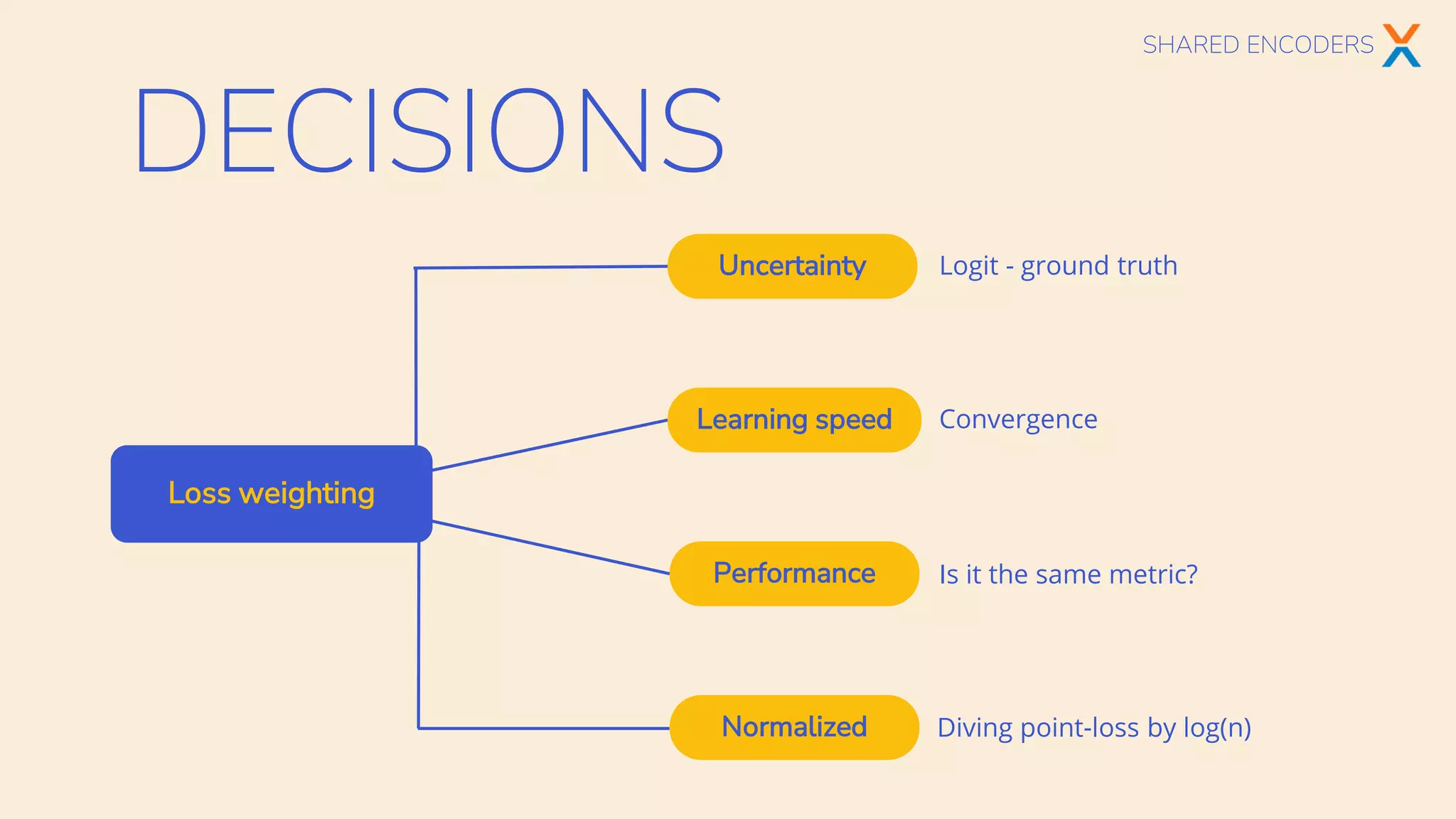
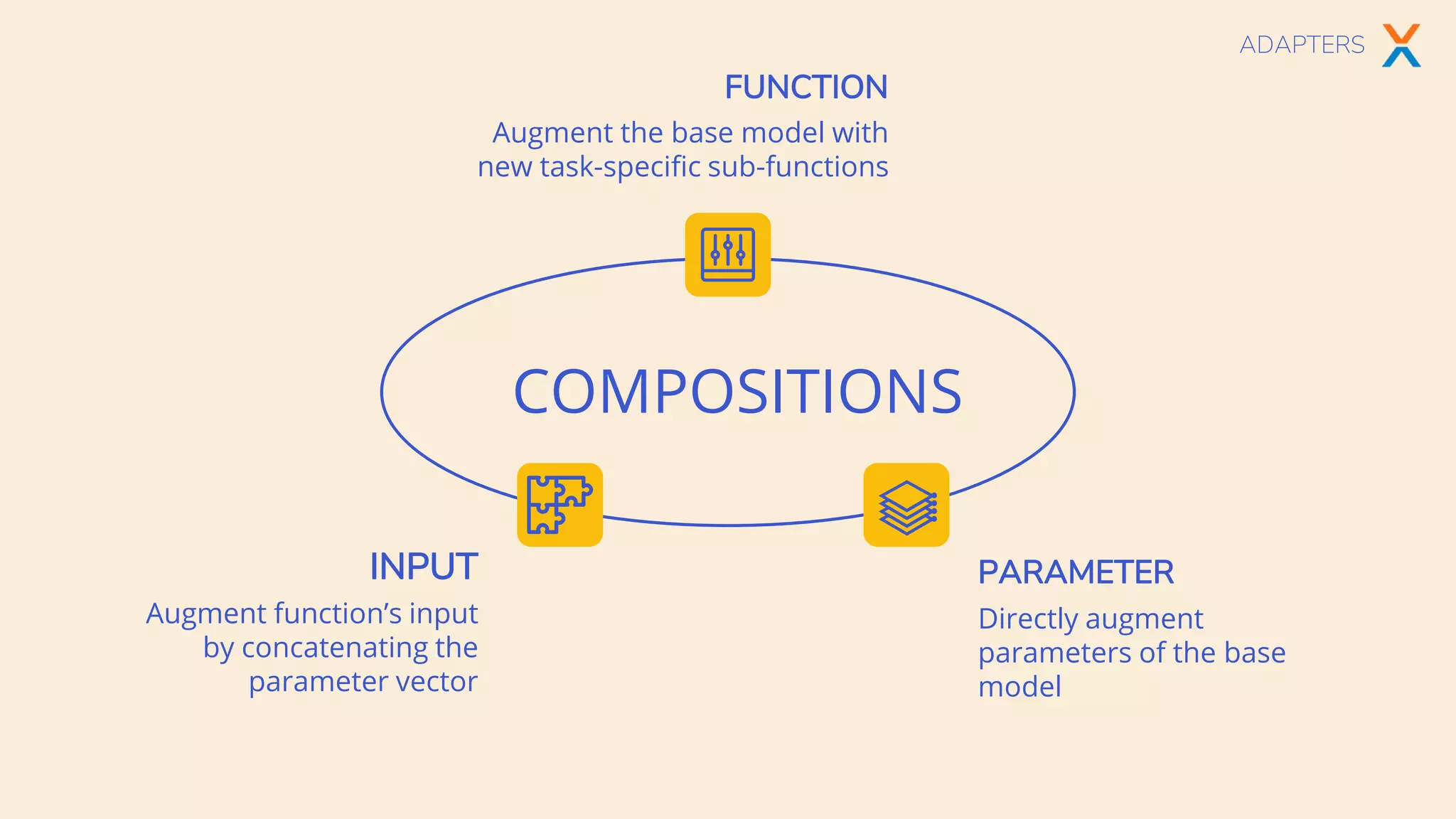
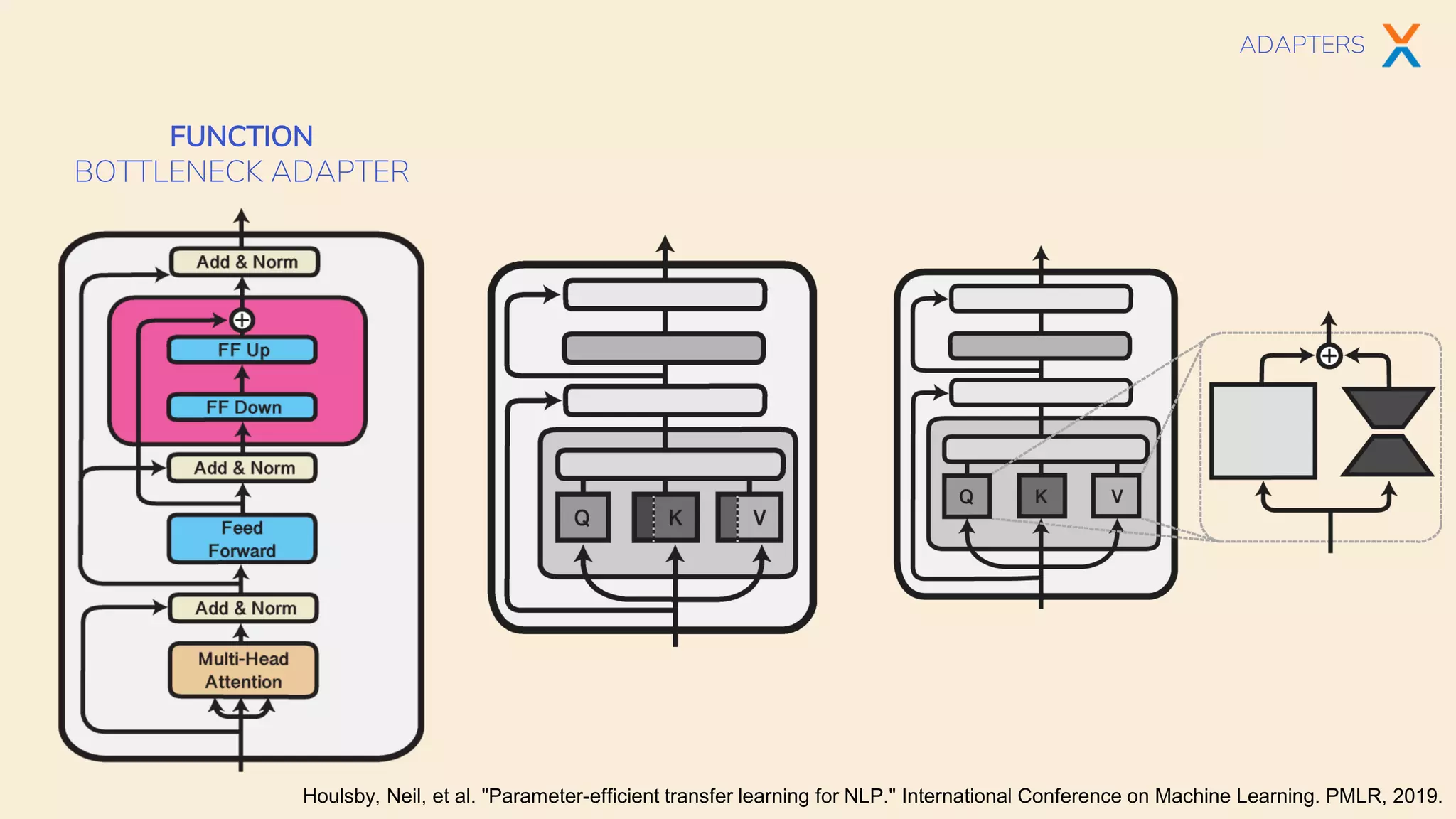
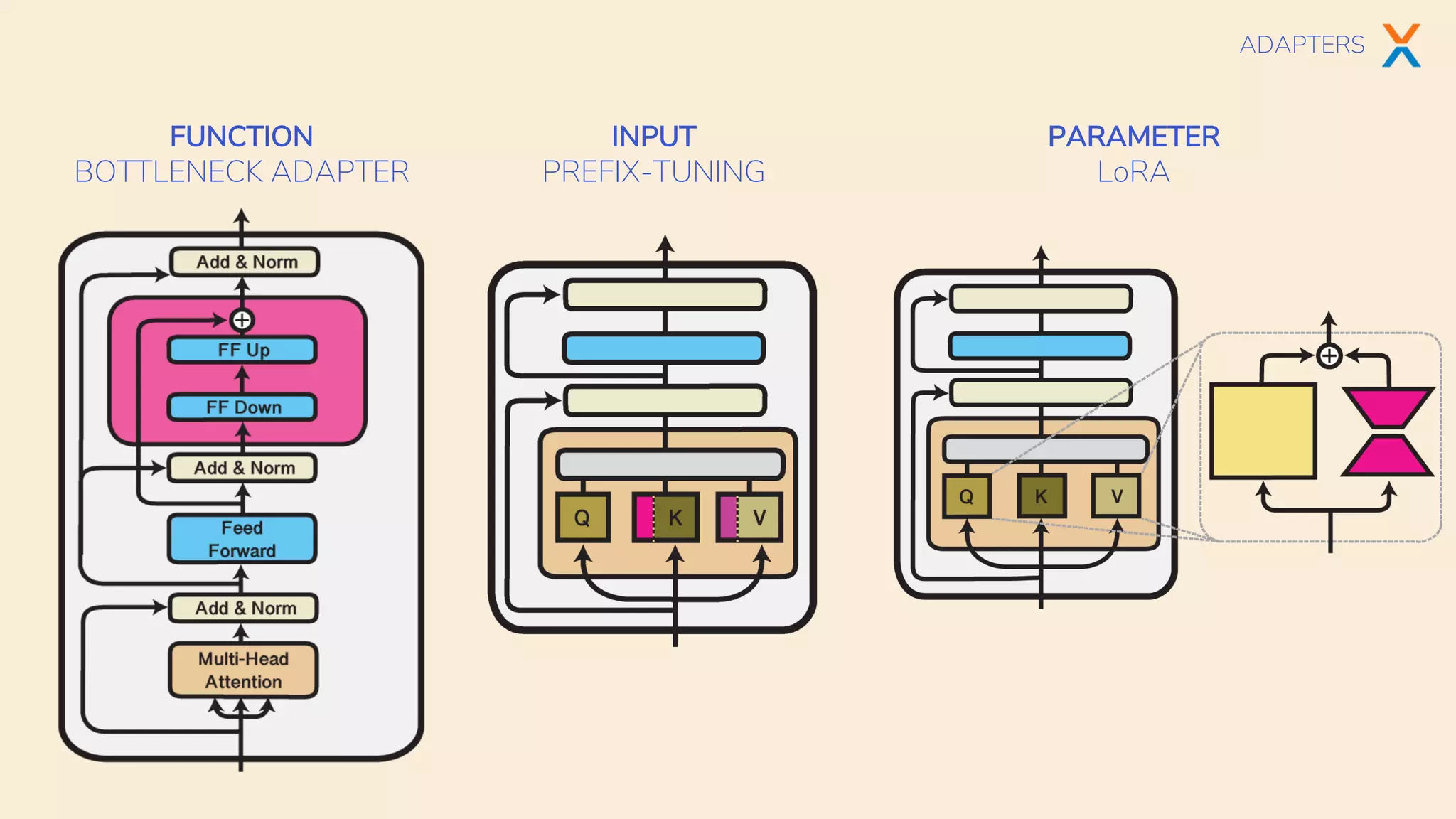
The document discusses multi-task learning in transformer-based architectures for natural language processing, highlighting techniques such as shared encoders, adapters, and hypernetworks. It emphasizes the advantages of these methods in terms of data efficiency, parameter modularity, and performance gains over traditional single-task learning. Various models and their training implications, along with the challenges of aligning datasets and managing gradient directions, are also explored.