Embed presentation
Download to read offline





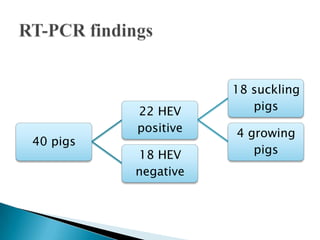
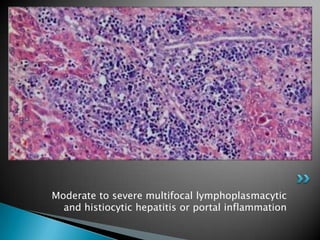
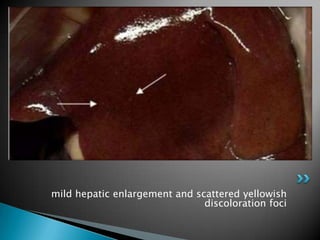
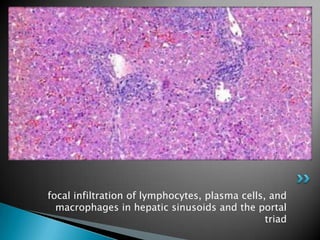

This document summarizes the detection of swine hepatitis E virus (HEV) in pig livers in Jeju Island, South Korea. Liver samples from pigs showed mild to moderate multifocal hepatitis and portal inflammation. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing detected swine HEV infection in the liver tissue. The conclusions are that swine HEV infection can occur in very young pigs and PCR methods are more sensitive for diagnosing infectious diseases compared to other tests.









