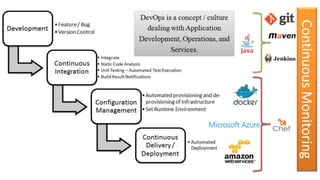
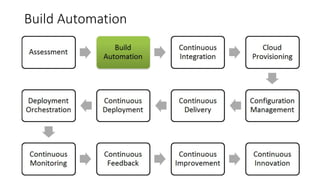
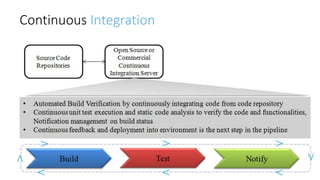
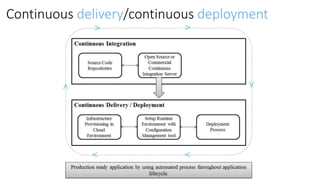
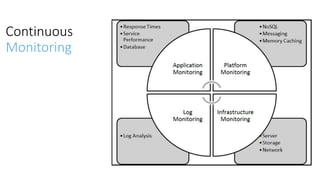
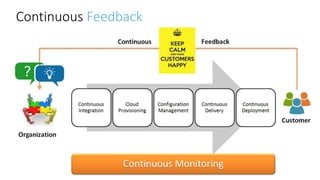
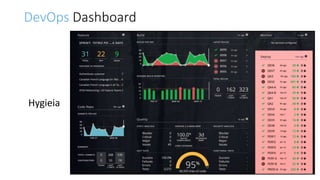
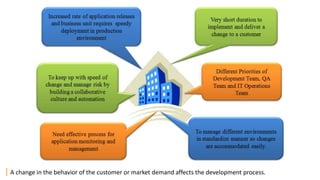
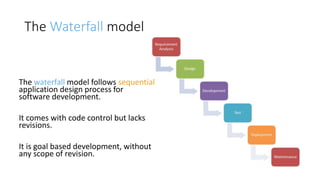
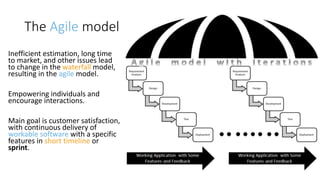
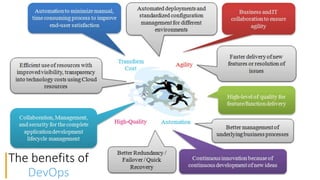
The document discusses DevOps as a culture and approach that enhances efficiency through collaboration between development and operations teams. It outlines the DevOps lifecycle, emphasizing continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous monitoring, while highlighting the tools and technologies that facilitate these processes. The importance of adopting an agile mindset and addressing customer demands for rapid feature delivery is also emphasized, along with the cultural aspects of DevOps that go beyond just technical tools.









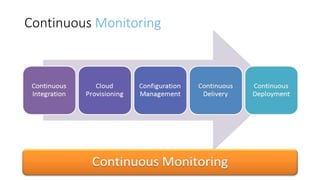
![The DevOps lifecycle
– it’s all about continues
Continuous Integration (CI), Continuous
Testing (CT), and Continuous Delivery (CD),
are a significant part of DevOps culture.
CI [ automatic builds, unit tests, packaging
process]
CD [ application delivery pipeline across
different environments]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devopsconceptstoolsandtechnologiesv1-180304144843/85/DevOps-concepts-tools-and-technologies-v1-0-14-320.jpg)