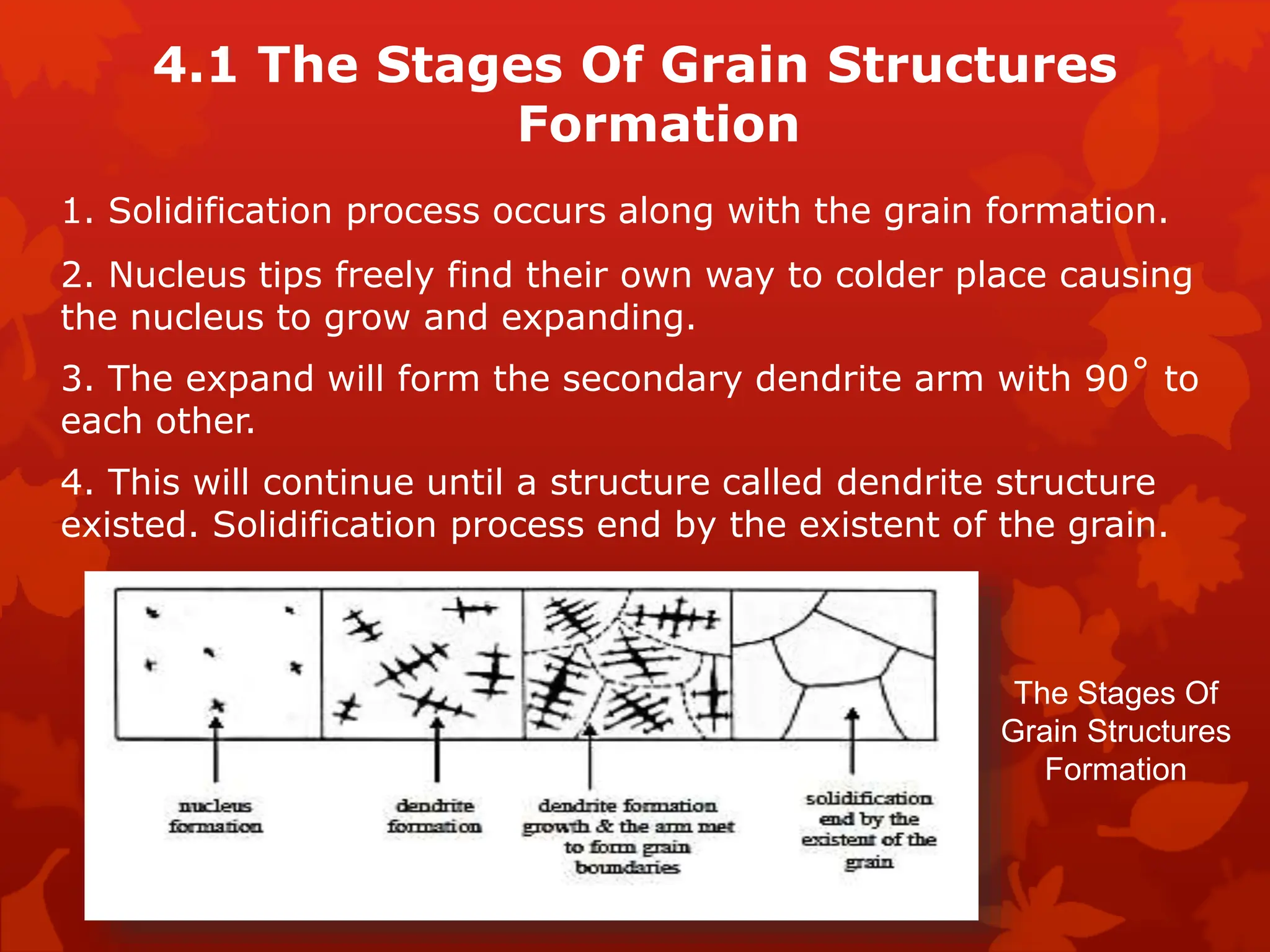
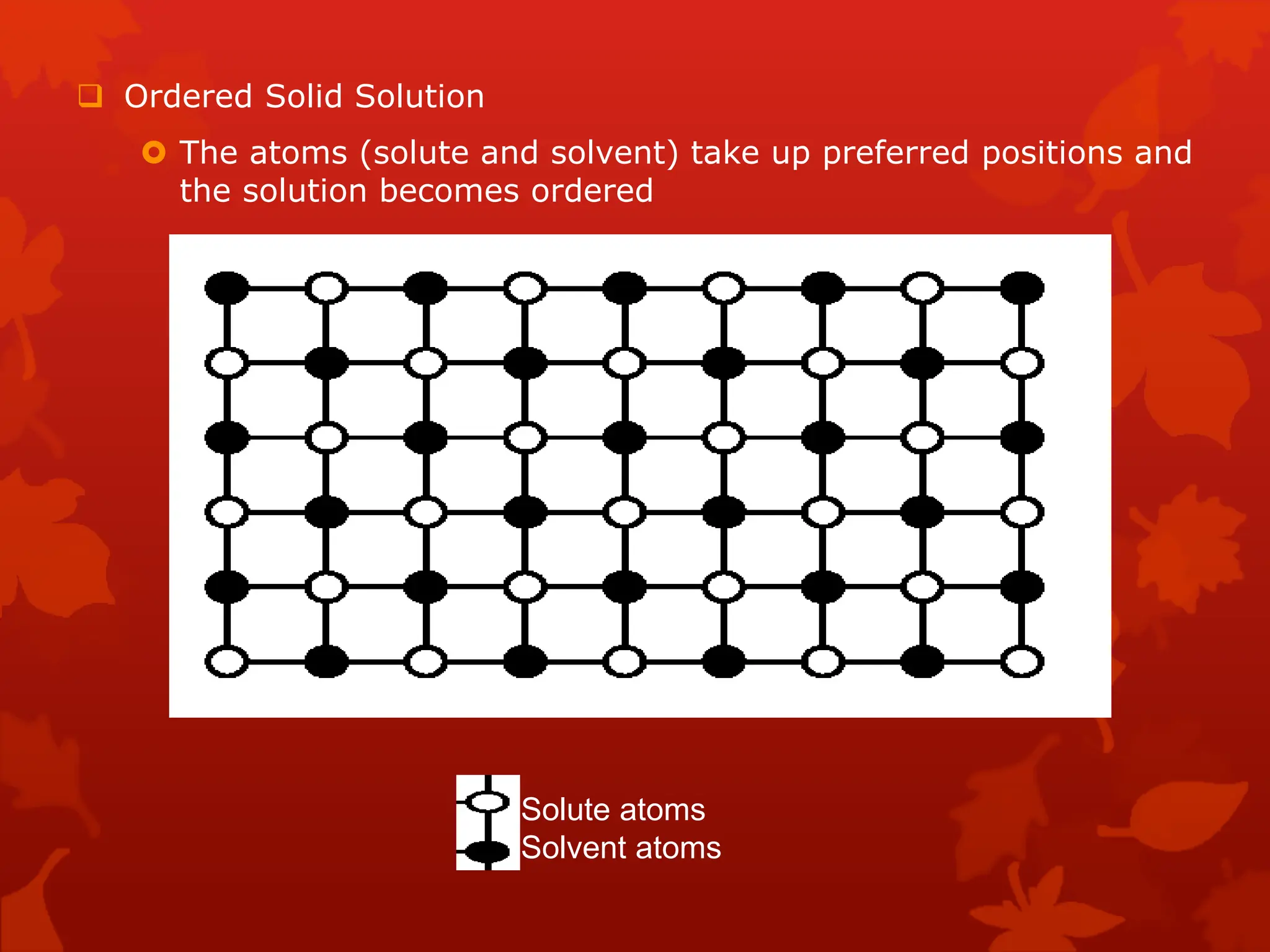
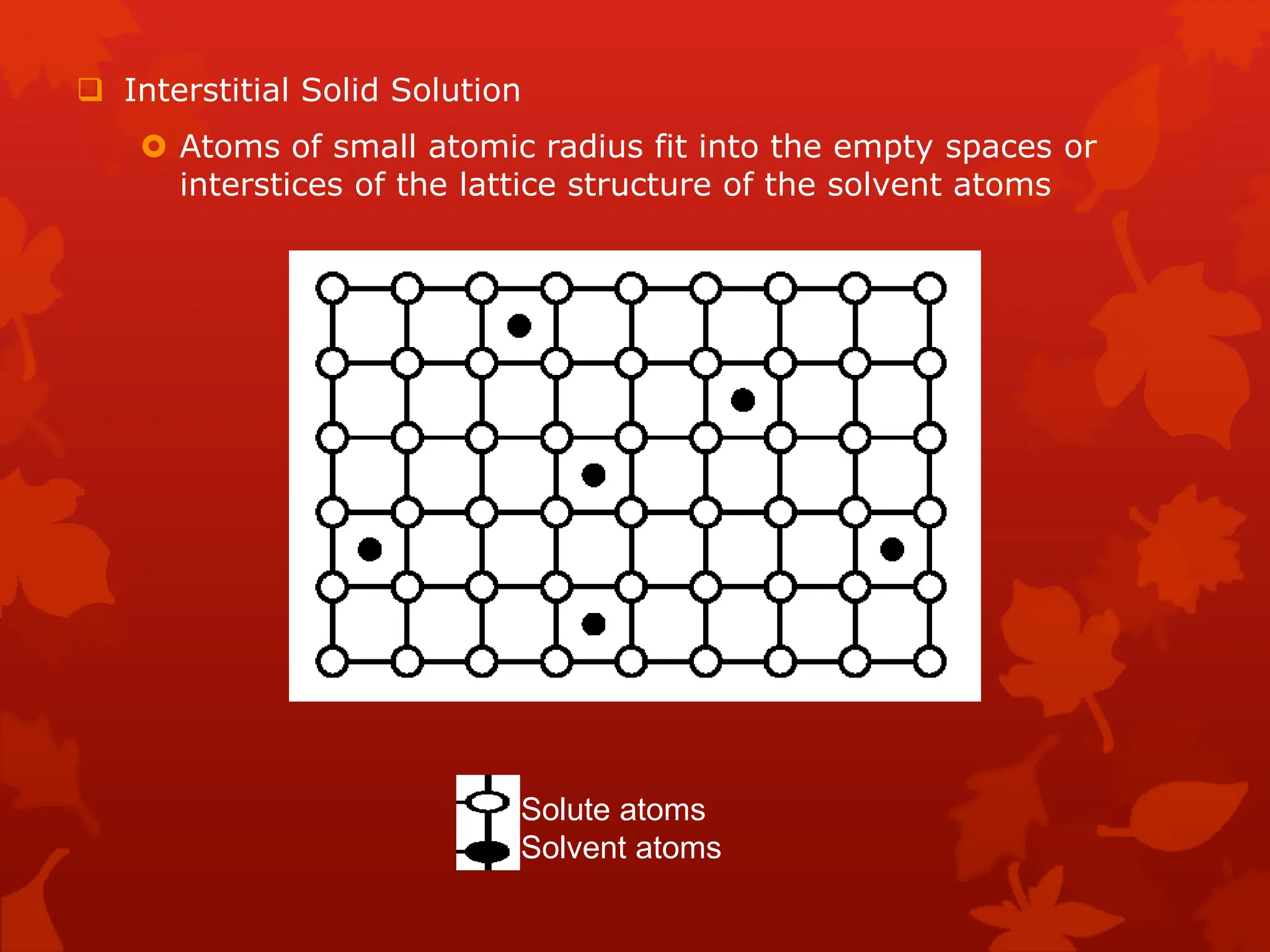
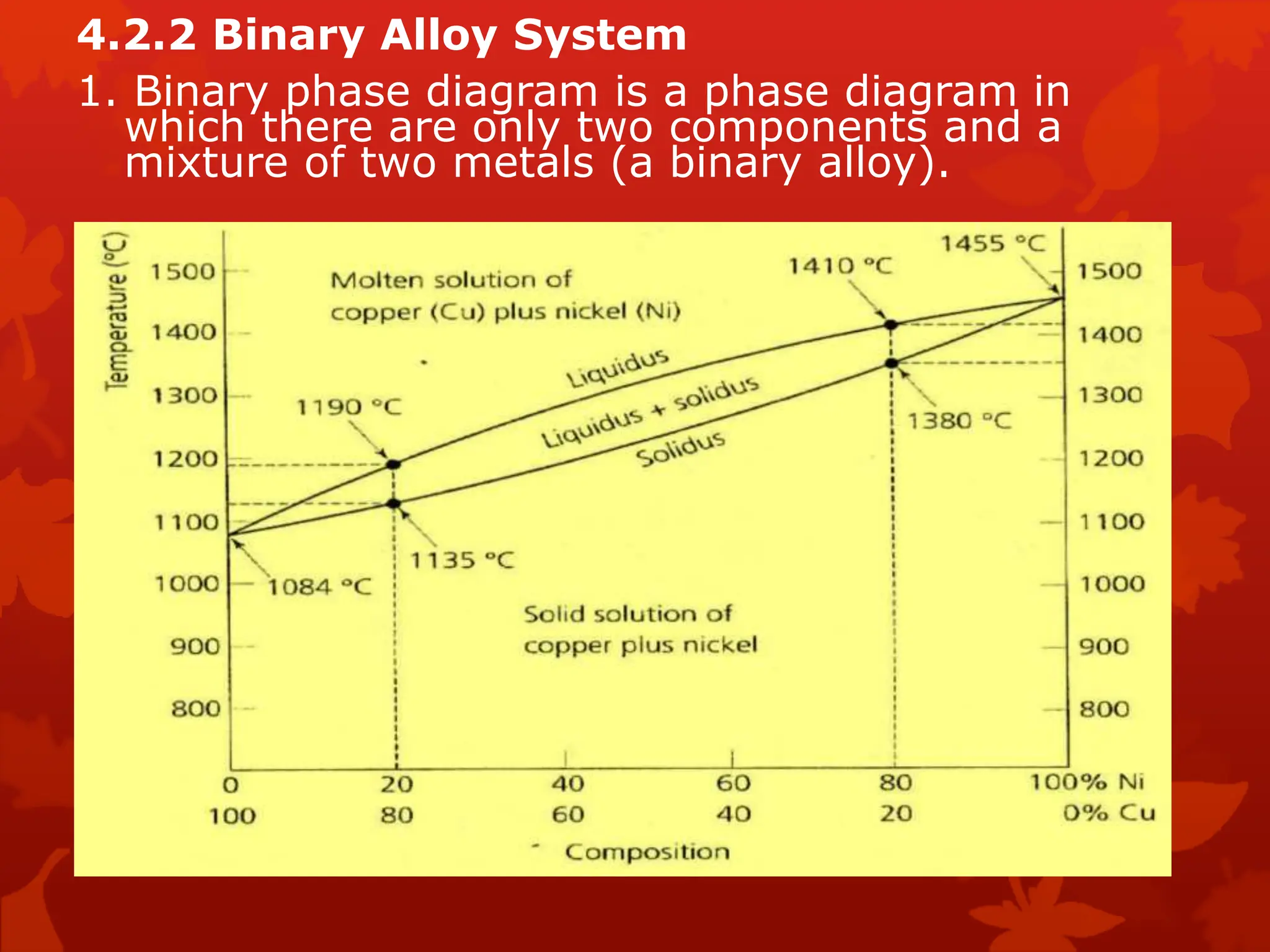
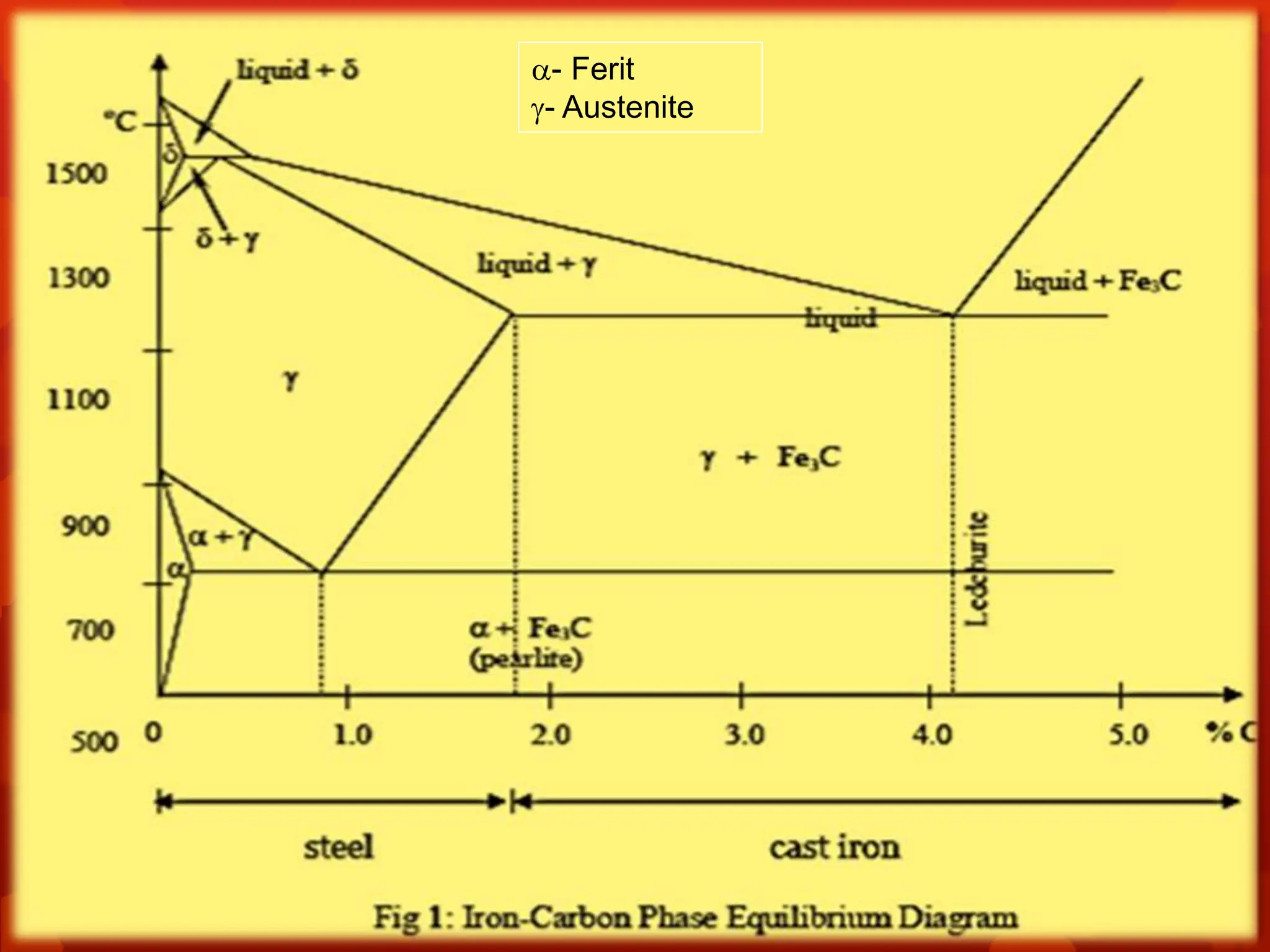
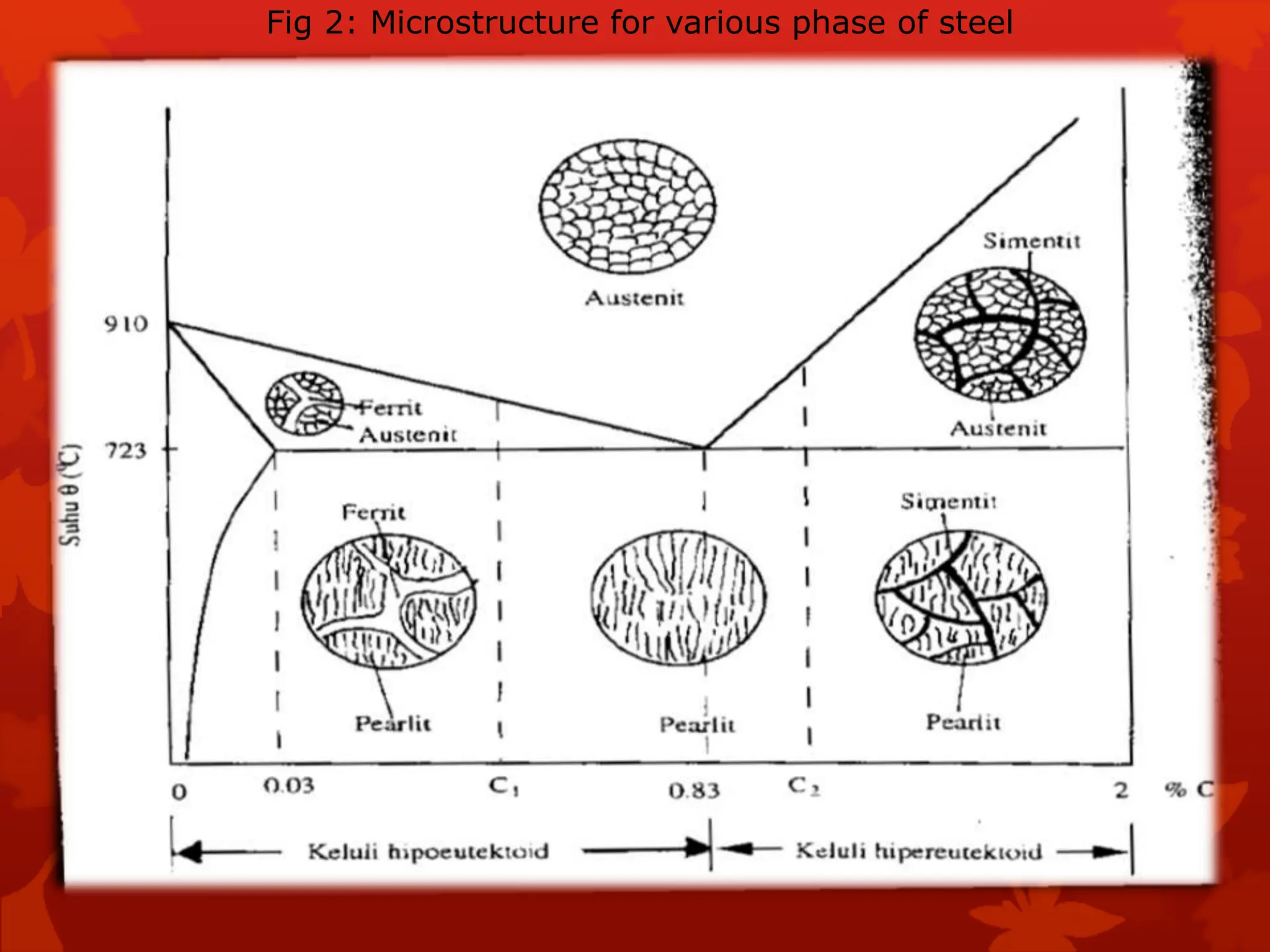
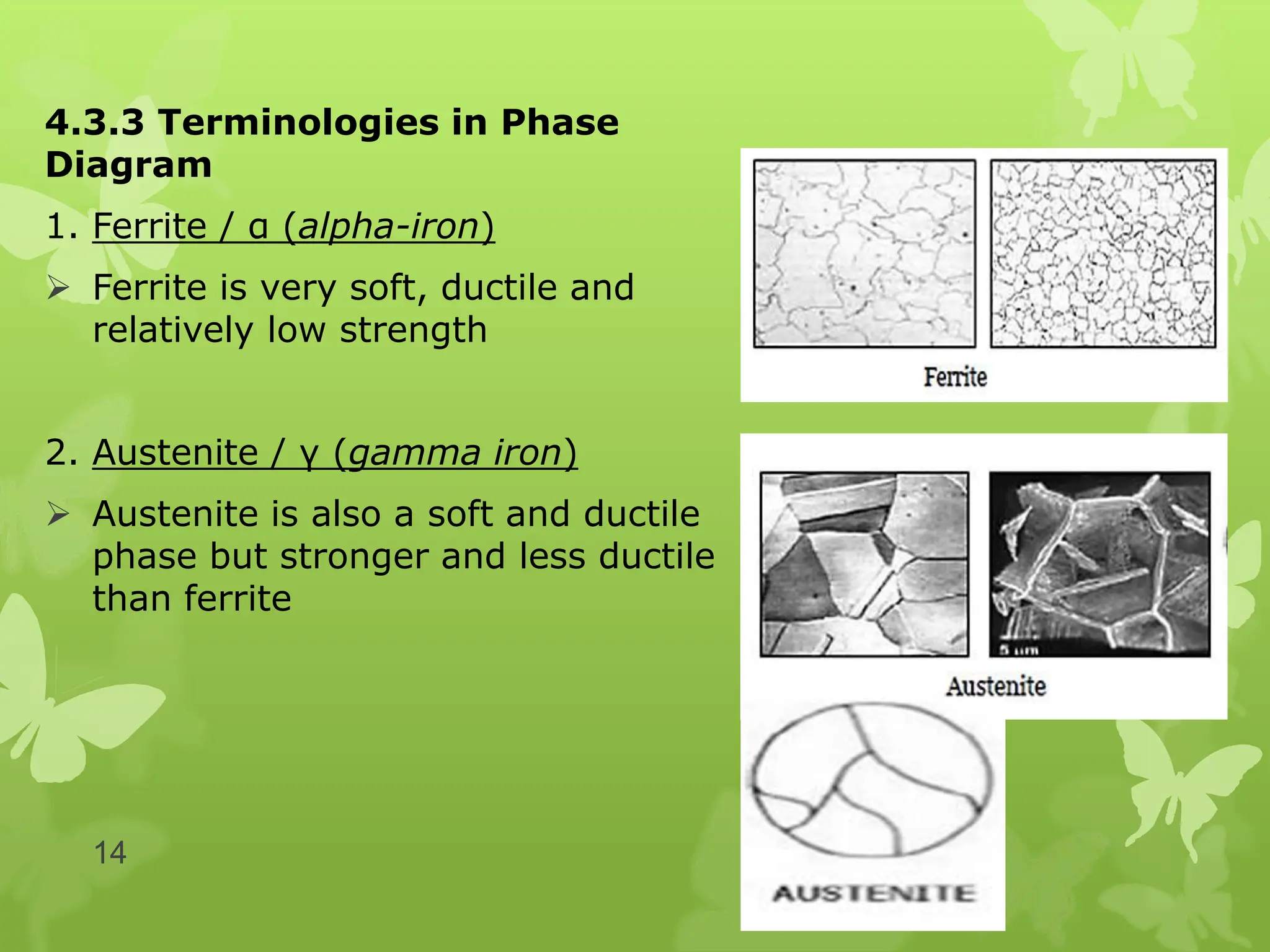
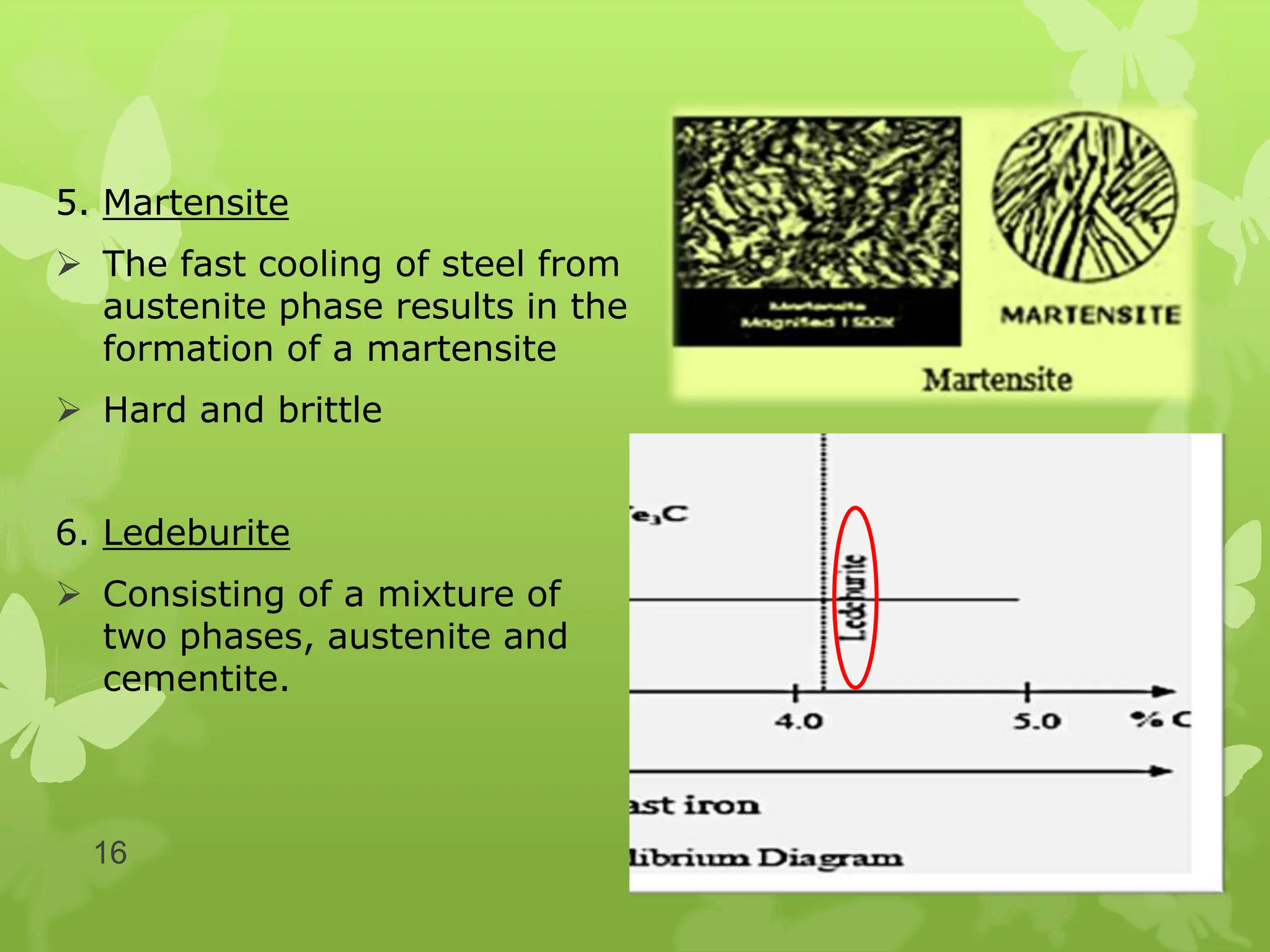
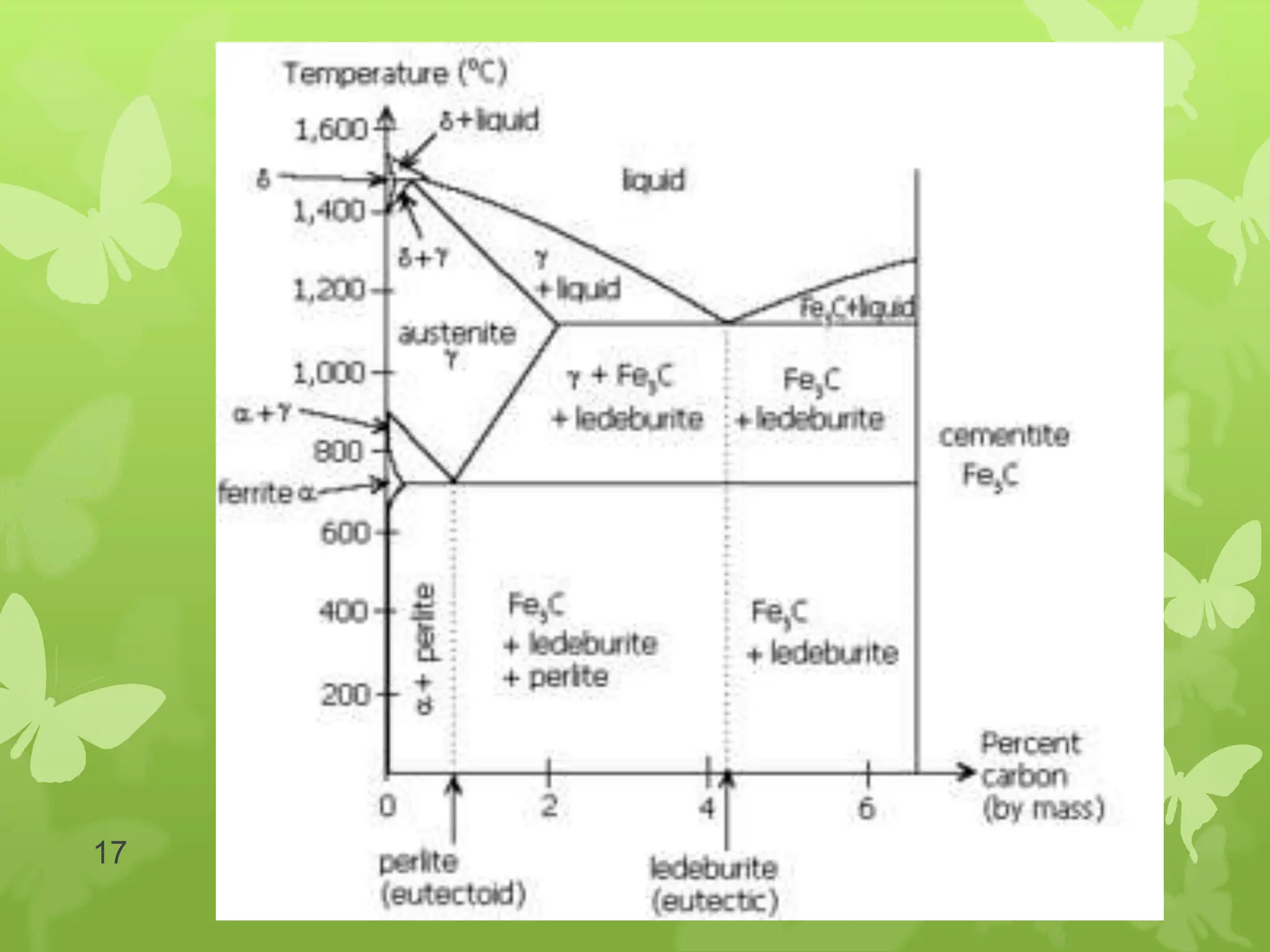
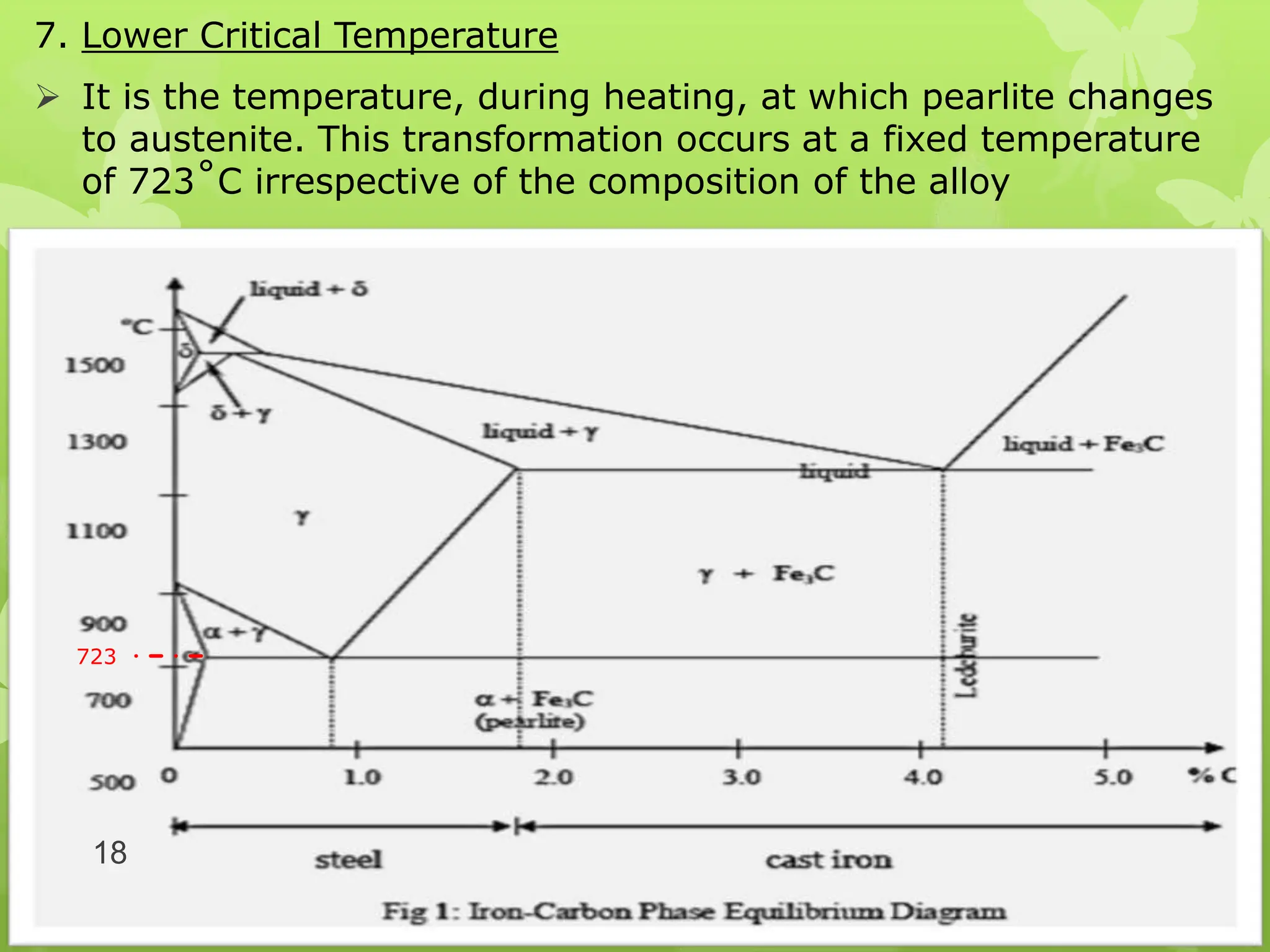
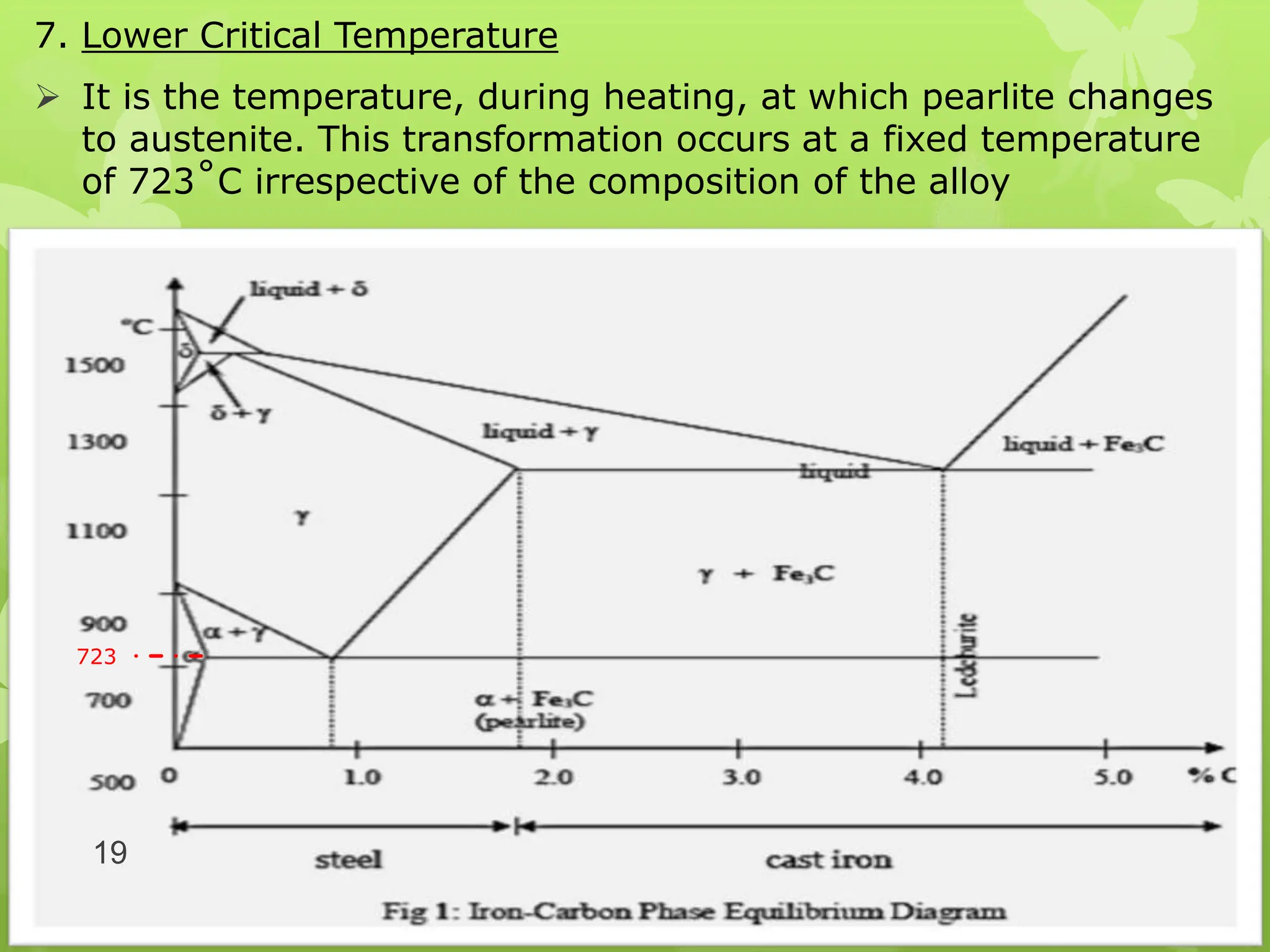
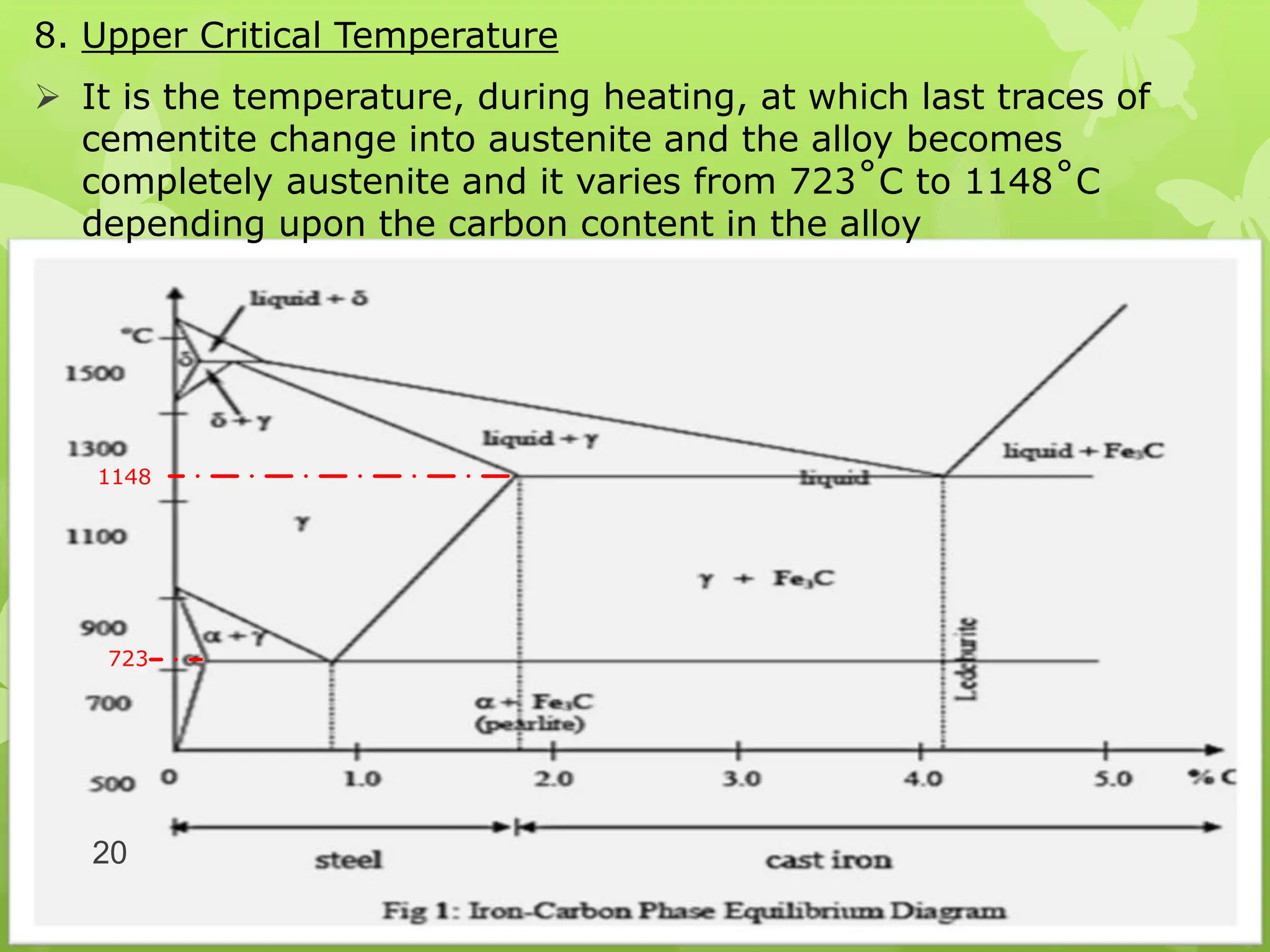
The document discusses material science concepts related to solid solutions and phase diagrams. It begins by describing the stages of grain structure formation during solidification. It then differentiates between base metals and alloys, describing various types of solid solutions like disordered, ordered, and interstitial. Terminologies in phase diagrams are explained, including phases, equilibrium, composition, liquidus, and solidus temperatures. Binary alloy systems containing two components are discussed. Finally, the key aspects of the iron-carbon phase diagram are summarized, including the various phases like ferrite, austenite, cementite, pearlite, and martensite that form at different temperature ranges and carbon concentrations.