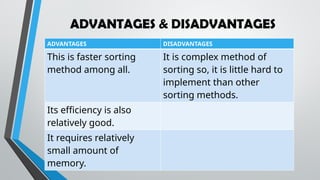
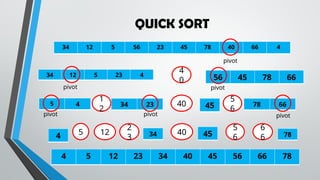
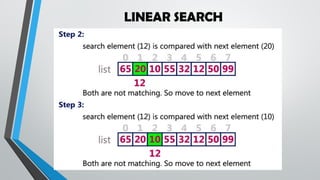
The document explains sorting and searching algorithms, detailing various sorting methods such as selection sort, merge sort, bubble sort, quick sort, and insertion sort, along with their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it covers searching techniques including linear search and binary search, highlighting their applicability based on data organization. Students are encouraged to learn these algorithms and apply them through various activities.



























![BINARY SEARCH
Let say, we want to search whether 21 is in the list
4 7 8 10 14 21 22 36 62 77
First determine the middle(pivot) of the list using this formula:
middle = (lowest index) + ( highest index) /2
In this example it will be :
[0] [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9]
4 7 8 10 14 21 22 36 62 77
(0 + 9)/ 2 = 4.5
M= 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dfc30233chapter61-241108131856-7fcbff0e/85/DFC30233_CHAPTER-6-1-pptxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx-34-320.jpg)
![BINARY SEARCH
[0] [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9]
4 7 8 10 14 21 22 36 62 77
F M L
Key = 21
M = 14
21 != 14
21>14
[0] [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9]
4 7 8 10 14 21 22 36 62 77](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dfc30233chapter61-241108131856-7fcbff0e/85/DFC30233_CHAPTER-6-1-pptxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx-35-320.jpg)
![BINARY SEARCH
[5] [6] [7] [8] [9]
21 22 36 62 77
(5 + 9)/ 2 = 7
M= 7
Key = 21
M = 36
21 != 36
21<36
[5] [6] [7] [8] [9]
21 22 36 62 77
F M L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dfc30233chapter61-241108131856-7fcbff0e/85/DFC30233_CHAPTER-6-1-pptxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx-36-320.jpg)
![BINARY SEARCH
[5] [6]
21 22
(5 + 6)/ 2 = 5.5
M= 5
Key = 21
M = 21
21 = 21
Searching stop and successful
F M L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dfc30233chapter61-241108131856-7fcbff0e/85/DFC30233_CHAPTER-6-1-pptxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx-37-320.jpg)