This document provides information on drug dosage calculations using measurements and conversions. It includes:
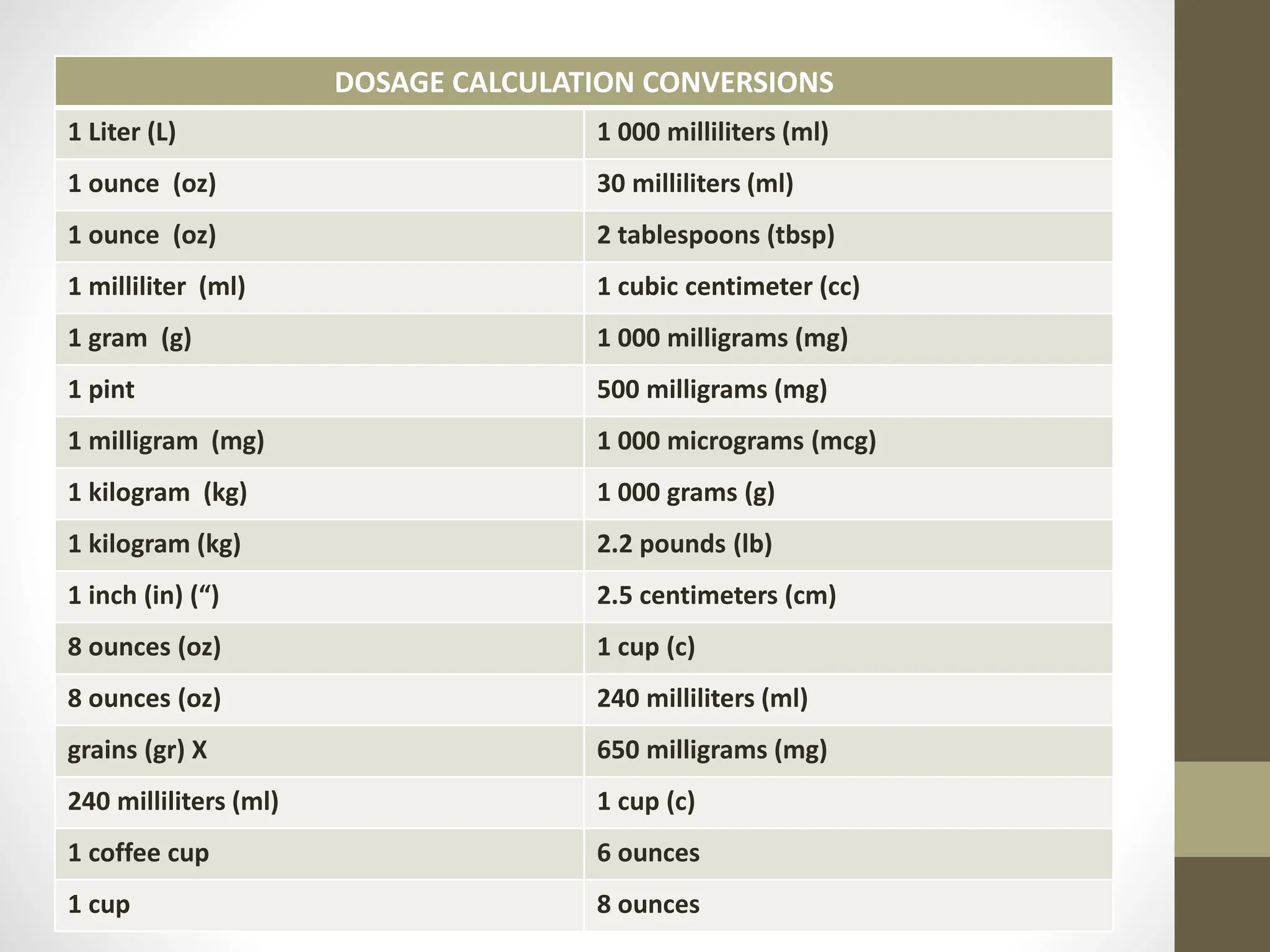
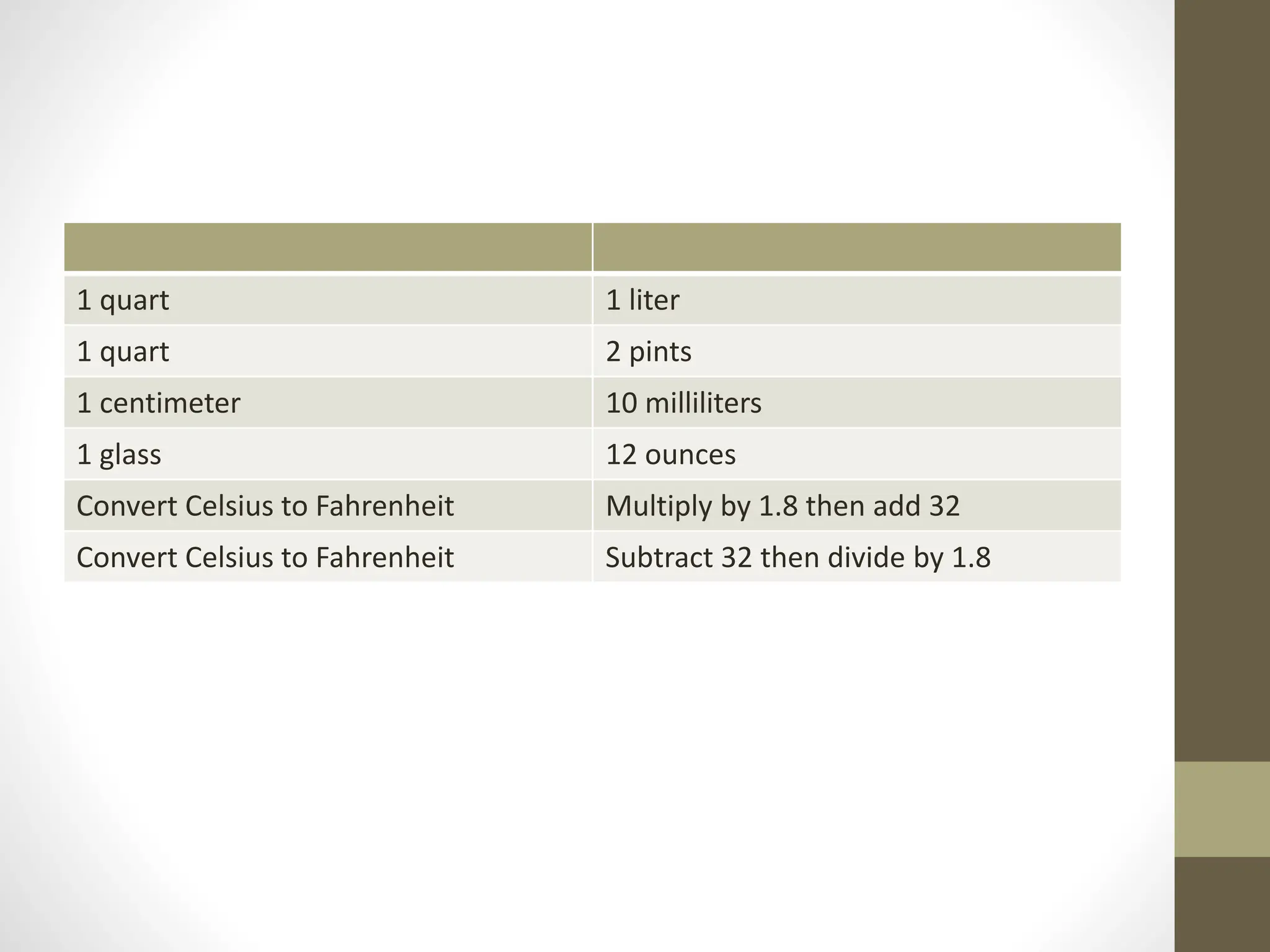
1) Common measurement conversions between units like liters, milliliters, ounces, and grams.
2) A formula for calculating drug dosage: Desired Dose x Volume on Hand/Concentration = amount to be given.
3) An example dosage calculation using this formula to determine the volume of morphine to administer based on the ordered dose and available concentration.
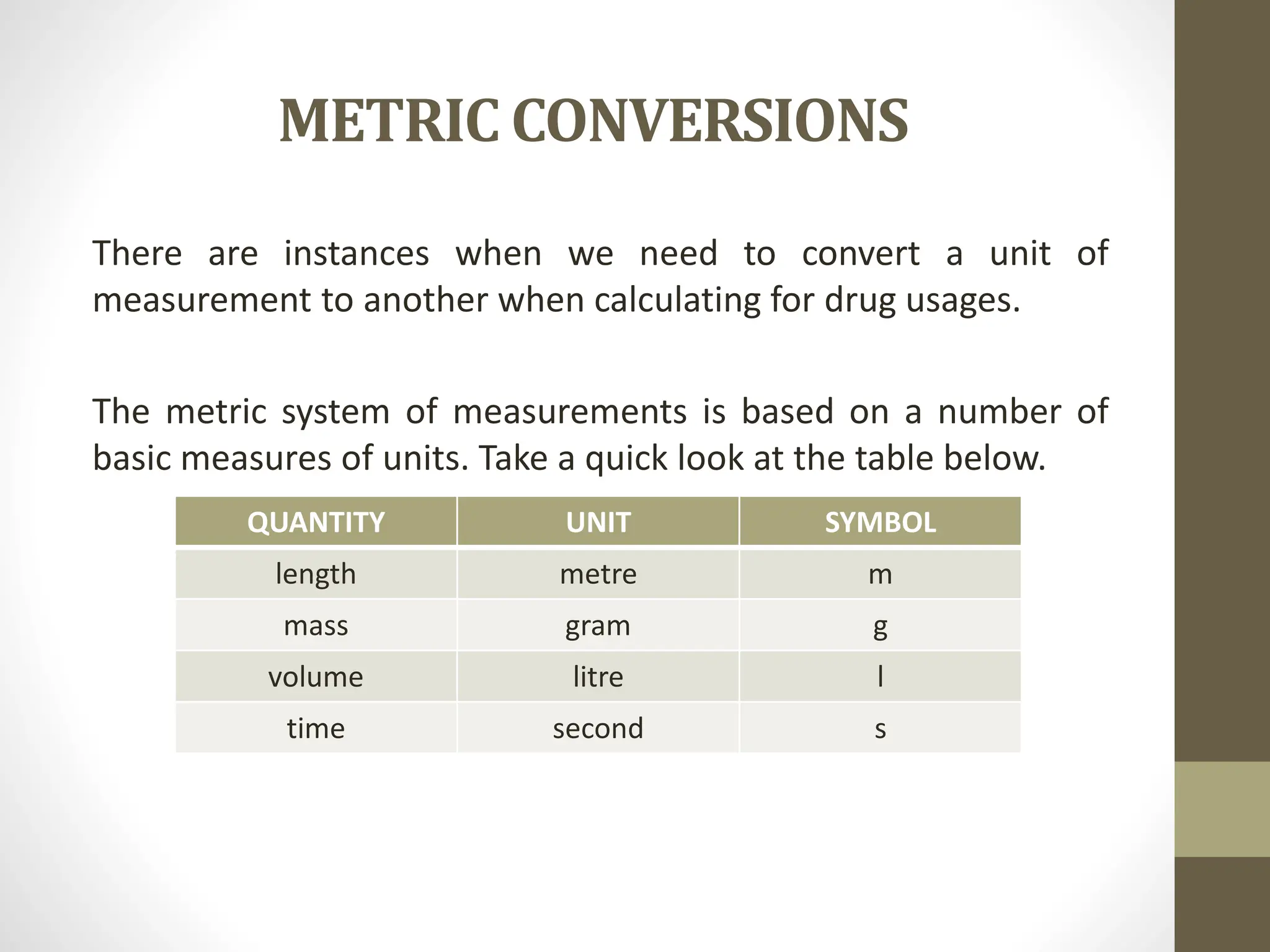
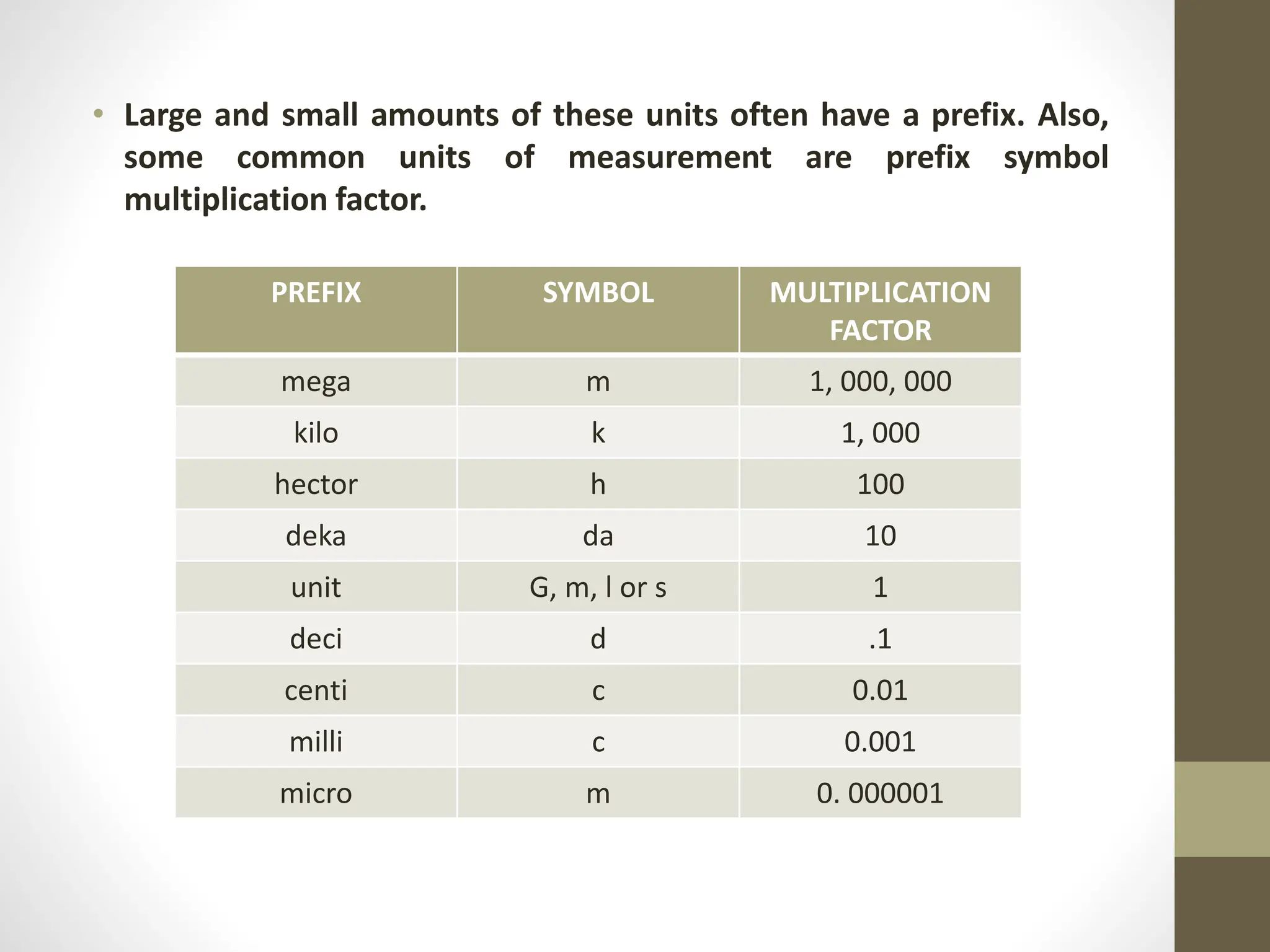
4) Information on metric conversions between units like kilograms, grams, milligrams, and micrograms using prefixes and moving the decimal place.