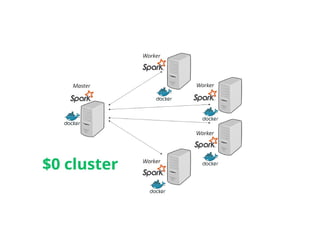
Kubernetes, a leading container orchestration platform, provides a robust environment for deploying and managing distributed applications. By deploying Spark on Kubernetes, you can take advantage of Kubernetes’ features such as dynamic scaling, fault tolerance, and resource allocation, ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization.