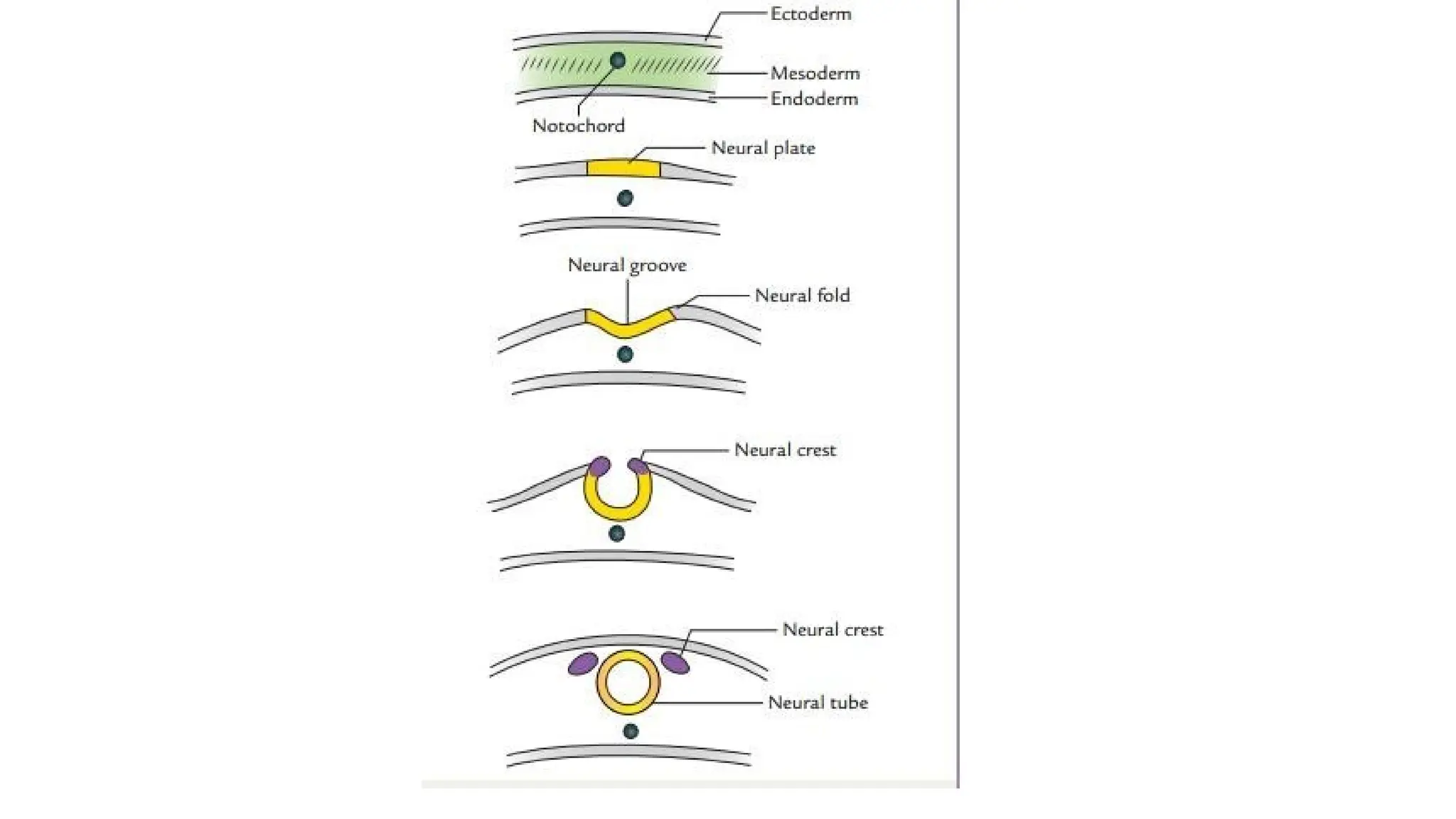
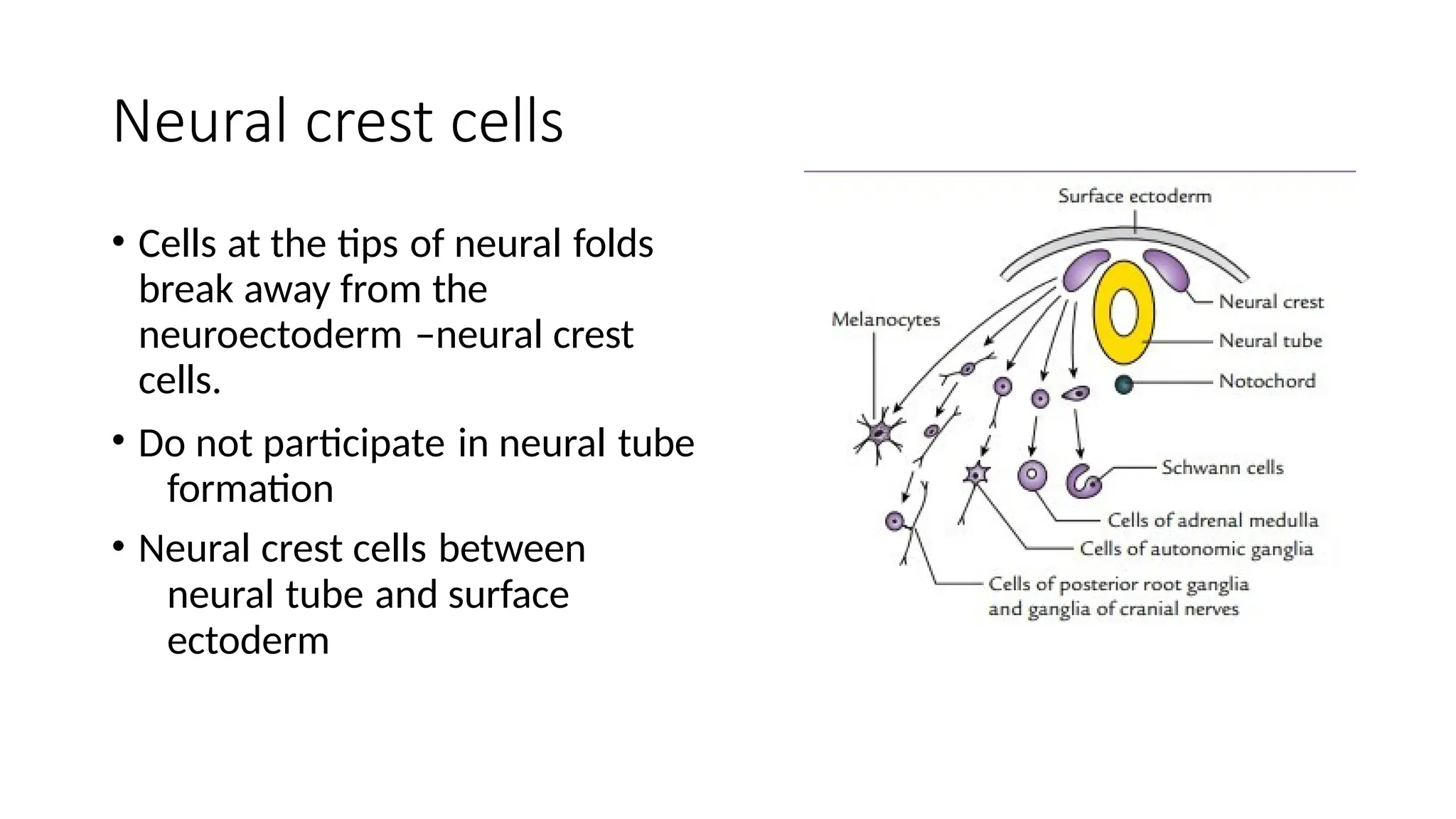
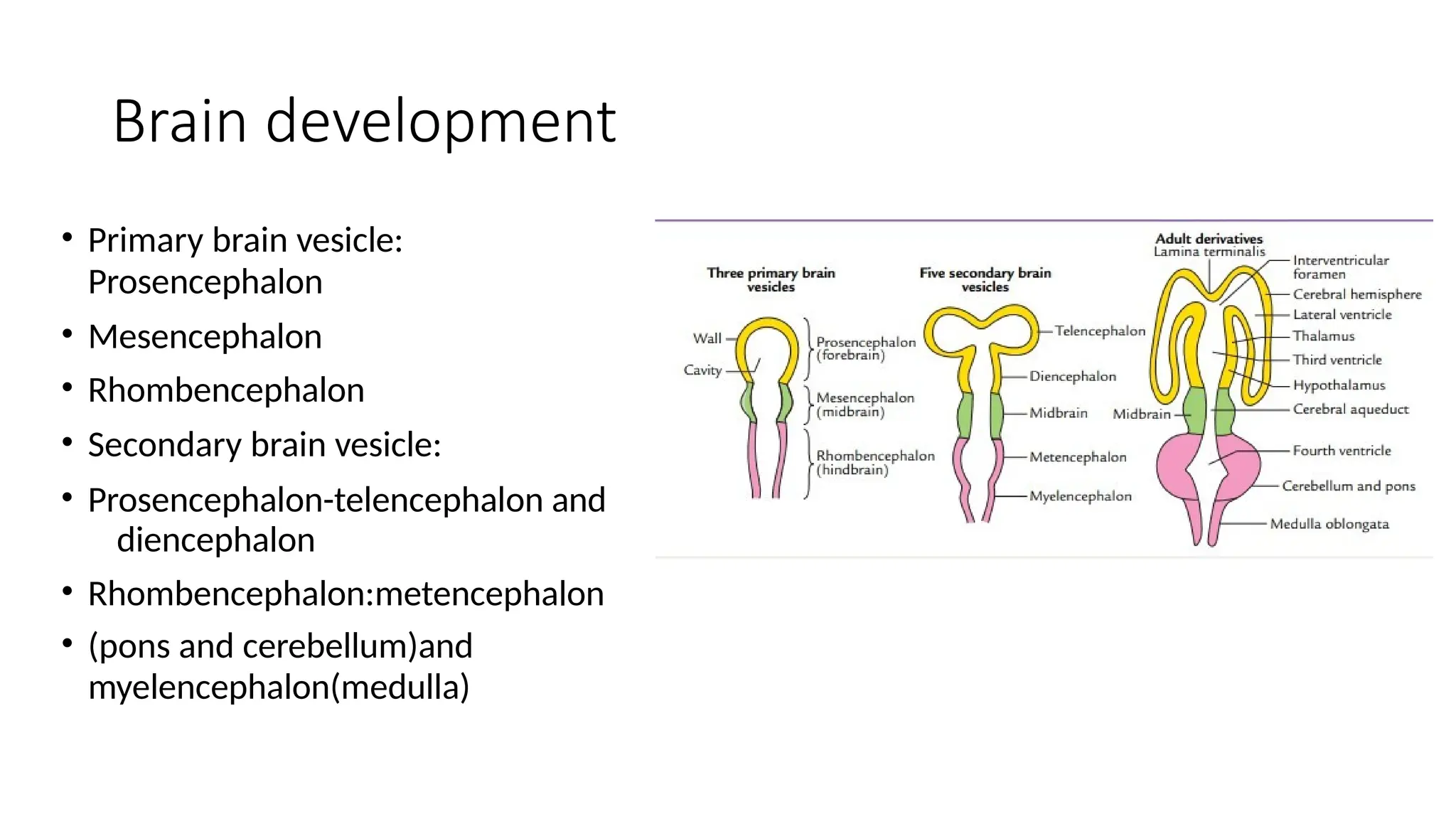
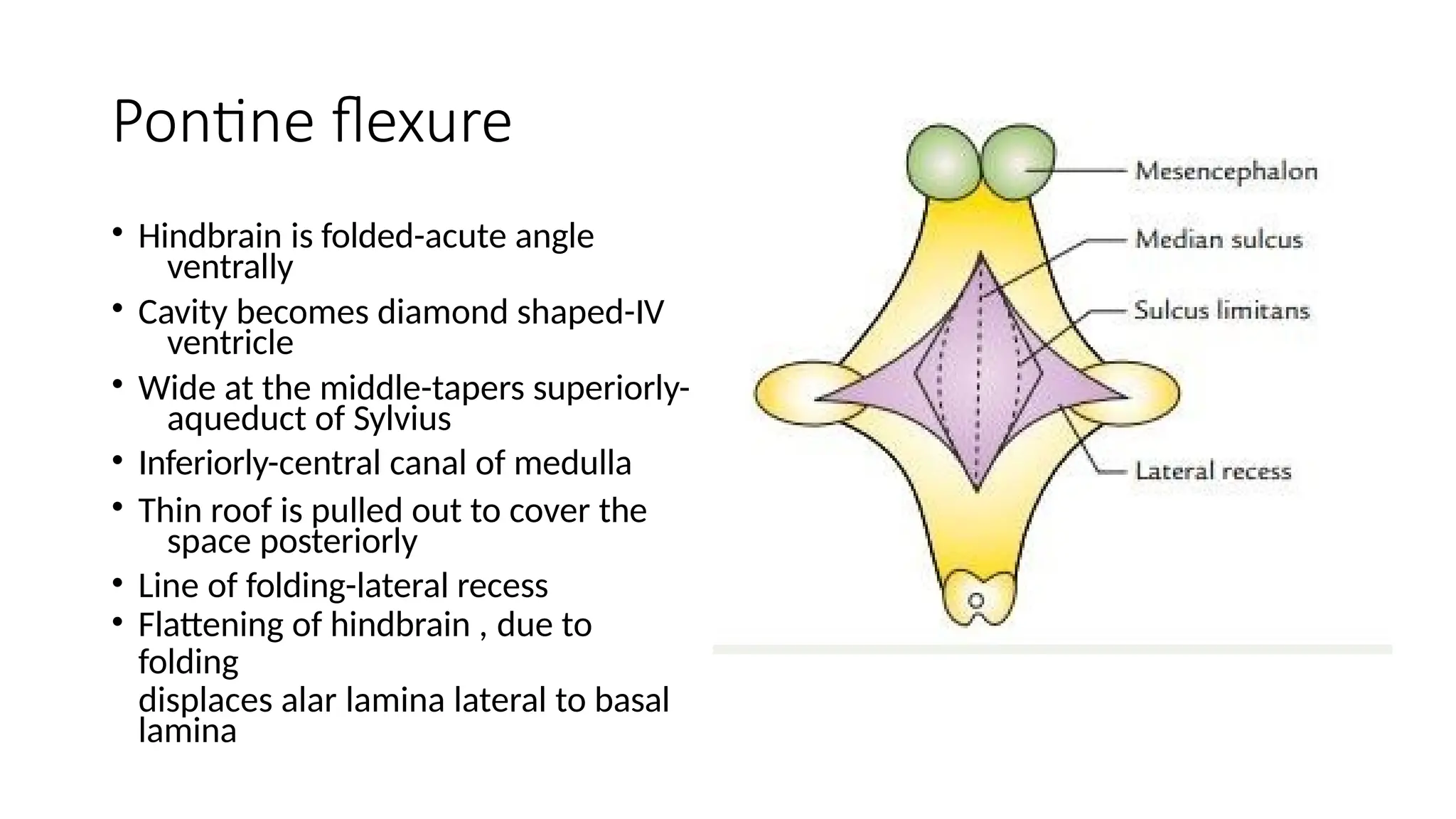
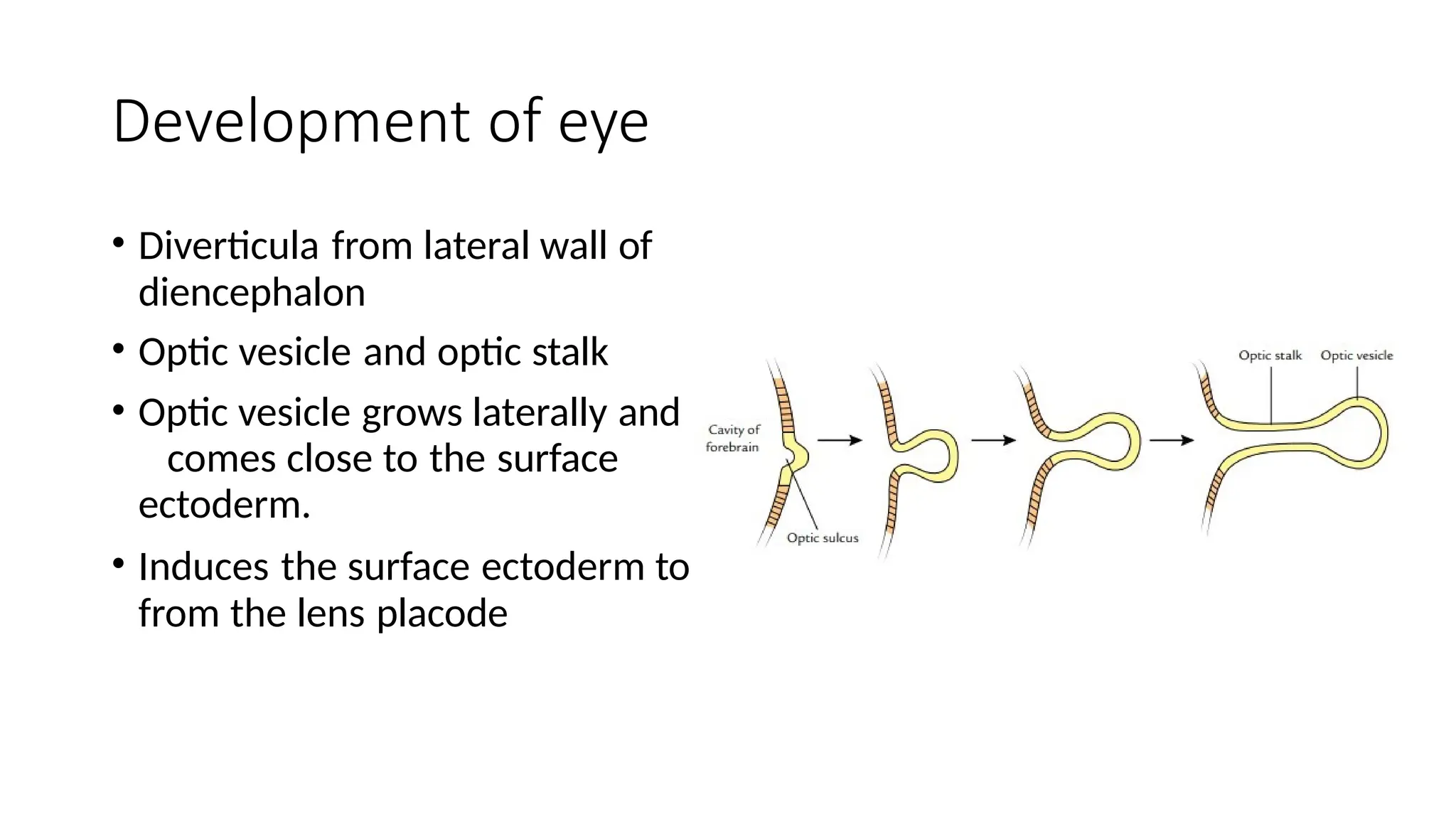
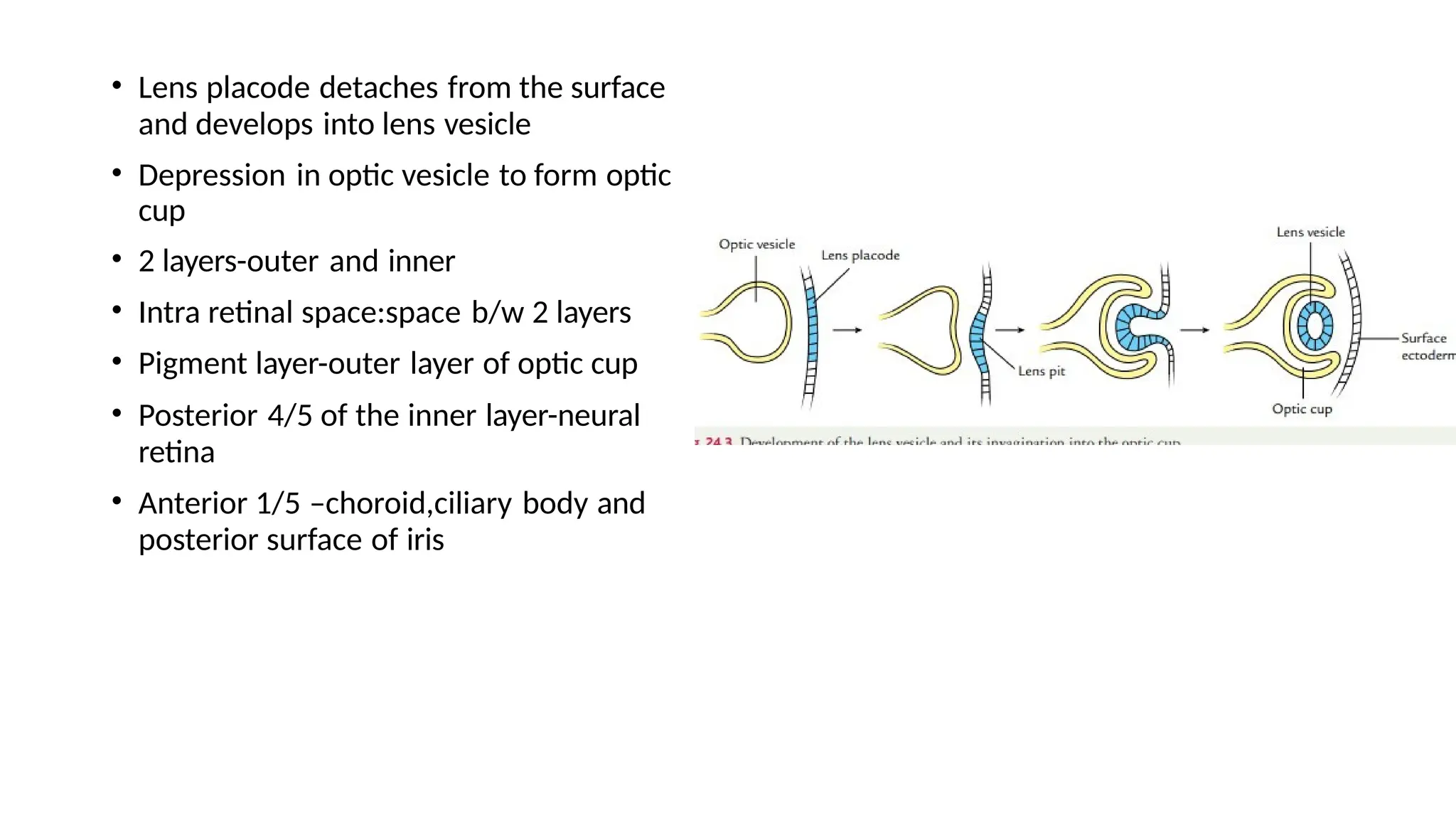
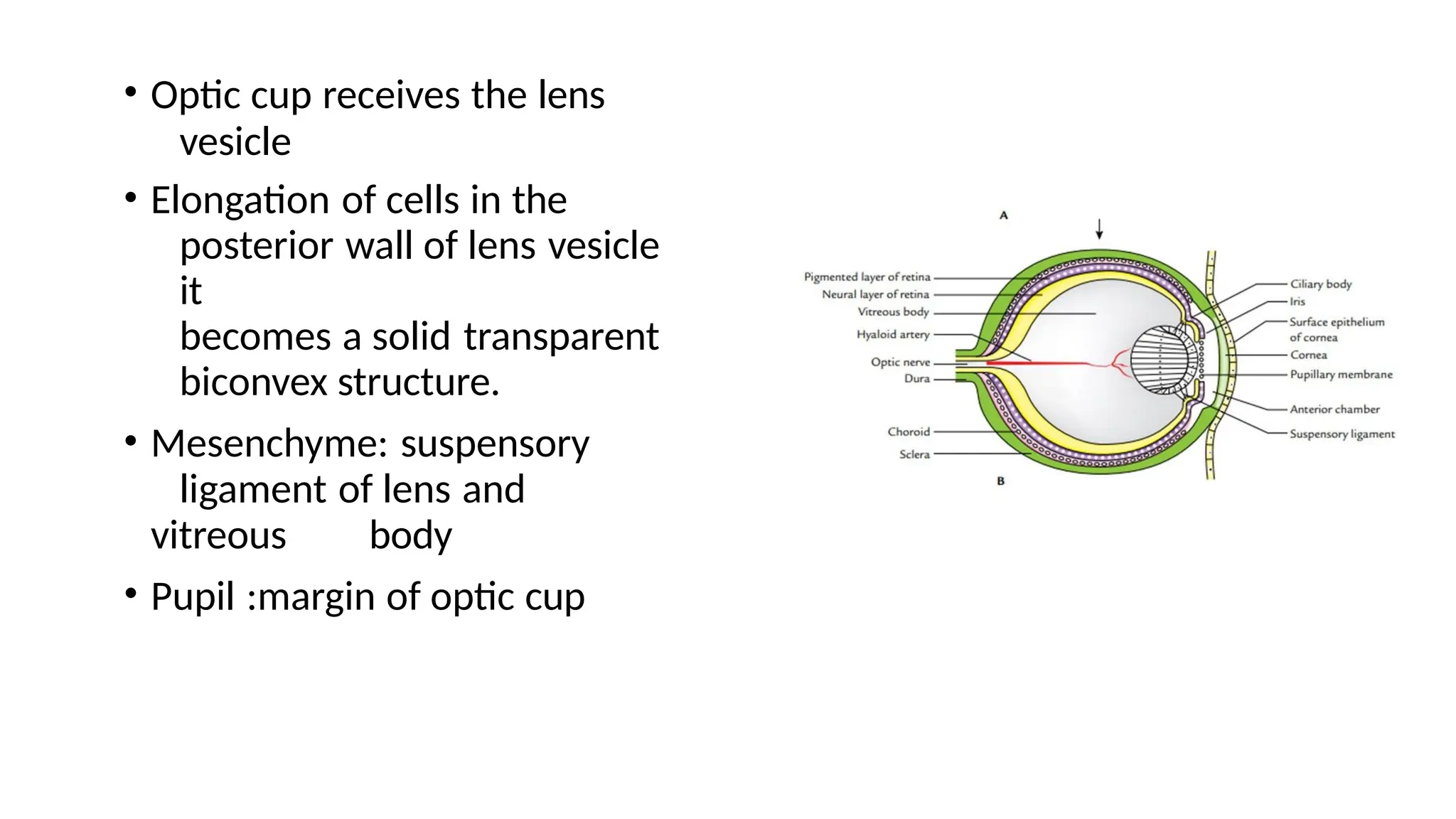
The document outlines the development of the central nervous system (CNS), detailing the process of neurulation, spinal cord formation, and the progression of brain structures including primary and secondary brain vesicles. It describes the formation of the eye and ear, highlighting key anatomical changes such as the development of optic structures and the division of the ear into external and middle components. Comprehensive stages of growth and structural organization within the CNS are emphasized throughout the document.