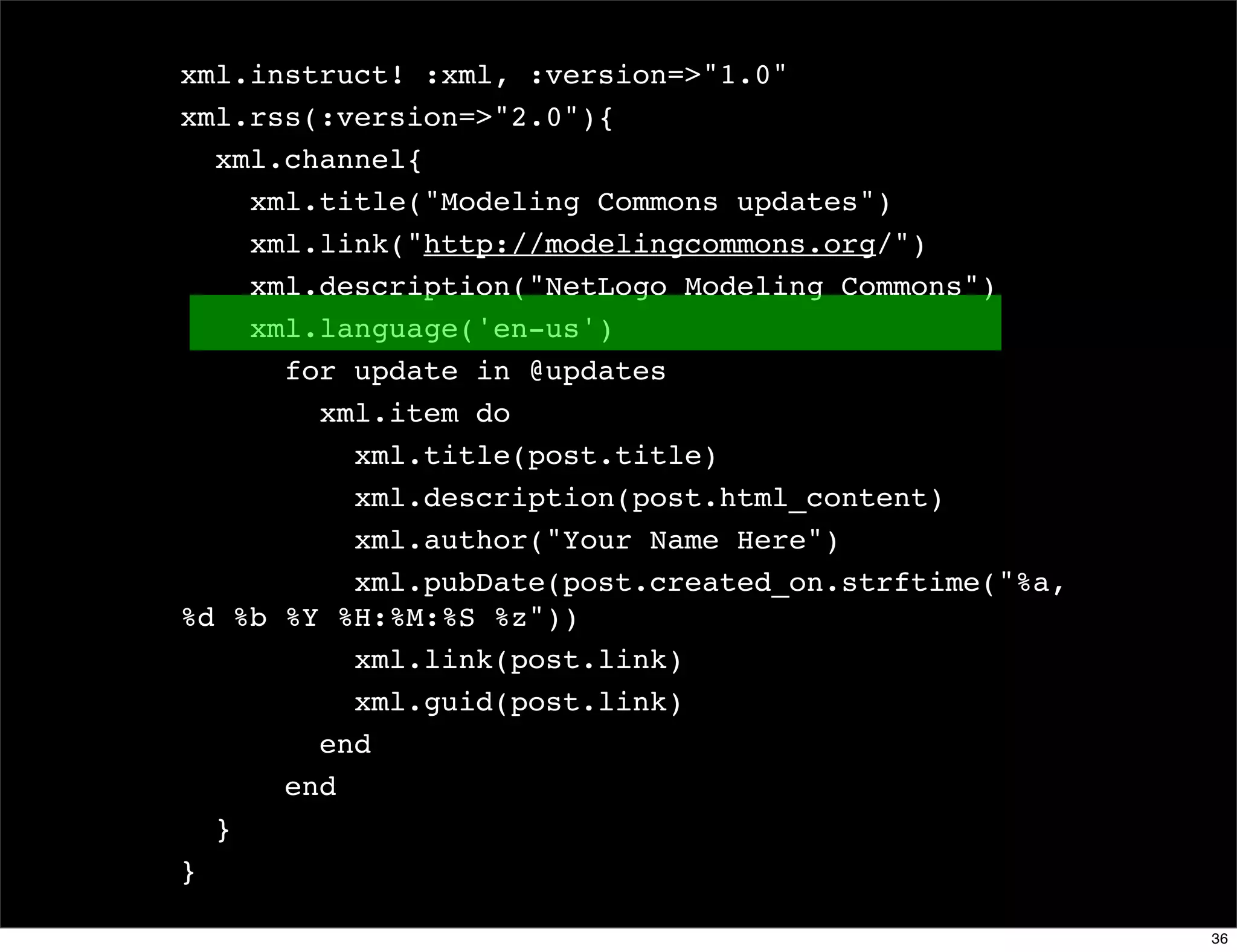
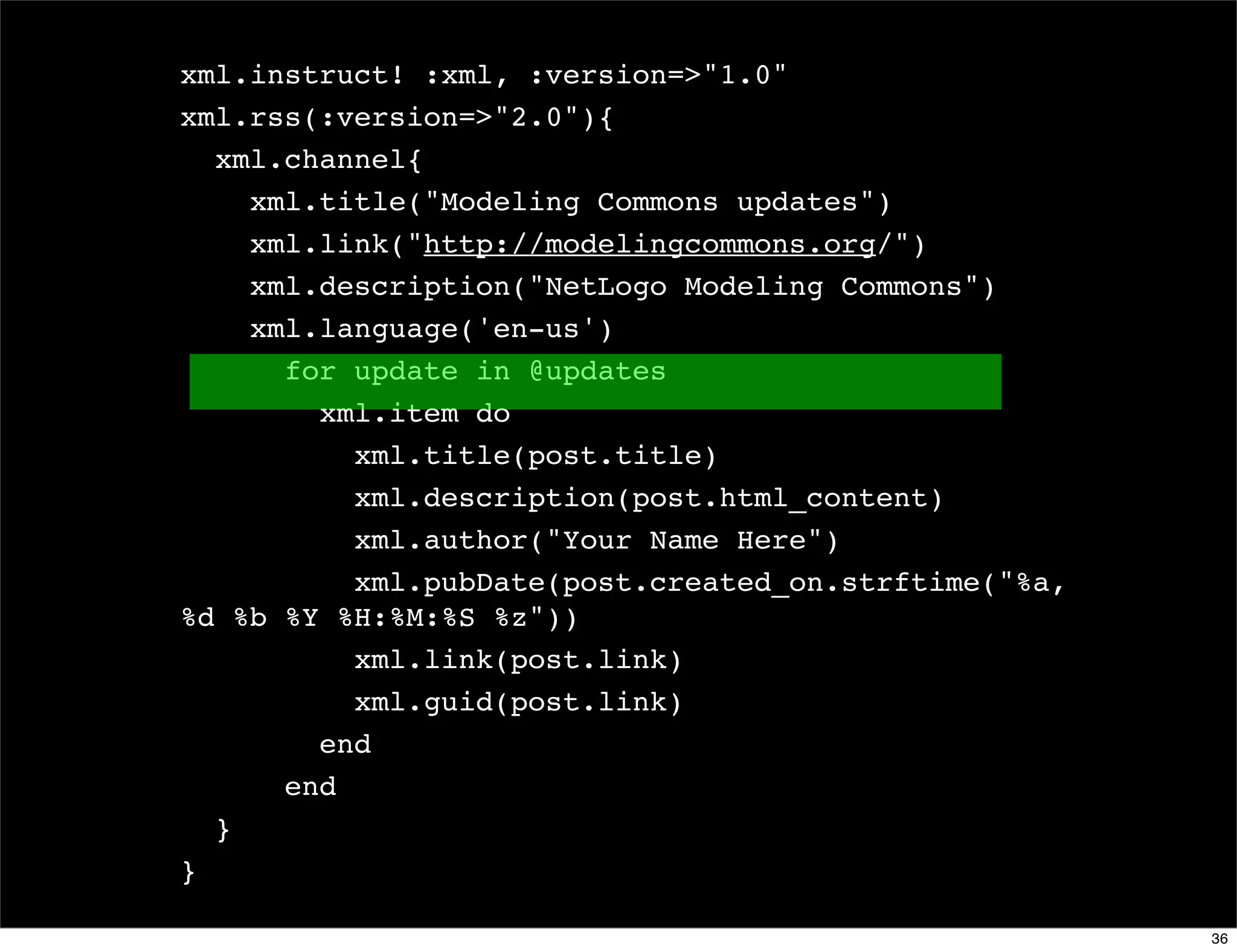
The document discusses dynamic languages, highlighting their characteristics such as dynamic typing and flexible object models, which result in shorter and more reusable code. It contrasts dynamic languages with static languages, emphasizing that in dynamic languages, the programmer has greater control over the programming process. Examples of dynamic languages mentioned include Ruby, Python, JavaScript, and Lisp.








![Values, not variables,
have types
x = 5
=> 5
x.class
=> Fixnum
x = [1,2,3]
=> [1, 2, 3]
x.class
=> Array
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-9-2048.jpg)
![Values, not variables,
have types
x = 5
=> 5
x.class
=> Fixnum
x = [1,2,3]
=> [1, 2, 3]
x.class
=> Array
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-10-2048.jpg)
![Values, not variables,
have types
x = 5
=> 5
x.class
=> Fixnum
x = [1,2,3]
=> [1, 2, 3]
x.class
=> Array
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-11-2048.jpg)
![Values, not variables,
have types
x = 5
=> 5
x.class
=> Fixnum
x = [1,2,3]
=> [1, 2, 3]
x.class
=> Array
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-12-2048.jpg)
![Values, not variables,
have types
x = 5
=> 5
x.class
=> Fixnum
x = [1,2,3]
=> [1, 2, 3]
x.class
=> Array
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-13-2048.jpg)




![Flexible collections
a = [1, 2, 'three', [4, 5, 6]]
=> [1, 2, "three", [4, 5, 6]]
a.length
=> 4
a << {first_name:'Reuven',
last_name:'Lerner'}
=> [1, 2, "three", [4, 5, 6],
{:first_name=>"Reuven",
:last_name=>"Lerner"}]
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-18-2048.jpg)
![Flexible collections
Integer
a = [1, 2, 'three', [4, 5, 6]]
=> [1, 2, "three", [4, 5, 6]]
a.length
=> 4
a << {first_name:'Reuven',
last_name:'Lerner'}
=> [1, 2, "three", [4, 5, 6],
{:first_name=>"Reuven",
:last_name=>"Lerner"}]
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-19-2048.jpg)
![Flexible collections
Integer String
a = [1, 2, 'three', [4, 5, 6]]
=> [1, 2, "three", [4, 5, 6]]
a.length
=> 4
a << {first_name:'Reuven',
last_name:'Lerner'}
=> [1, 2, "three", [4, 5, 6],
{:first_name=>"Reuven",
:last_name=>"Lerner"}]
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-20-2048.jpg)
![Flexible collections
Integer String Array
a = [1, 2, 'three', [4, 5, 6]]
=> [1, 2, "three", [4, 5, 6]]
a.length
=> 4
a << {first_name:'Reuven',
last_name:'Lerner'}
=> [1, 2, "three", [4, 5, 6],
{:first_name=>"Reuven",
:last_name=>"Lerner"}]
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-21-2048.jpg)
![Flexible collections
Integer String Array
a = [1, 2, 'three', [4, 5, 6]]
=> [1, 2, "three", [4, 5, 6]]
a.length
=> 4
a << {first_name:'Reuven',
last_name:'Lerner'} Hash
=> [1, 2, "three", [4, 5, 6],
{:first_name=>"Reuven",
:last_name=>"Lerner"}]
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-22-2048.jpg)



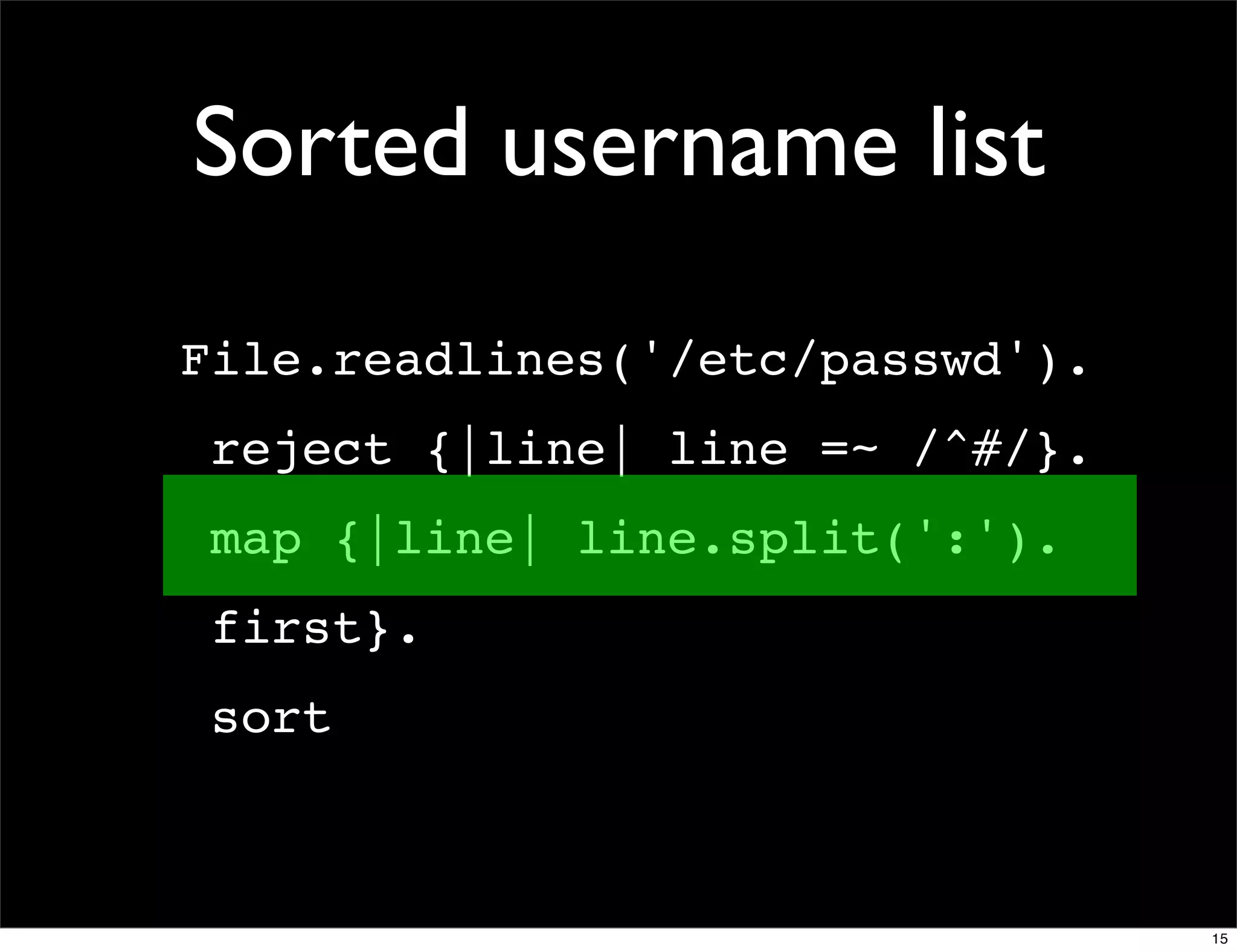
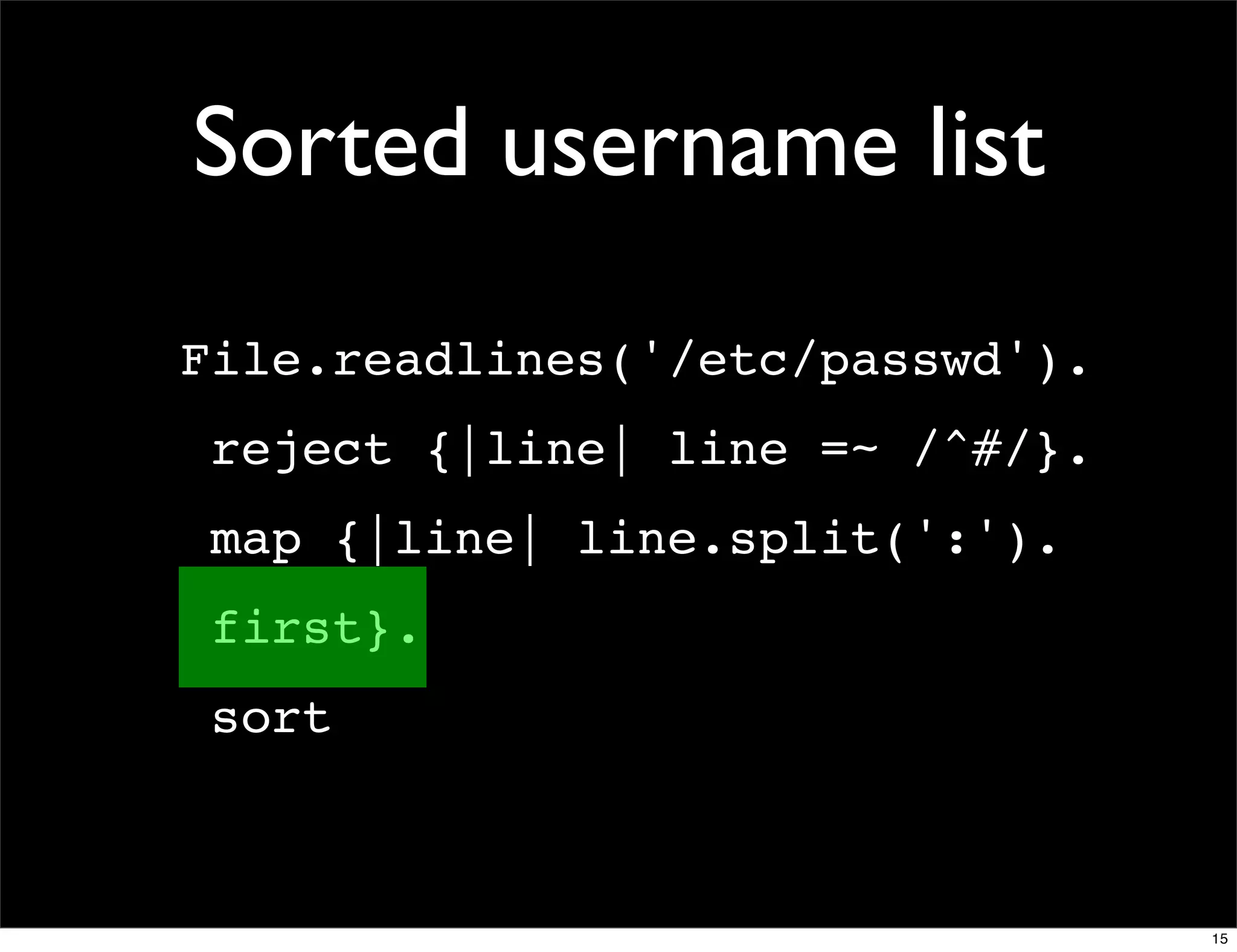
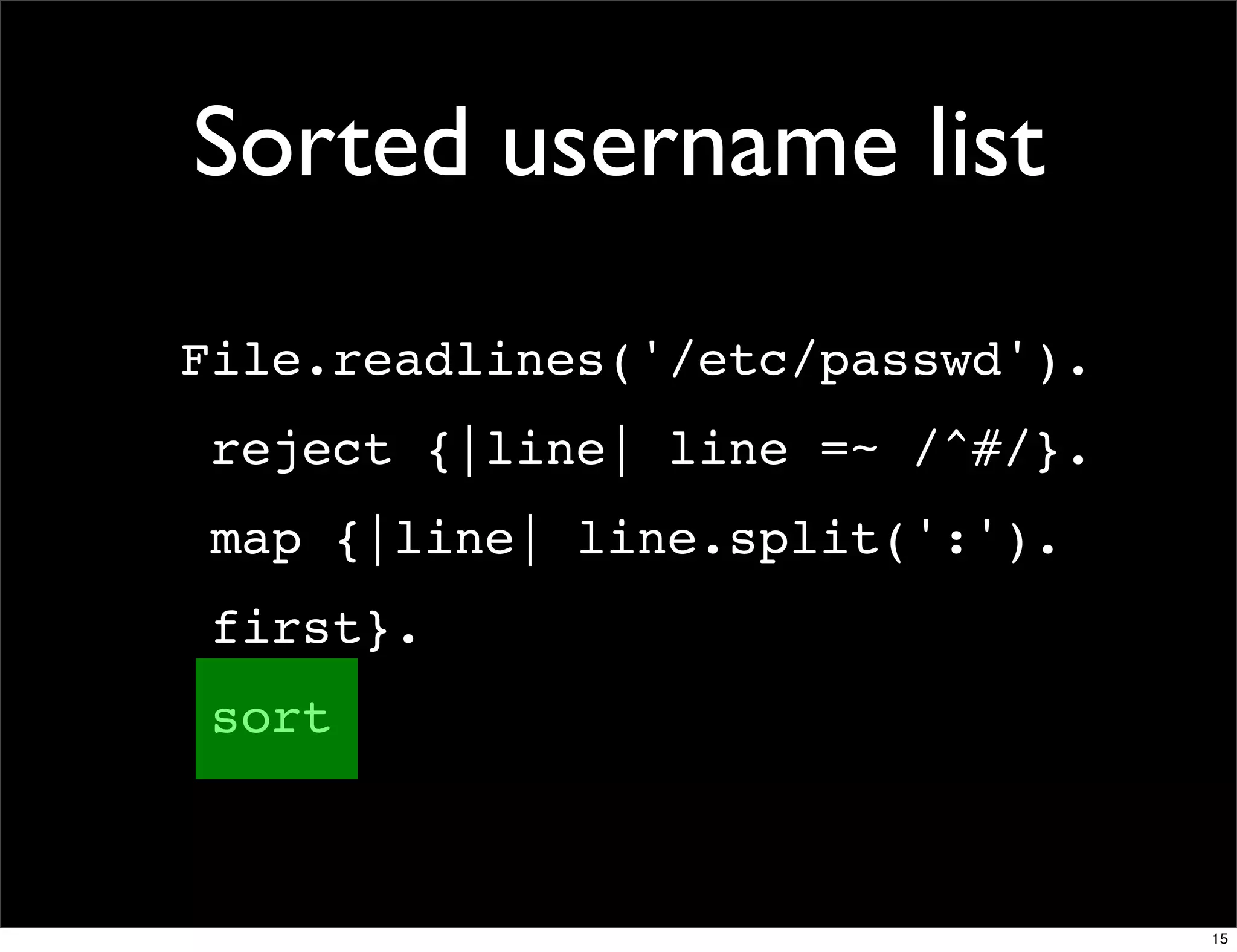
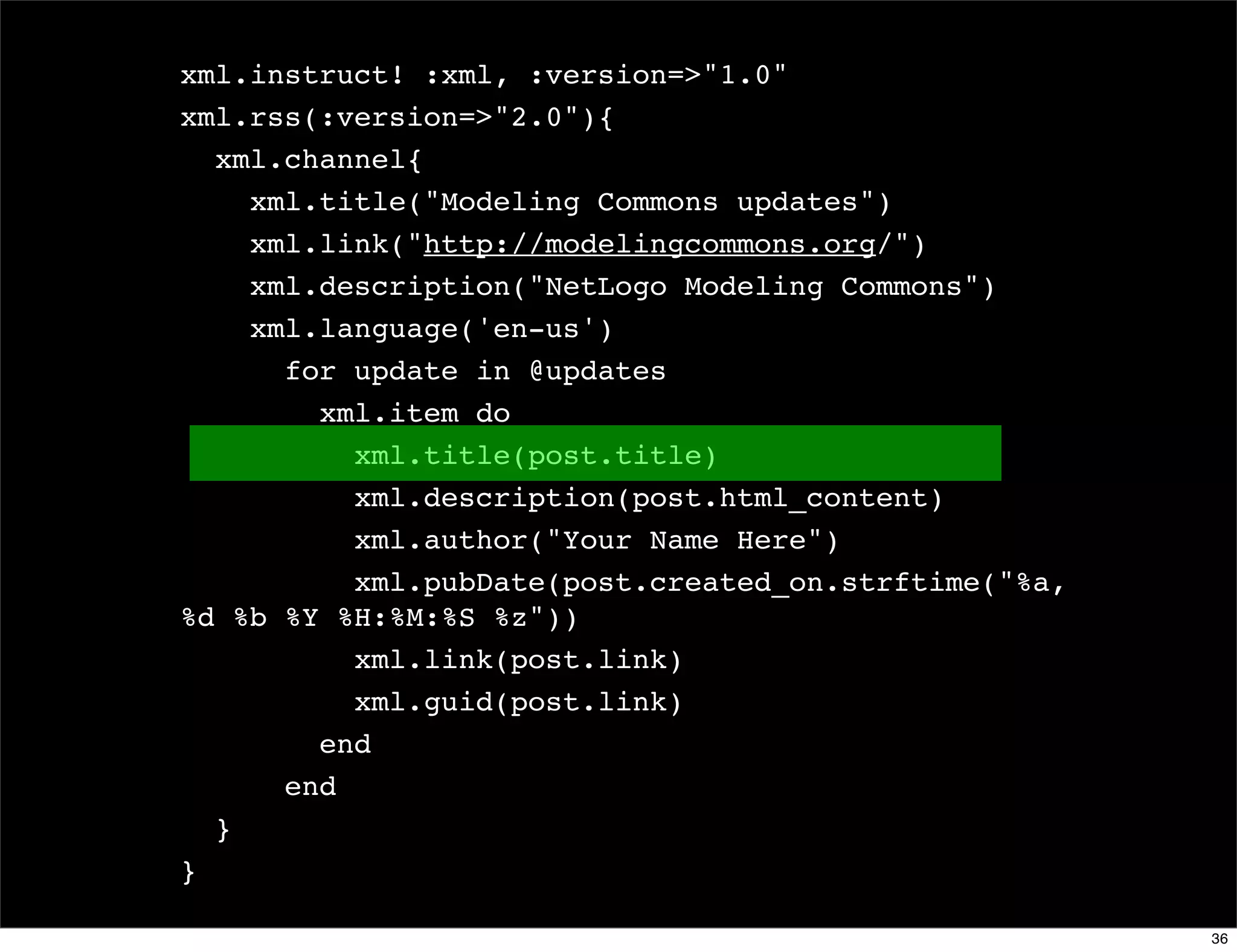
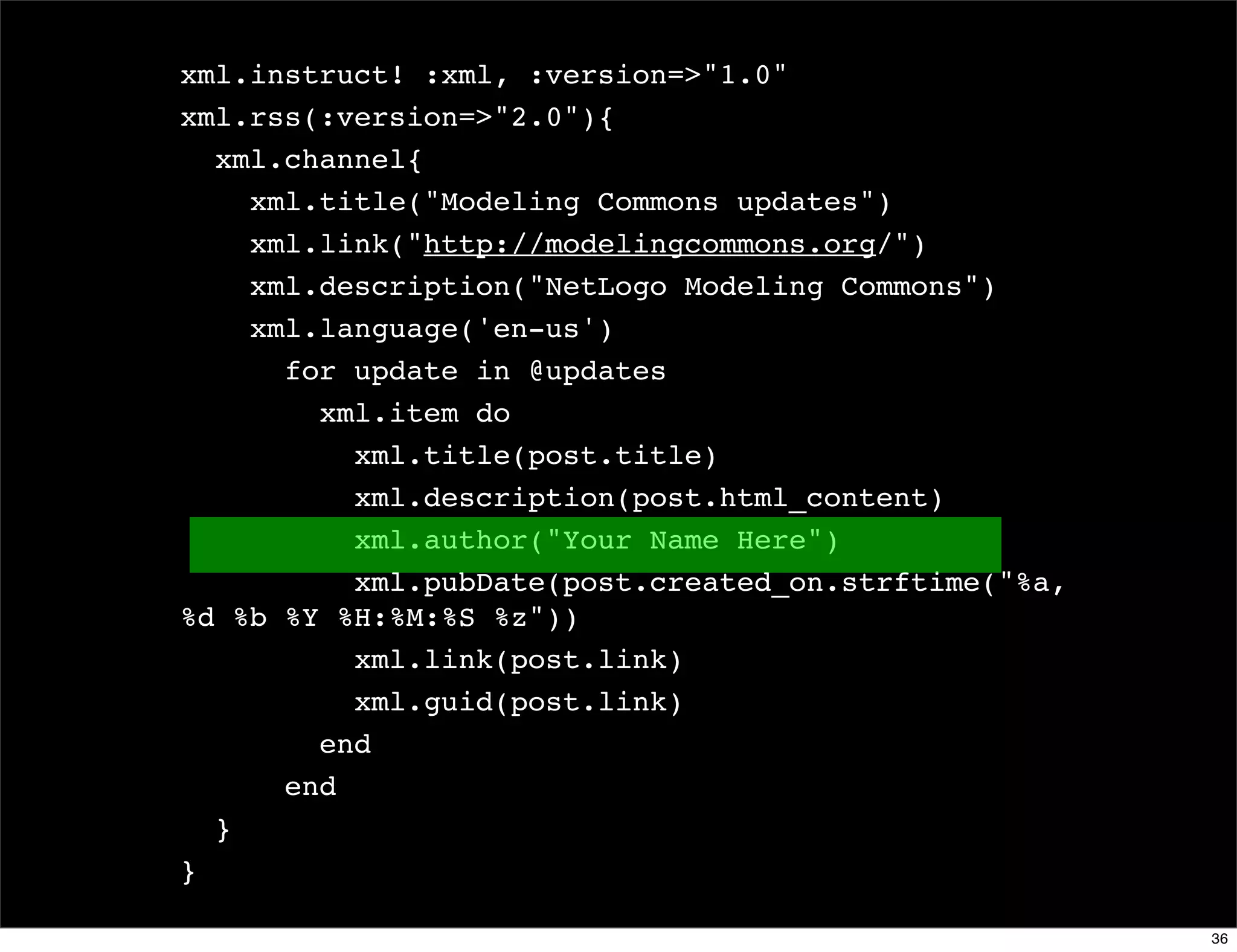
![Domain counter
domains = Hash.new(0)
File.readlines(list_member_file).each do |line|
email, domain = line.chomp.split('@')
domains[domain.downcase] += 1
end
domains.sort_by {|d| -d[1] }.
each {|d| puts "#{d[1]} #{d[0]}" }
domains.sort_by {|d| [-d[1], d[0]] }.
each {|d| puts "#{d[1]} #{d[0]}" }
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-31-2048.jpg)
![Domain counter
domains = Hash.new(0)
File.readlines(list_member_file).each do |line|
email, domain = line.chomp.split('@')
domains[domain.downcase] += 1
end
domains.sort_by {|d| -d[1] }.
each {|d| puts "#{d[1]} #{d[0]}" }
domains.sort_by {|d| [-d[1], d[0]] }.
each {|d| puts "#{d[1]} #{d[0]}" }
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-32-2048.jpg)
![Domain counter
domains = Hash.new(0)
File.readlines(list_member_file).each do |line|
email, domain = line.chomp.split('@')
domains[domain.downcase] += 1
end
domains.sort_by {|d| -d[1] }.
each {|d| puts "#{d[1]} #{d[0]}" }
domains.sort_by {|d| [-d[1], d[0]] }.
each {|d| puts "#{d[1]} #{d[0]}" }
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-33-2048.jpg)
![Domain counter
domains = Hash.new(0)
File.readlines(list_member_file).each do |line|
email, domain = line.chomp.split('@')
domains[domain.downcase] += 1
end
domains.sort_by {|d| -d[1] }.
each {|d| puts "#{d[1]} #{d[0]}" }
domains.sort_by {|d| [-d[1], d[0]] }.
each {|d| puts "#{d[1]} #{d[0]}" }
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-34-2048.jpg)
![Domain counter
domains = Hash.new(0)
File.readlines(list_member_file).each do |line|
email, domain = line.chomp.split('@')
domains[domain.downcase] += 1
end
domains.sort_by {|d| -d[1] }.
each {|d| puts "#{d[1]} #{d[0]}" }
domains.sort_by {|d| [-d[1], d[0]] }.
each {|d| puts "#{d[1]} #{d[0]}" }
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-35-2048.jpg)
![Domain counter
domains = Hash.new(0)
File.readlines(list_member_file).each do |line|
email, domain = line.chomp.split('@')
domains[domain.downcase] += 1
end
domains.sort_by {|d| -d[1] }.
each {|d| puts "#{d[1]} #{d[0]}" }
domains.sort_by {|d| [-d[1], d[0]] }.
each {|d| puts "#{d[1]} #{d[0]}" }
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-36-2048.jpg)
![Domain counter
domains = Hash.new(0)
File.readlines(list_member_file).each do |line|
email, domain = line.chomp.split('@')
domains[domain.downcase] += 1
end
domains.sort_by {|d| -d[1] }.
each {|d| puts "#{d[1]} #{d[0]}" }
domains.sort_by {|d| [-d[1], d[0]] }.
each {|d| puts "#{d[1]} #{d[0]}" }
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-37-2048.jpg)

![Real-time require
require 'jobs/a'
require 'jobs/b'
require 'jobs/c'
Dir["#{Rails.root}/app/jobs/
*.rb"].
each { |file| require file }
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-39-2048.jpg)
![Real-time require
require 'jobs/a'
require 'jobs/b'
require 'jobs/c'
Dir["#{Rails.root}/app/jobs/
*.rb"].
each { |file| require file }
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-40-2048.jpg)
![Real-time require
require 'jobs/a'
require 'jobs/b'
require 'jobs/c'
Dir["#{Rails.root}/app/jobs/
*.rb"].
each { |file| require file }
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-41-2048.jpg)

![Defining classes
class Person
end
=> nil
p = Person.new
=> #<Person:0x00000102105740>
p.class
=> Person
p.class.ancestors
=> [Person, Object, Wirble::Shortcuts,
PP::ObjectMixin, Kernel, BasicObject]
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-43-2048.jpg)
![Defining classes
class Person
end
=> nil
p = Person.new
=> #<Person:0x00000102105740>
p.class
=> Person
p.class.ancestors
=> [Person, Object, Wirble::Shortcuts,
PP::ObjectMixin, Kernel, BasicObject]
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-44-2048.jpg)
![Defining classes
class Person
end
=> nil
p = Person.new
=> #<Person:0x00000102105740>
p.class
=> Person
p.class.ancestors
=> [Person, Object, Wirble::Shortcuts,
PP::ObjectMixin, Kernel, BasicObject]
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-45-2048.jpg)
![Defining classes
class Person
end
=> nil
p = Person.new
=> #<Person:0x00000102105740>
p.class
=> Person
p.class.ancestors
=> [Person, Object, Wirble::Shortcuts,
PP::ObjectMixin, Kernel, BasicObject]
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-46-2048.jpg)
![Defining classes
class Person
end
=> nil
p = Person.new
=> #<Person:0x00000102105740>
p.class
=> Person
p.class.ancestors
=> [Person, Object, Wirble::Shortcuts,
PP::ObjectMixin, Kernel, BasicObject]
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-47-2048.jpg)
![Reflection
> p.methods # or Person.instance_methods
=>
[:po, :poc, :pretty_print, :pretty_print_cycle,
:pretty_print_instance_variables, :pretty_print_inspect,
:nil?, :, :, :!, :eql?, :hash, :=>, :class, :singleton_class,
:clone, :dup, :initialize_dup, :initialize_clone, :taint,
:tainted?, :untaint, :untrust, :untrusted?, :trust, :freeze,
:frozen?, :to_s, :inspect, :methods, :singleton_methods,
:protected_methods, :private_methods, :public_methods,
:instance_variables, :instance_variable_get,
:instance_variable_set, :instance_variable_defined?,
:instance_of?, :kind_of?, :is_a?, :tap, :send, :public_send,
:respond_to?, :respond_to_missing?, :extend, :display,
:method, :public_method, :define_singleton_method, :__id__,
:object_id, :to_enum, :enum_for, :pretty_inspect, :ri, :,
:equal?, :!, :!, :instance_eval, :instance_exec, :__send__]
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-48-2048.jpg)
![Predicates
p.methods.grep(/?$/)
=>
[:nil?, :eql?, :tainted?,
:untrusted?, :frozen?,
:instance_variable_defined?,
:instance_of?, :kind_of?, :is_a?,
:respond_to?, :respond_to_missing?,
:equal?]
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-49-2048.jpg)
![“Local” methods
class Person
def blah
"blah"
end
end
=> nil
p = Person.new
p.class.instance_methods -
p.class.superclass.instance_methods
=> [:blah]
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-50-2048.jpg)
![“Local” methods
class Person
def blah
"blah"
end
end
=> nil
p = Person.new
p.class.instance_methods -
p.class.superclass.instance_methods
=> [:blah]
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-51-2048.jpg)
![“Local” methods
class Person
def blah
"blah"
end
end
=> nil
p = Person.new
p.class.instance_methods -
p.class.superclass.instance_methods
=> [:blah]
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-52-2048.jpg)
![“Local” methods
class Person
def blah
"blah"
end
end
=> nil
p = Person.new
p.class.instance_methods -
p.class.superclass.instance_methods
=> [:blah]
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-53-2048.jpg)







![Define similar methods
['preview', 'applet', 'info',
'procedures', 'discuss', 'files',
'history', 'tags', 'family', 'upload',
'permissions'].each do |tab_name|
define_method(
"browse_#{tab_name}_tab".to_sym ) do
render :layout => 'browse_tab'
end
end
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-61-2048.jpg)
![Define similar methods
['preview', 'applet', 'info',
'procedures', 'discuss', 'files',
'history', 'tags', 'family', 'upload',
'permissions'].each do |tab_name|
define_method(
"browse_#{tab_name}_tab".to_sym ) do
render :layout => 'browse_tab'
end
end
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-62-2048.jpg)
![Define similar methods
['preview', 'applet', 'info',
'procedures', 'discuss', 'files',
'history', 'tags', 'family', 'upload',
'permissions'].each do |tab_name|
define_method(
"browse_#{tab_name}_tab".to_sym ) do
render :layout => 'browse_tab'
end
end
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-63-2048.jpg)
![Define similar methods
['preview', 'applet', 'info',
'procedures', 'discuss', 'files',
'history', 'tags', 'family', 'upload',
'permissions'].each do |tab_name|
define_method(
"browse_#{tab_name}_tab".to_sym ) do
render :layout => 'browse_tab'
end
end
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-64-2048.jpg)
![Define similar methods
['preview', 'applet', 'info',
'procedures', 'discuss', 'files',
'history', 'tags', 'family', 'upload',
'permissions'].each do |tab_name|
define_method(
"browse_#{tab_name}_tab".to_sym ) do
render :layout => 'browse_tab'
end
end
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-65-2048.jpg)
![Searching by result
'a'.what?('A')
"a".upcase == "A"
"a".capitalize == "A"
"a".swapcase == "A"
"a".upcase! == "A"
"a".capitalize! == "A"
"a".swapcase! == "A"
[:upcase, :capitalize, :swapcase,
:upcase!, :capitalize!, :swapcase!]
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-66-2048.jpg)
![Searching by result
'a'.what?('A')
"a".upcase == "A"
"a".capitalize == "A"
"a".swapcase == "A"
"a".upcase! == "A"
"a".capitalize! == "A"
"a".swapcase! == "A"
[:upcase, :capitalize, :swapcase,
:upcase!, :capitalize!, :swapcase!]
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-67-2048.jpg)
![Searching by result
'a'.what?('A')
"a".upcase == "A"
"a".capitalize == "A"
"a".swapcase == "A"
"a".upcase! == "A"
"a".capitalize! == "A"
"a".swapcase! == "A"
[:upcase, :capitalize, :swapcase,
:upcase!, :capitalize!, :swapcase!]
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-68-2048.jpg)
![Searching by result
'a'.what?('A')
"a".upcase == "A"
"a".capitalize == "A"
"a".swapcase == "A"
"a".upcase! == "A"
"a".capitalize! == "A"
"a".swapcase! == "A"
[:upcase, :capitalize, :swapcase,
:upcase!, :capitalize!, :swapcase!]
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-69-2048.jpg)




![Example: RSpec
it "should have a unique name" do
c1 = Currency.new(@valid_attributes)
c1.save!
c2 =
Currency.new(
:name => @valid_attributes[:name],
:abbreviation => 'XYZ')
c1.should be_valid
c2.should_not be_valid
end
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-74-2048.jpg)
![Example: RSpec
it "should have a unique name" do
c1 = Currency.new(@valid_attributes)
c1.save!
c2 =
Currency.new(
:name => @valid_attributes[:name],
:abbreviation => 'XYZ')
c1.should be_valid
c2.should_not be_valid
end
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-75-2048.jpg)
![Example: RSpec
it "should have a unique name" do
c1 = Currency.new(@valid_attributes)
c1.save!
c2 =
Currency.new(
:name => @valid_attributes[:name],
:abbreviation => 'XYZ')
c1.should be_valid
c2.should_not be_valid
end
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-76-2048.jpg)

![Dynamic finders
Reading.find_all_by_longitude_and_d
evice_id(0, 3)
=> [#<Reading id: 46, longitude:
#<BigDecimal:24439a8,'0.0',9(18)>,
latitude: ... ]
Reading.instance_methods.grep(/
long/)
=> []
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-78-2048.jpg)
![Dynamic finders
Reading.find_all_by_longitude_and_d
evice_id(0, 3)
=> [#<Reading id: 46, longitude:
#<BigDecimal:24439a8,'0.0',9(18)>,
latitude: ... ]
Reading.instance_methods.grep(/
long/)
=> []
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-79-2048.jpg)
![Dynamic finders
Reading.find_all_by_longitude_and_d
evice_id(0, 3)
=> [#<Reading id: 46, longitude:
#<BigDecimal:24439a8,'0.0',9(18)>,
latitude: ... ]
Reading.instance_methods.grep(/
long/)
=> []
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-80-2048.jpg)
![Hash methods as keys
class Hash
def method_missing(name, *args)
if has_key?(name)
self[name]
end
end
end
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-81-2048.jpg)
![Example
h = {a:1, b:2} => 3
=> {:a=>1, :b=>2} h.c
h[:a] => nil
=> 1 h[:d] = 4
h.a => 4
=> 1 h.d
h['c'] = 3 => 4
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-82-2048.jpg)
![Example
h = {a:1, b:2} => 3
=> {:a=>1, :b=>2} h.c
h[:a] => nil
=> 1 h[:d] = 4
h.a => 4
=> 1 h.d
h['c'] = 3 => 4
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-83-2048.jpg)
![Example
h = {a:1, b:2} => 3
=> {:a=>1, :b=>2} h.c
h[:a] => nil
=> 1 h[:d] = 4
h.a => 4
=> 1 h.d
h['c'] = 3 => 4
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-84-2048.jpg)
![Example
h = {a:1, b:2} => 3
=> {:a=>1, :b=>2} h.c
h[:a] => nil
=> 1 h[:d] = 4
h.a => 4
=> 1 h.d
h['c'] = 3 => 4
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-85-2048.jpg)
![Example
h = {a:1, b:2} => 3
=> {:a=>1, :b=>2} h.c
h[:a] => nil
=> 1 h[:d] = 4
h.a => 4
=> 1 h.d
h['c'] = 3 => 4
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-86-2048.jpg)
![Example
h = {a:1, b:2} => 3
=> {:a=>1, :b=>2} h.c
h[:a] => nil
=> 1 h[:d] = 4
h.a => 4
=> 1 h.d
h['c'] = 3 => 4
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-87-2048.jpg)
![Example
h = {a:1, b:2} => 3
=> {:a=>1, :b=>2} h.c
h[:a] => nil
=> 1 h[:d] = 4
h.a => 4
=> 1 h.d
h['c'] = 3 => 4
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-88-2048.jpg)
![Example
h = {a:1, b:2} => 3
=> {:a=>1, :b=>2} h.c
h[:a] => nil
=> 1 h[:d] = 4
h.a => 4
=> 1 h.d
h['c'] = 3 => 4
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-89-2048.jpg)
![Hash method access
class Hash
def method_missing(method_name, *arguments)
if has_key?(method_name)
self[method_name]
elsif has_key?(method_name.to_s)
self[method_name.to_s]
else
nil
end
end
end
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-90-2048.jpg)
![Hash method access
class Hash
def method_missing(method_name, *arguments)
if has_key?(method_name)
self[method_name]
elsif has_key?(method_name.to_s)
self[method_name.to_s]
else
nil
end
end
end
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-91-2048.jpg)
![Hash method access
class Hash
def method_missing(method_name, *arguments)
if has_key?(method_name)
self[method_name]
elsif has_key?(method_name.to_s)
self[method_name.to_s]
else
nil
end
end
end
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-92-2048.jpg)
![Hash method access
class Hash
def method_missing(method_name, *arguments)
if has_key?(method_name)
self[method_name]
elsif has_key?(method_name.to_s)
self[method_name.to_s]
else
nil
end
end
end
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-93-2048.jpg)
![Hash method access
class Hash
def method_missing(method_name, *arguments)
if has_key?(method_name)
self[method_name]
elsif has_key?(method_name.to_s)
self[method_name.to_s]
else
nil
end
end
end
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-94-2048.jpg)
![Hash method access
class Hash
def method_missing(method_name, *arguments)
if has_key?(method_name)
self[method_name]
elsif has_key?(method_name.to_s)
self[method_name.to_s]
else
nil
end
end
end
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiclanguagesforsoftwarecraftmanshipgroup-110322154717-phpapp02/75/Dynamic-languages-for-software-craftmanship-group-95-2048.jpg)