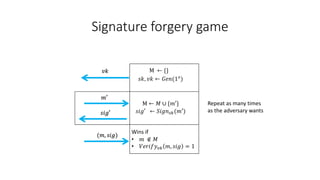
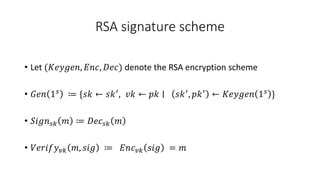
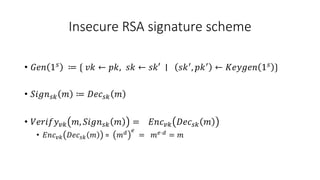
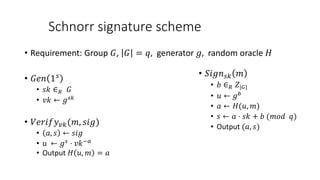
- A digital signature allows the holder of a secret key to sign a document, and anyone with the public verification key can verify the signature is valid and correct. It is not possible to forge a signature even with the verification key.
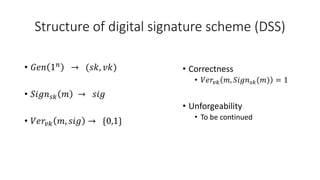
- A digital signature scheme (DSS) involves key generation, signing messages with the secret key, and verifying signatures with the public key. It satisfies correctness, meaning signatures can be verified, and unforgeability, meaning signatures cannot be forged.
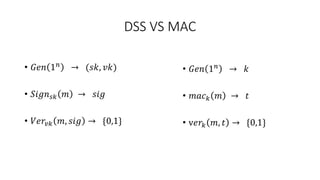
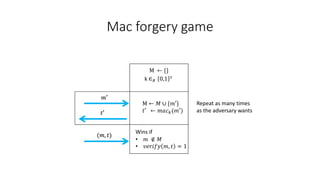
- While message authentication codes (MACs) also provide signature functionality by signing with a secret key, they are not considered true signatures because verification may not be possible without the secret key. Signatures use public/private key pairs to