Embed presentation
Download to read offline

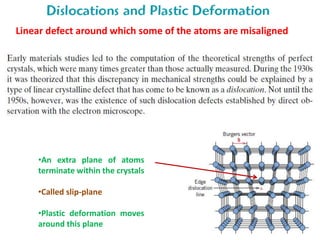
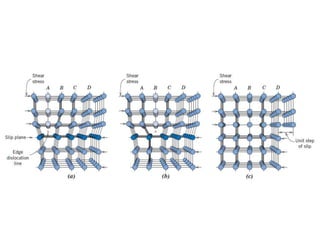
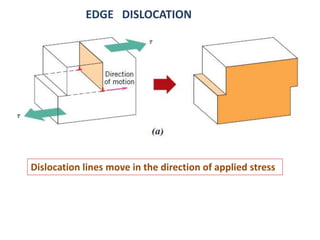
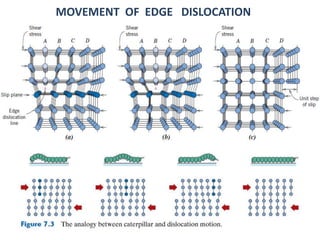
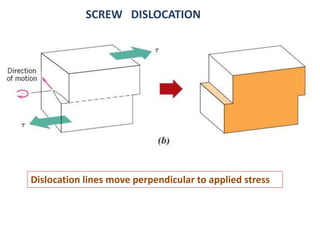
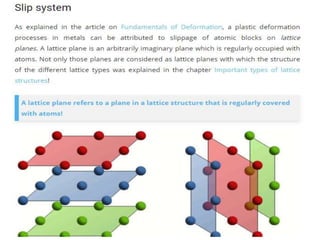
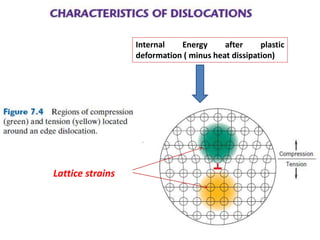
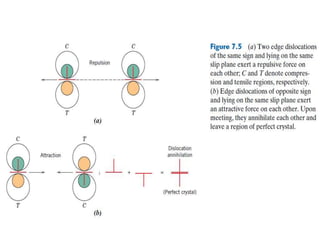

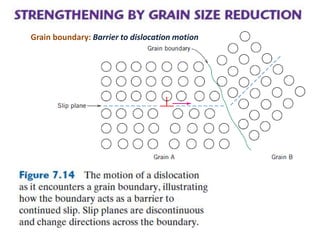

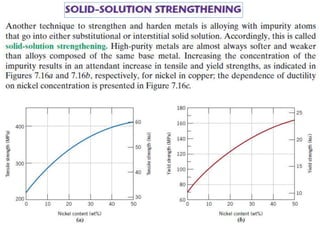
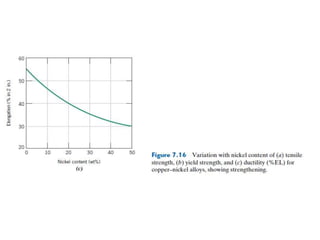
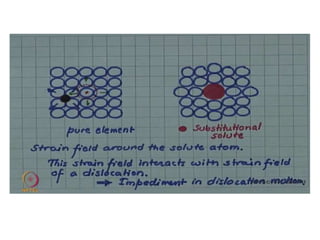
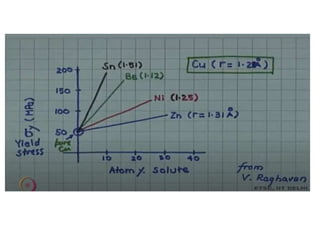
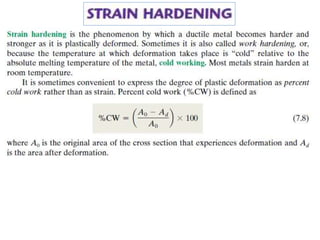
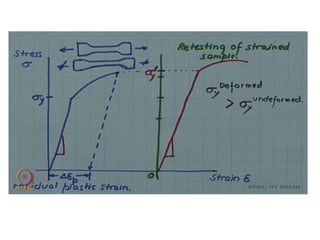
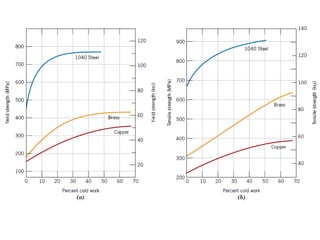
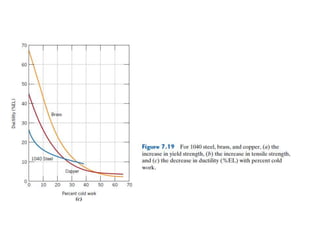


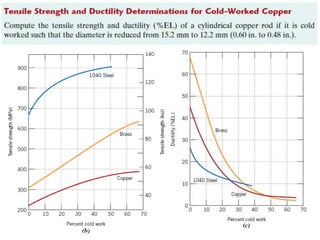
Dislocations are linear defects in crystals affecting atomic alignment and facilitating plastic deformation. The movement of dislocation lines, influenced by applied stress, plays a critical role in the mechanical properties of metals, where restricting this motion increases strength. Fine-grained materials, with a larger total grain boundary area, result in reduced dislocation motion, leading to harder and stronger metals.






















