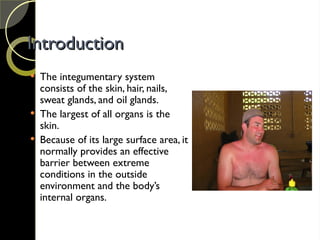
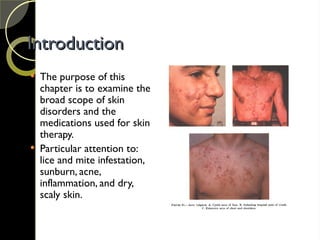
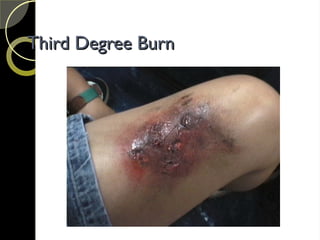
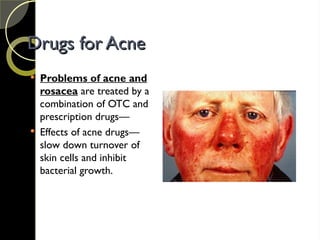
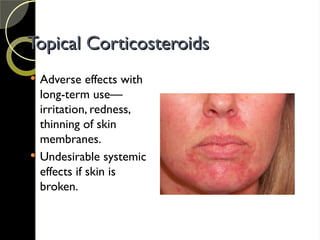
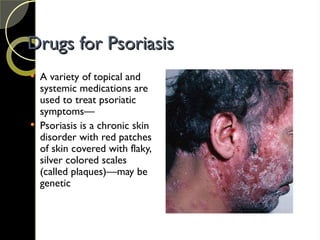
The document discusses the integumentary system and various skin disorders, outlining their causes, symptoms, and classifications. It details treatment options for conditions such as lice, acne, sunburn, dermatitis, and psoriasis, including both over-the-counter and prescription medications. The chapter emphasizes the importance of understanding skin disorders and the therapeutic approaches available to manage them.