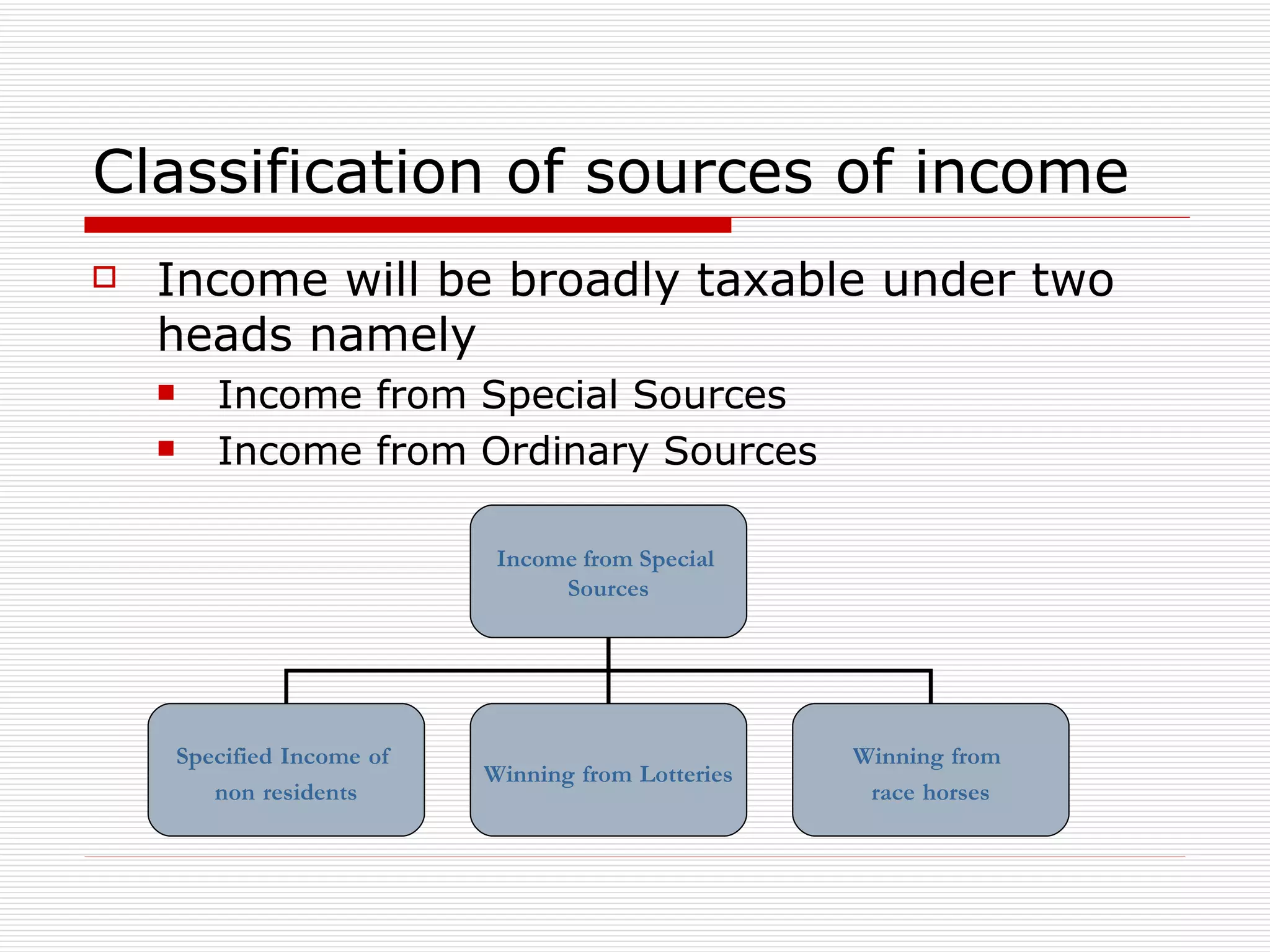
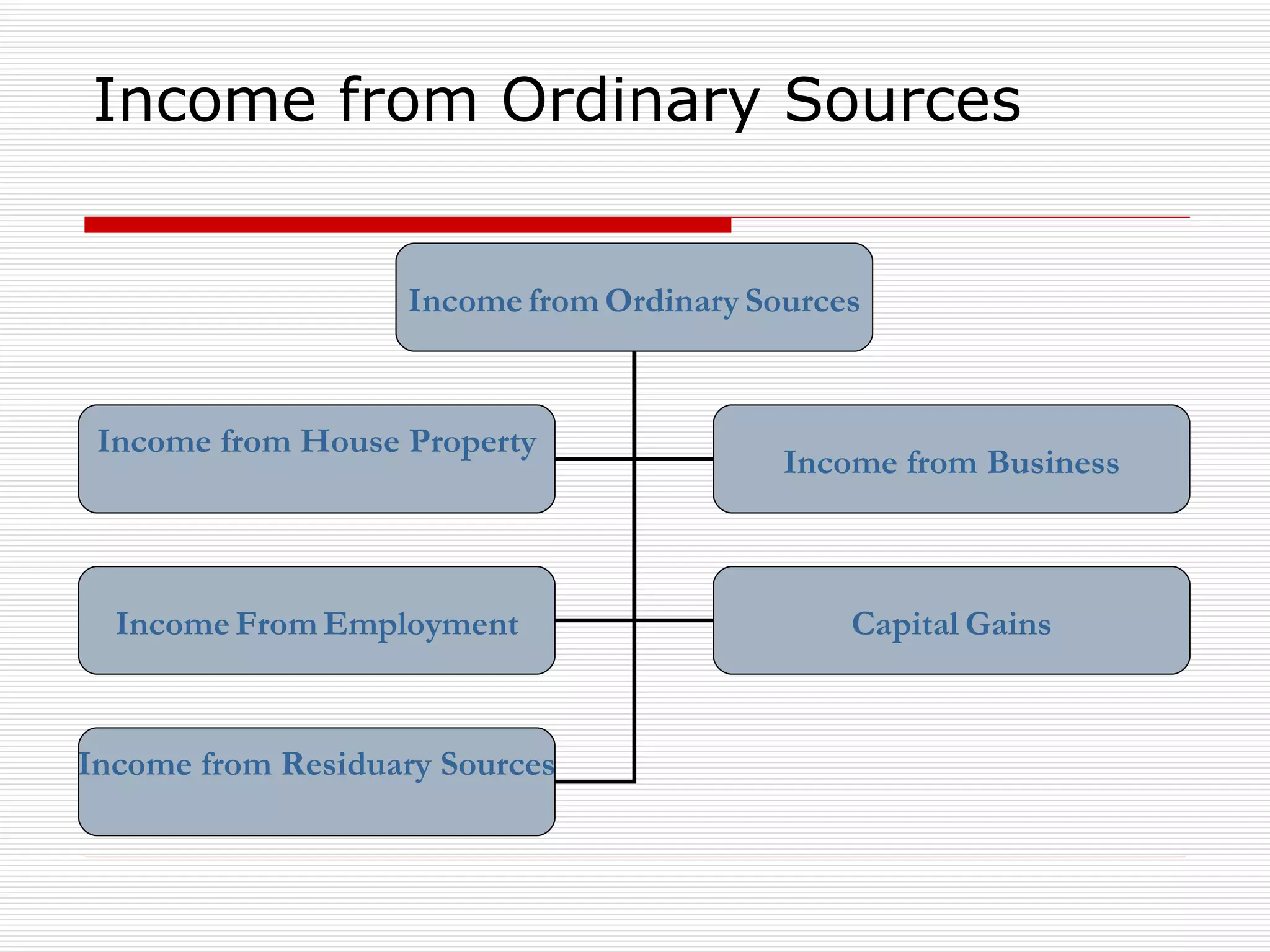
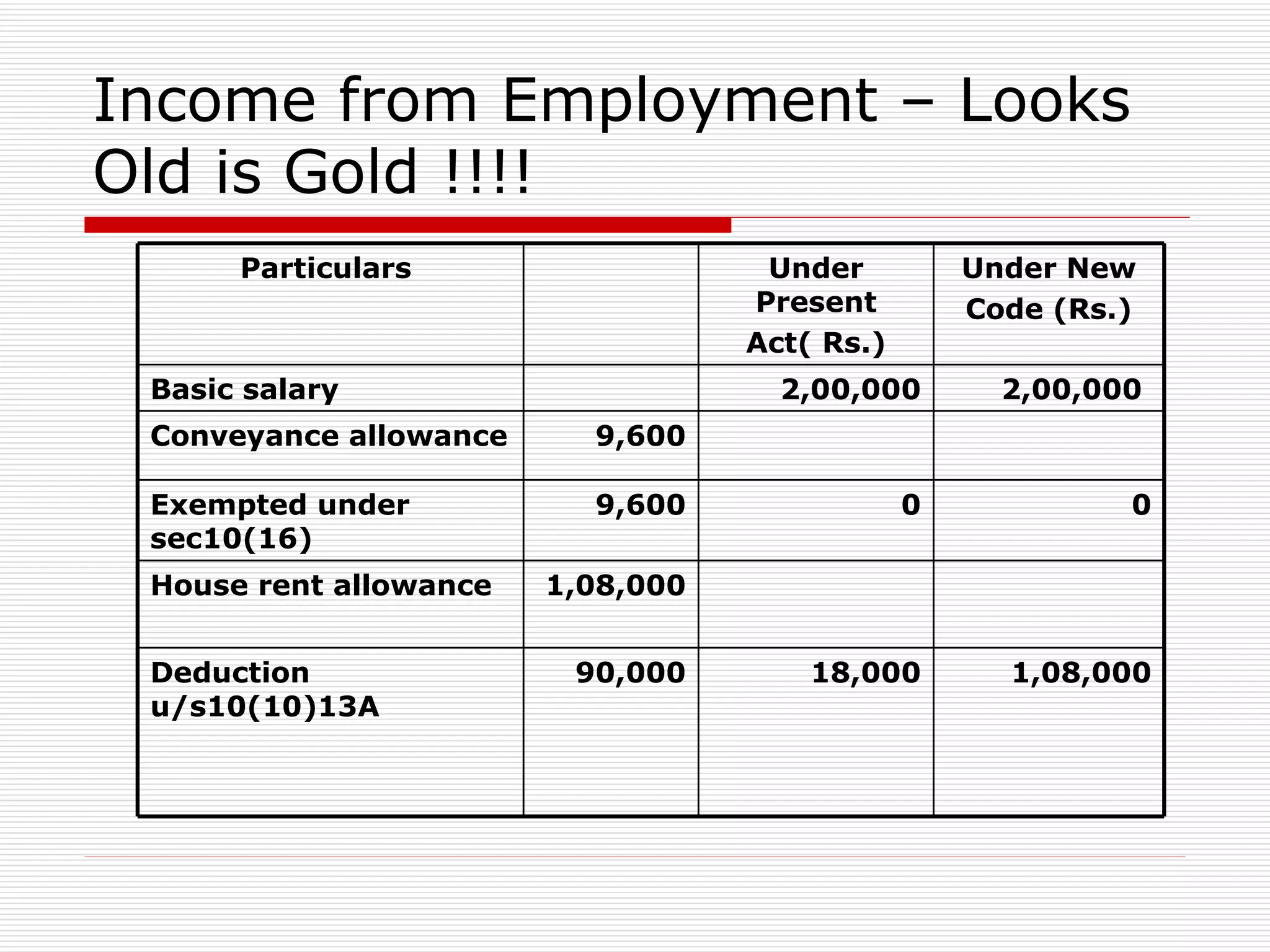
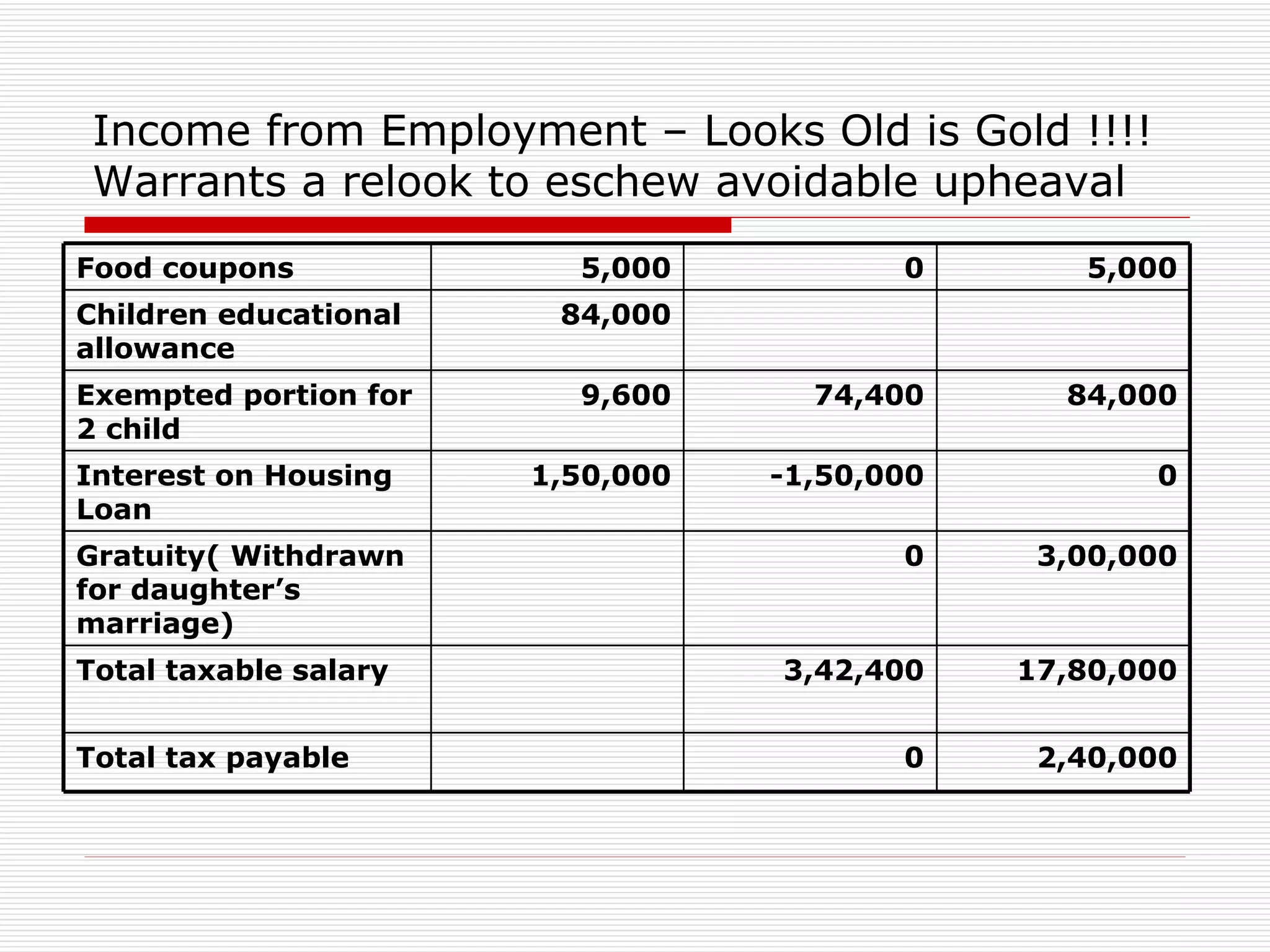
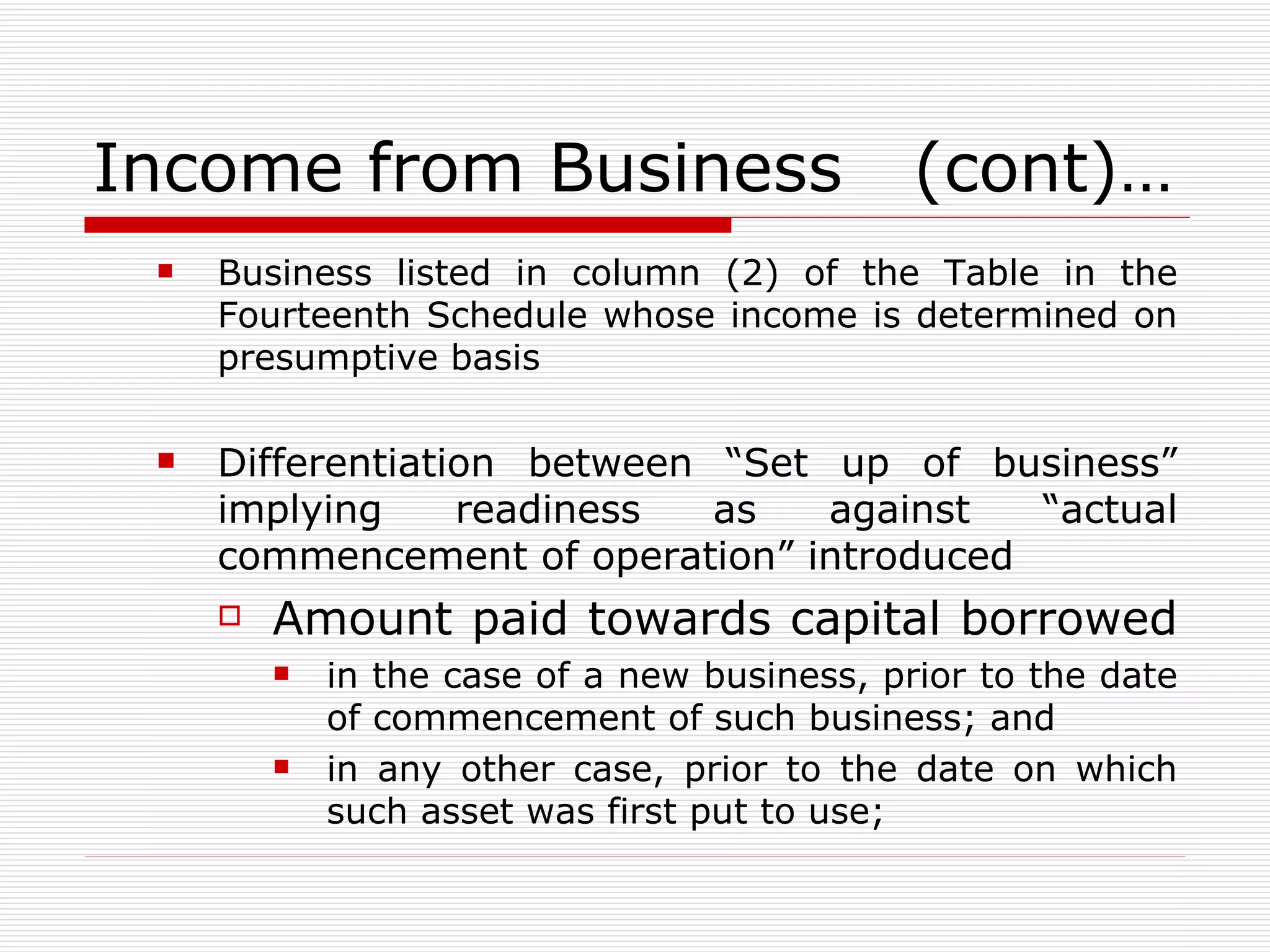
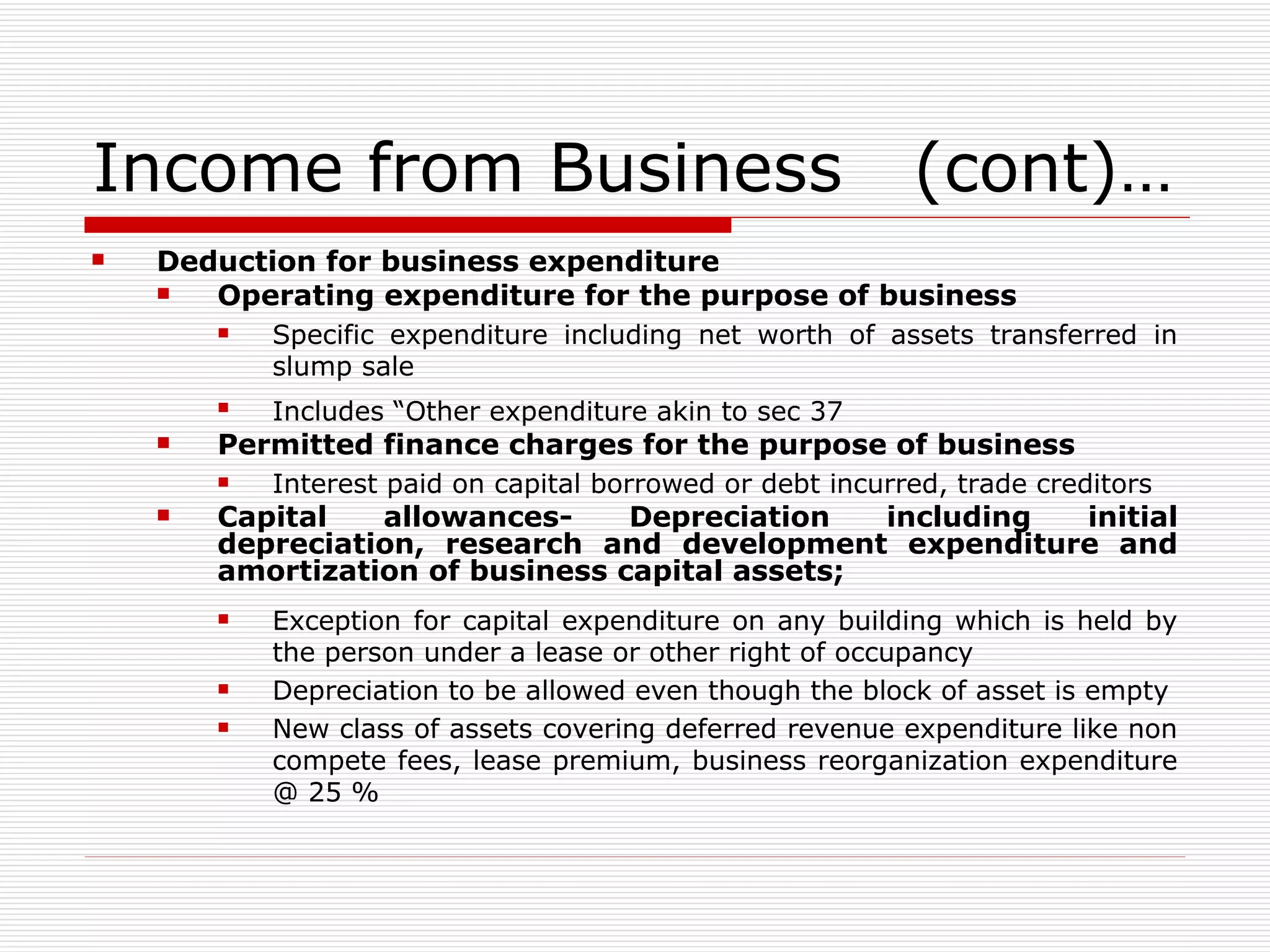
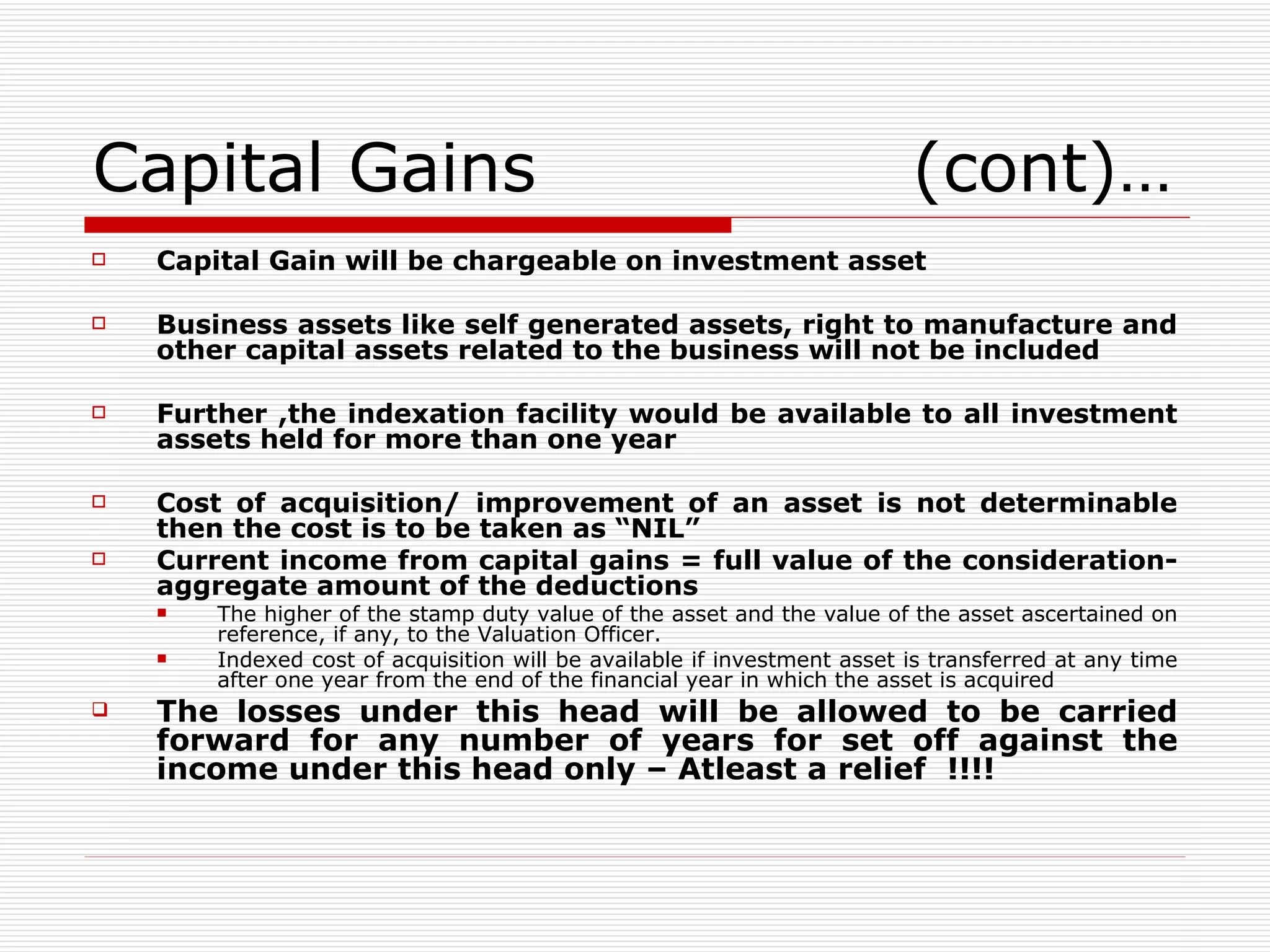
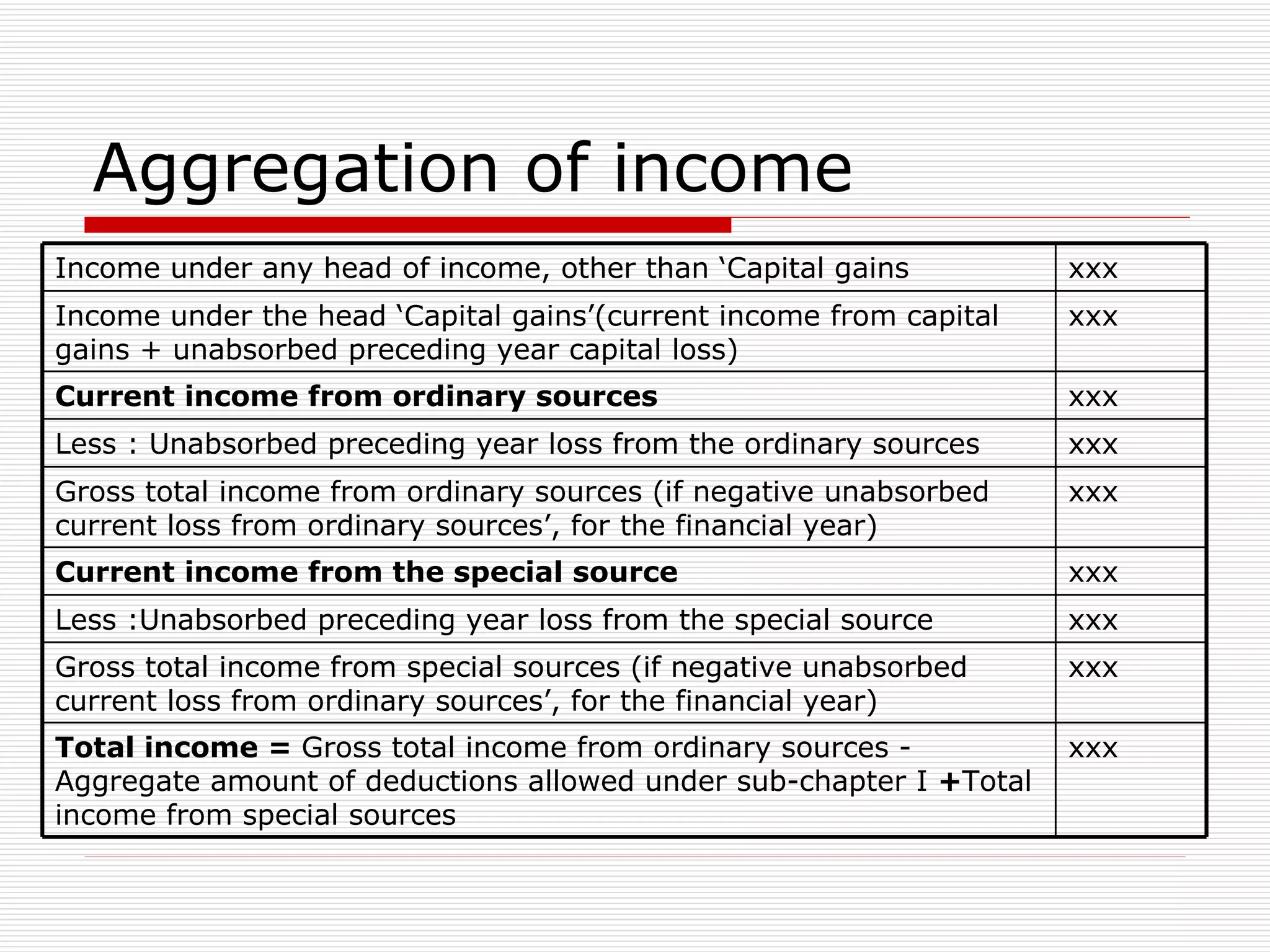
The document provides an overview of key aspects of the Direct Taxes Code Bill, 2009 in India, including rates of tax, definitions, scope of total income, tax deduction at source, and areas of direct tax covered. It discusses the classification of sources of income under the new bill such as income from house property, employment, business, capital gains, and residuary sources. It also covers proposals related to maintenance of accounts, computation of taxable income from various sources, tax incentives, and tax deductions.