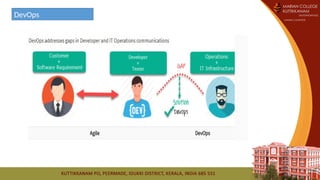
The document provides a comprehensive overview of DevOps, detailing its purpose, principles, lifecycle, and tools, emphasizing the need for collaboration between development and operations teams to enhance efficiency. It outlines the advantages and disadvantages of adopting DevOps practices, highlighting continuous improvement, automation, and customer-centric approaches. Additionally, the document discusses key tools such as Git, Jenkins, Docker, and Nagios, and concludes with homework assignments related to DevOps differentiation and roles.