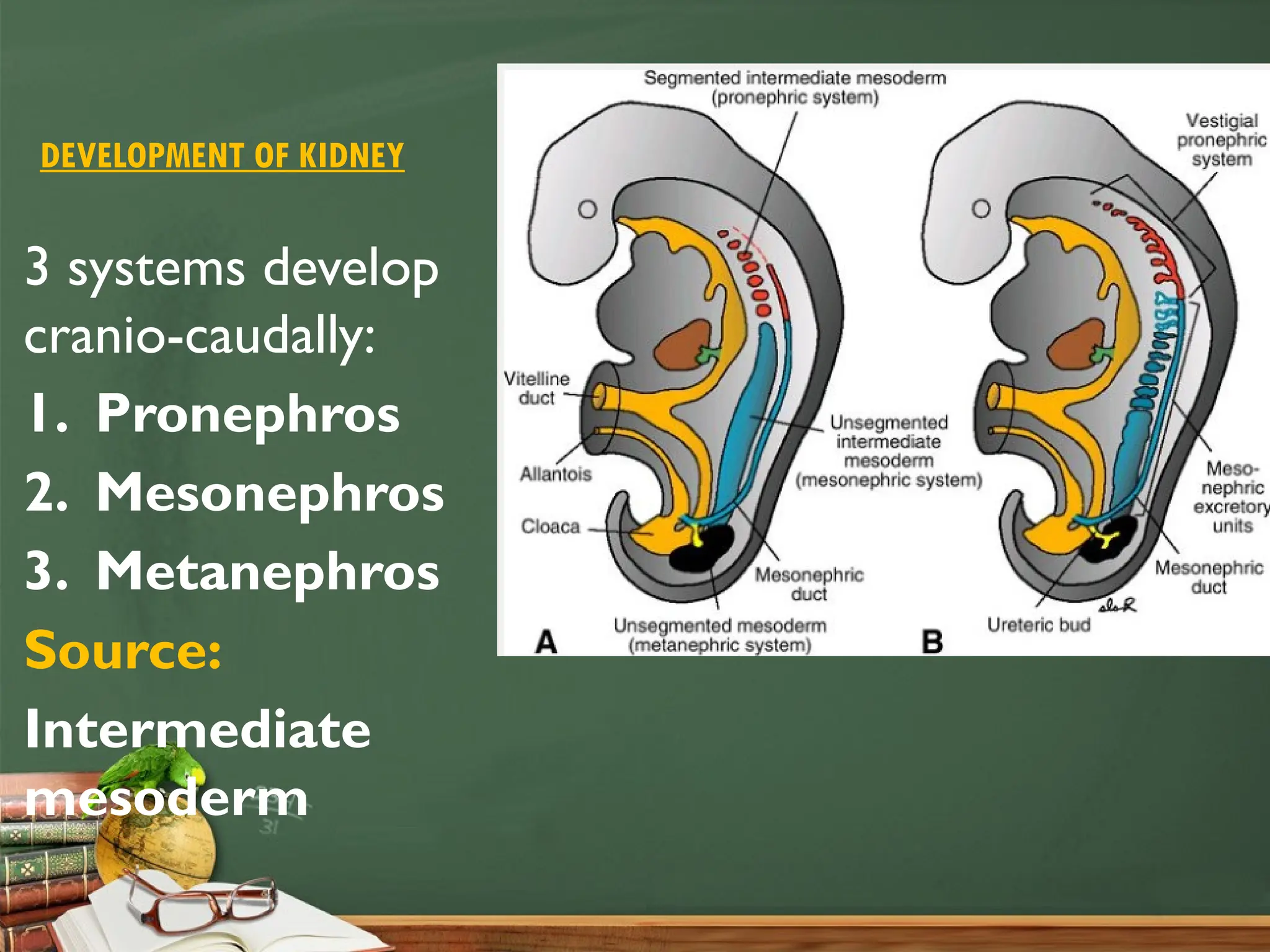
The document outlines the development of the renal system in humans, detailing the progression through three stages: pronephros, mesonephros, and metanephros, with each phase having distinct anatomical characteristics and functional roles. It discusses the structural evolution of kidneys, including the formation of renal corpuscles and nephron units, as well as the anatomical transitions from embryo to functional kidneys. Additionally, it addresses congenital anomalies associated with renal development and variations in urinary structures.