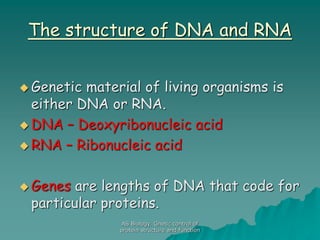
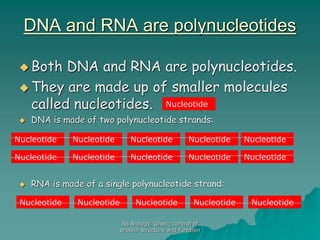
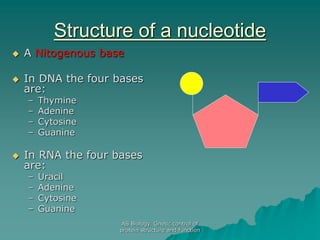
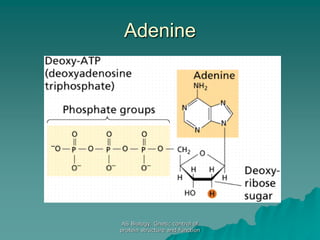
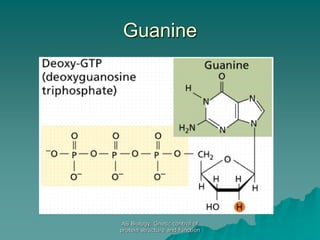
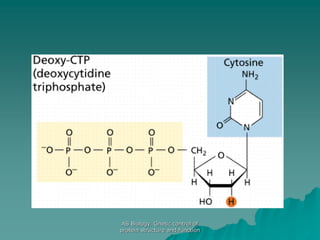
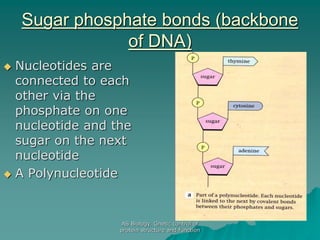
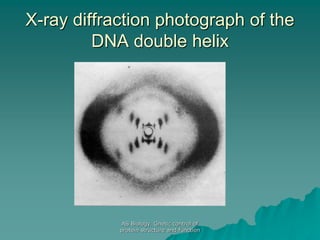
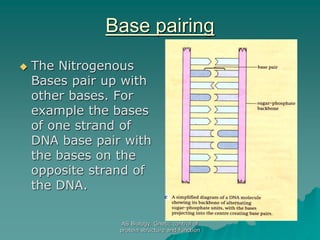
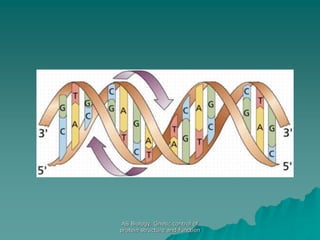
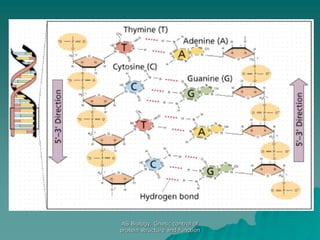
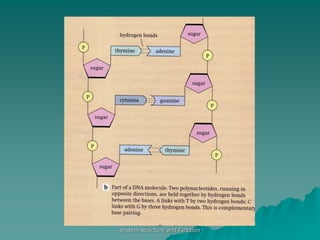
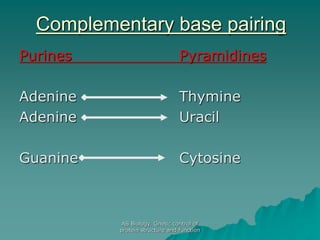
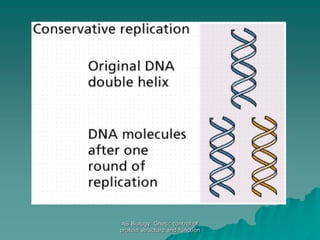
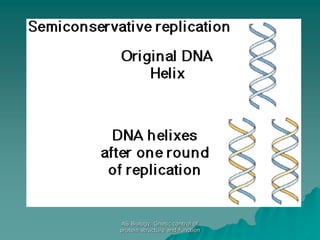
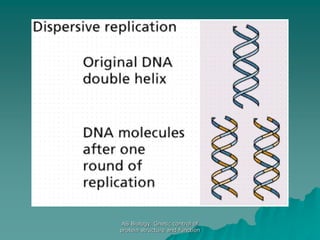
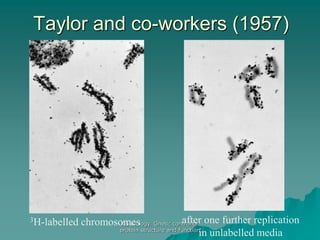
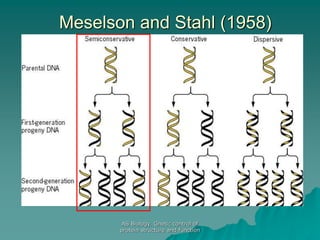
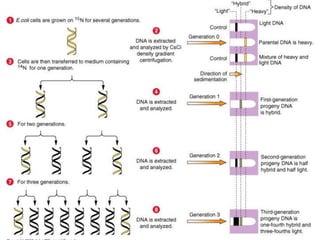
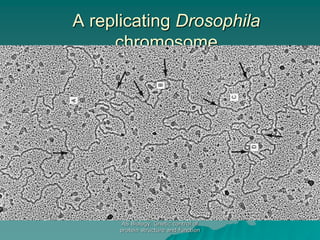
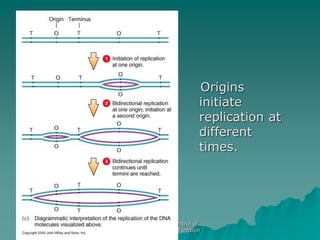
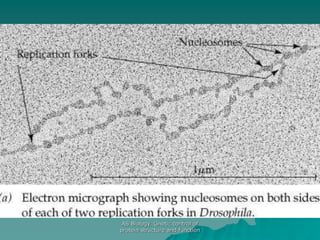
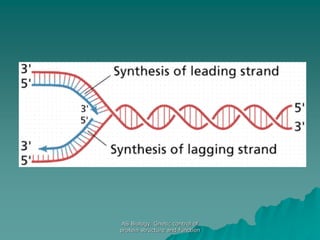
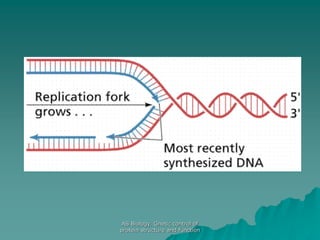
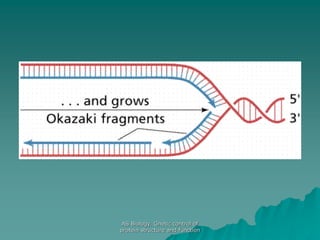
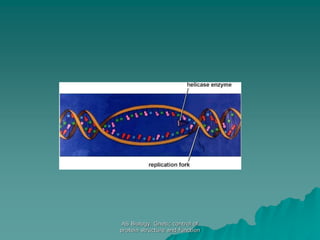
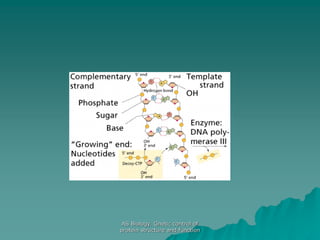
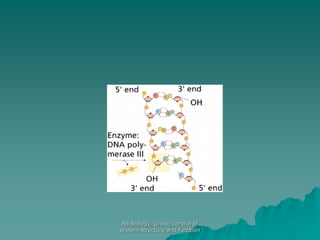
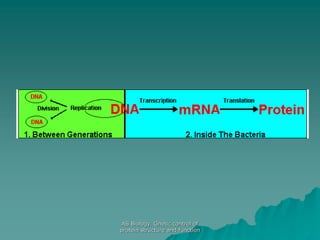
The document discusses the genetic control of protein structure and function. It describes how DNA and RNA are made up of nucleotides containing phosphate, sugar, and nitrogenous base groups. DNA exists as two polynucleotide strands held together by complementary base pairing between adenine and thymine or cytosine and guanine. Genes located on DNA code for specific proteins. The structure of DNA was discovered by Watson and Crick in 1953 using X-ray crystallography which showed the double helix structure. DNA replicates semi-conservatively as demonstrated by Meselson-Stahl experiments. Genetic information is passed accurately from parent to offspring cells during replication.