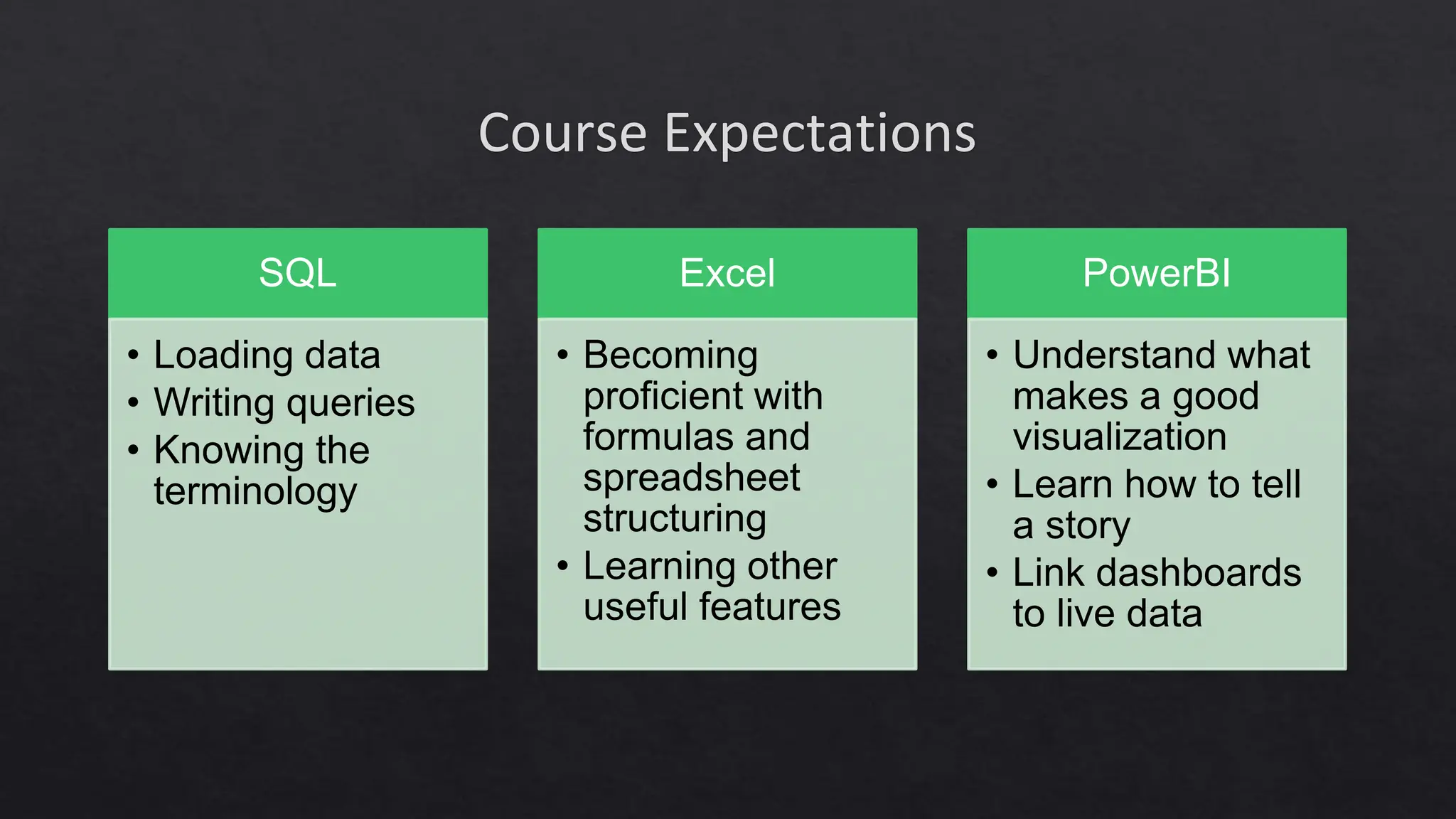
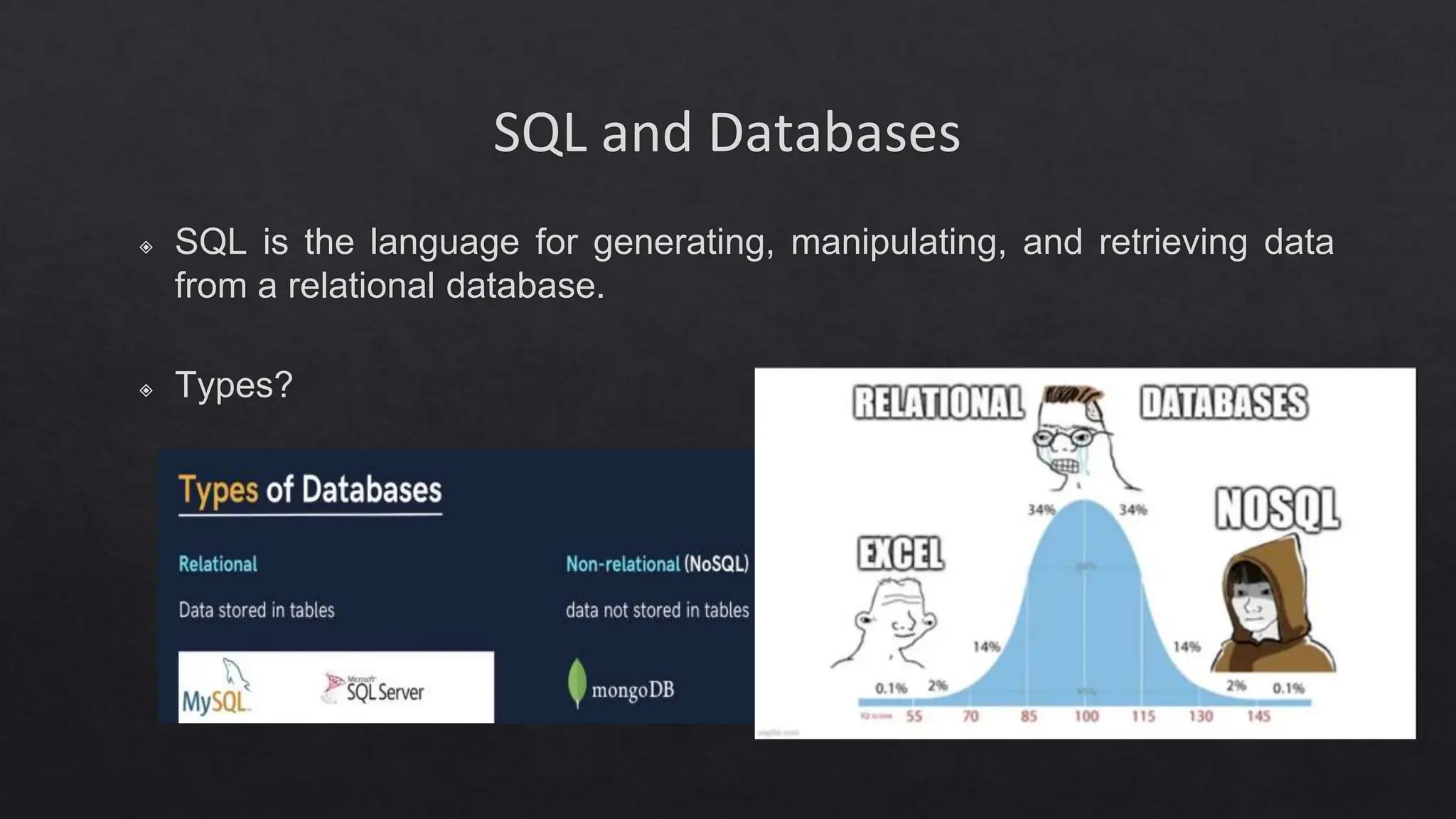
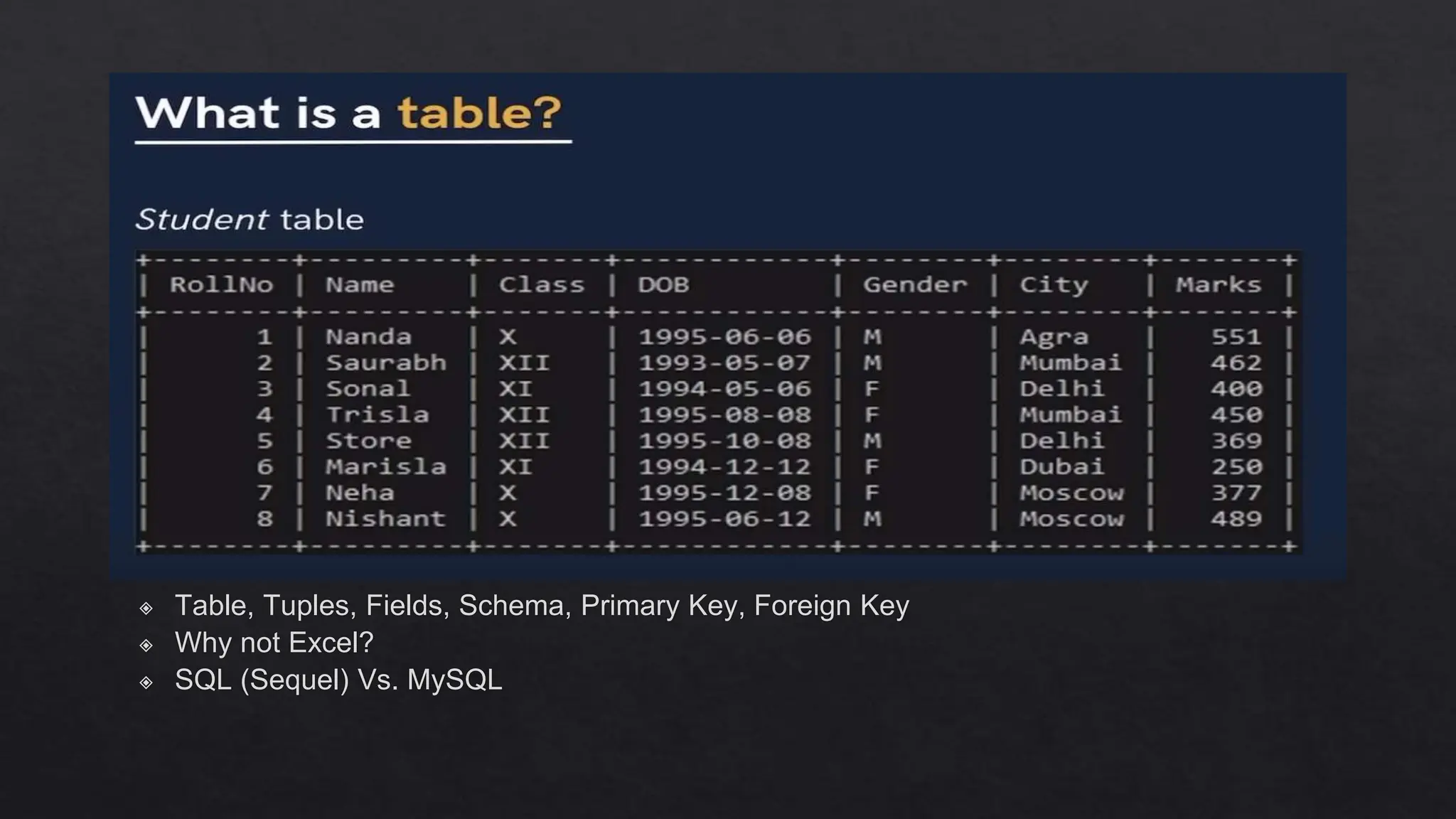
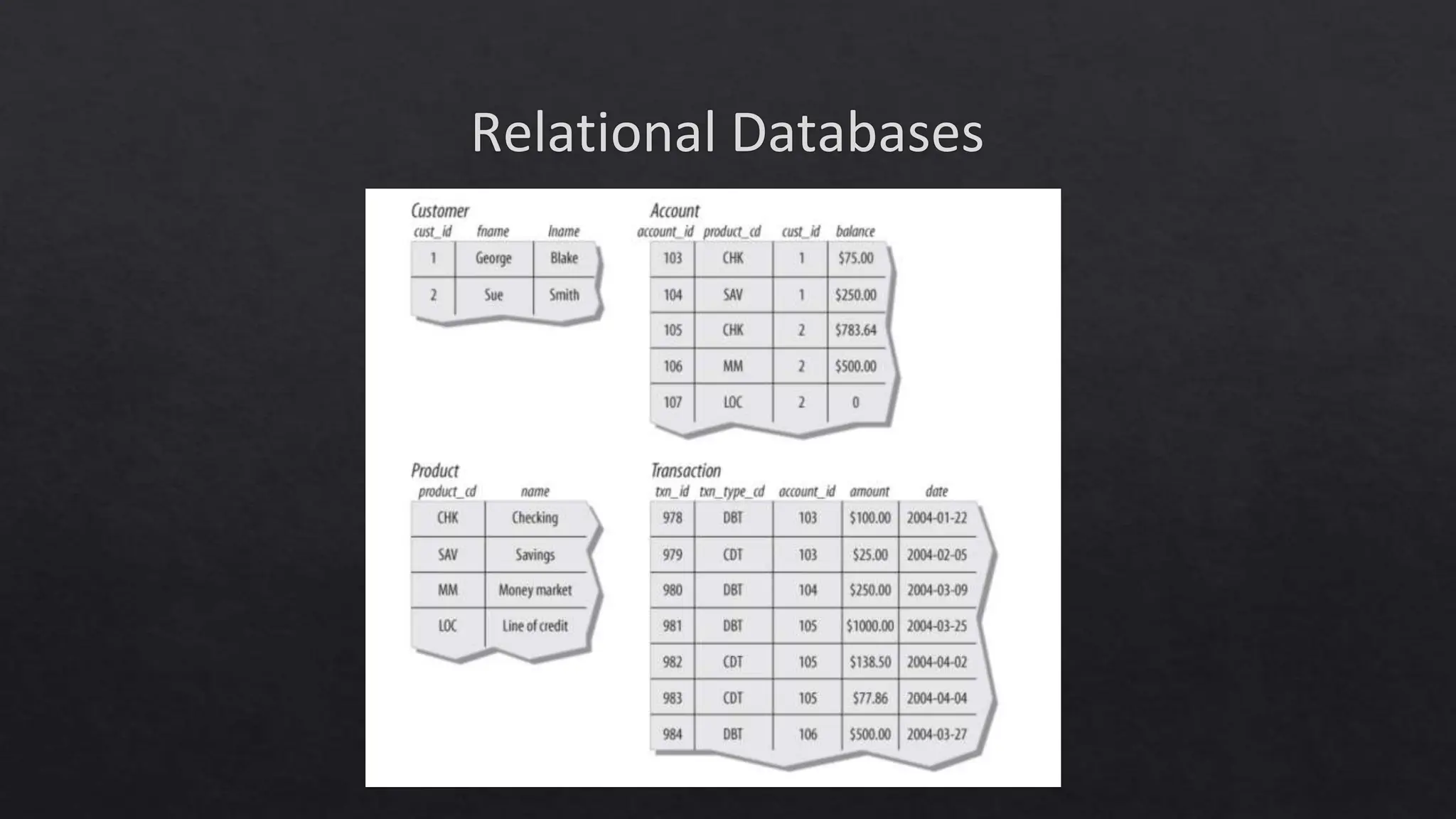
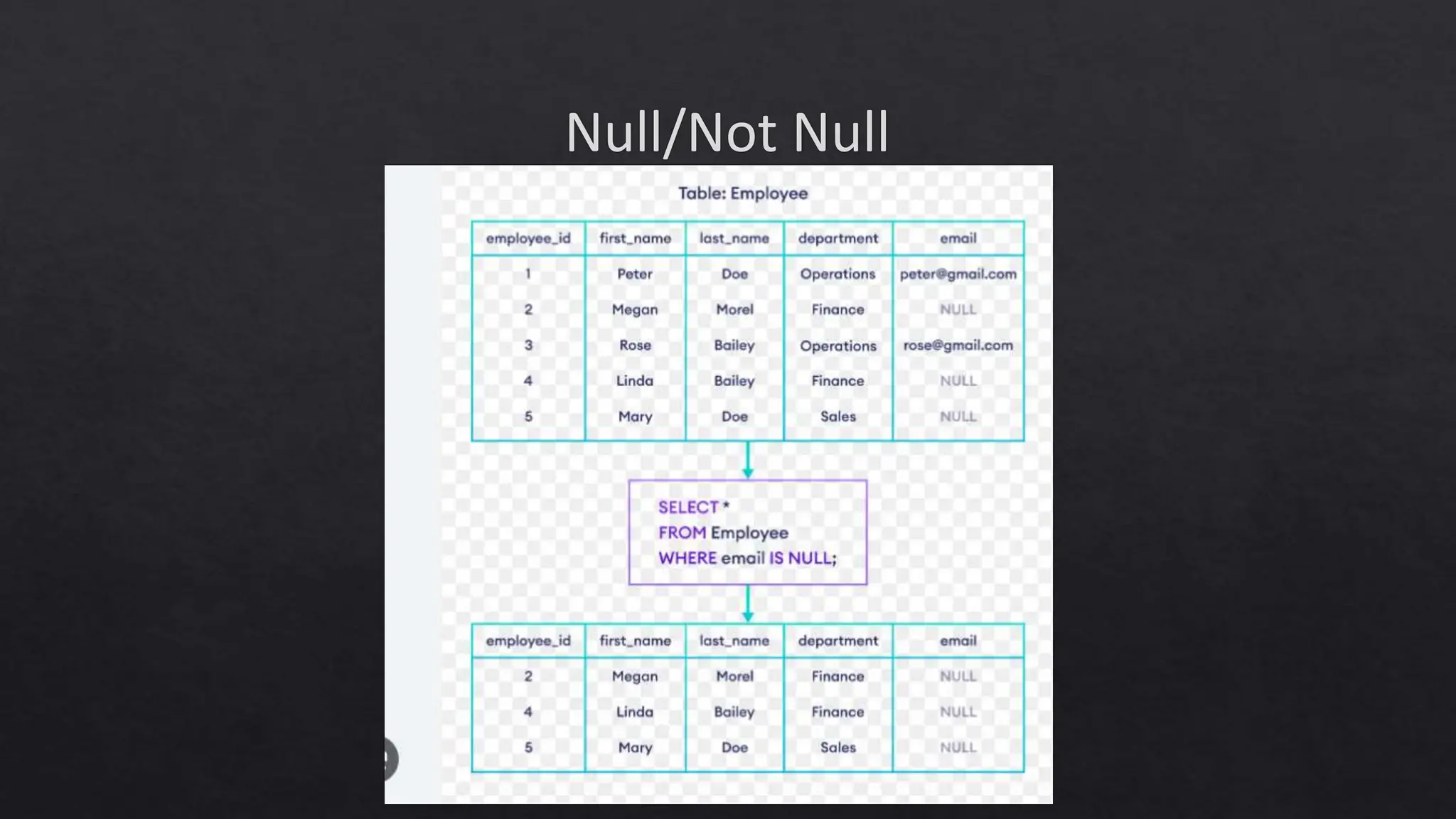
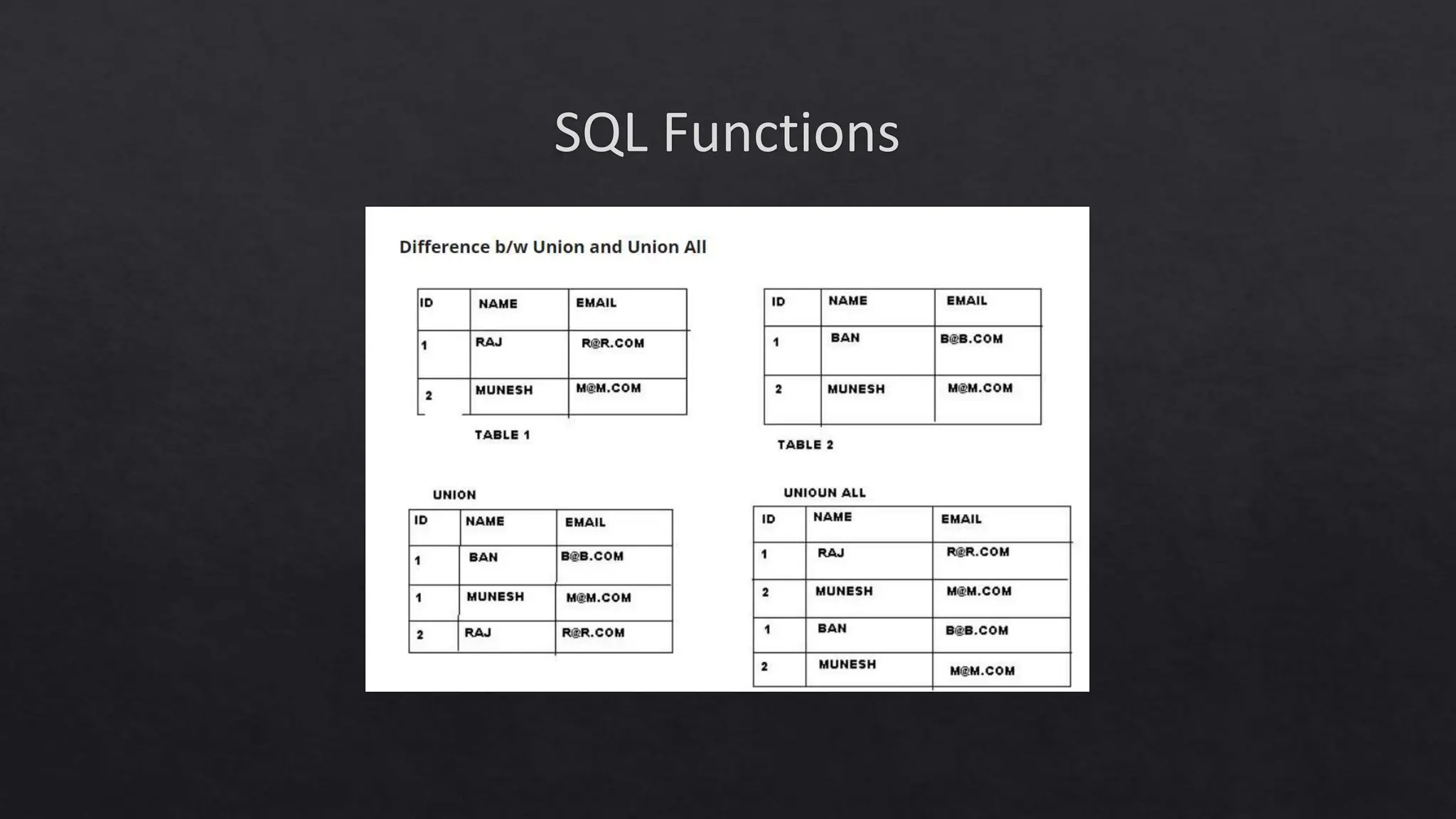
This document outlines the course expectations for a SQL lecture series, covering topics such as SQL basics, data manipulation, and database management. It mentions the importance of understanding various database structures, commands, and SQL functions in practical applications. The lecture series will progressively address advanced concepts including relational databases, data types, and SQL functions like window functions and date operations.












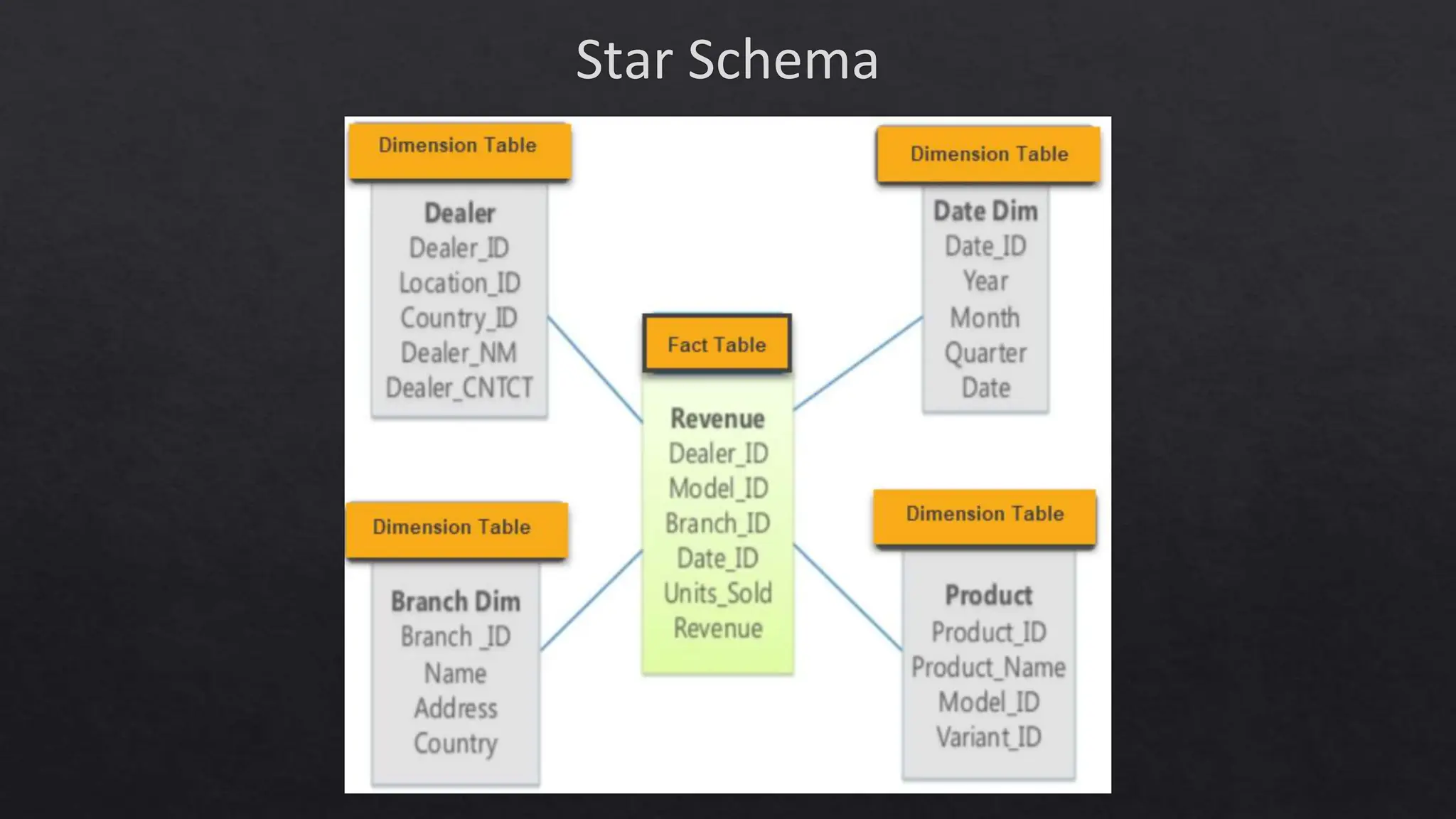
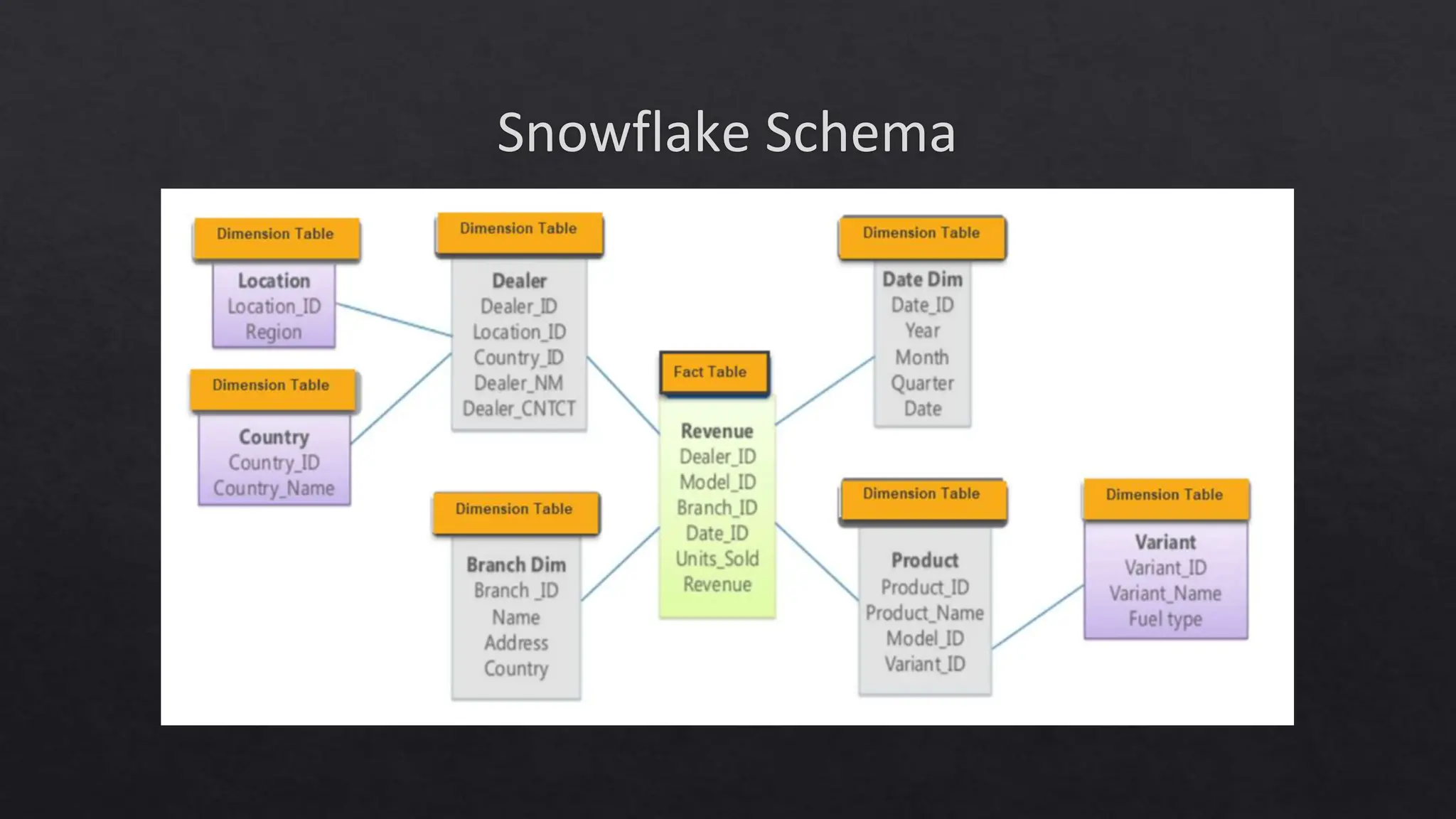
![Topics to Cover in Lecture 2
◈ Text vs Numbers
◈ Comments in SQL: #, --, /*
◈ Not equal to sign
◈ Between command
◈ '[acs]%’ '[!acs]%’
◈ '[a-f]%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dmv-alllecturessql-240607073149-a8db1b5f/75/DMV-All-Lectures-SQL-pptxpComplete-SQL-24-2048.jpg)



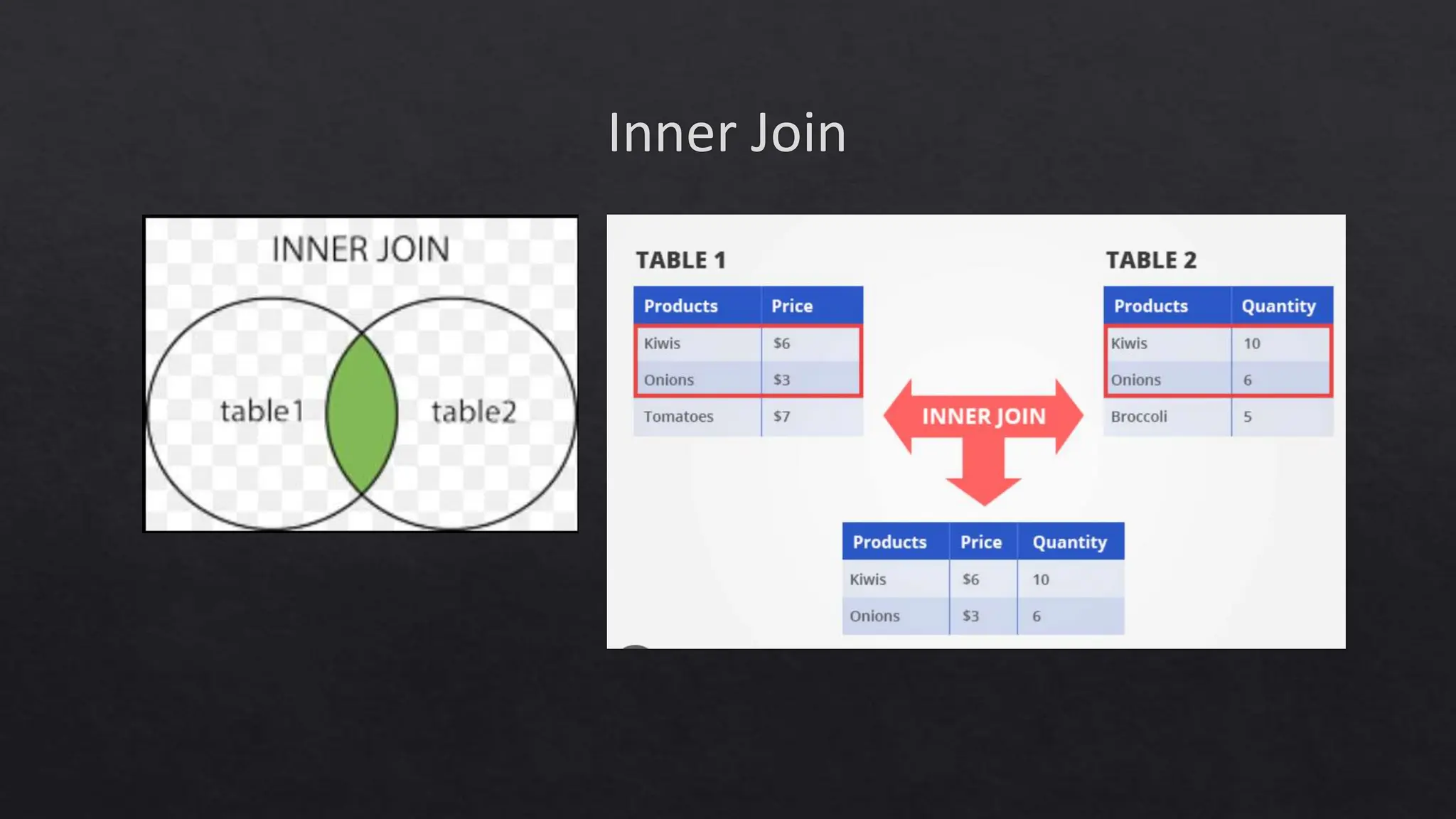



![SQL Functions
◈ TRIM([characters FROM ]string): removes leading spaces or the characters you specify. LTRIM, RTRIM.
◈ Window Functions:
◈ Over() to open a window: If no column is passed to over(), it is going create one window for all the
records, will iterate over all rows.
◈ Select *, max(salaray) over() as max_salary from employee: this will show max salary among all the
employees.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dmv-alllecturessql-240607073149-a8db1b5f/75/DMV-All-Lectures-SQL-pptxpComplete-SQL-38-2048.jpg)

