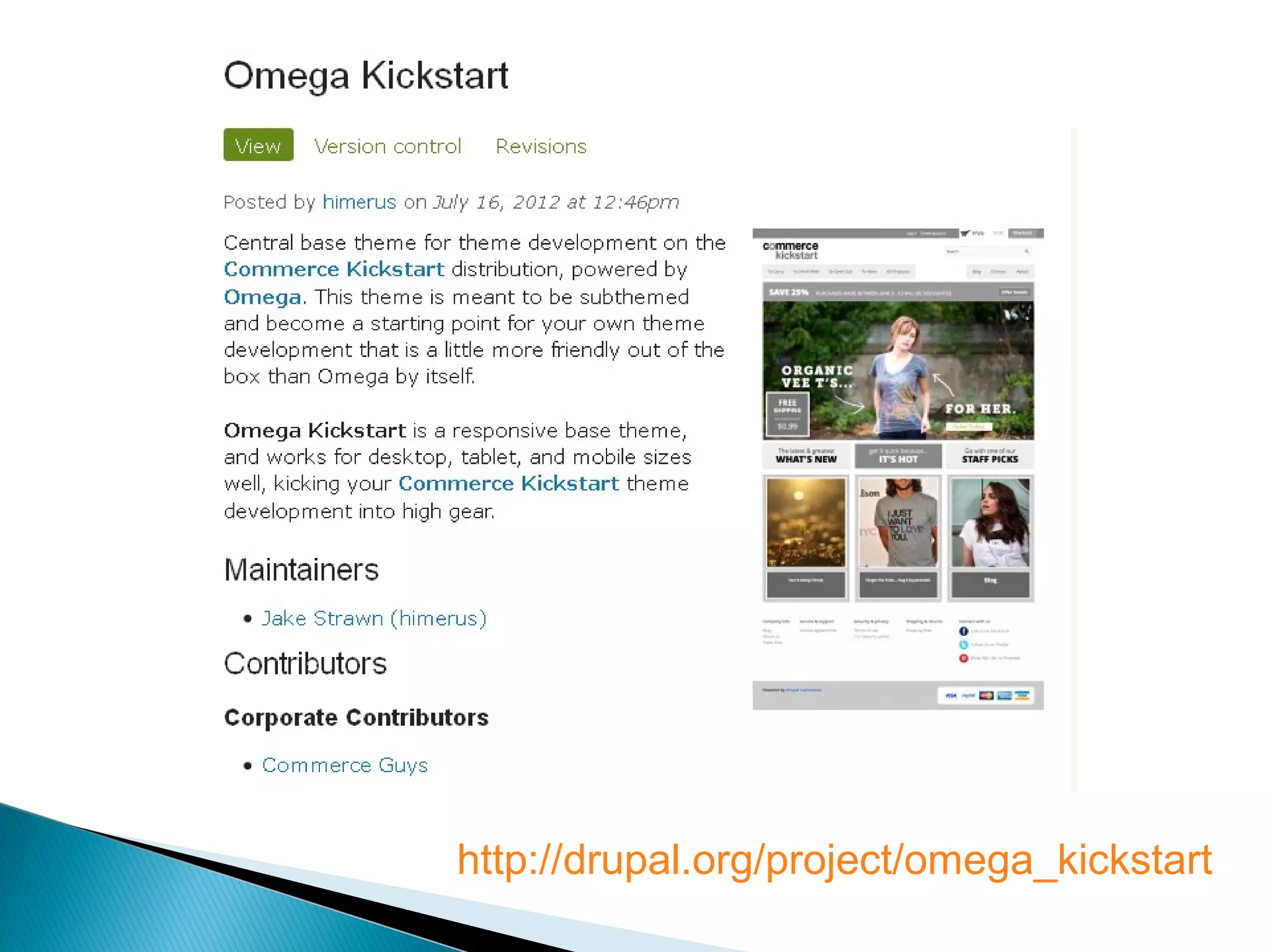
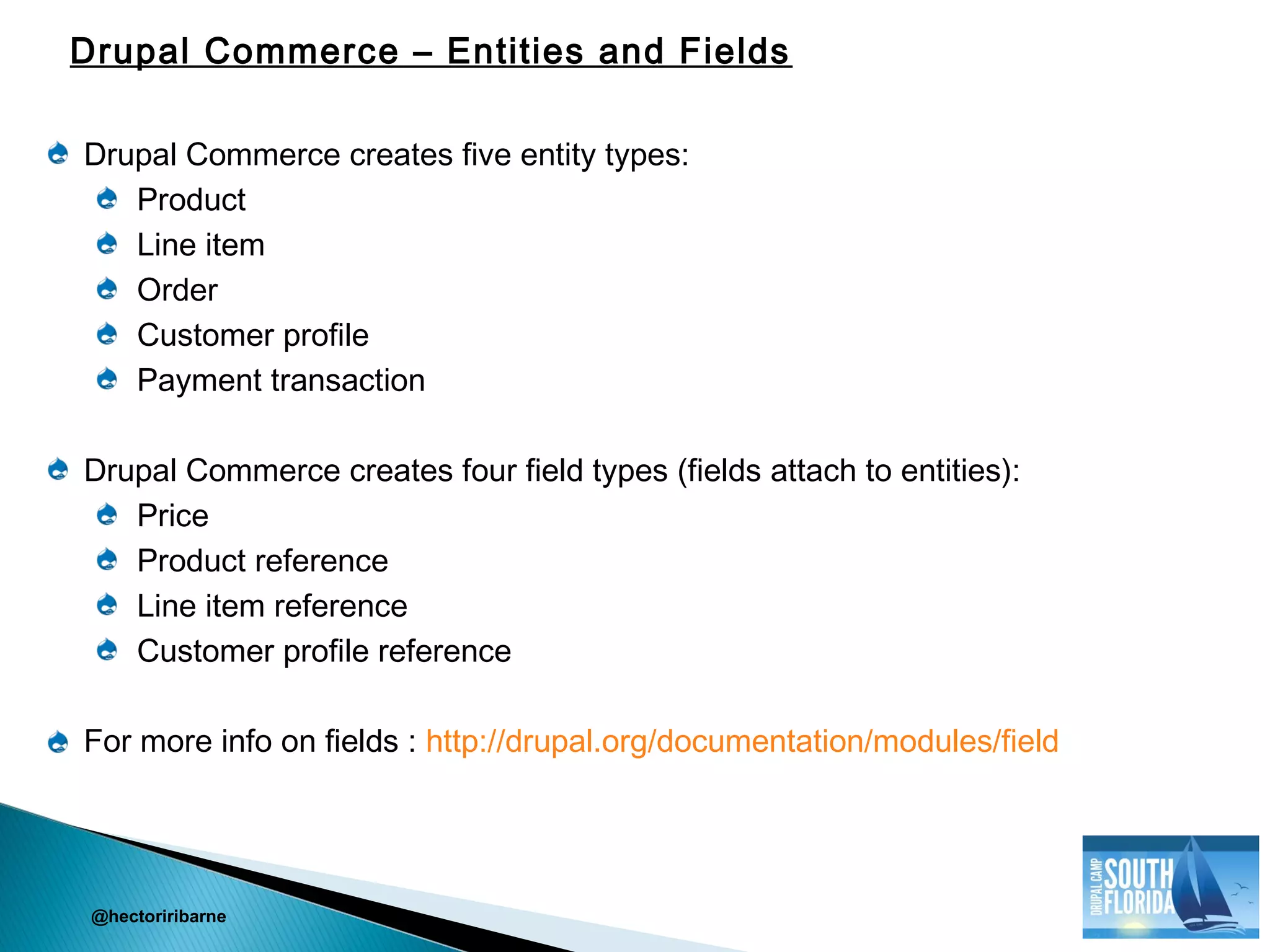
This document provides an introduction to Drupal Commerce, including its dependencies, entities, fields, products, pricing, checkout process, and use of Rules. It recommends getting familiar with the Views and Rules modules prior to using Drupal Commerce. Drupal Commerce is built on Drupal 7 and relies heavily on Entities and Rules. Commerce Kickstart is an installation profile that includes a basic Drupal Commerce site with example store content and configurations.