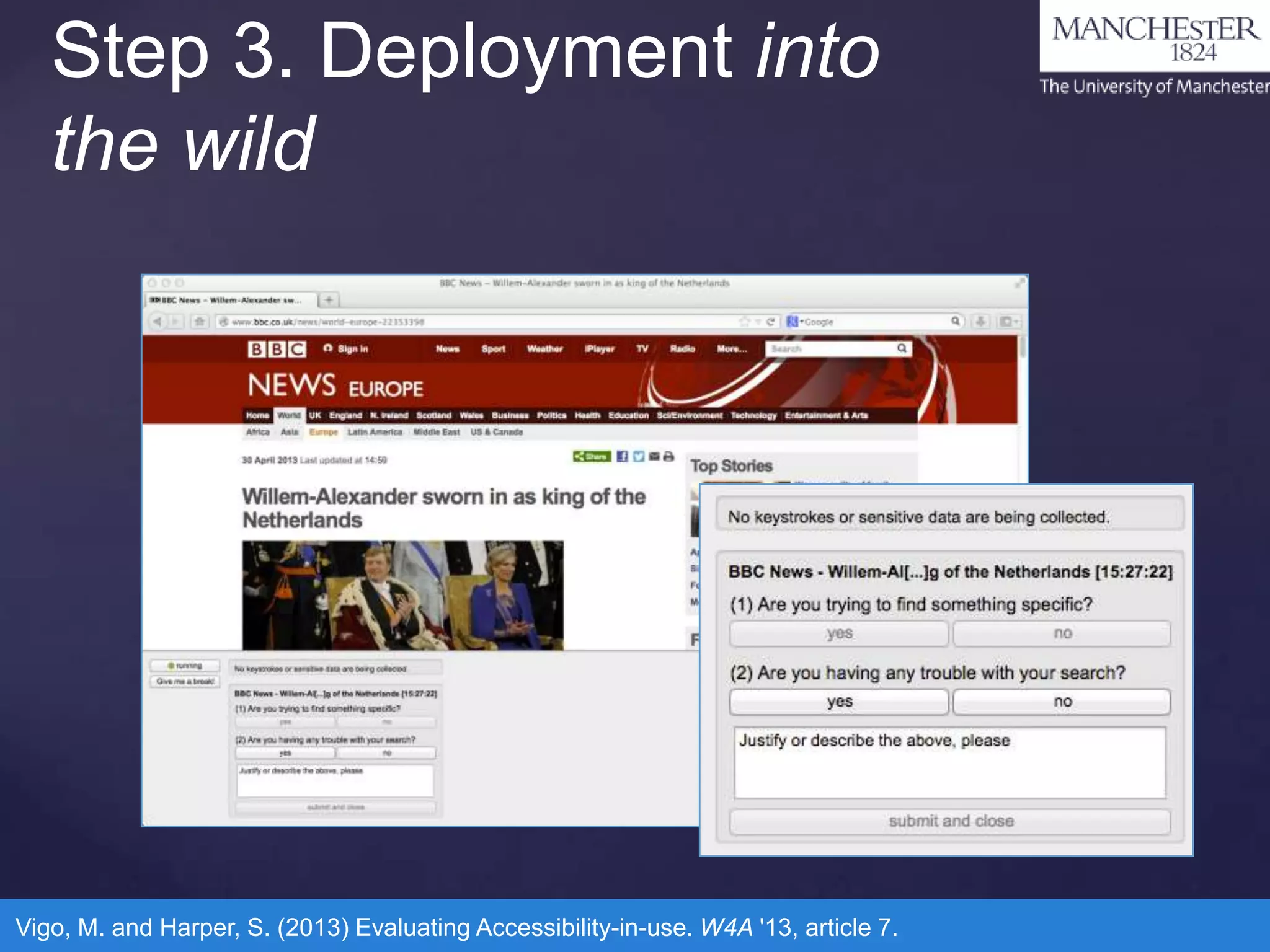
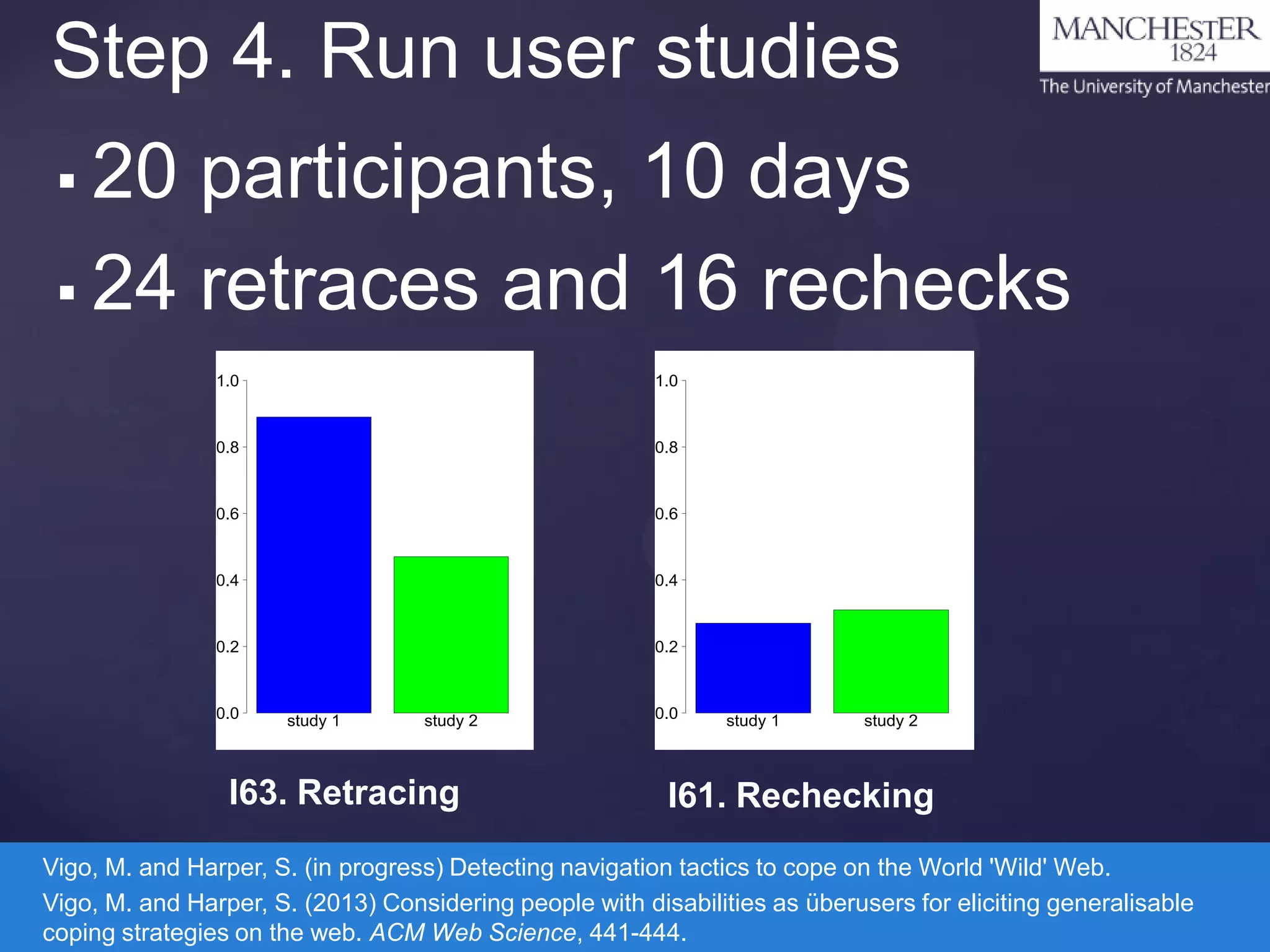
The document discusses the COPE project, which aims to identify coping strategies used by visually disabled users while interacting with the web and develop methods for automatic detection of these strategies. It proposes a four-step methodology involving observation, implementation of detection algorithms, deployment into the real world, and user studies to gather data and improve web accessibility. The findings indicate an overlap in the problems faced by users with disabilities and mainstream users, emphasizing the need for better accessibility solutions.