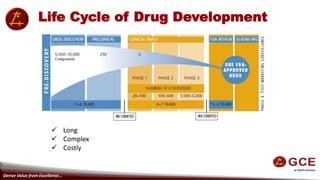
The document outlines the multi-step process of drug development from pre-discovery through clinical trials and regulatory approval. It begins with basic research to understand disease mechanisms, followed by drug discovery and pre-clinical testing in animals. If pre-clinical data is promising, an IND application is submitted for human trials. Phase 1-3 clinical trials progressively involve more patients to test safety, efficacy, and long-term effects. With positive results, an NDA is submitted for regulatory review. If approved, phase 4 trials monitor drug use in broader populations. The process takes 10-15 years and over $800 million on average to bring a new drug to market.