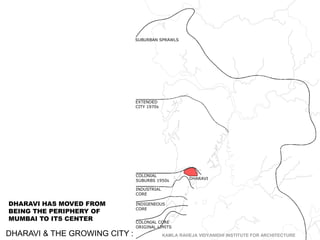
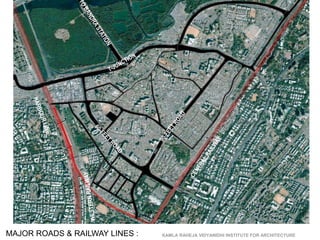
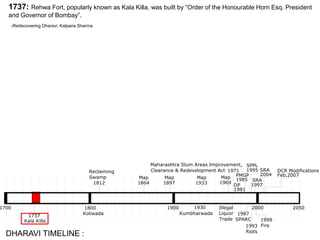
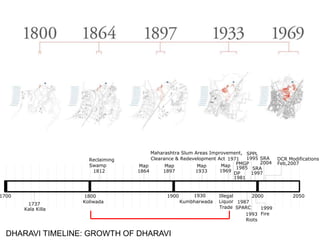
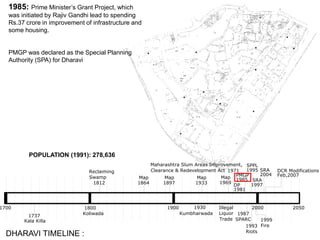
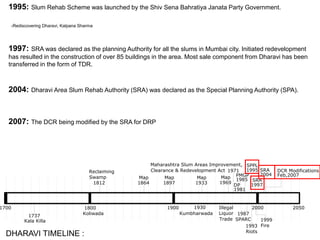
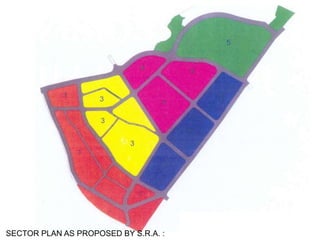
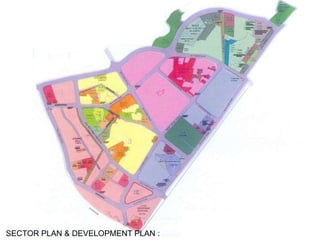
The document summarizes the redevelopment plan for Dharavi in Mumbai, India. It provides a timeline of Dharavi's growth from 1737 to present day and outlines the sector plan proposed by the Slum Rehabilitation Authority. It also lists several concerns and critiques of the redevelopment plan, including legal issues around procedures not being followed, a lack of community participation and transparency in the planning process, unclear financial aspects, and deficiencies in the work done by the appointed consultant.