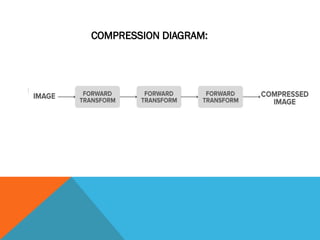
The document discusses image compression, a process that reduces the size of image files by either eliminating data or utilizing algorithms. It highlights the significance of mathematical transforms in compression, outlines types of error-free (lossless) compression such as Huffman and variable-length coding, and mentions applications in archiving medical documents and satellite imaging. The need for error-free compression is emphasized due to the specific requirements of different types of images.