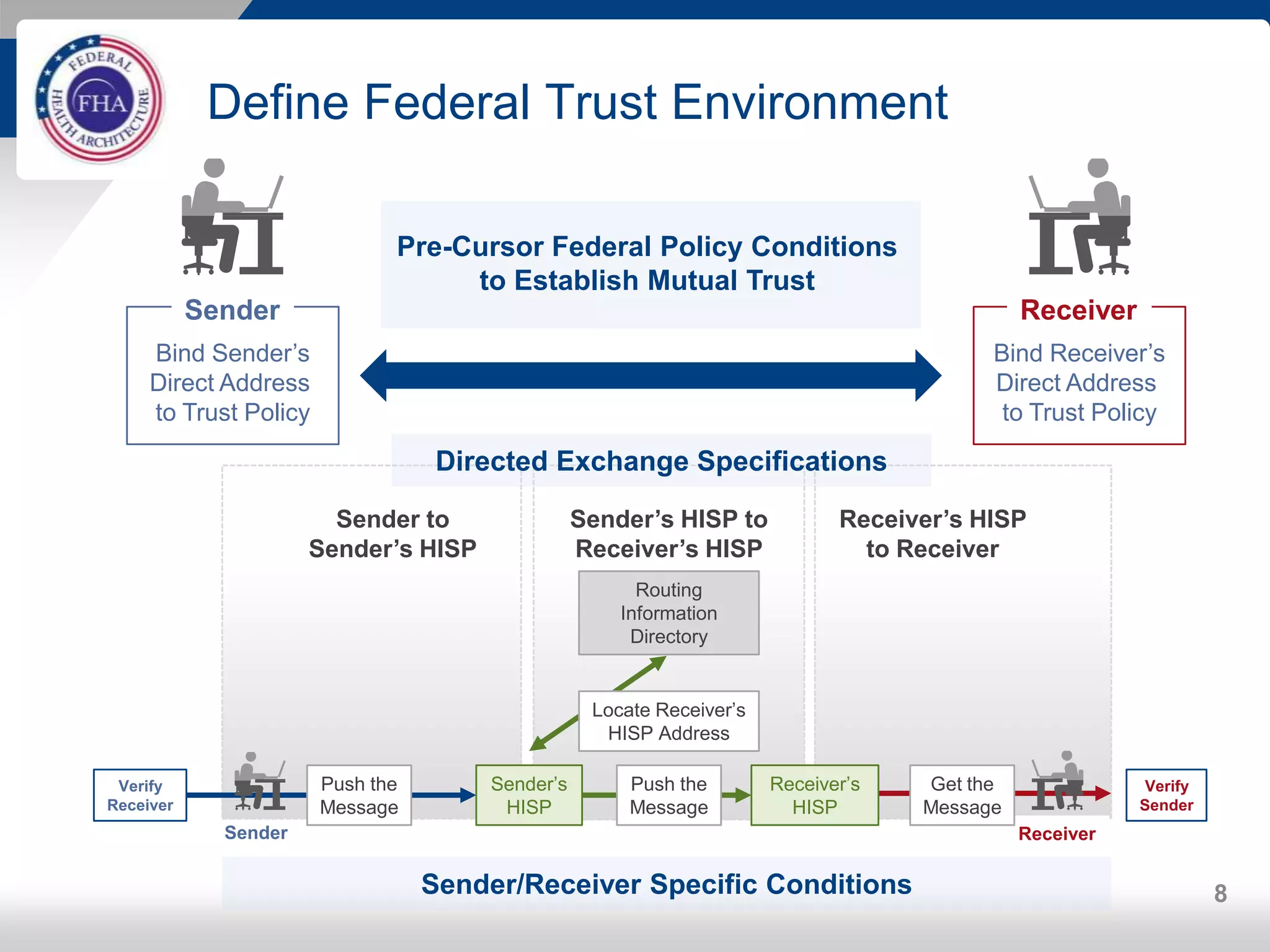
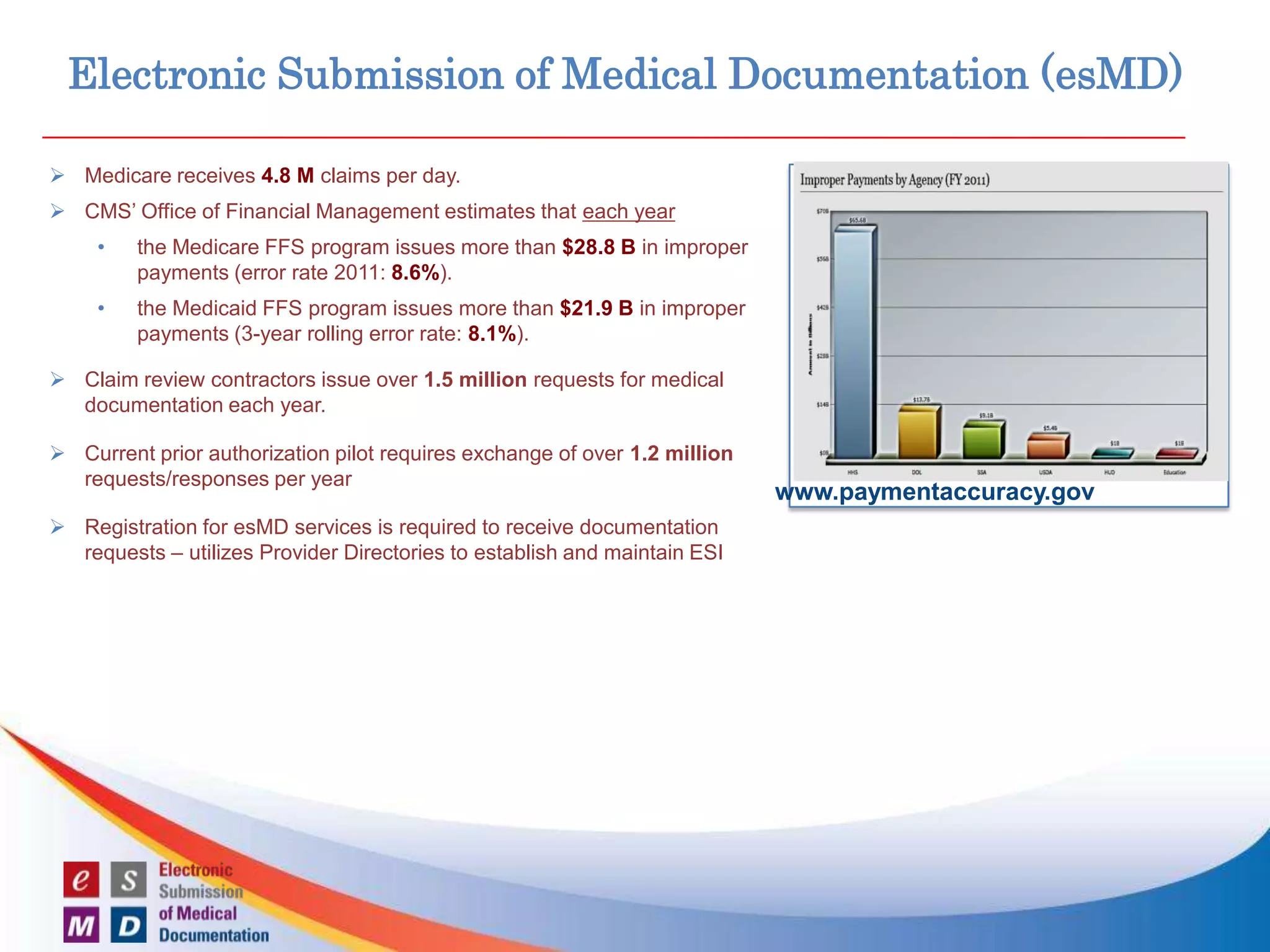
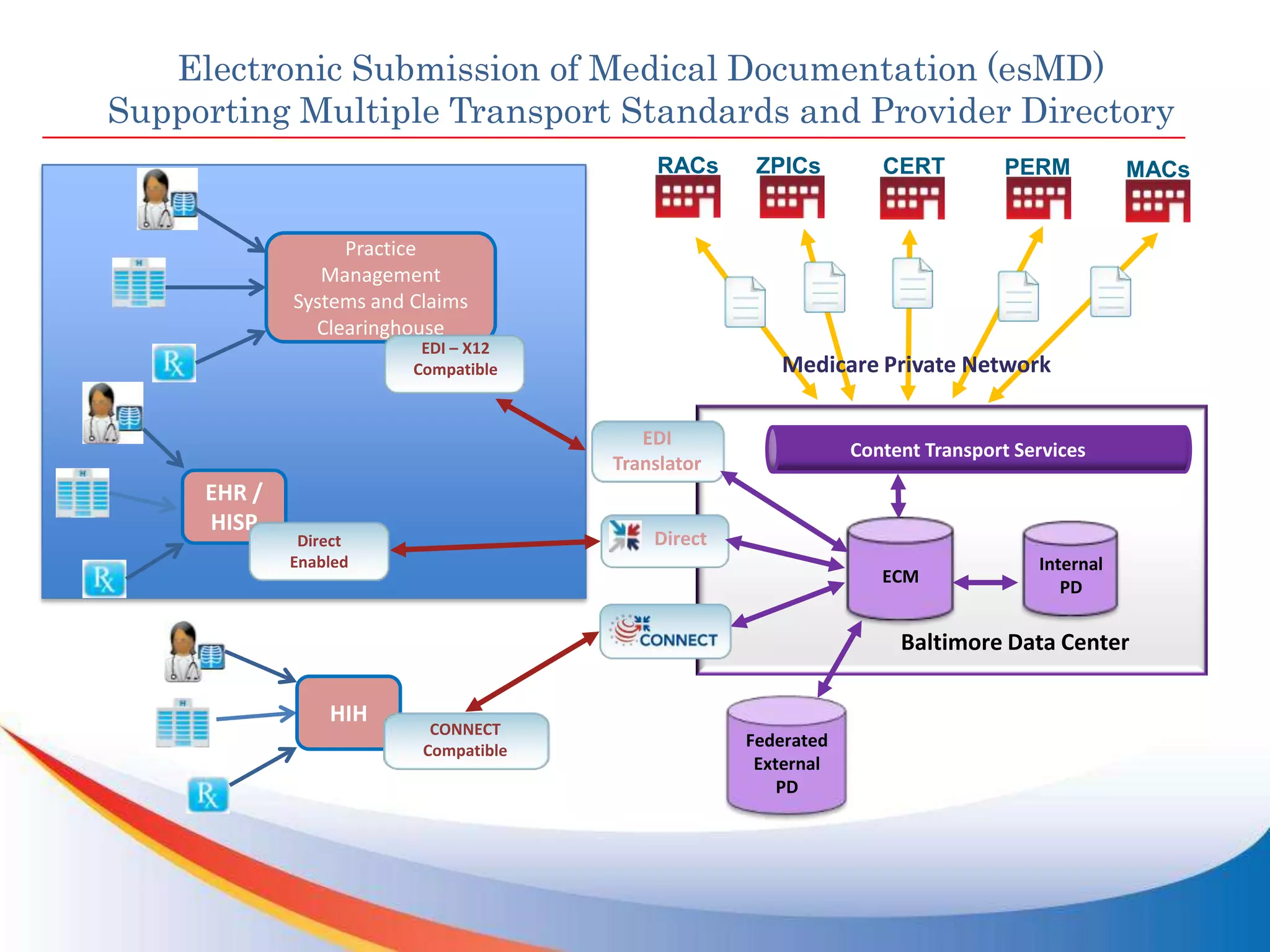
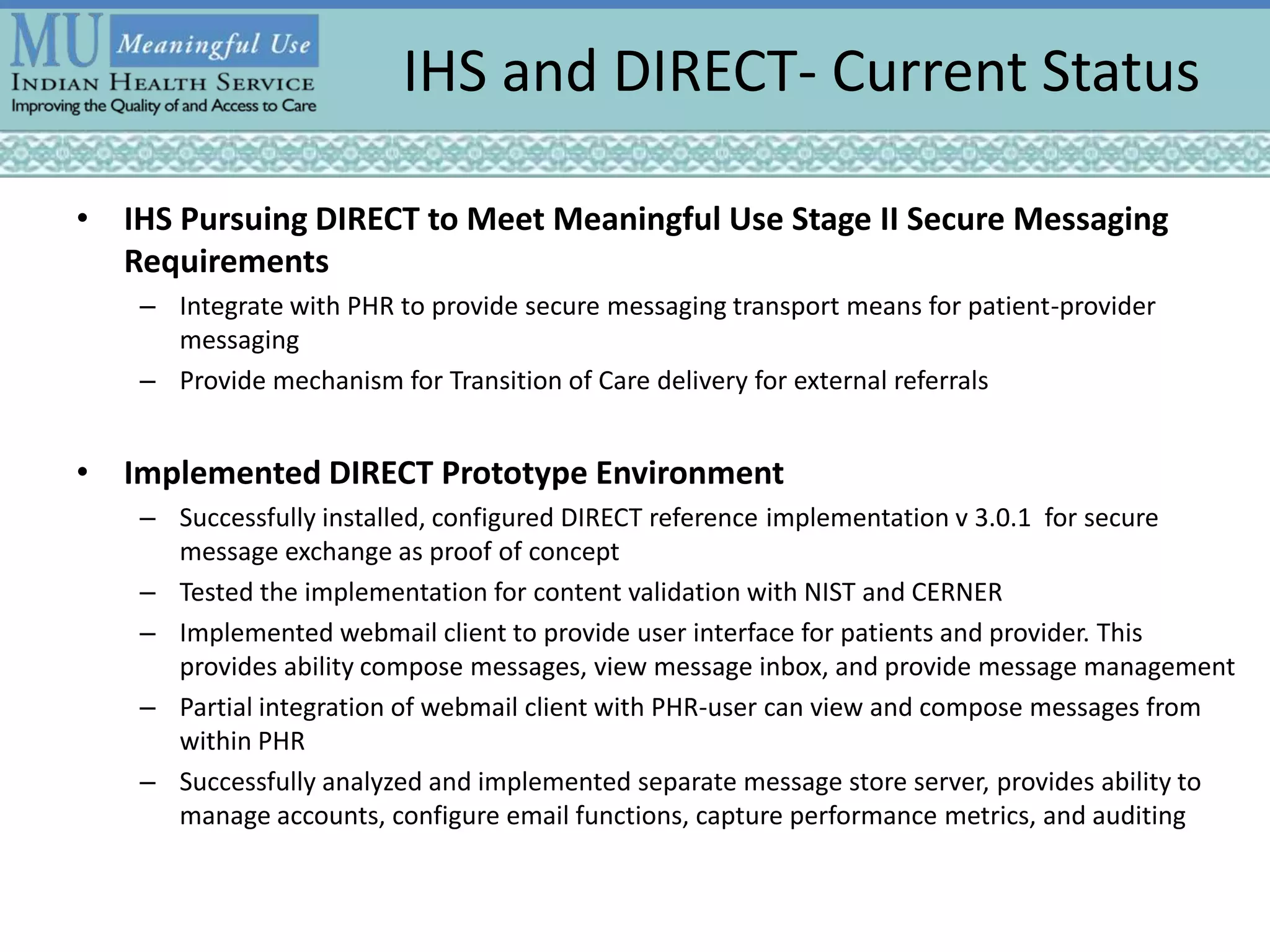
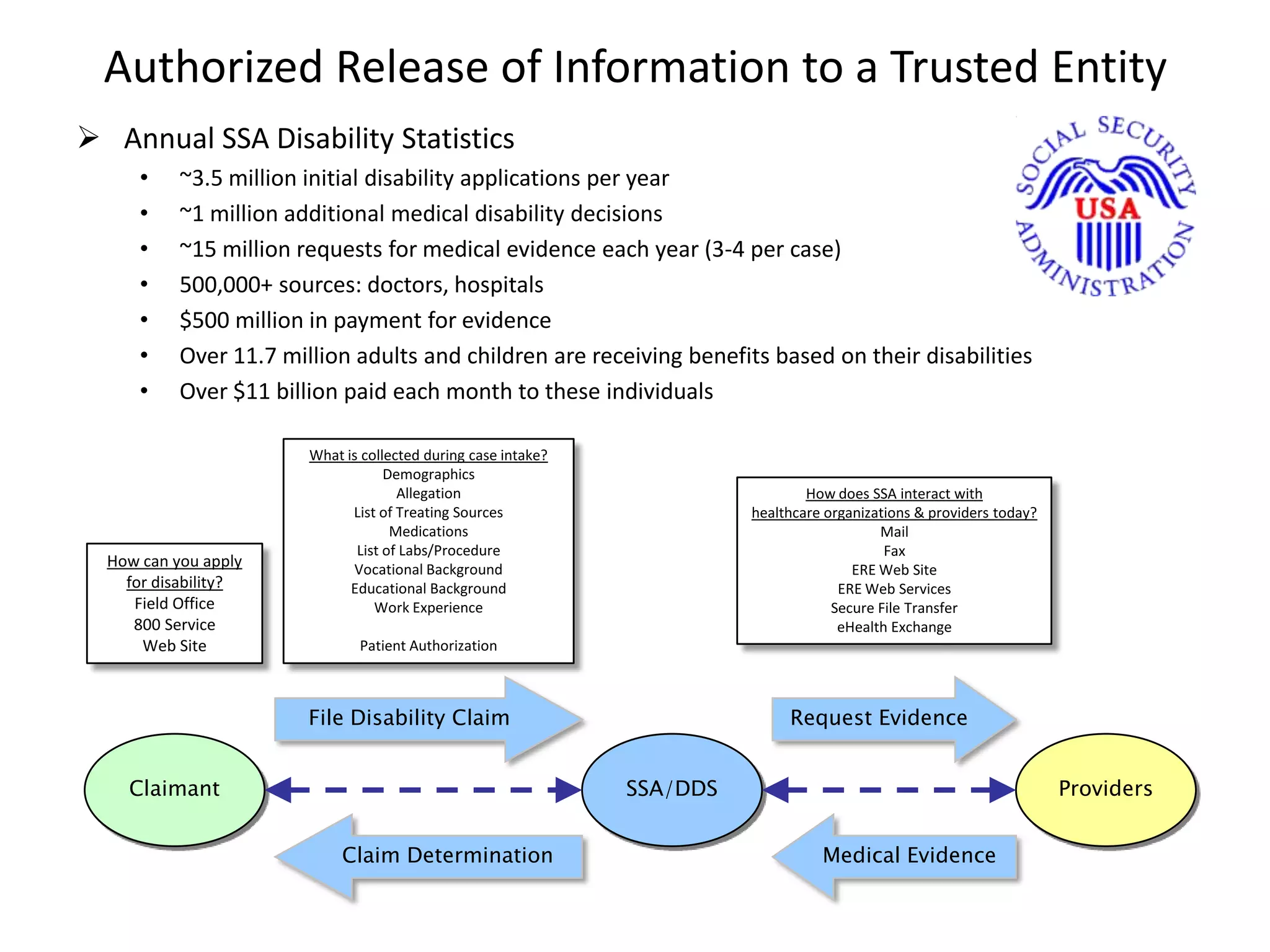
The FHA Directed Exchange Workgroup provides updates on efforts to increase the adoption of Direct for health information exchange between federal agencies and non-federal entities. They are educating federal partners on Direct technology and policies, developing common understanding of use cases and security requirements, and identifying baseline documents and FAQs. Establishing a common federal Direct policy would greatly increase its adoption for information exchange. Focused workgroups address Directed exchange, security, and interoperability issues. Risks to Directed exchange between agencies are being identified and recommendations will be provided to ONC.