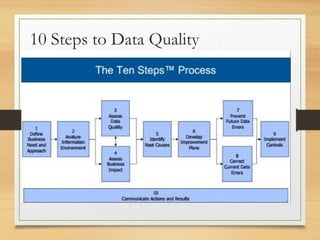
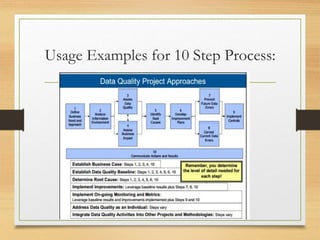
This document summarizes a book review presentation on Danette McGilvray's book "Executing Data Quality Projects". The presentation covers the book's introduction and stated purpose of providing a systematic approach for improving data quality. It also summarizes the book's methodology, key concepts, and 10 step framework for data quality projects. Finally, the presentation discusses usage examples and potential next steps for the organization's data quality program and priority projects.