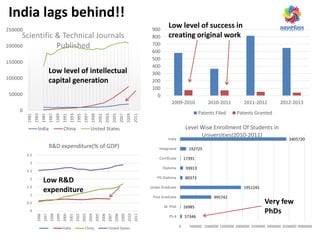
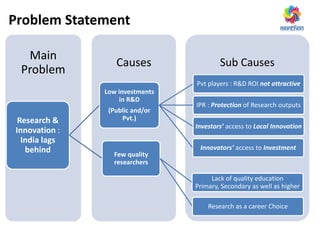
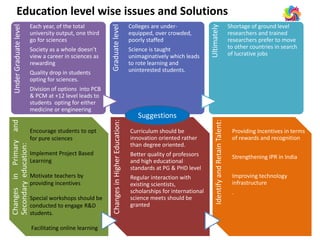
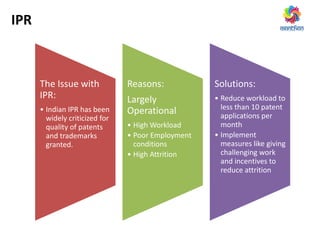
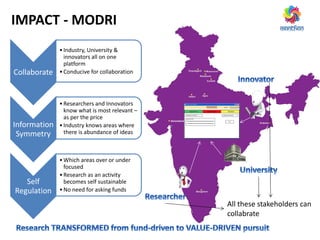
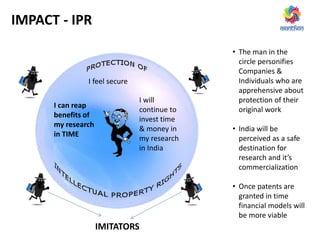
The document discusses ways to promote research and innovation in India. It notes that India lags behind countries like the US and China in key metrics like R&D expenditure and number of scientific publications and patents. It identifies low investments in R&D and lack of quality education and researchers as major causes. The document proposes solutions like creating a market-oriented database to connect researchers and industry, strengthening the patent process, and reforming education with a focus on research. It argues these changes would help develop research talent, make research a more attractive career, and boost collaboration between academia and industry.