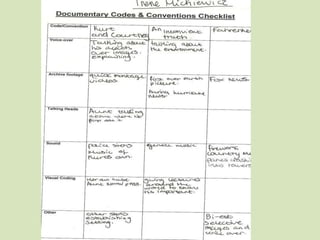
A documentary is a non-fictional film that presents a narrative about real people, events or issues. It uses various cinematic techniques to communicate meaning and persuade viewers. Some key conventions include:
1) Exposition at the beginning introduces the main themes. Dramatic footage is used to engage viewers and position them to believe the documentary's perspective.
2) Voiceovers allow filmmakers to directly comment and provide context.
3) Interviews give a sense of realism by allowing subjects to speak about events. They validate the filmmaker's views.
4) Archival footage, titles, reconstructions, and visual codes like location and attire also shape the narrative.