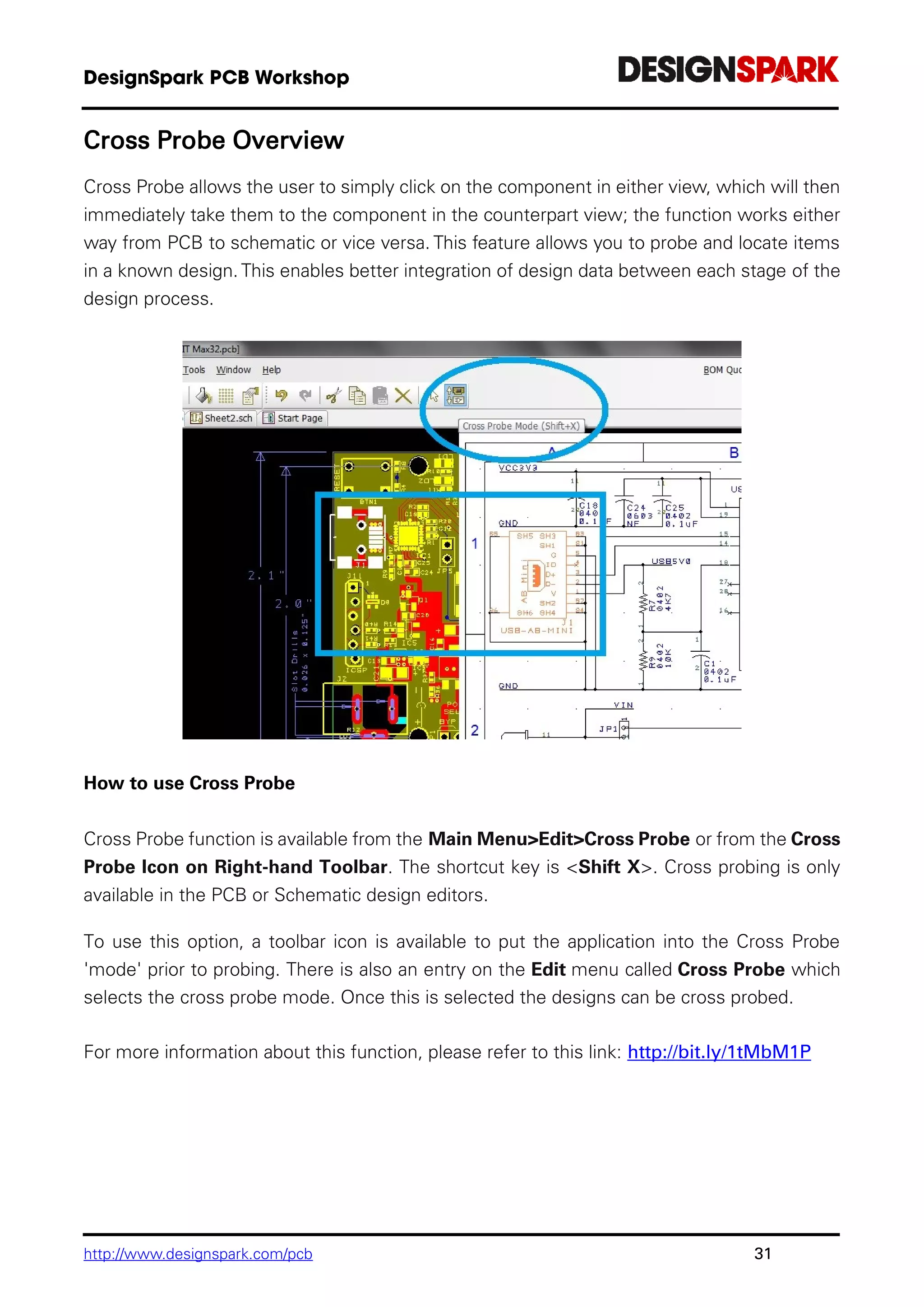
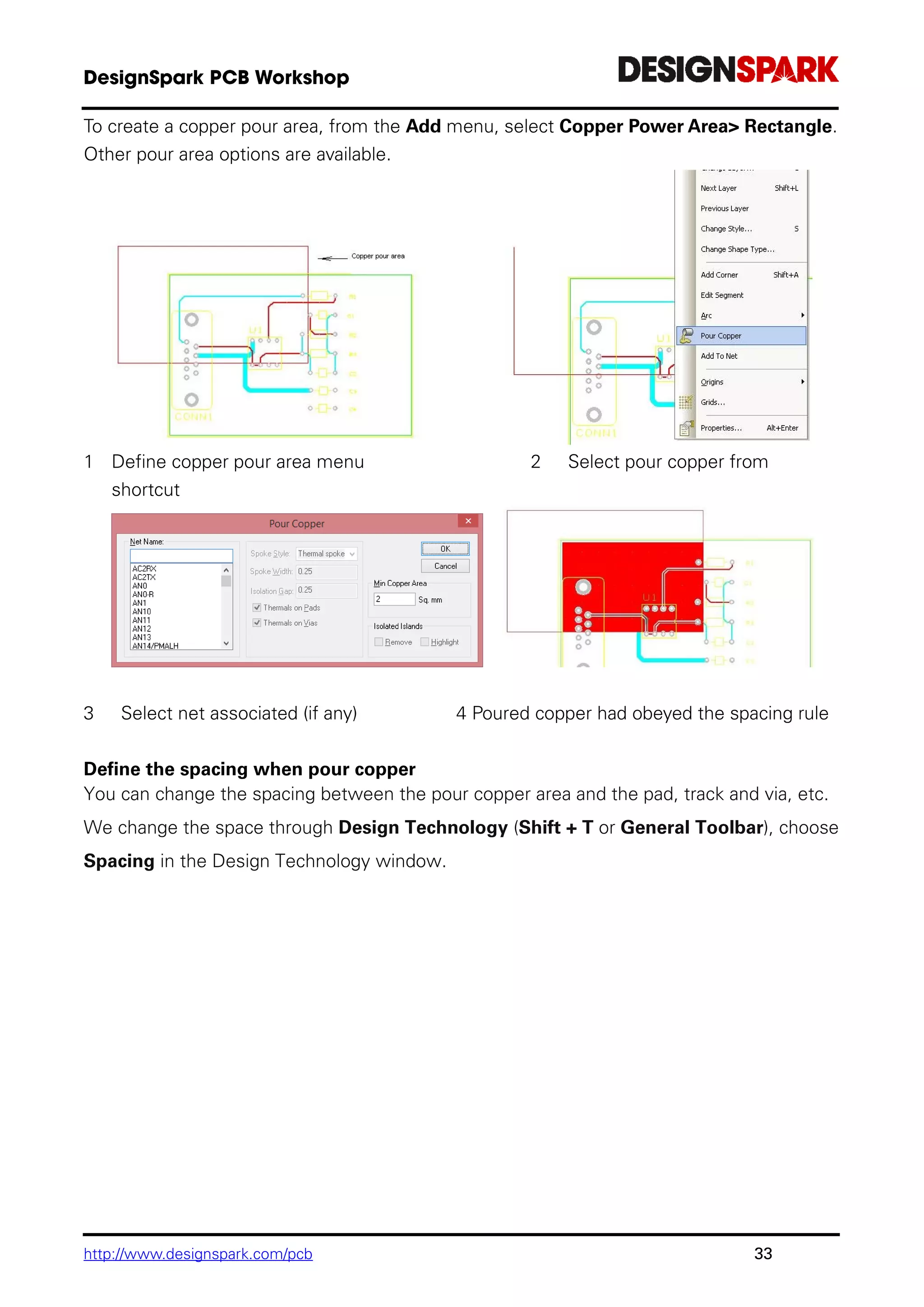
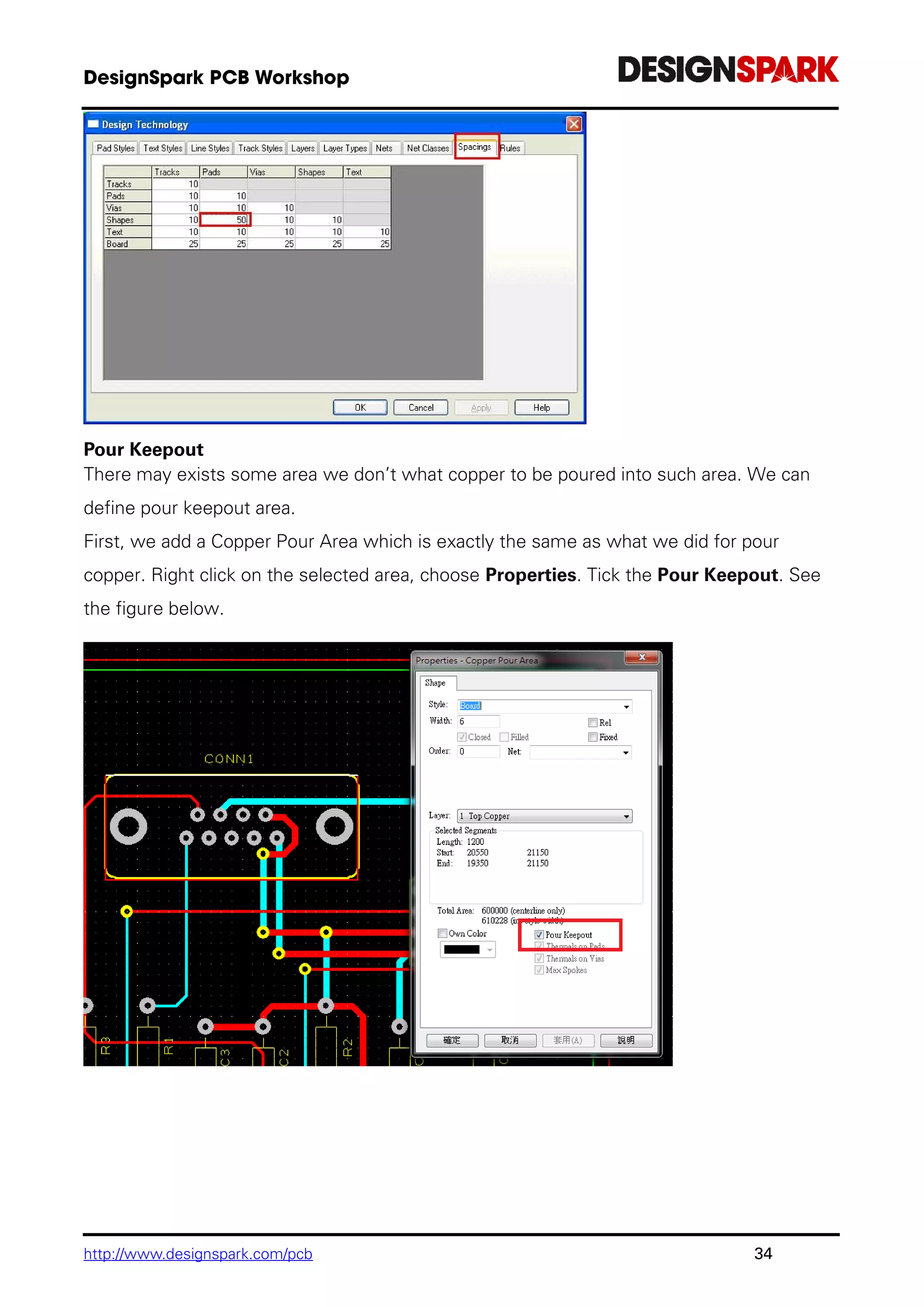
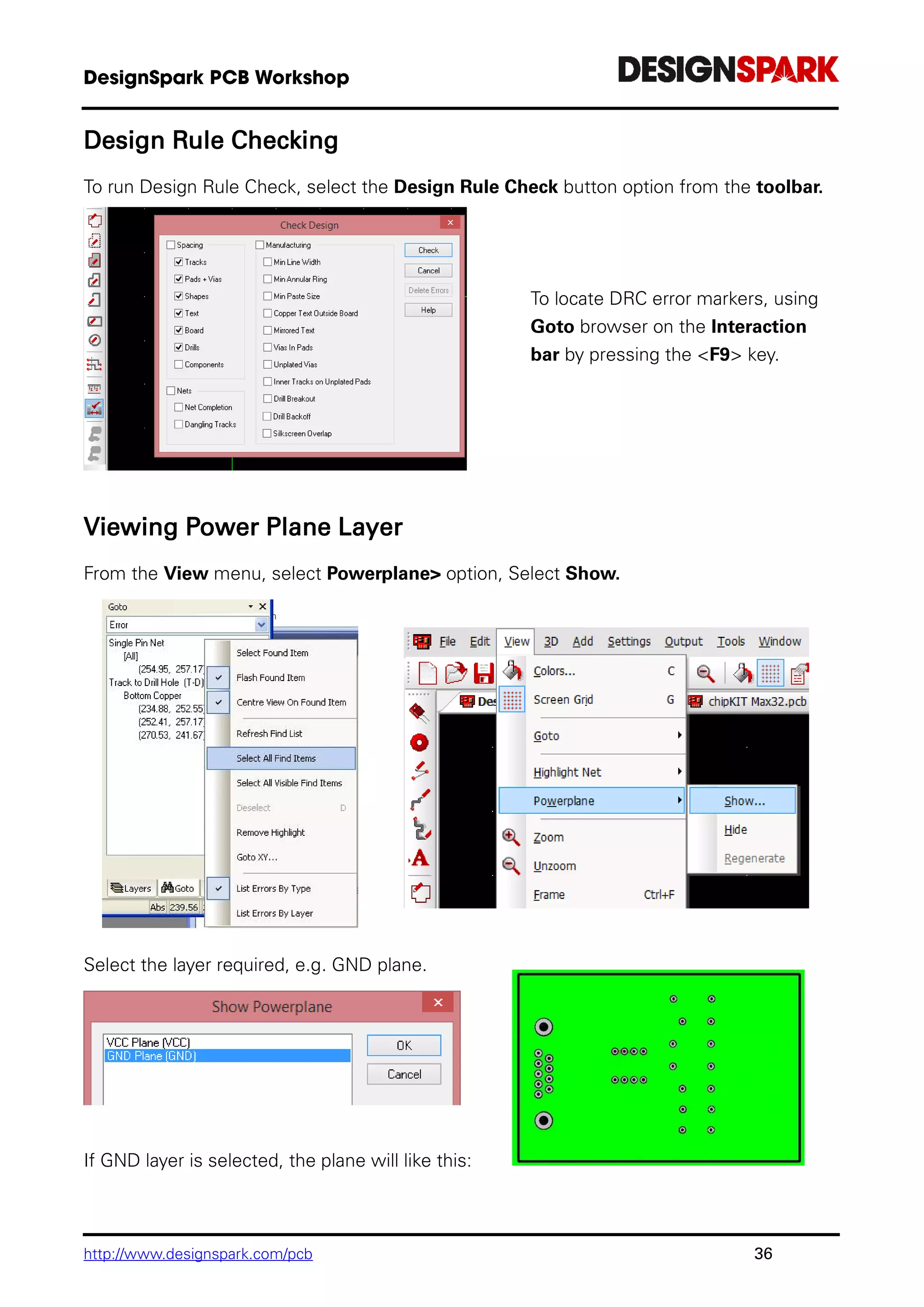
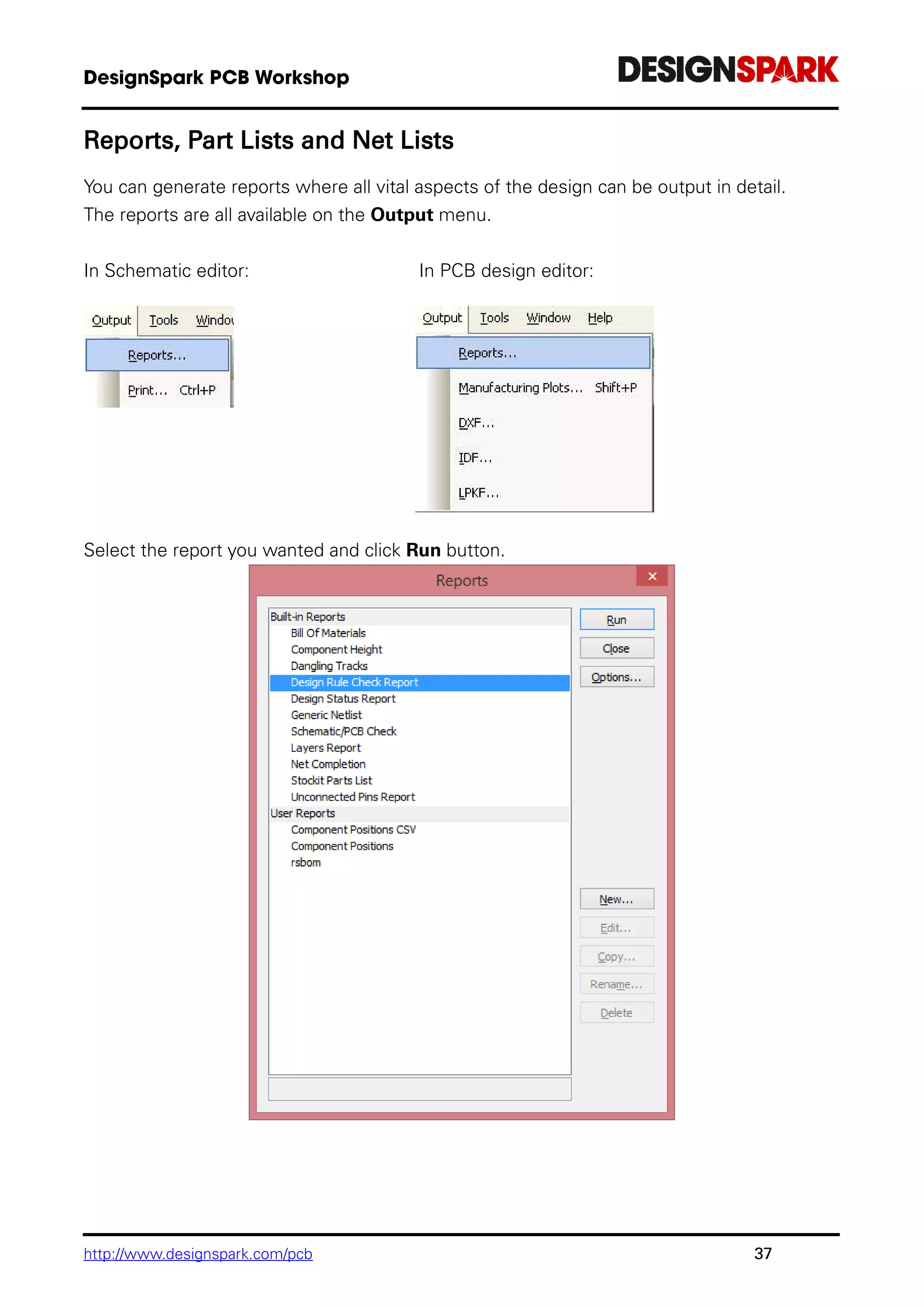
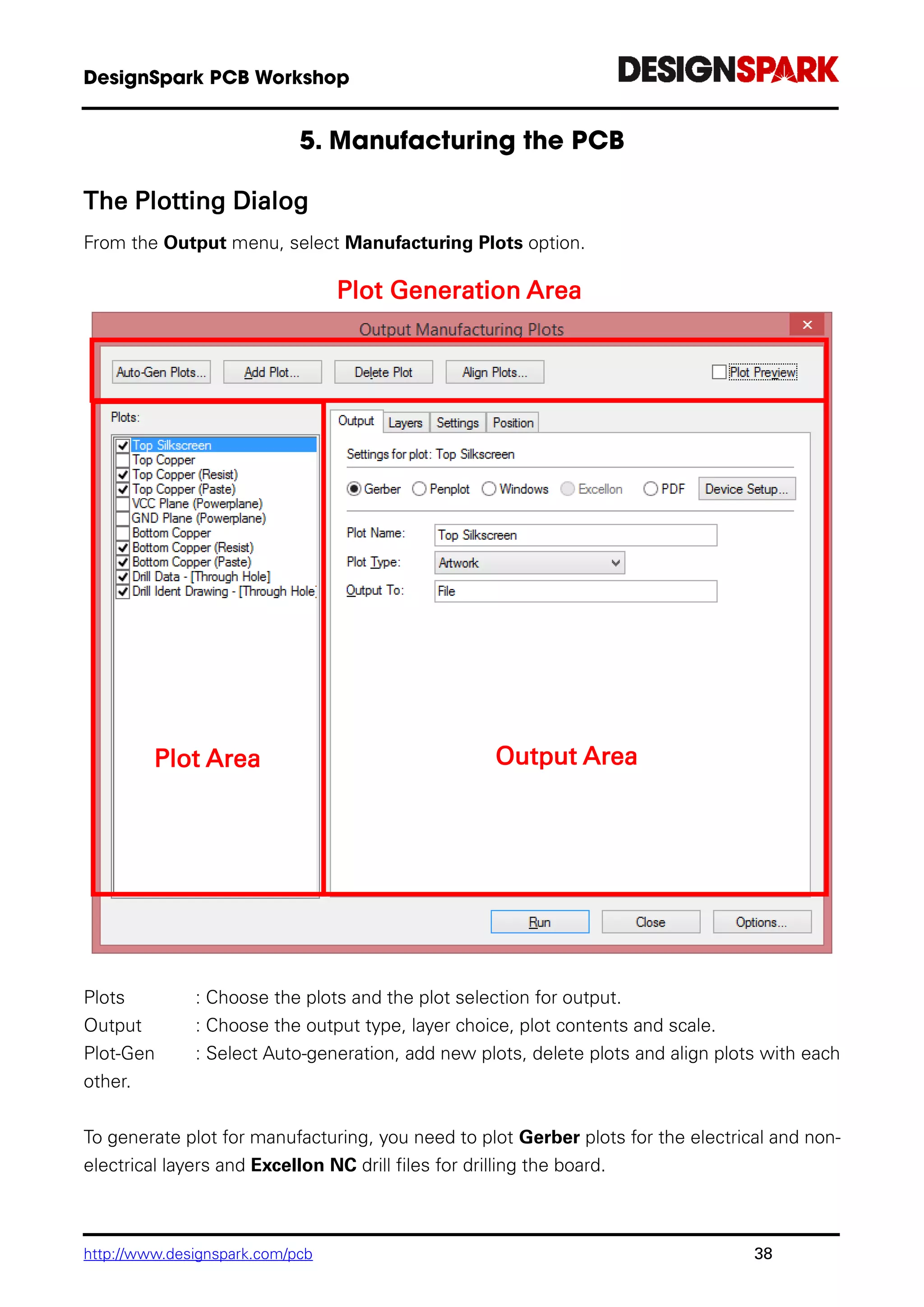
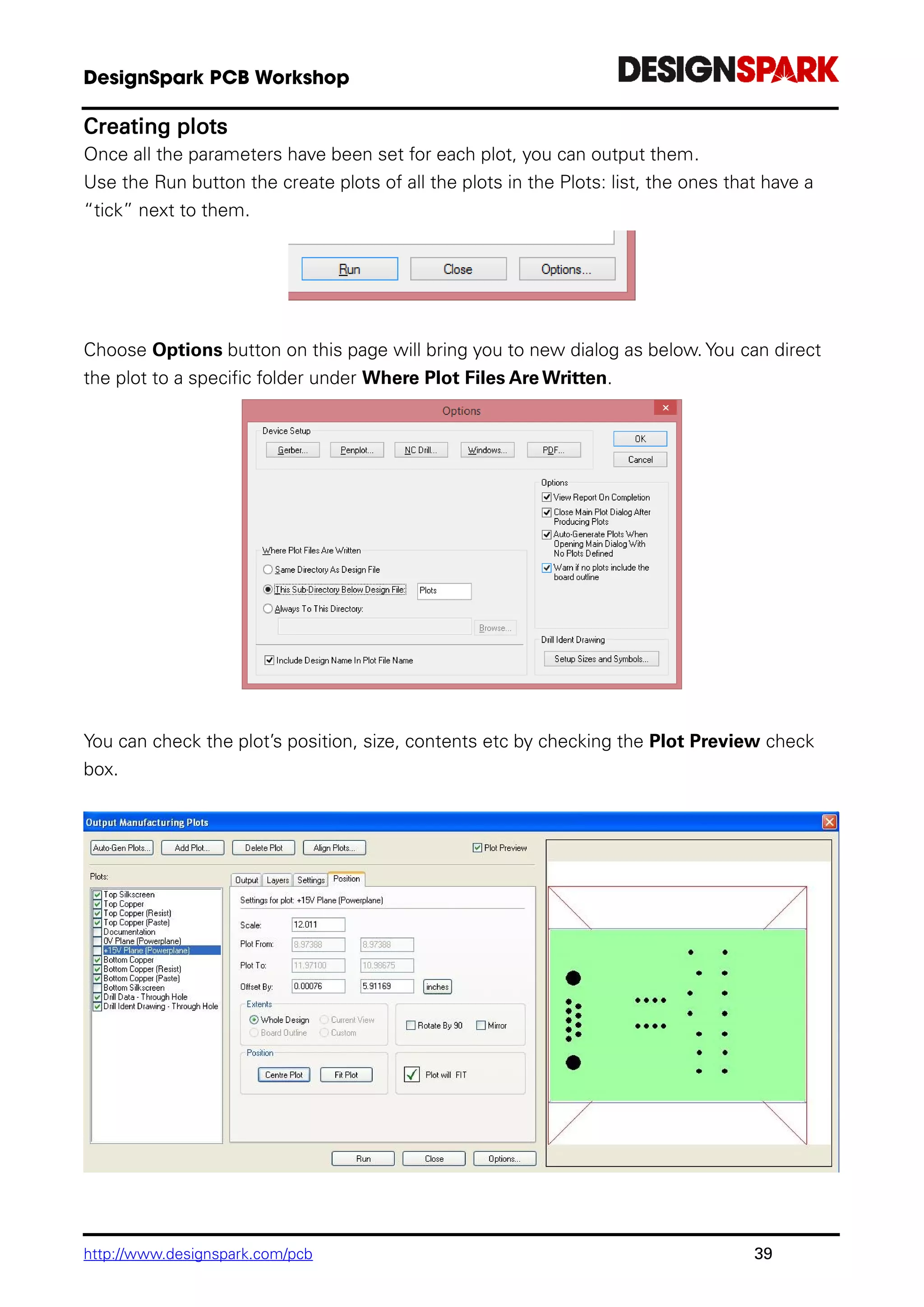
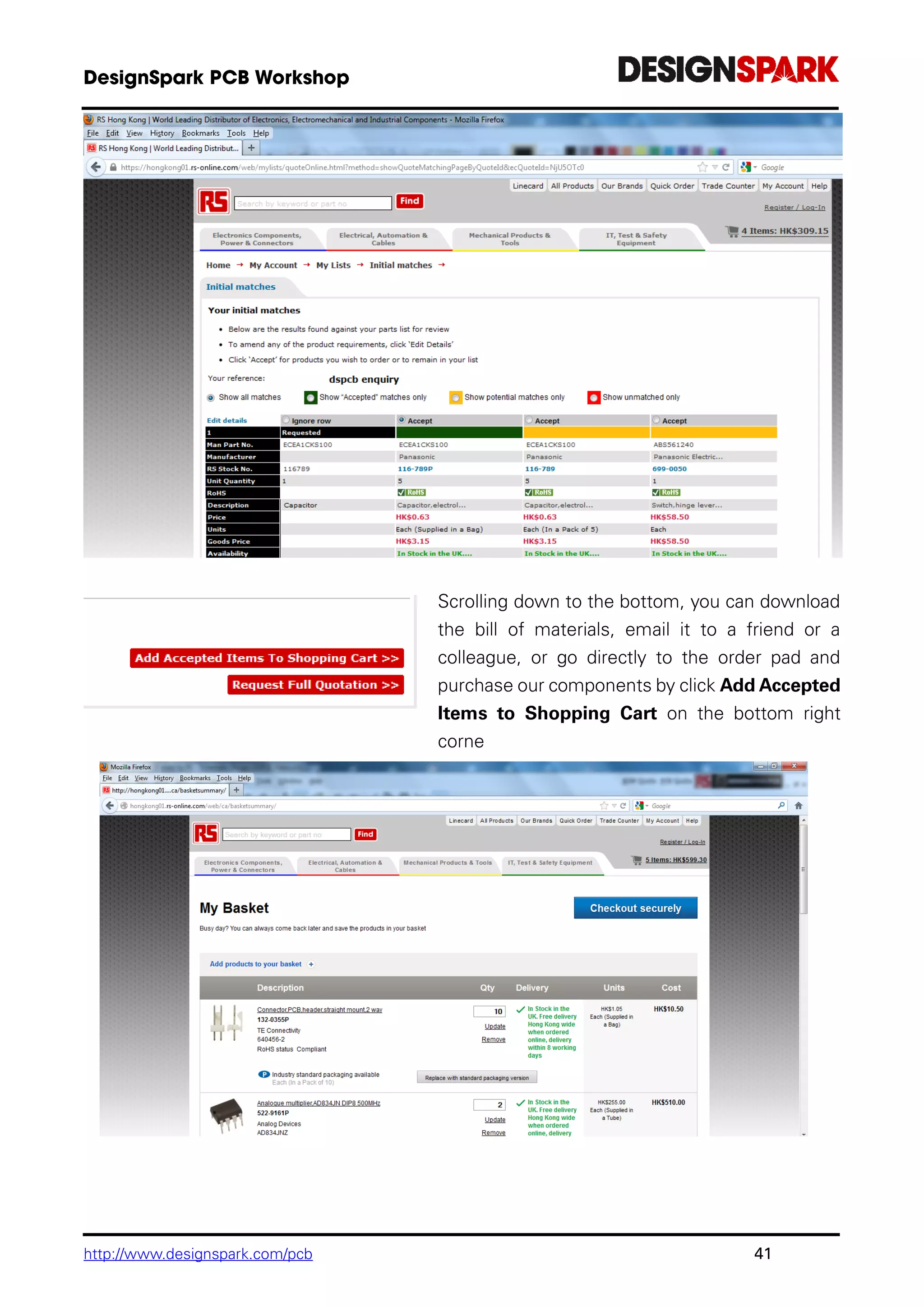
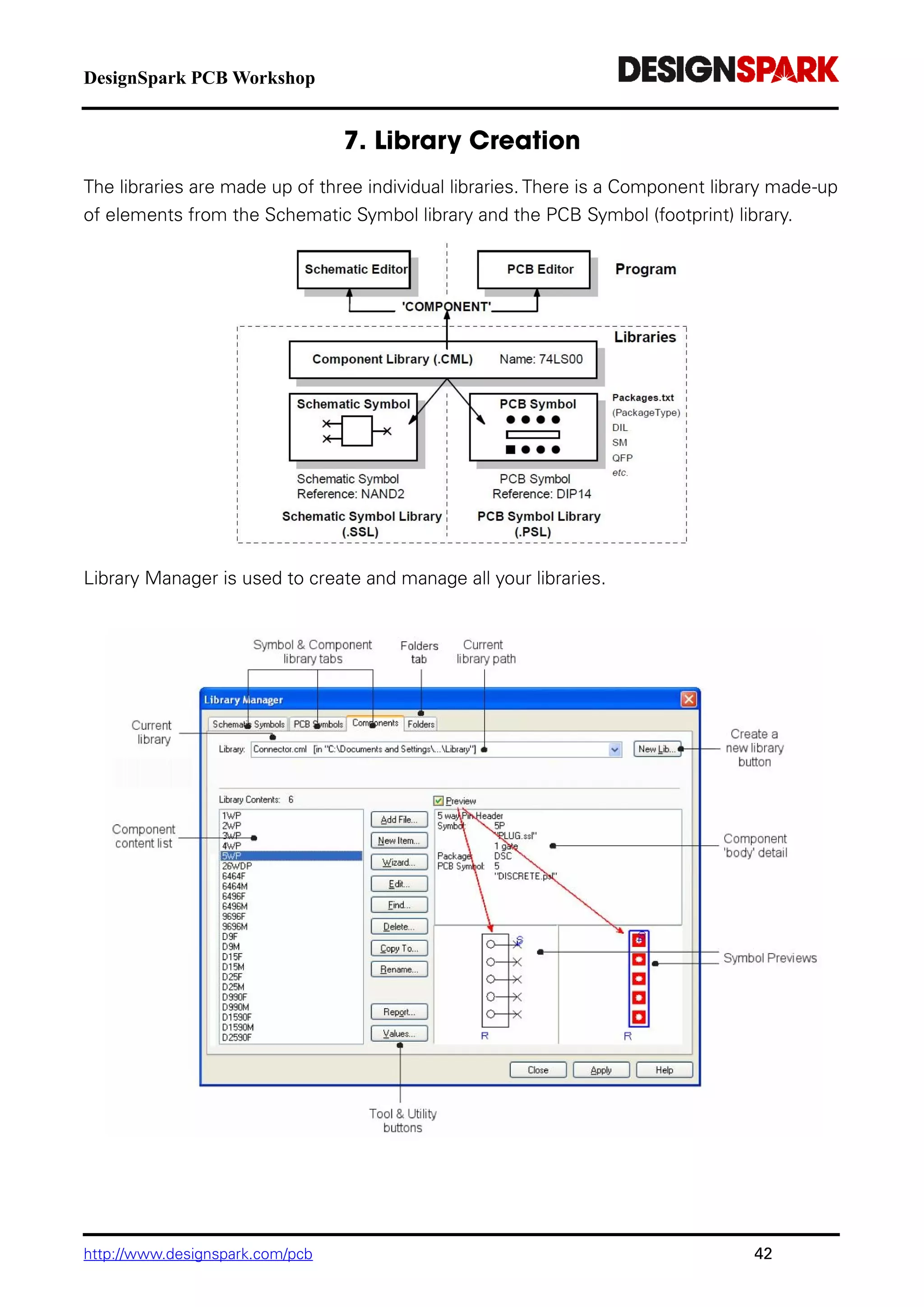
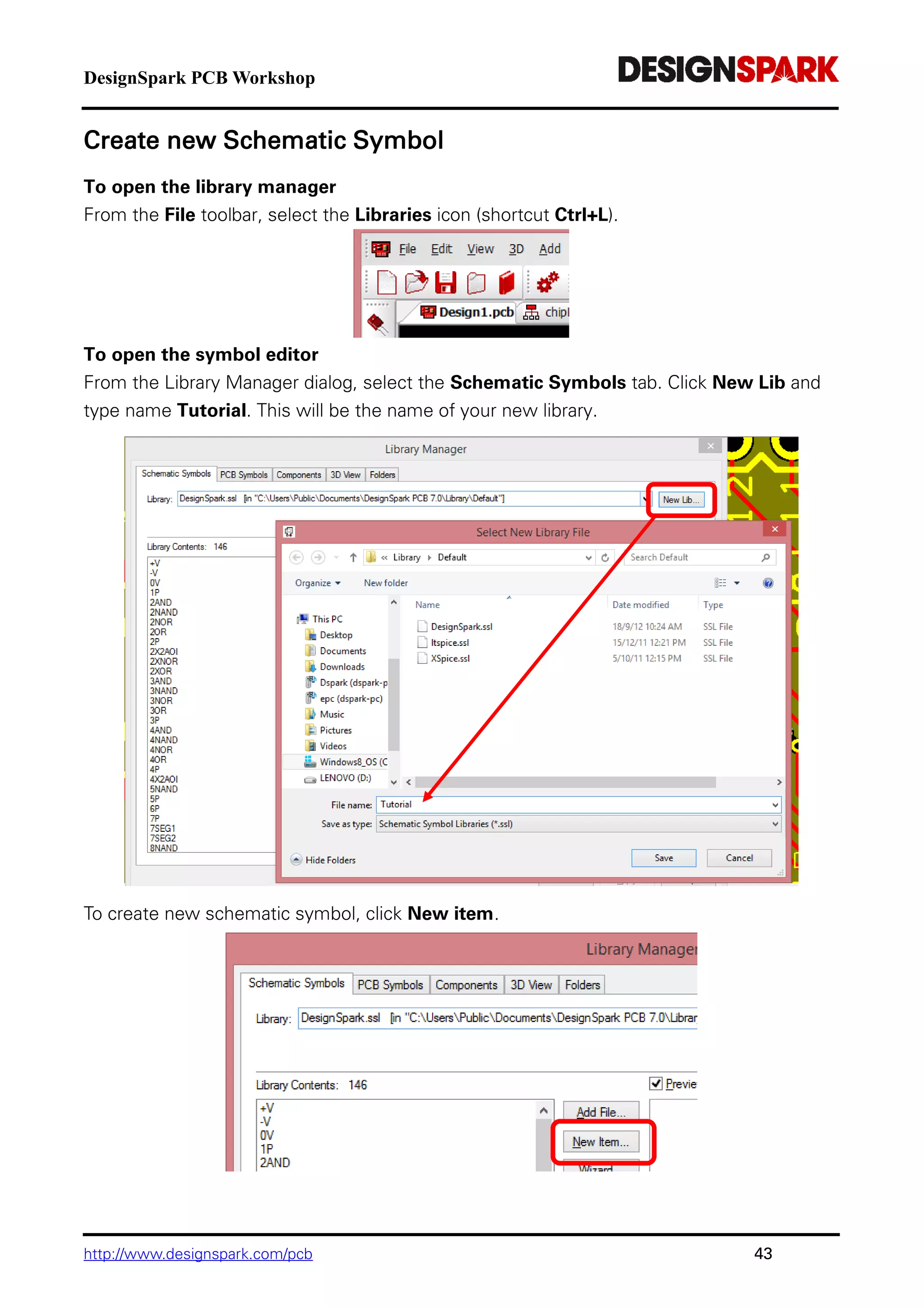
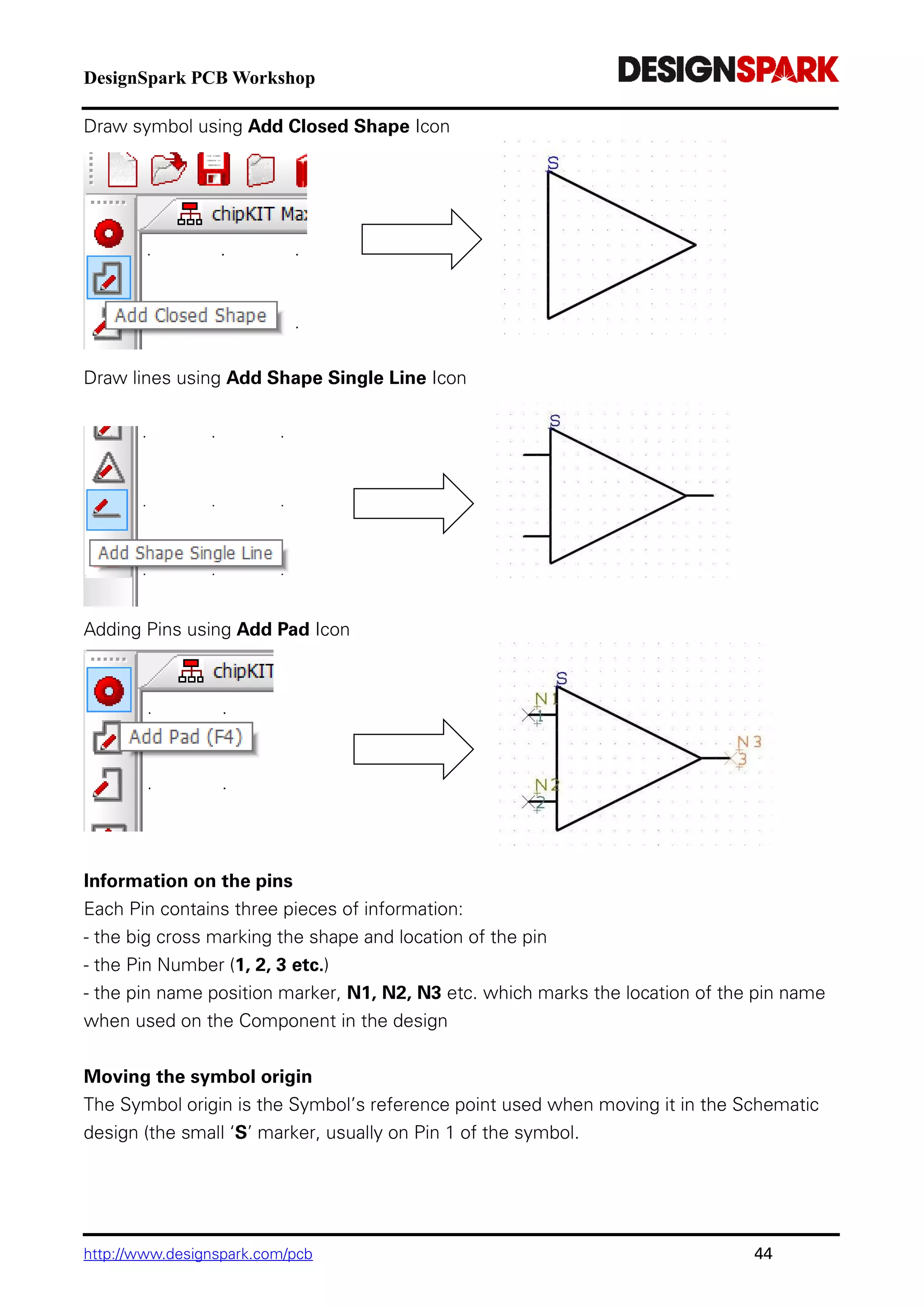
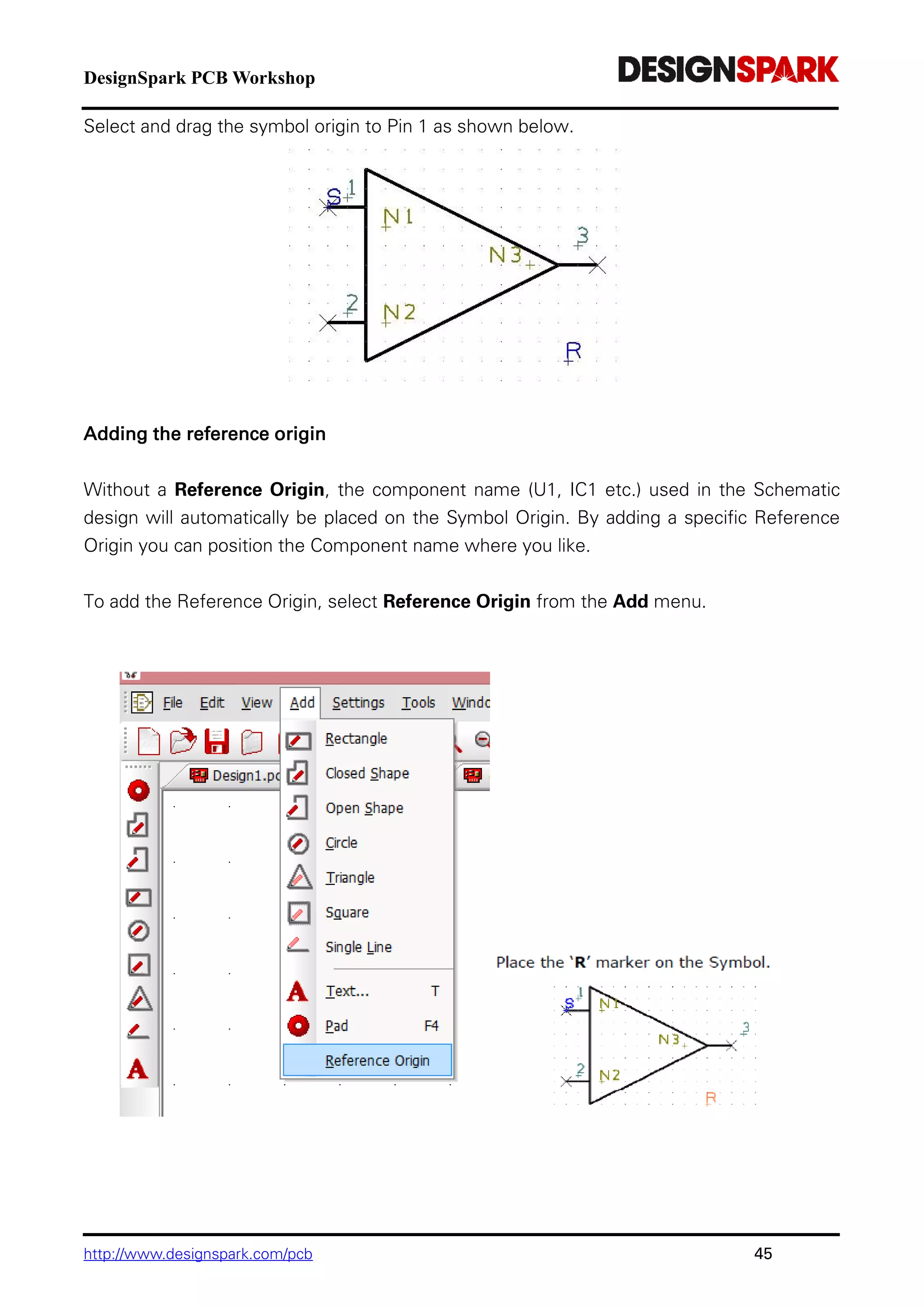
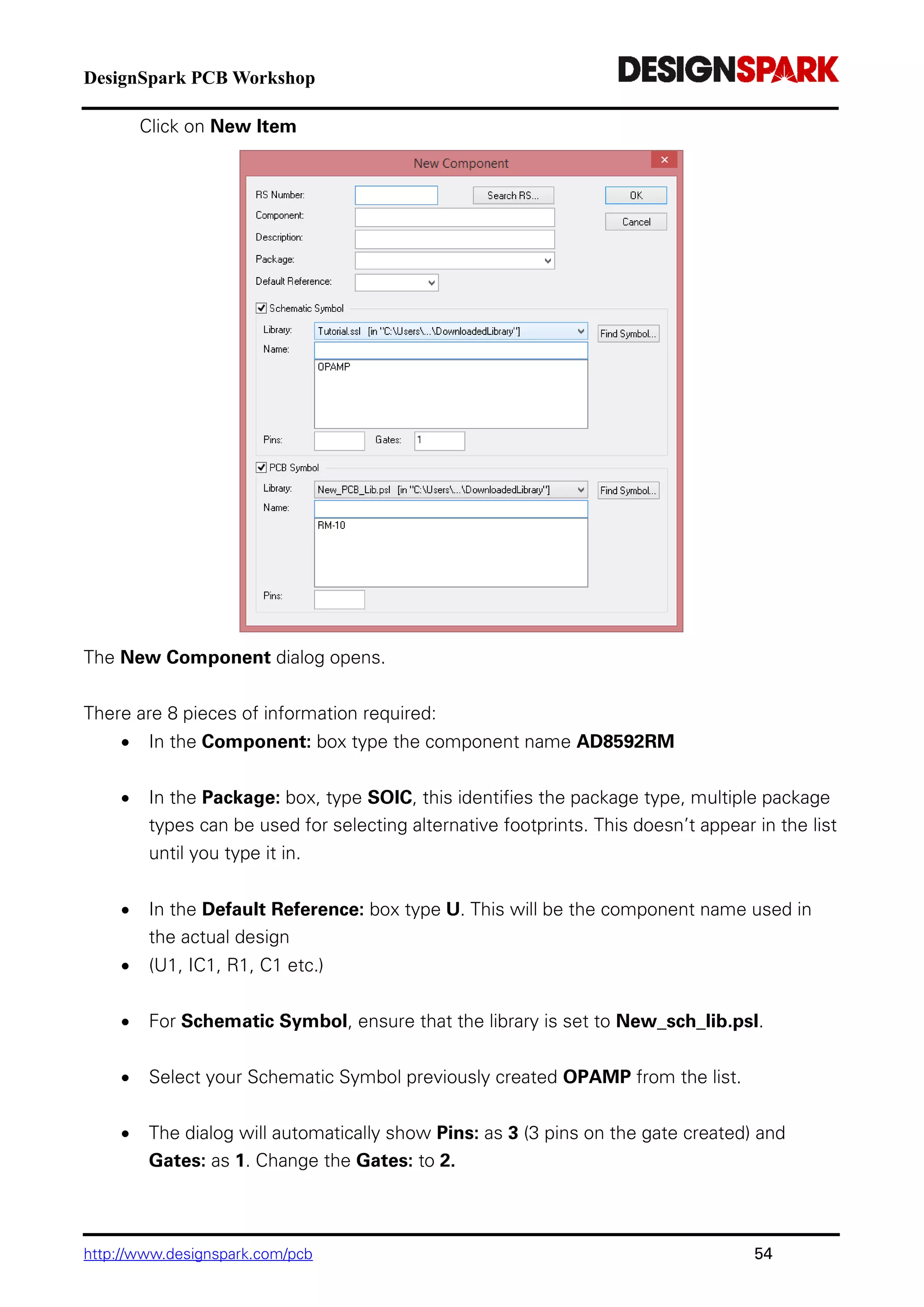
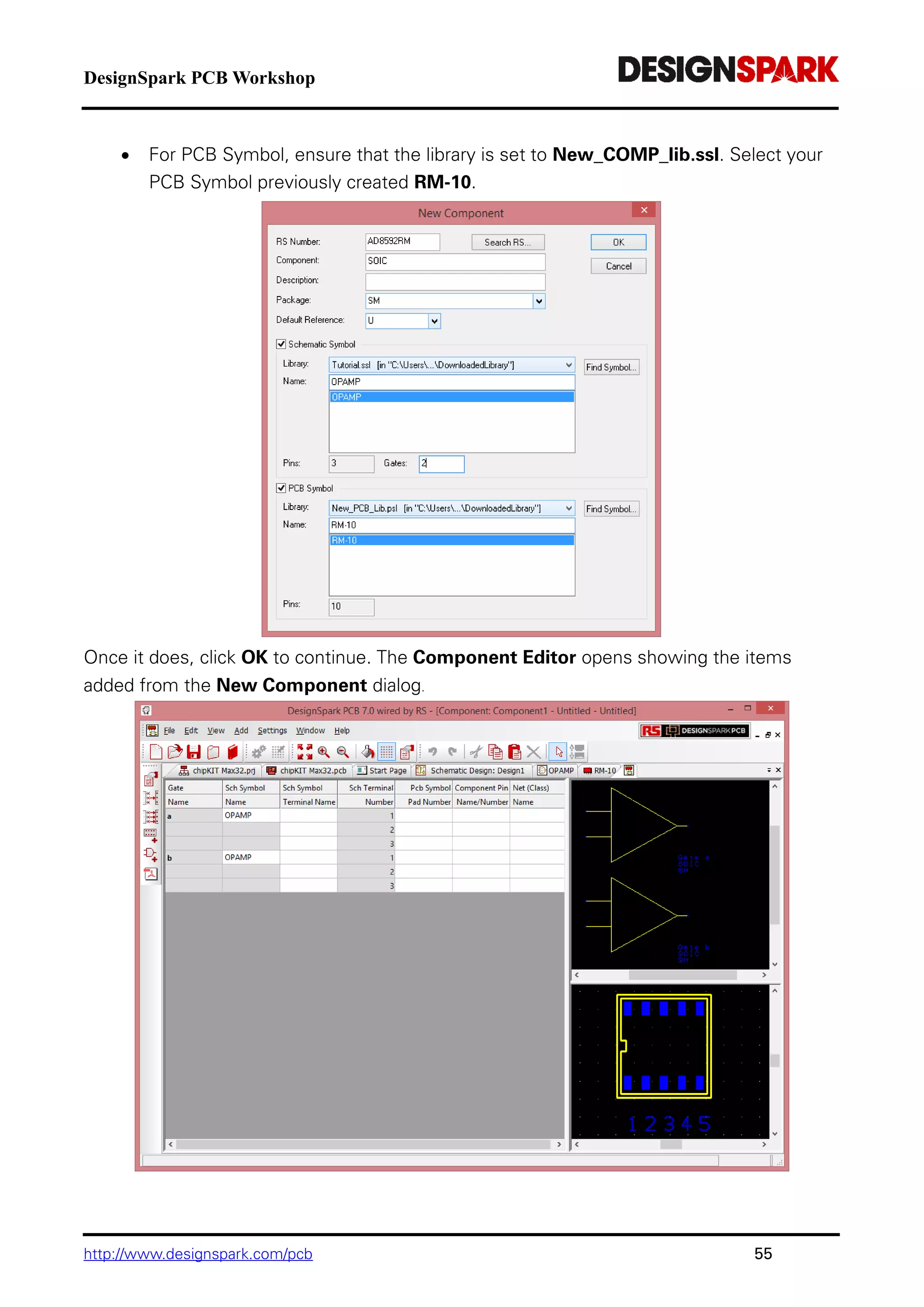
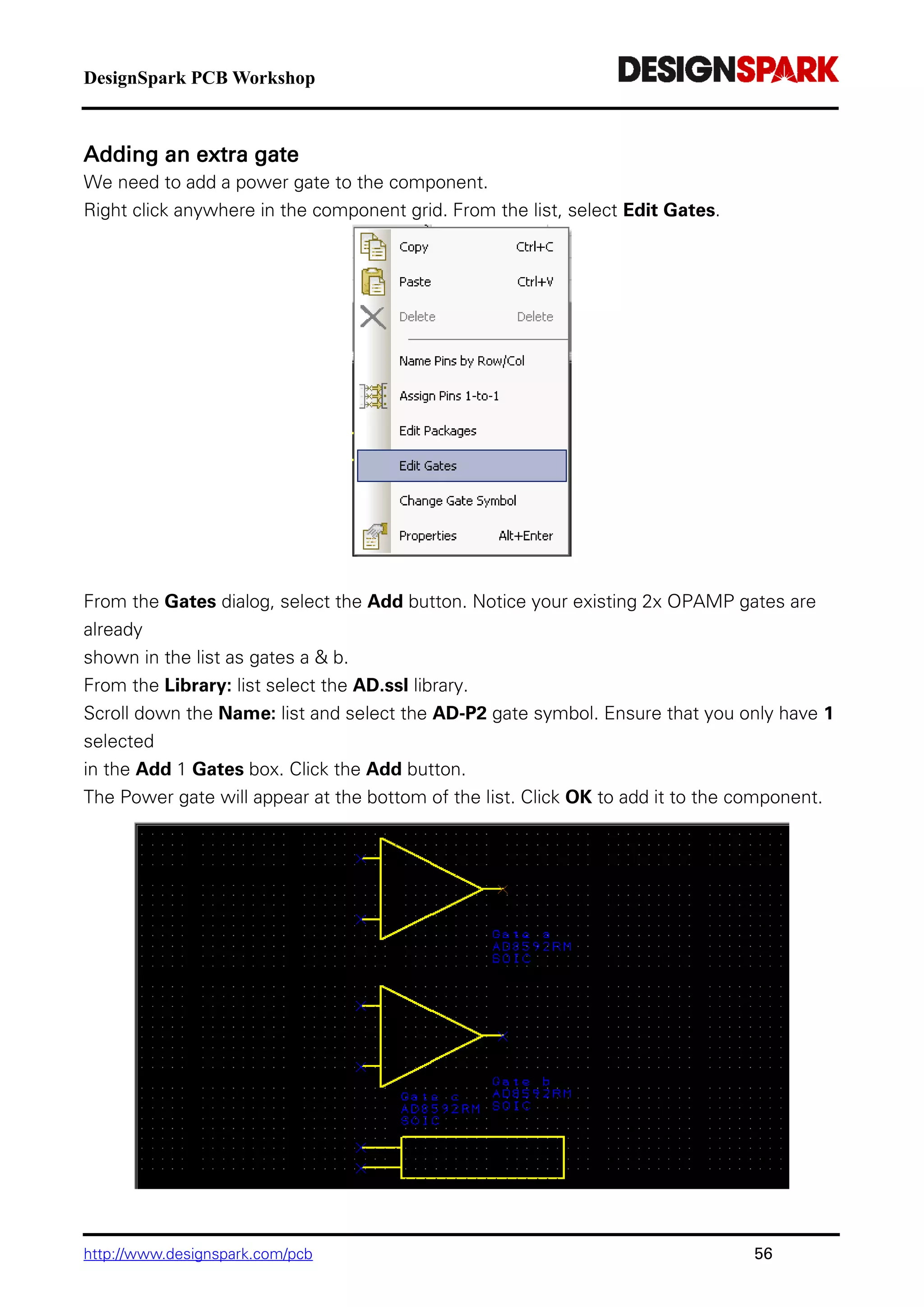
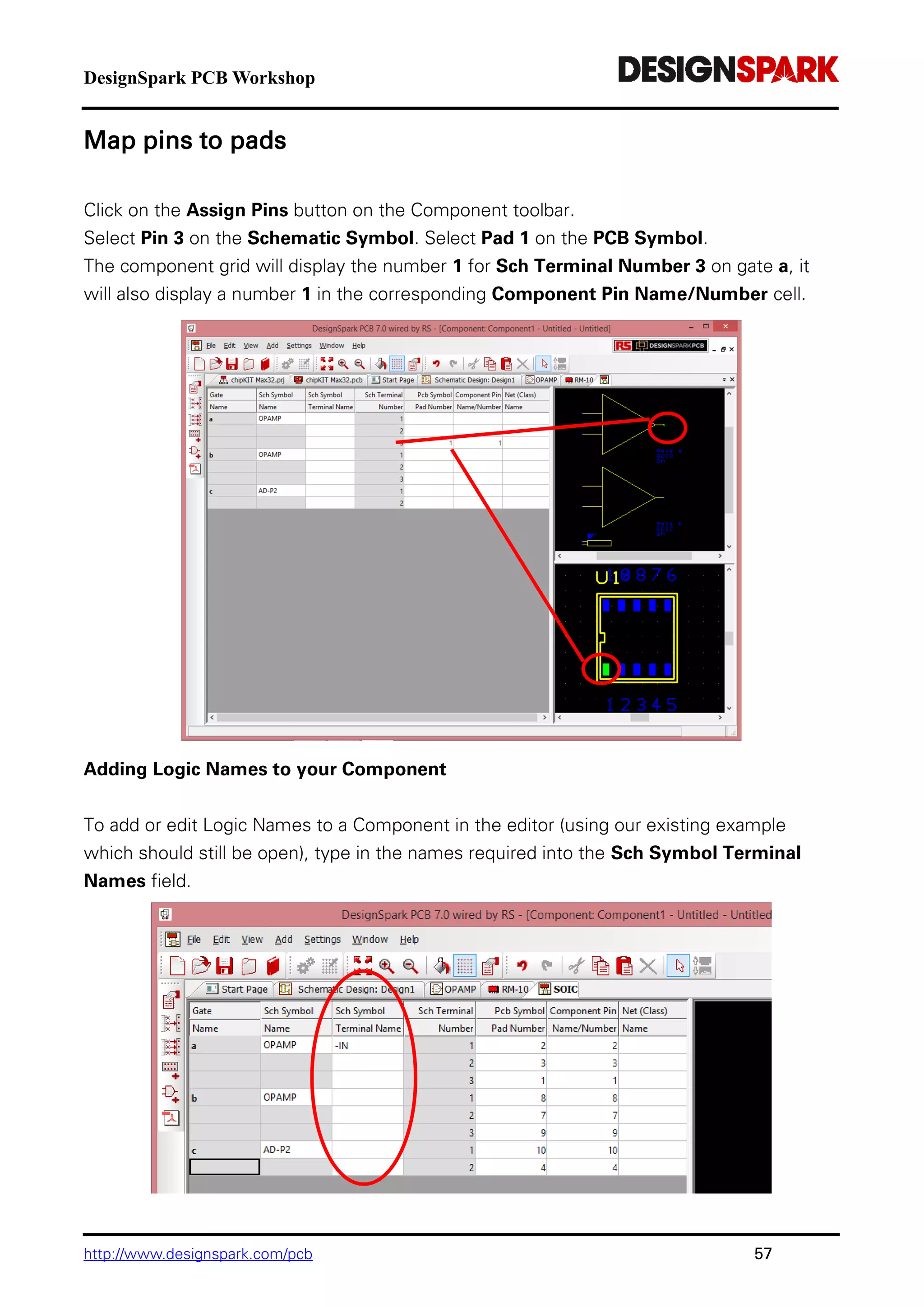
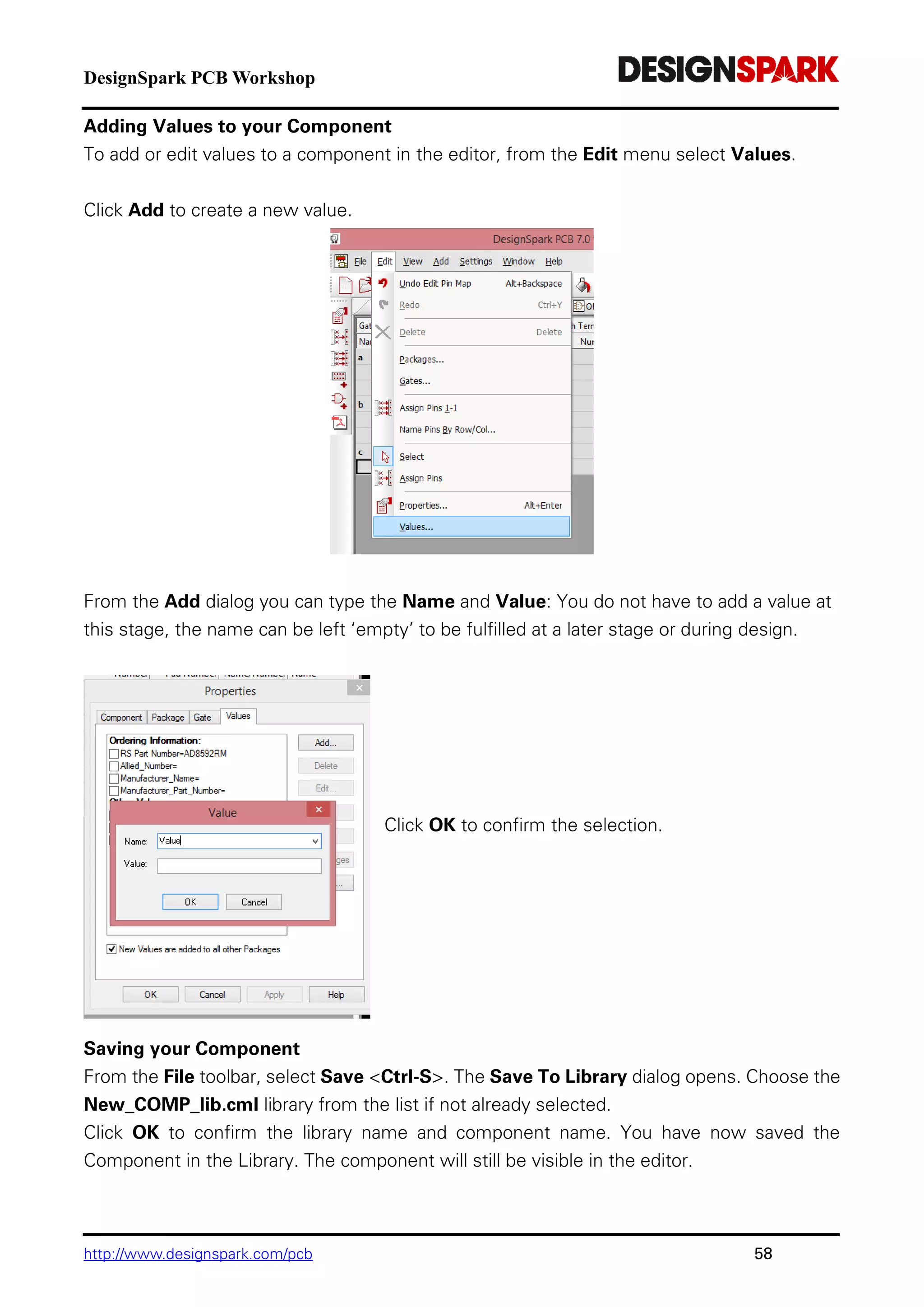
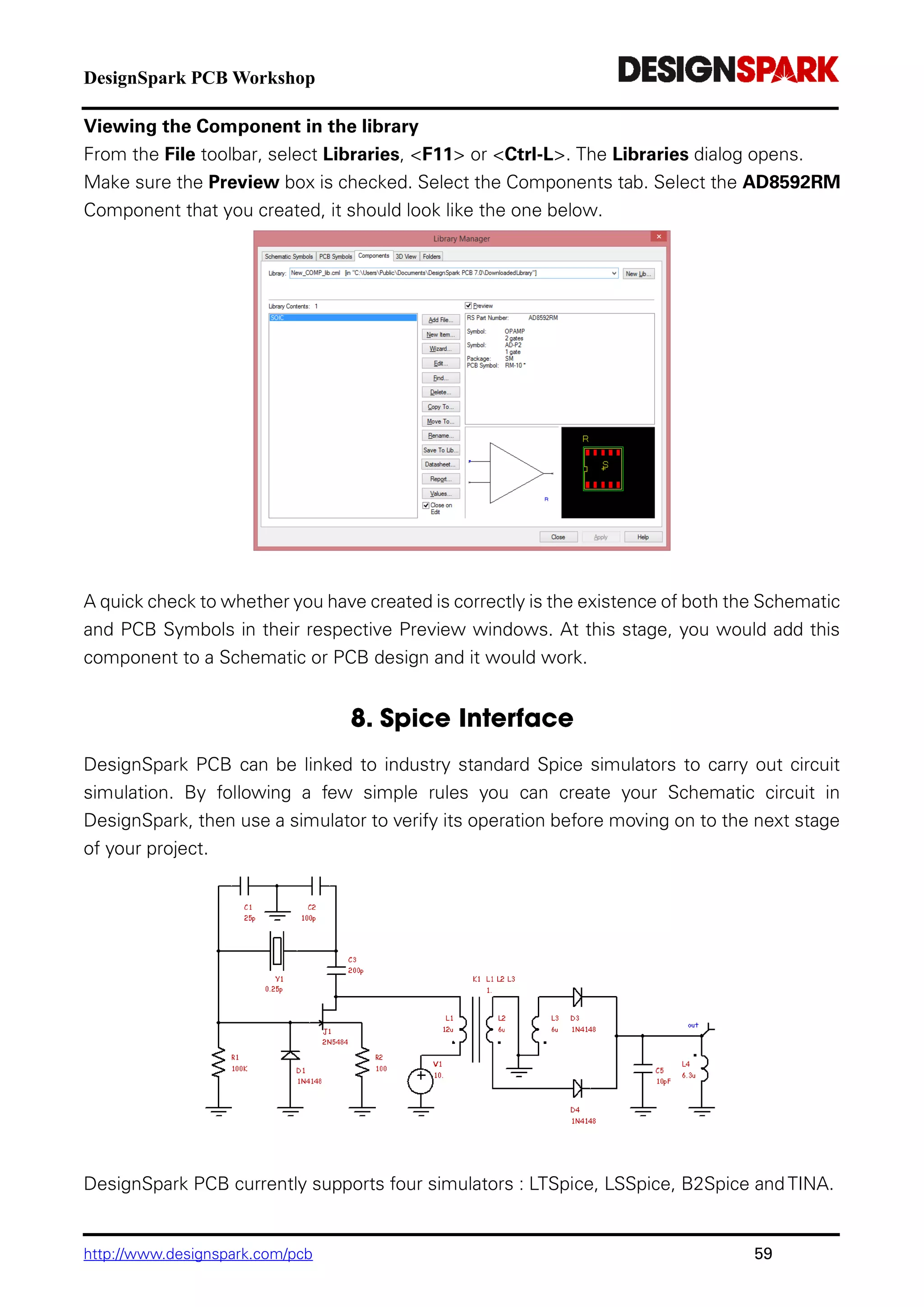
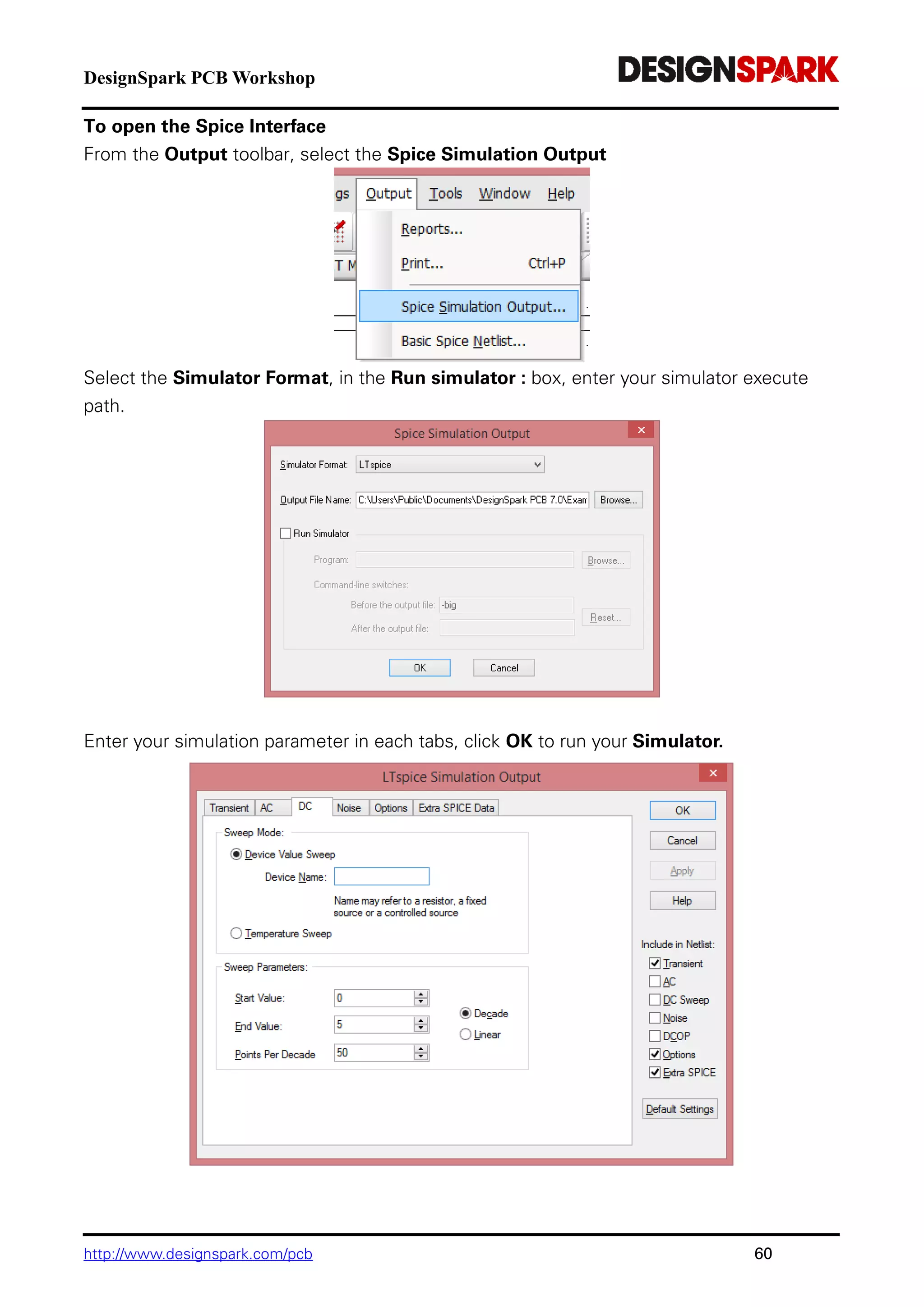
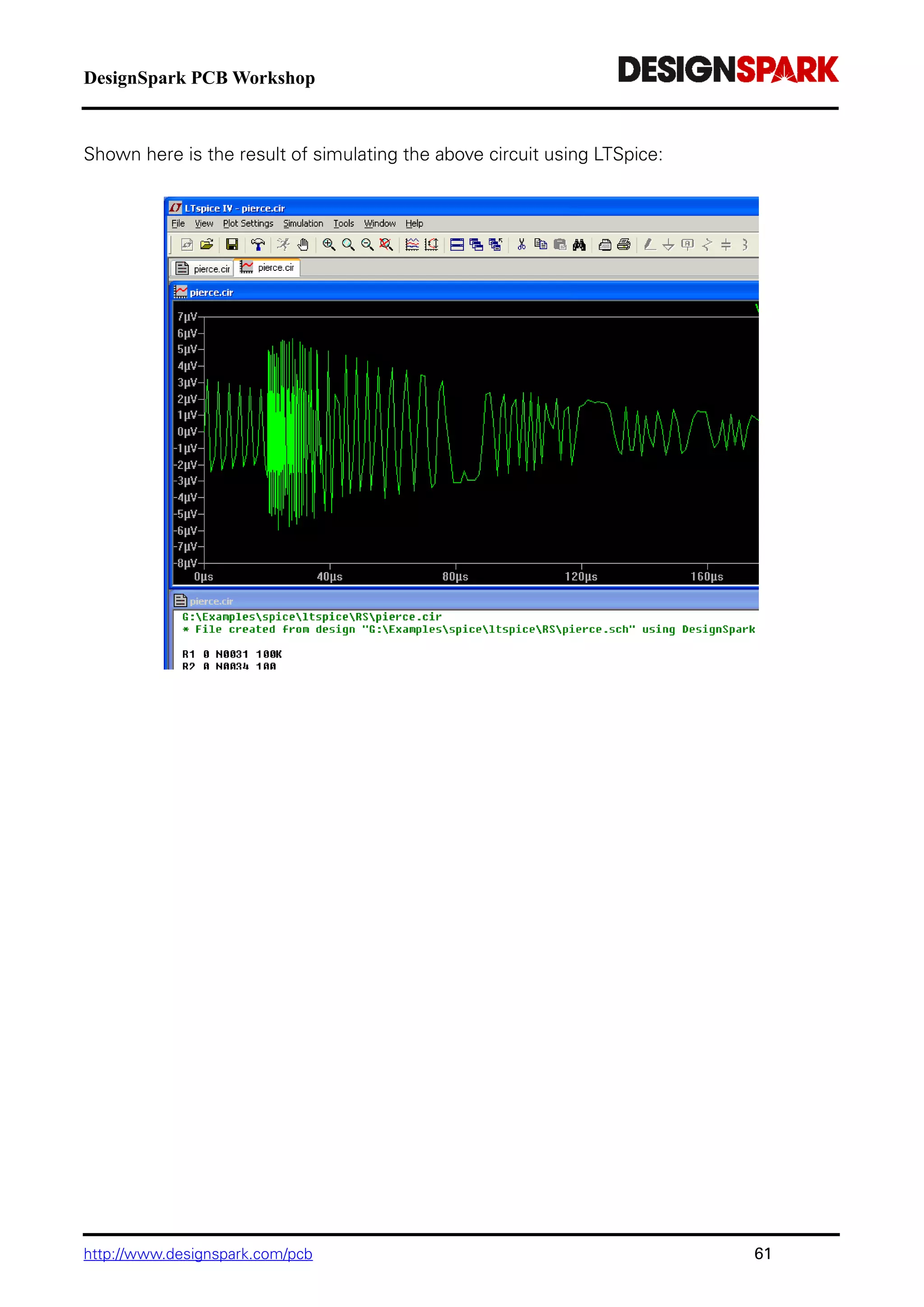
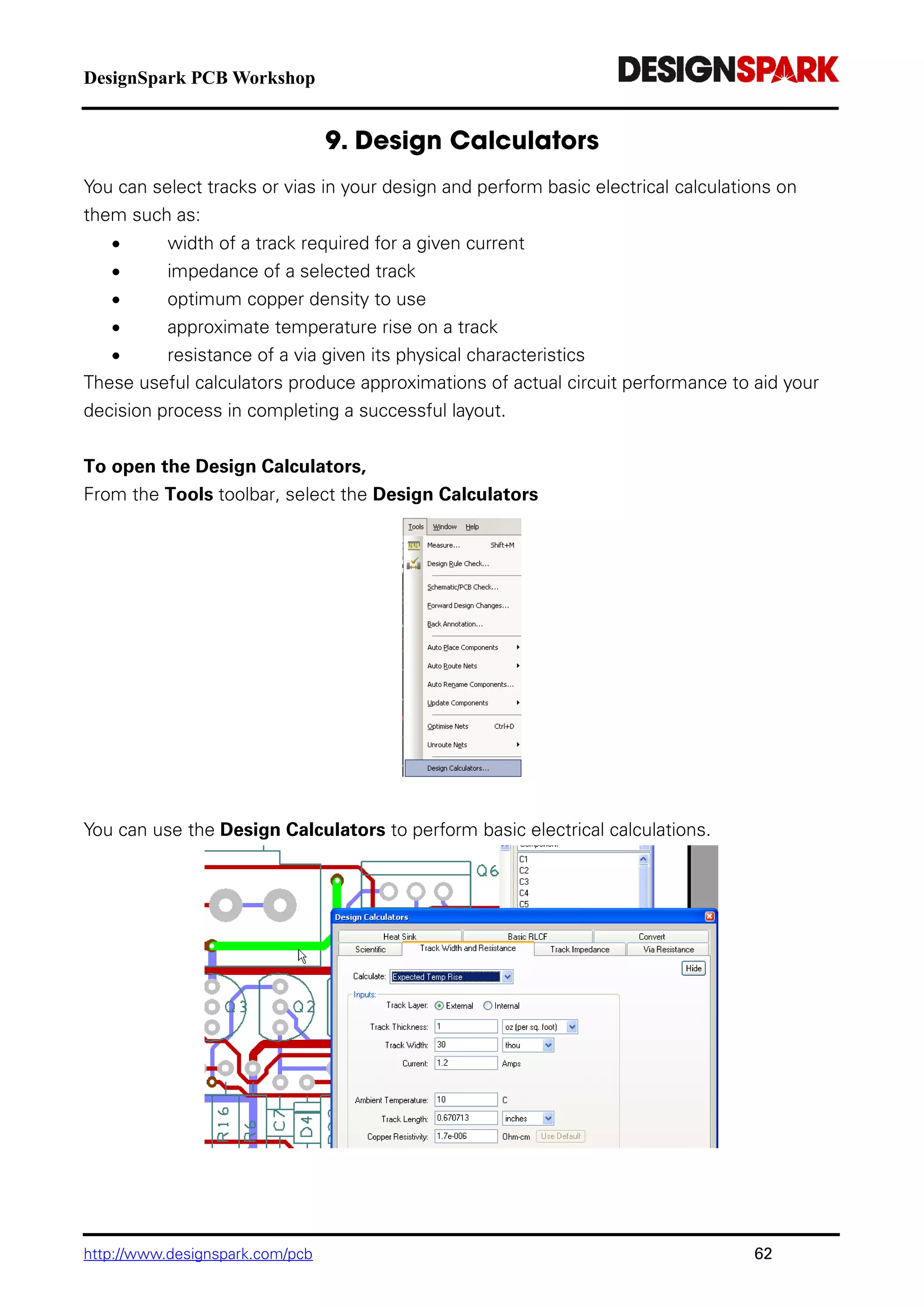
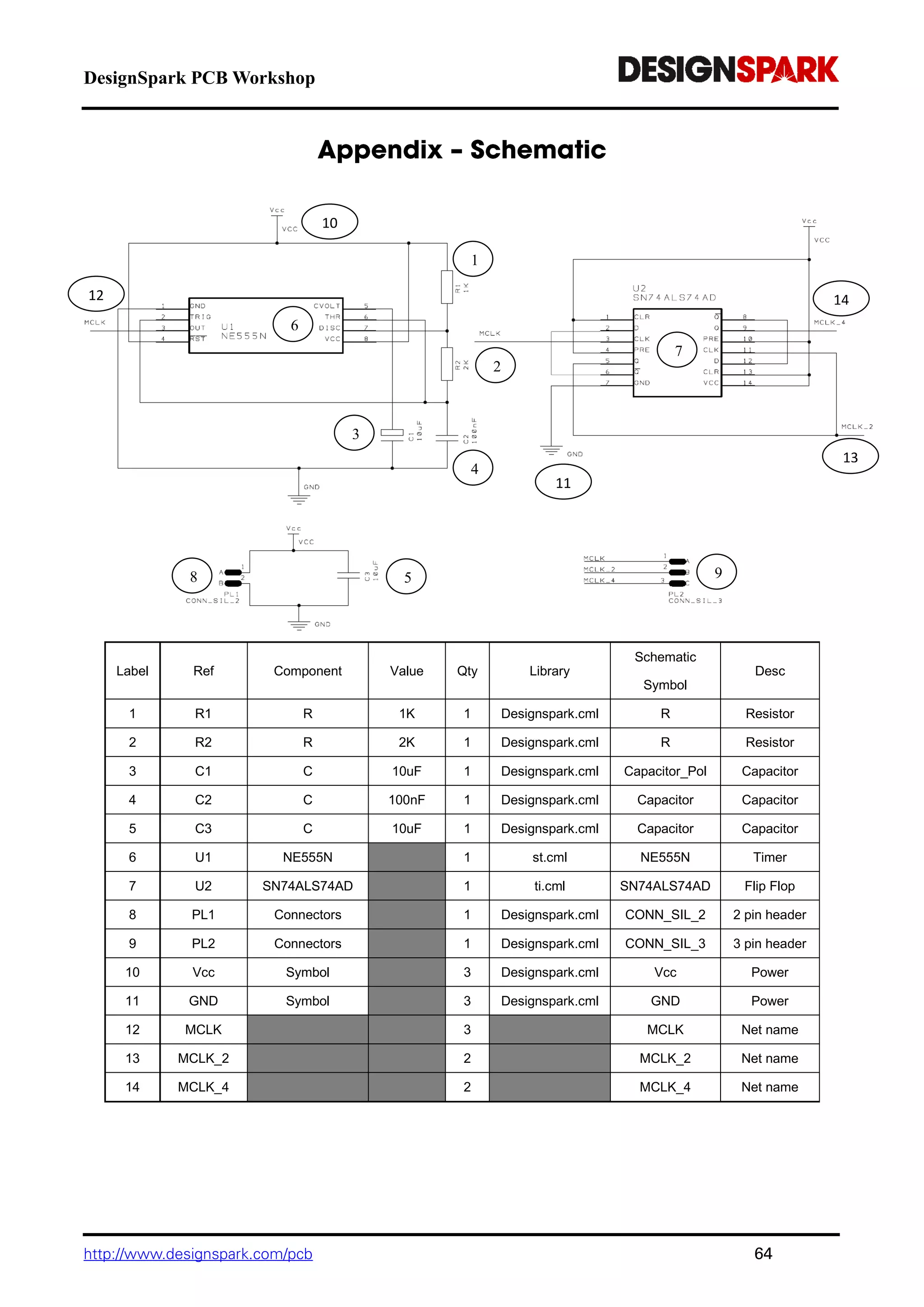
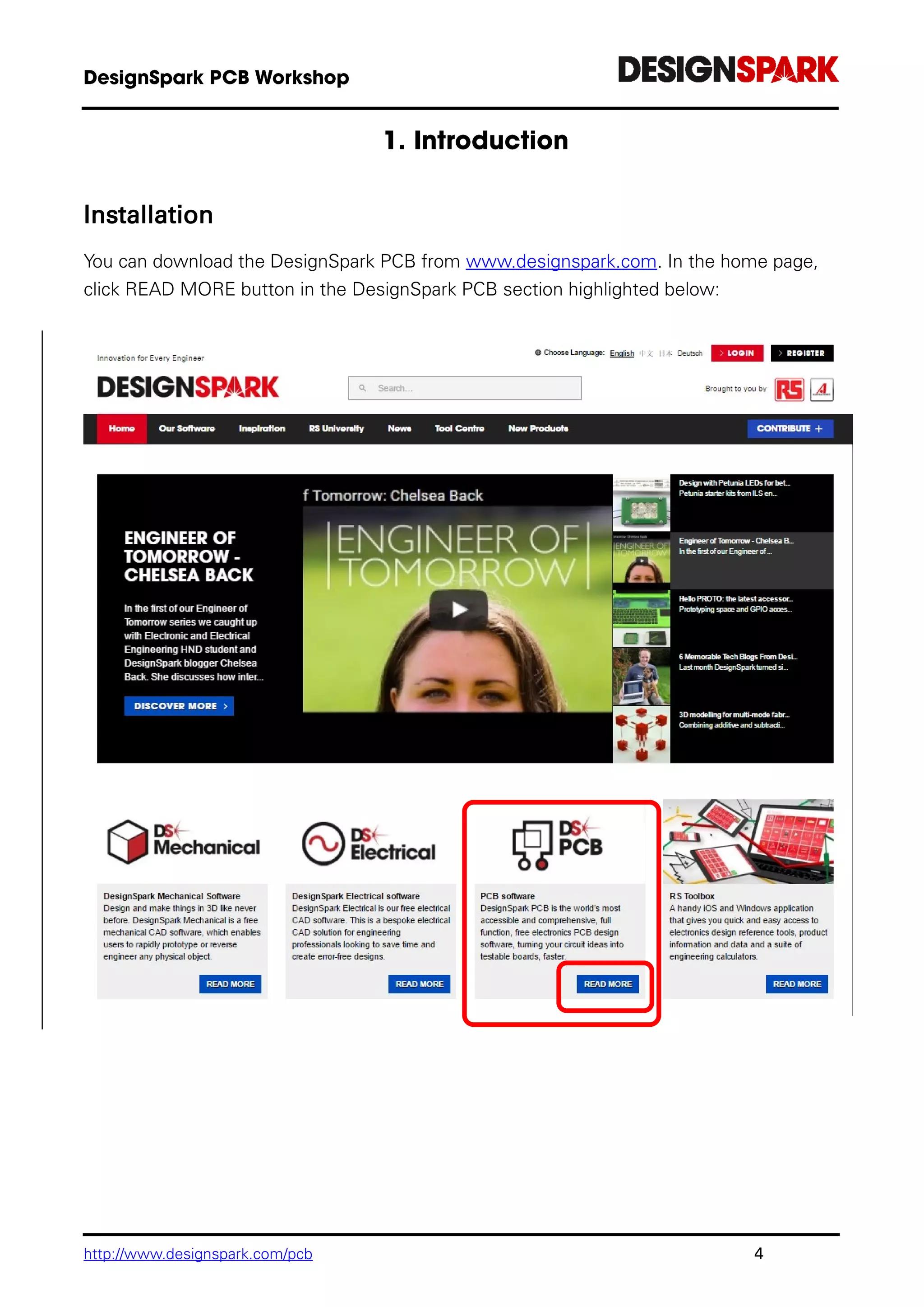
The document is a comprehensive guide for using the DesignSpark PCB software, detailing installation steps, key tools, layout techniques, and component management. It covers adding components, routing designs, managing layers, and performing design rule checks while also providing shortcuts and commands for efficient usage. Additionally, the document includes tutorials for both schematic and PCB designs to facilitate users in creating their projects effectively.









![http://www.designspark.com/pcb 26
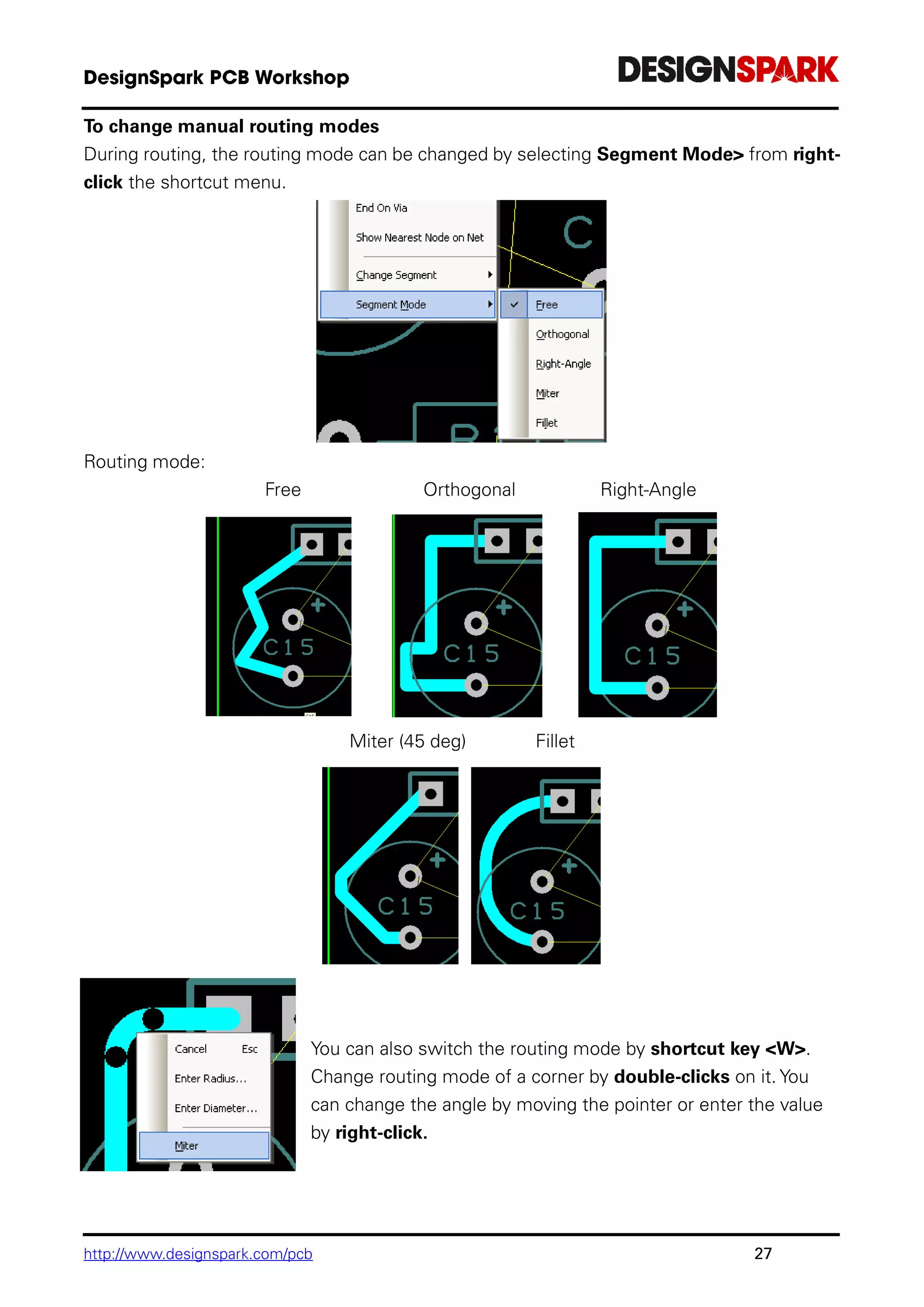
Enable MiterTrack in autorouter by check the box [MiterTrack].
Another dialog window will pop out to let you select the MITRE shape (Curved, any angle
or the default 45 deg) and specified the MITRE size.
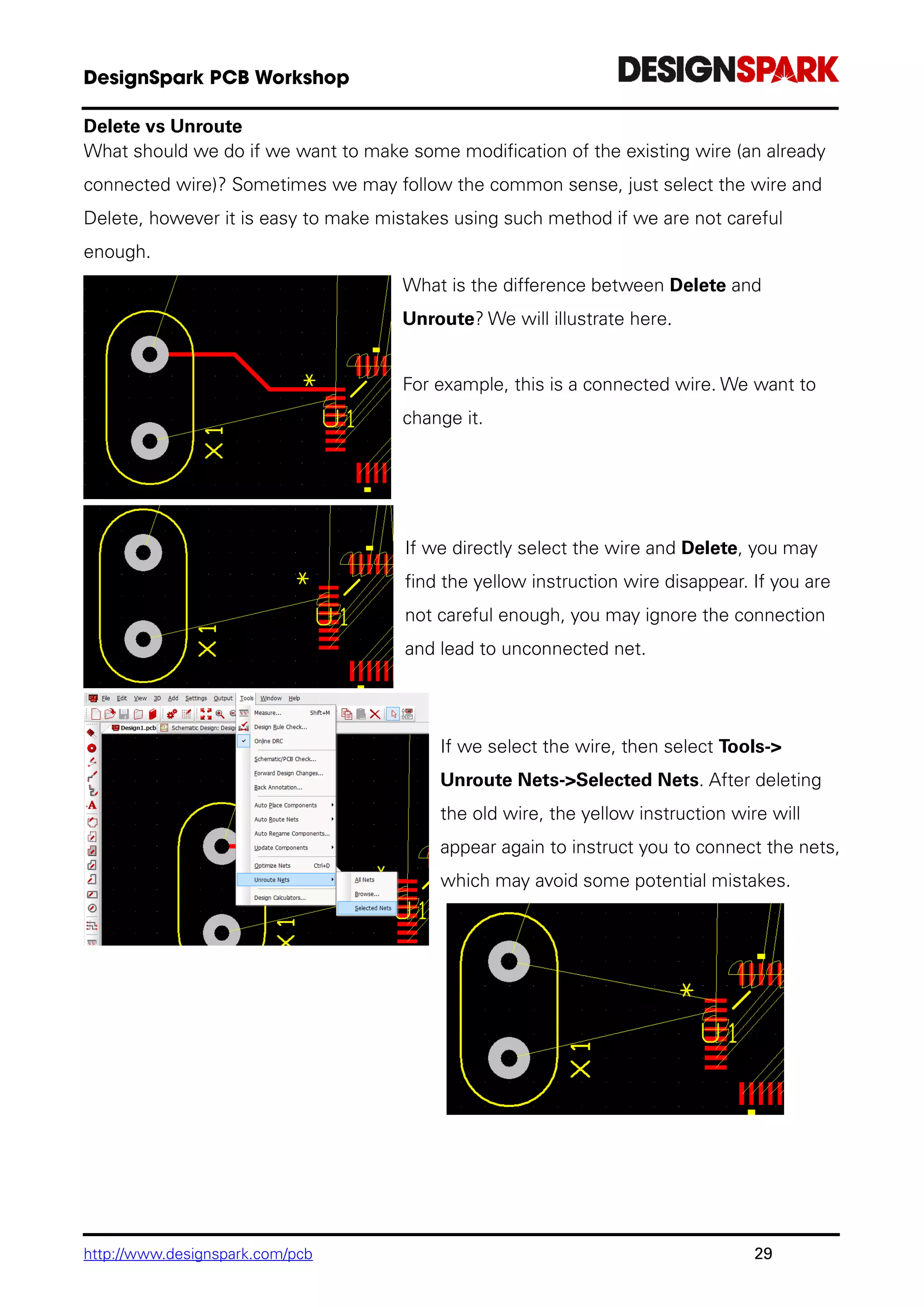
Unrouting the design
The Unroute Nets> option is available on the Tools menu.
To unroute all nets, from Tools menu under Unroute Nets>, select All Nets.
You can always restore the routes using Undo<Ctrl-Z>.
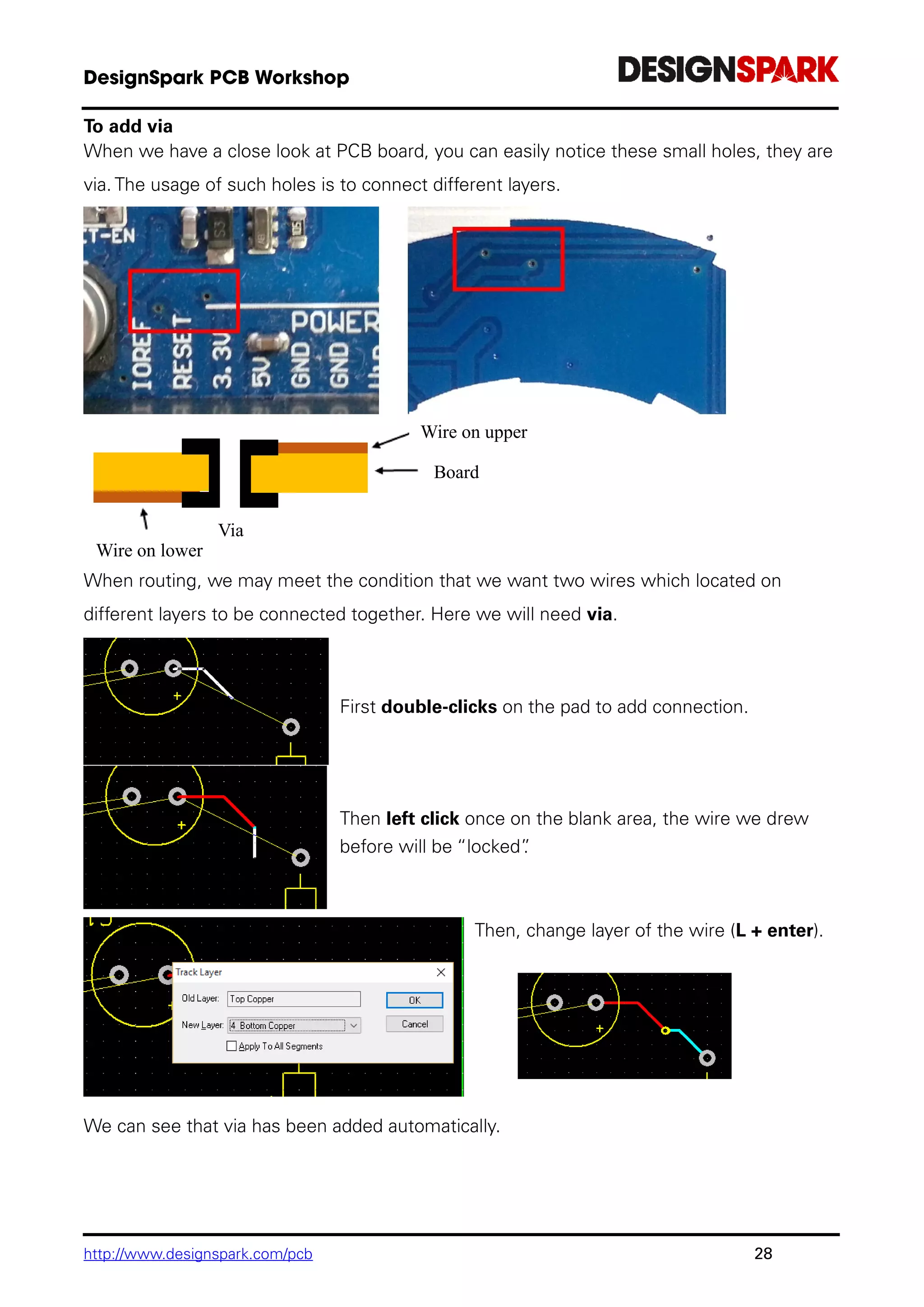
Method 2: Manual Routing
Start routing track manually by double-click on the connection.
Single-Click, once editing, this will insert a corner to the change routing direction.
<L> followed by <Enter> will enable a layer change to the opposite side of the design. This
can be used during editing, or afterwards on selection of a track.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designsparkpcbworkshopnotes2018-190129021259/75/DesignSpark-PCB-Workshop-Notes-2018-26-2048.jpg)