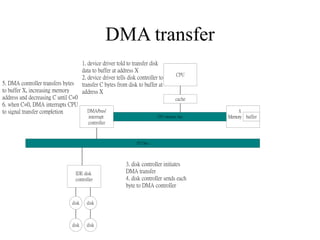
Direct Memory Access (DMA) allows data to be transferred directly between peripheral devices and memory without intervention from the CPU. The DMA controller initiates transfers by reading a DMA command from memory specifying the source, count, and destination. It then operates the memory bus directly to transfer data while the CPU continues other tasks. When the transfer is complete, the DMA controller interrupts the CPU. Handshaking between the DMA and device controllers coordinates the transfer of each word of data to or from memory.