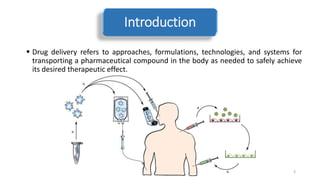
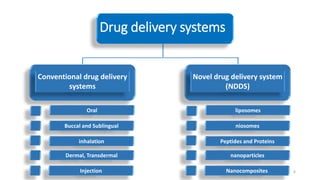
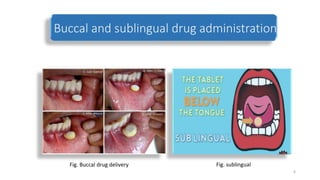
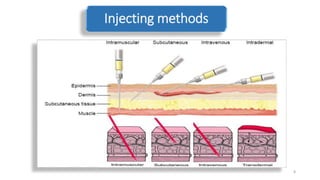
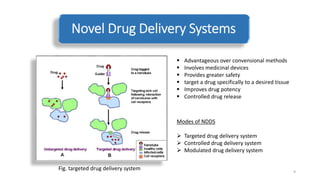
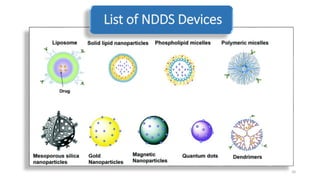
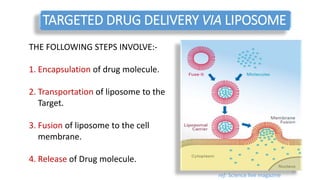
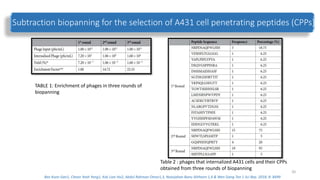
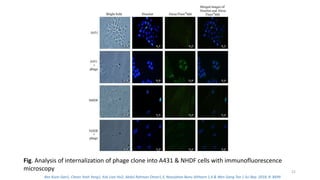
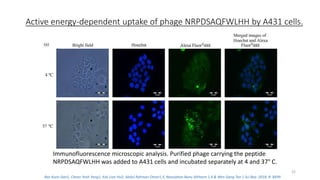
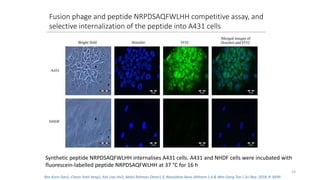
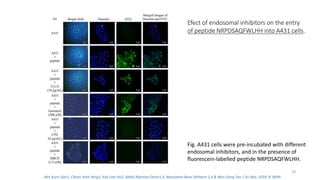
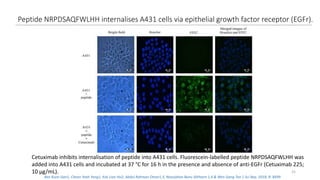
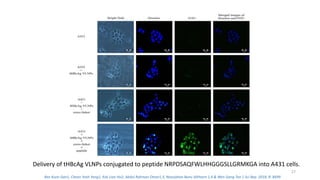
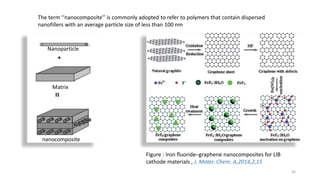
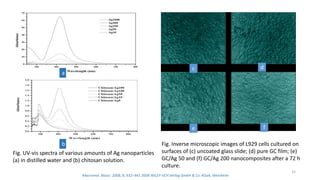
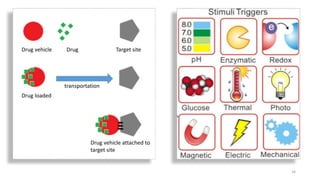
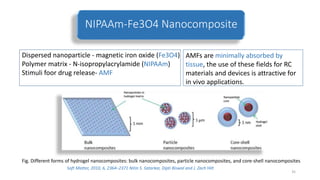
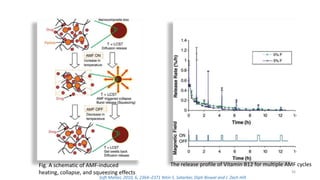
The document discusses various drug delivery methods including conventional methods like oral, injection, and transdermal delivery as well as novel methods like liposomes, peptides, nanoparticles, and nanocomposites. Liposomes are described as tiny bubbles enclosed by a phospholipid bilayer that can encapsulate drug molecules and target delivery to specific tissues. Peptide drug delivery uses short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds to deliver drugs. Nanocomposites embed nano-sized particles in a polymer matrix, exhibiting enhanced properties while reducing cytotoxicity. Novel drug delivery provides benefits over conventional methods like reduced side effects, targeted delivery, and controlled release of drugs.