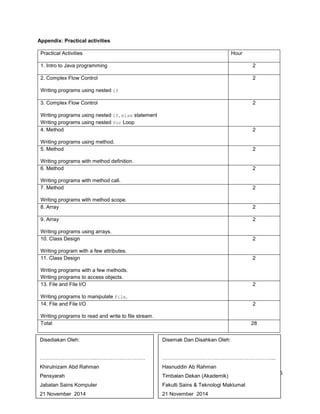
This document outlines the course details for 'Fundamentals of Programming' (DTCP 2023) offered in the 2014/2015 academic year, including course rationale, learning outcomes, assessment methods, and a detailed syllabus. It emphasizes Java programming principles and includes topics such as complex flow control, methods, arrays, and file I/O. The course comprises lectures and practical sessions, totaling 120 student learning hours and yielding 3 credit hours.