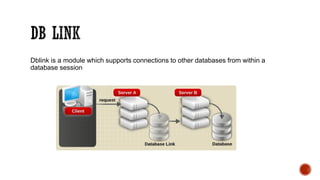
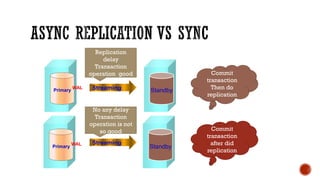
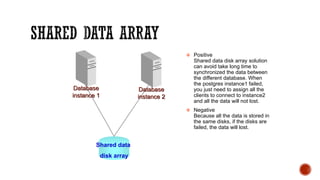
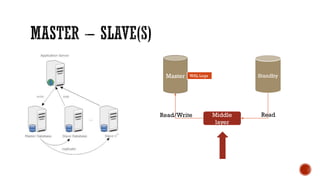
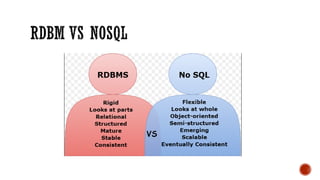
The document discusses various concepts in databases including:
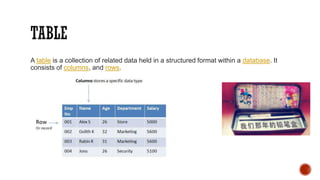
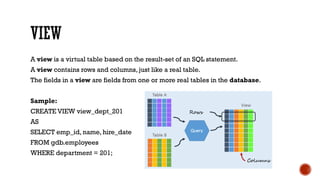
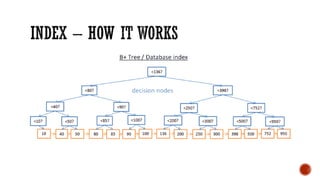
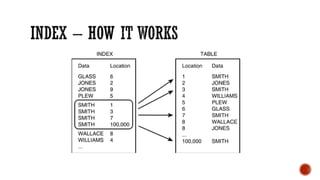
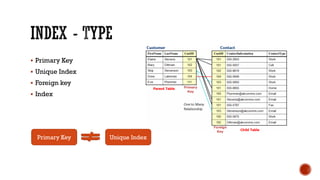
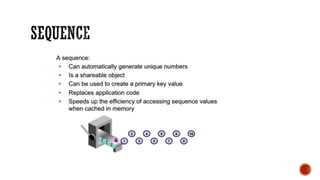
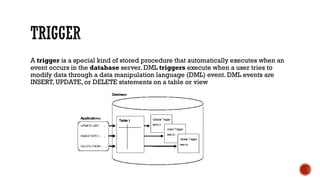
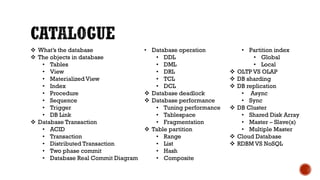
1) The core components of a database including tables, views, indexes, procedures, and triggers.
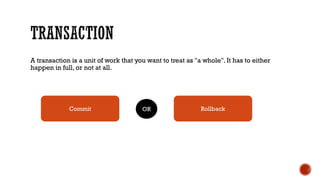
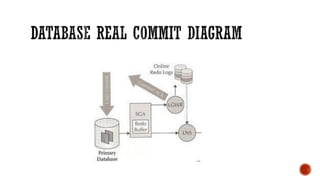
2) Transaction management concepts such as ACID properties, transactions, distributed transactions, and two phase commit.
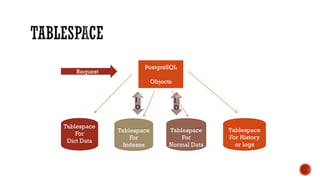
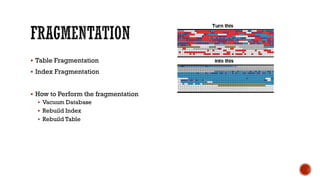
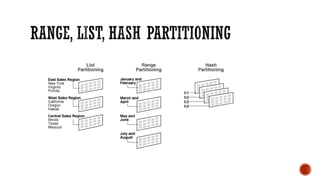
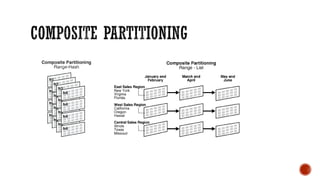
3) Performance topics including tablespaces, fragmentation, partitioning, indexing, and tuning.
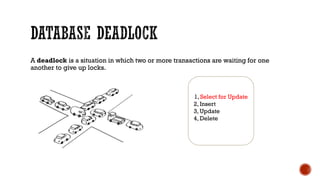
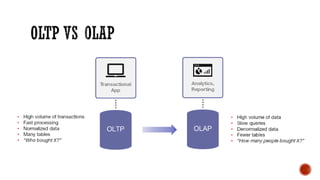
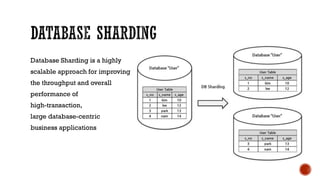
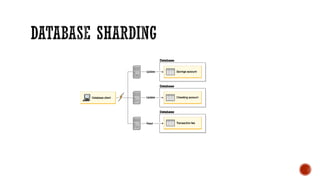
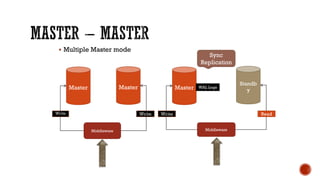
4) Additional topics such as deadlocks, OLTP vs OLAP, sharding, replication, clustering, and cloud databases.