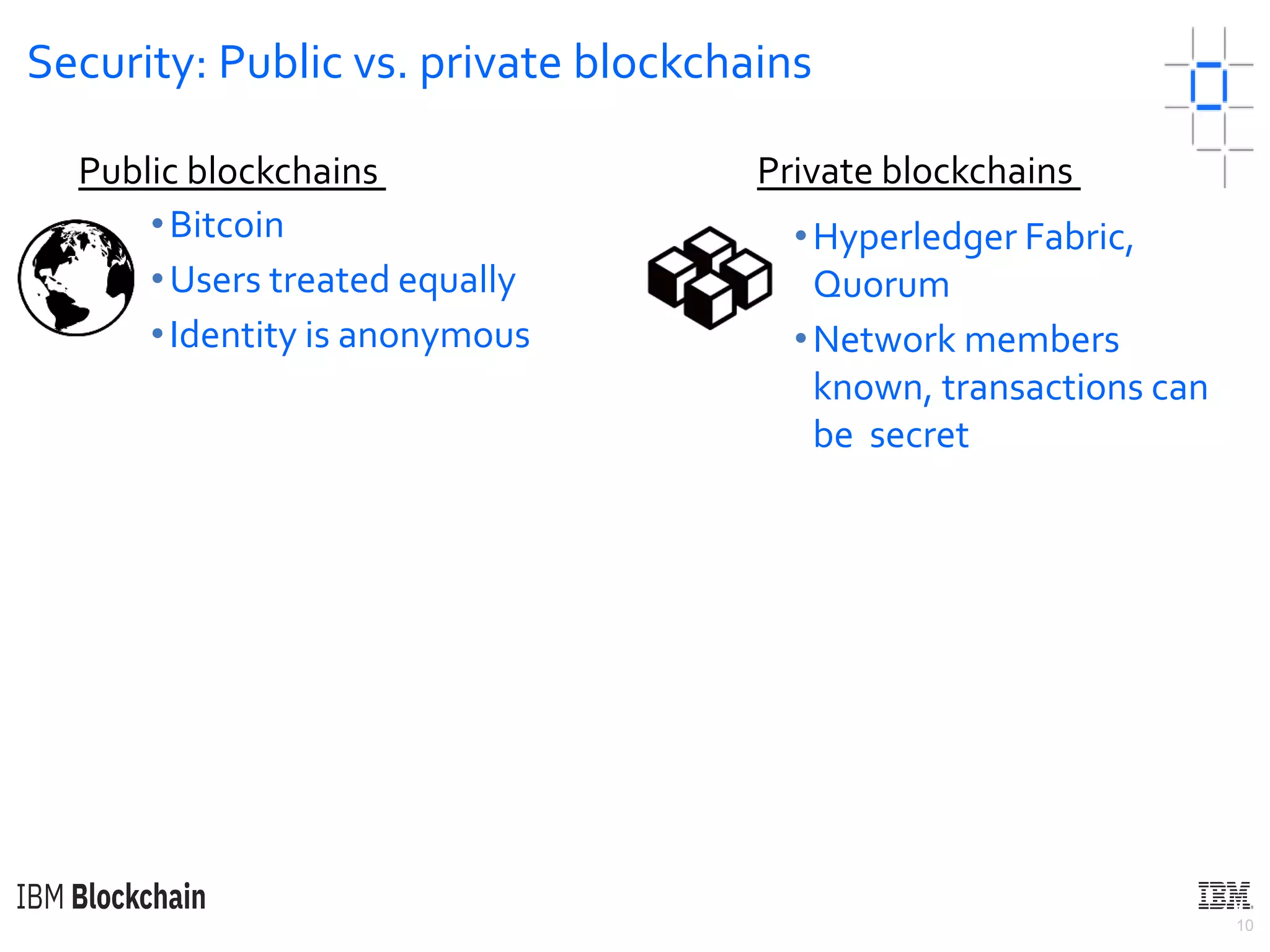
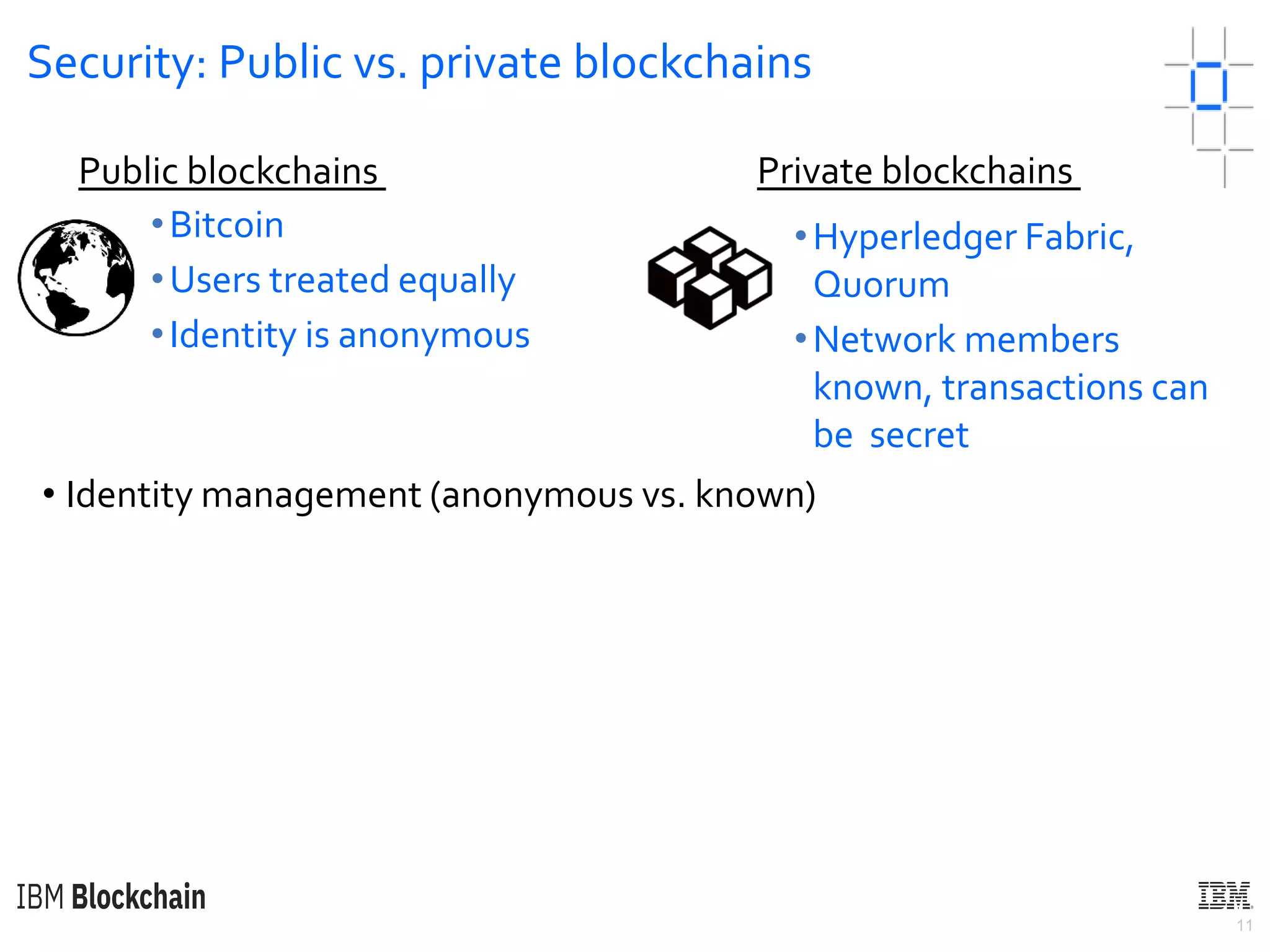
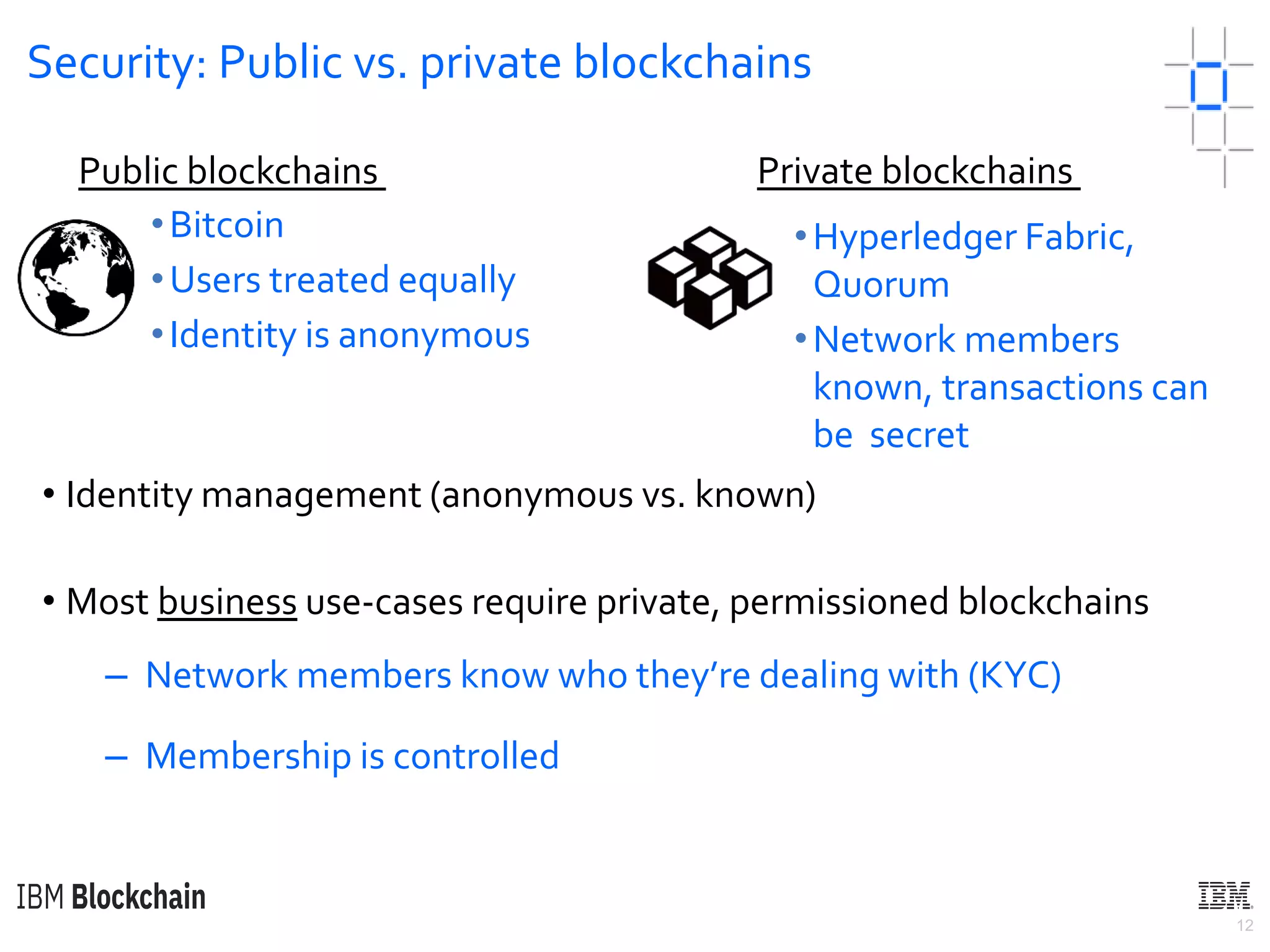
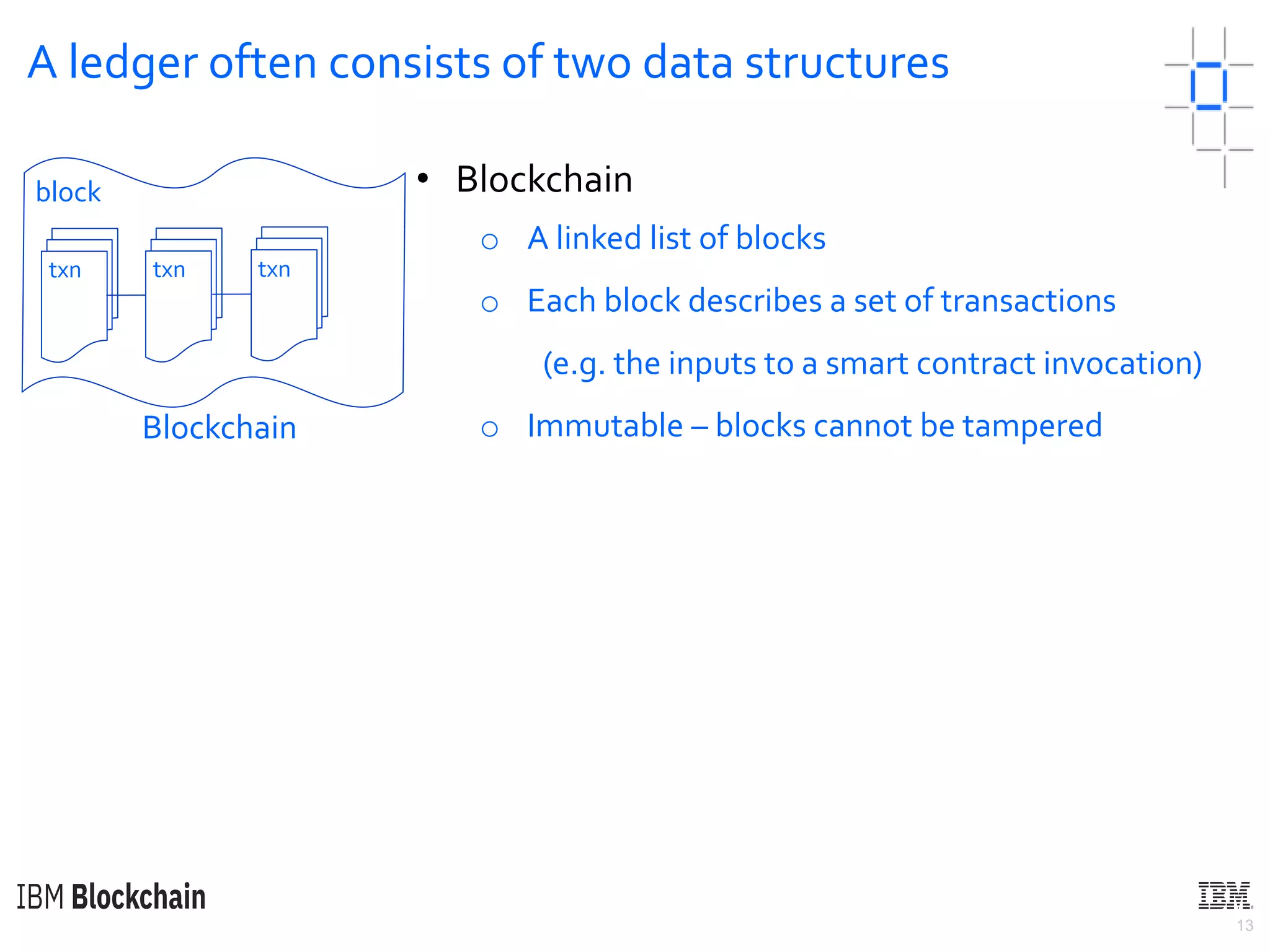
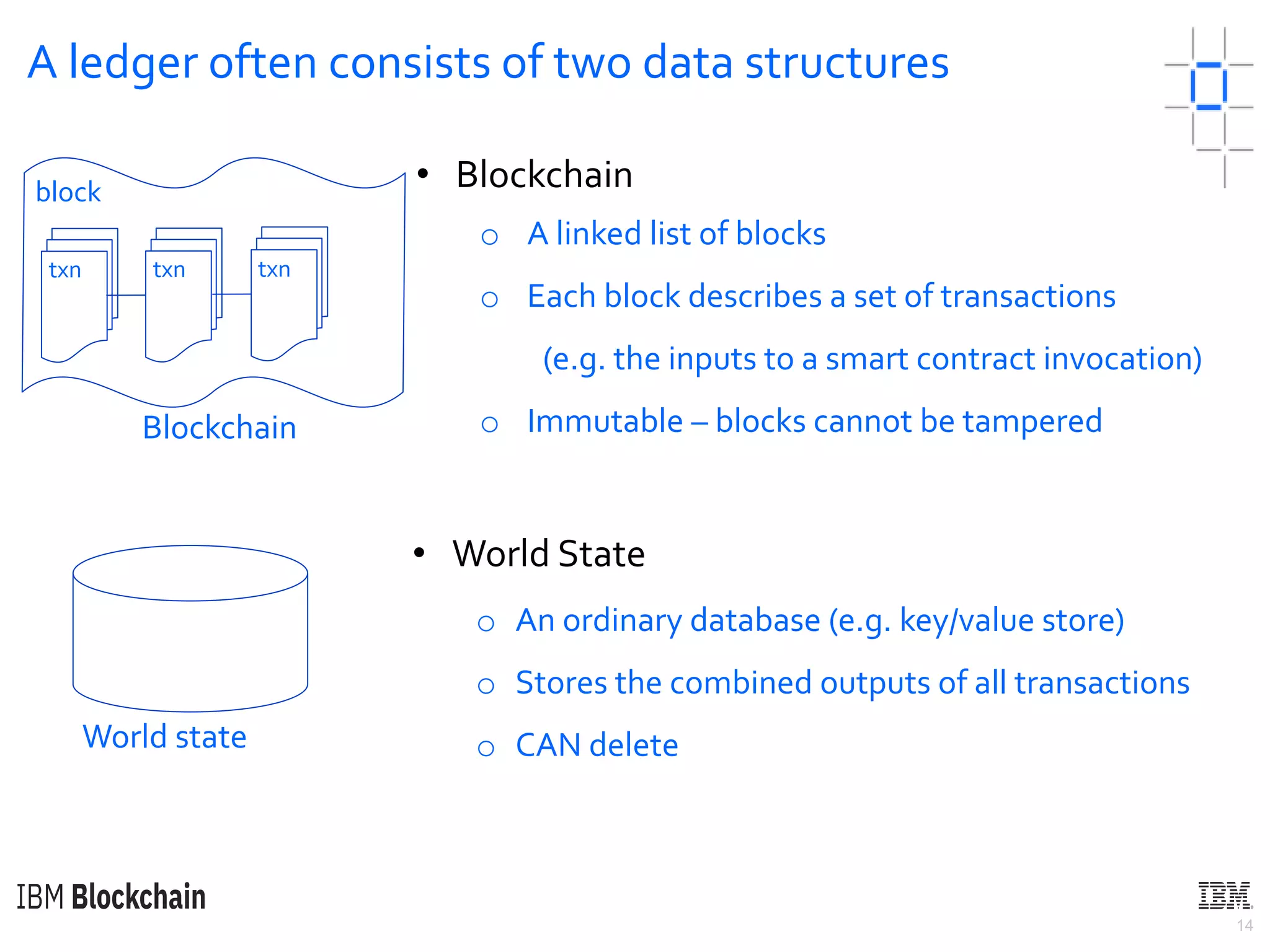
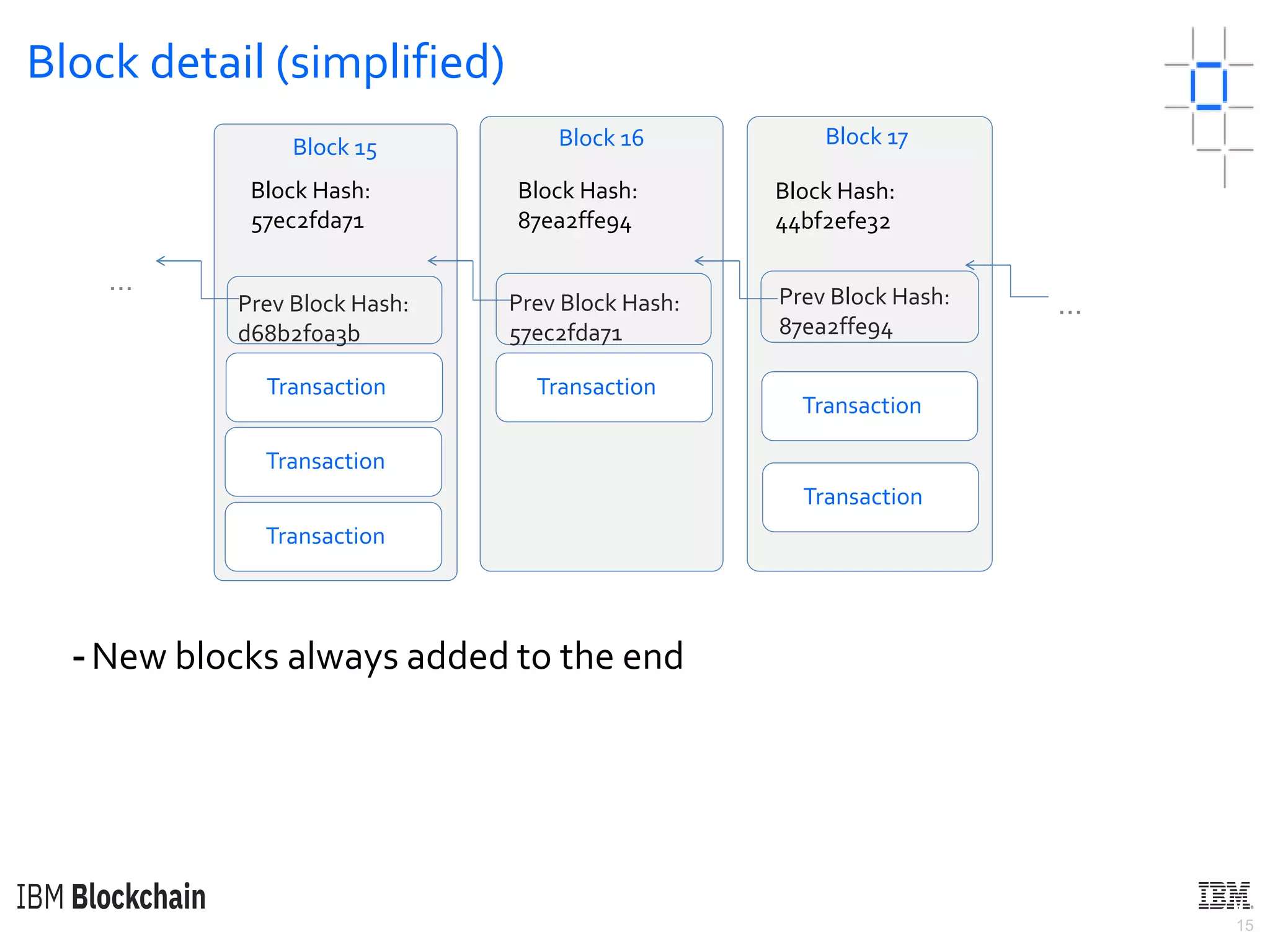
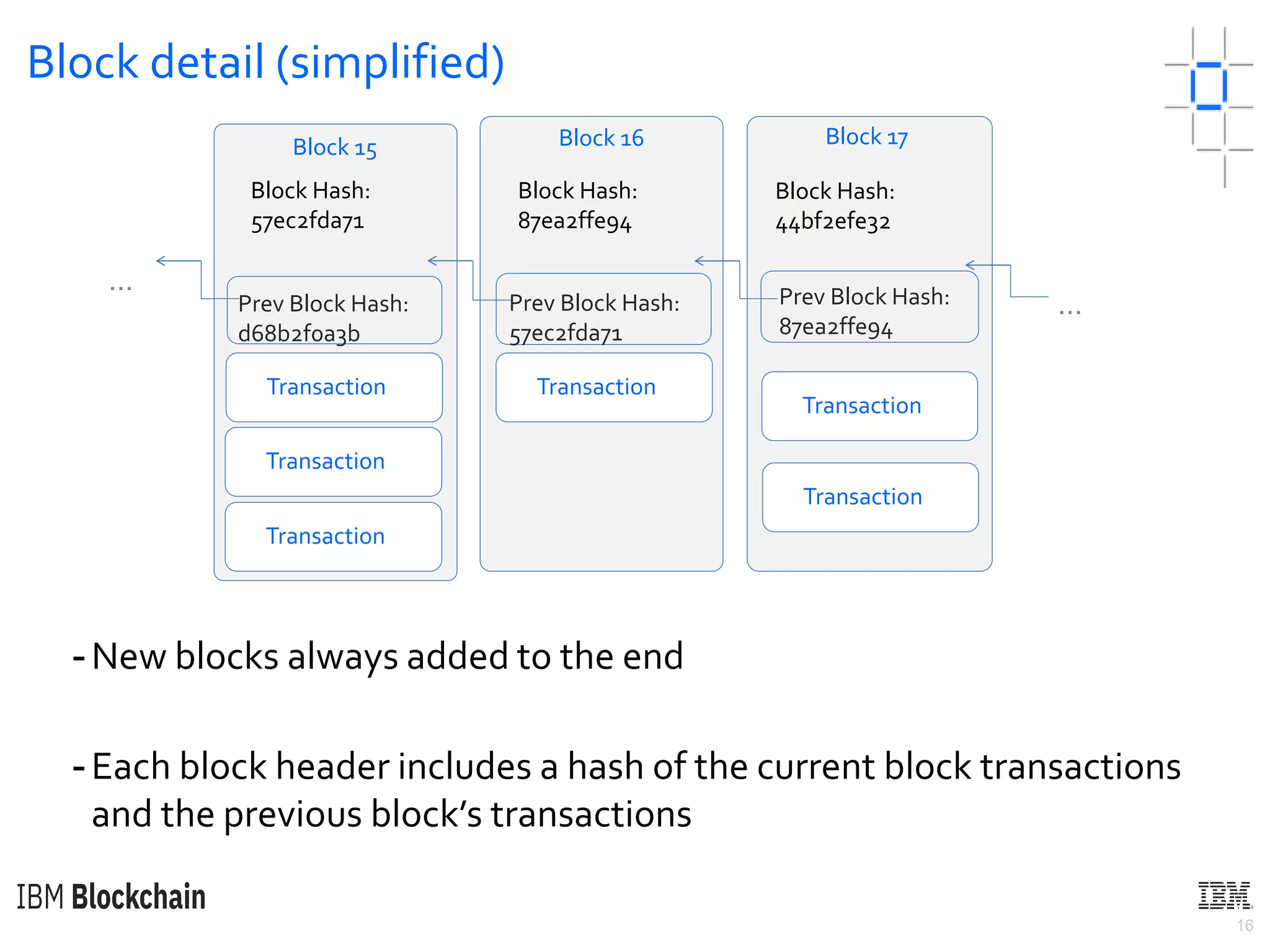
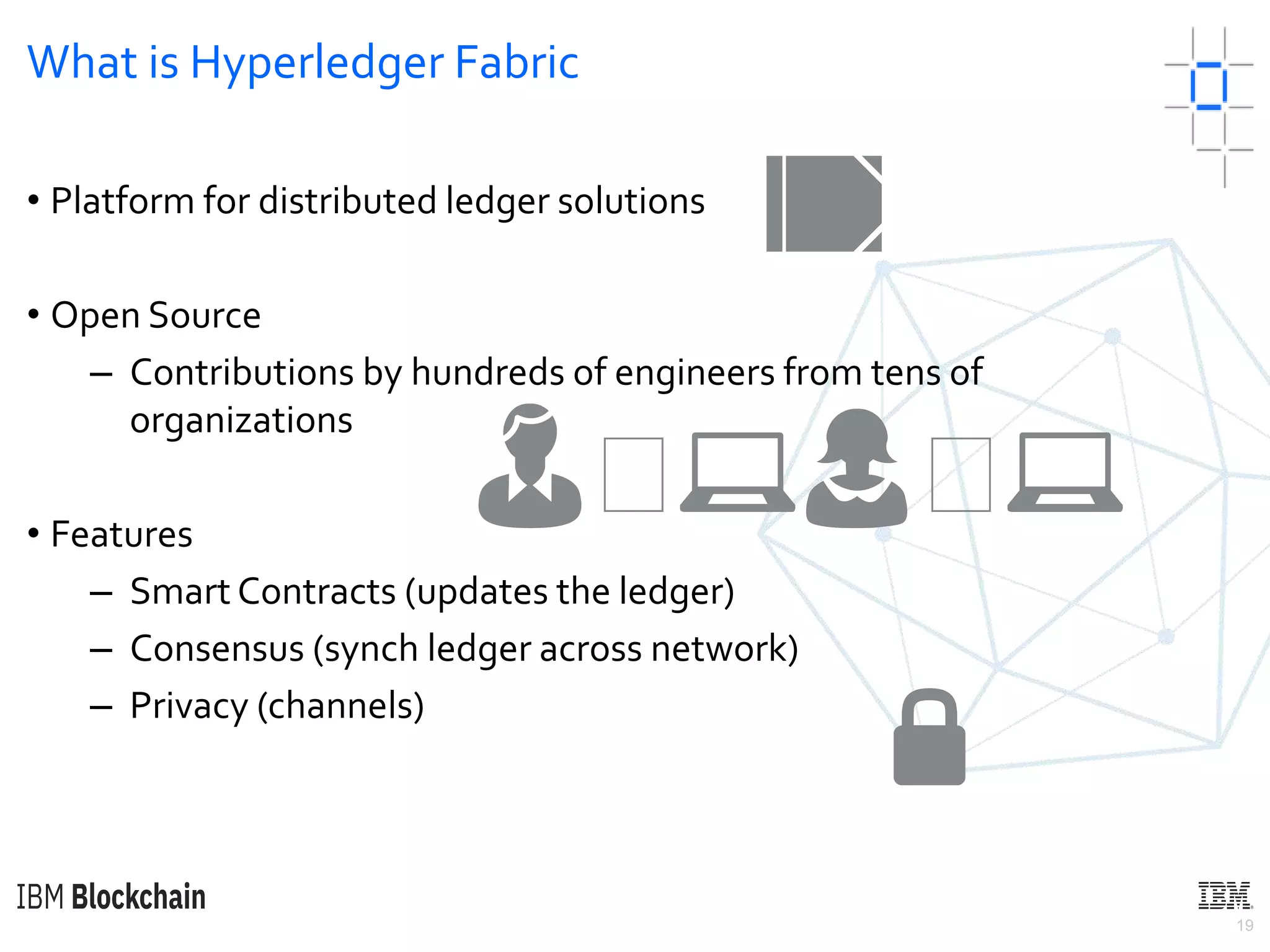
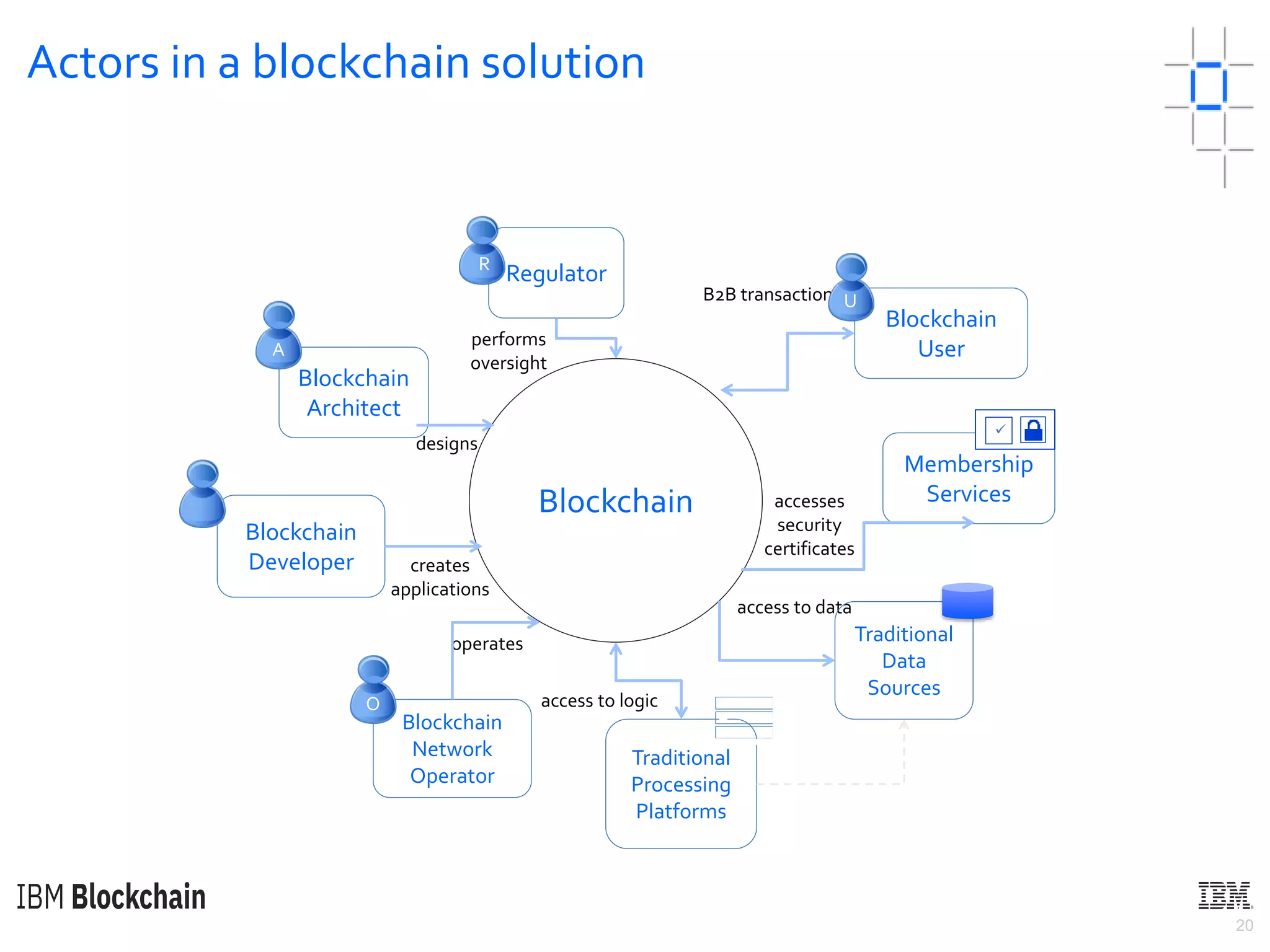
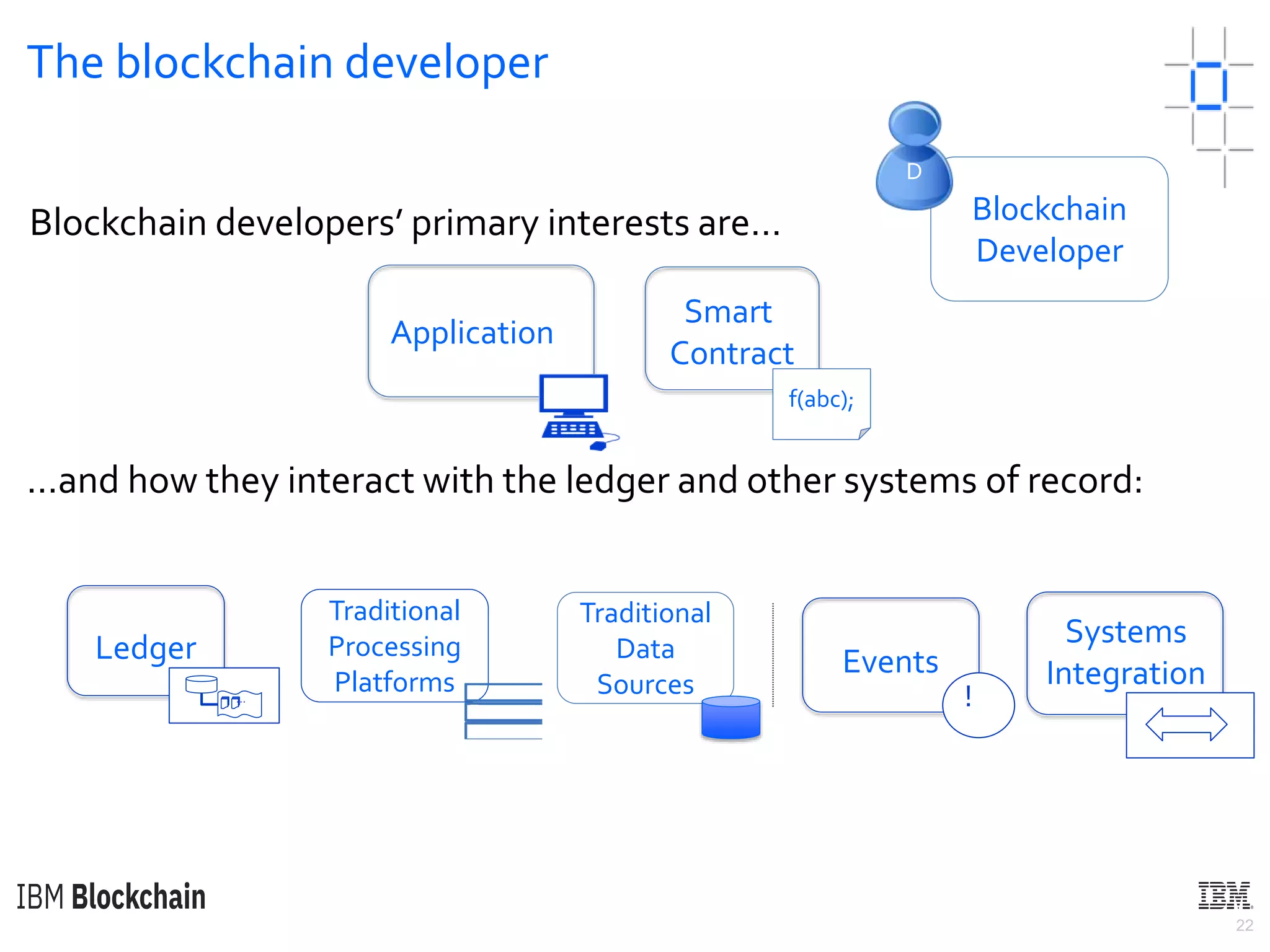
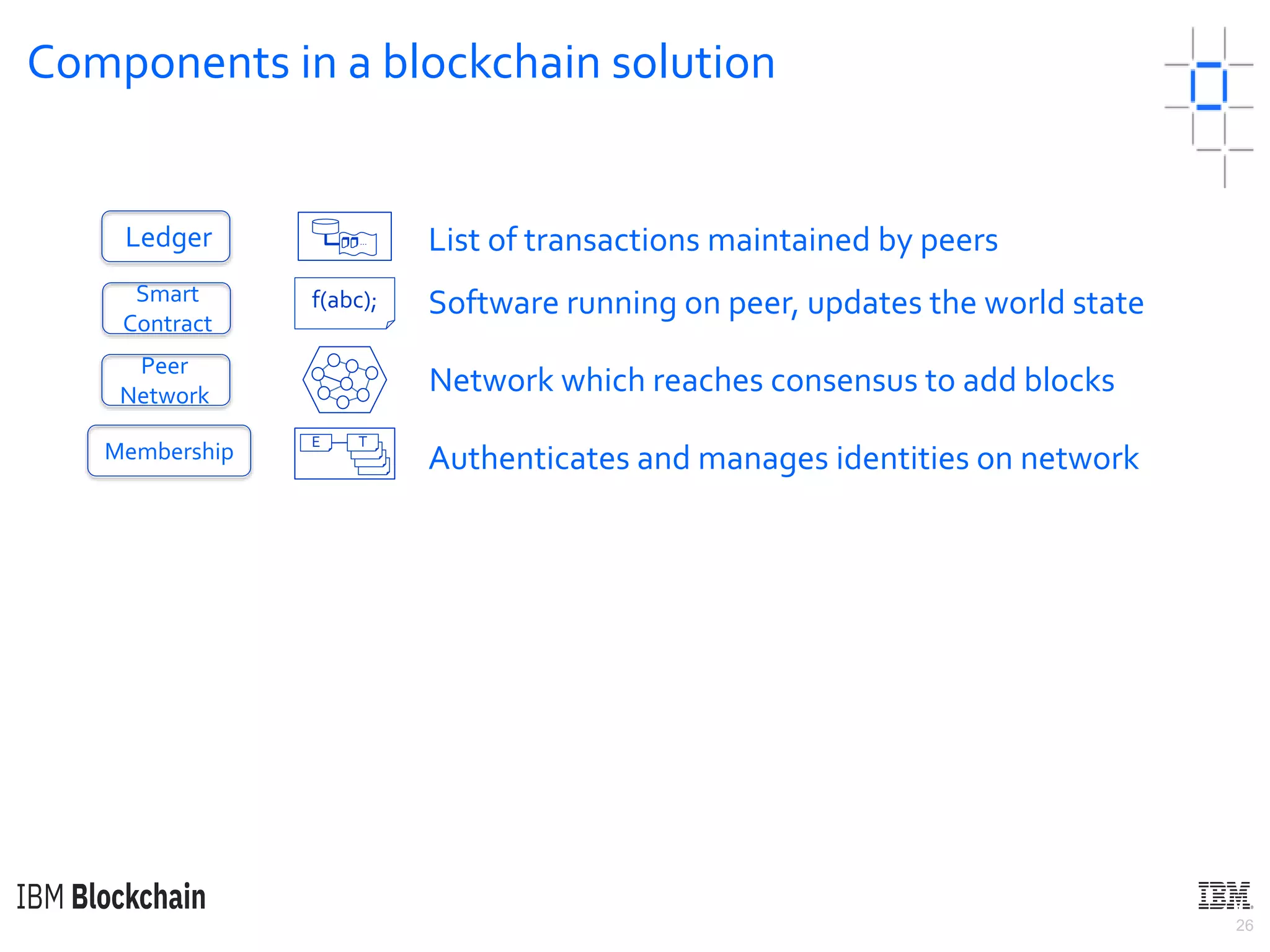
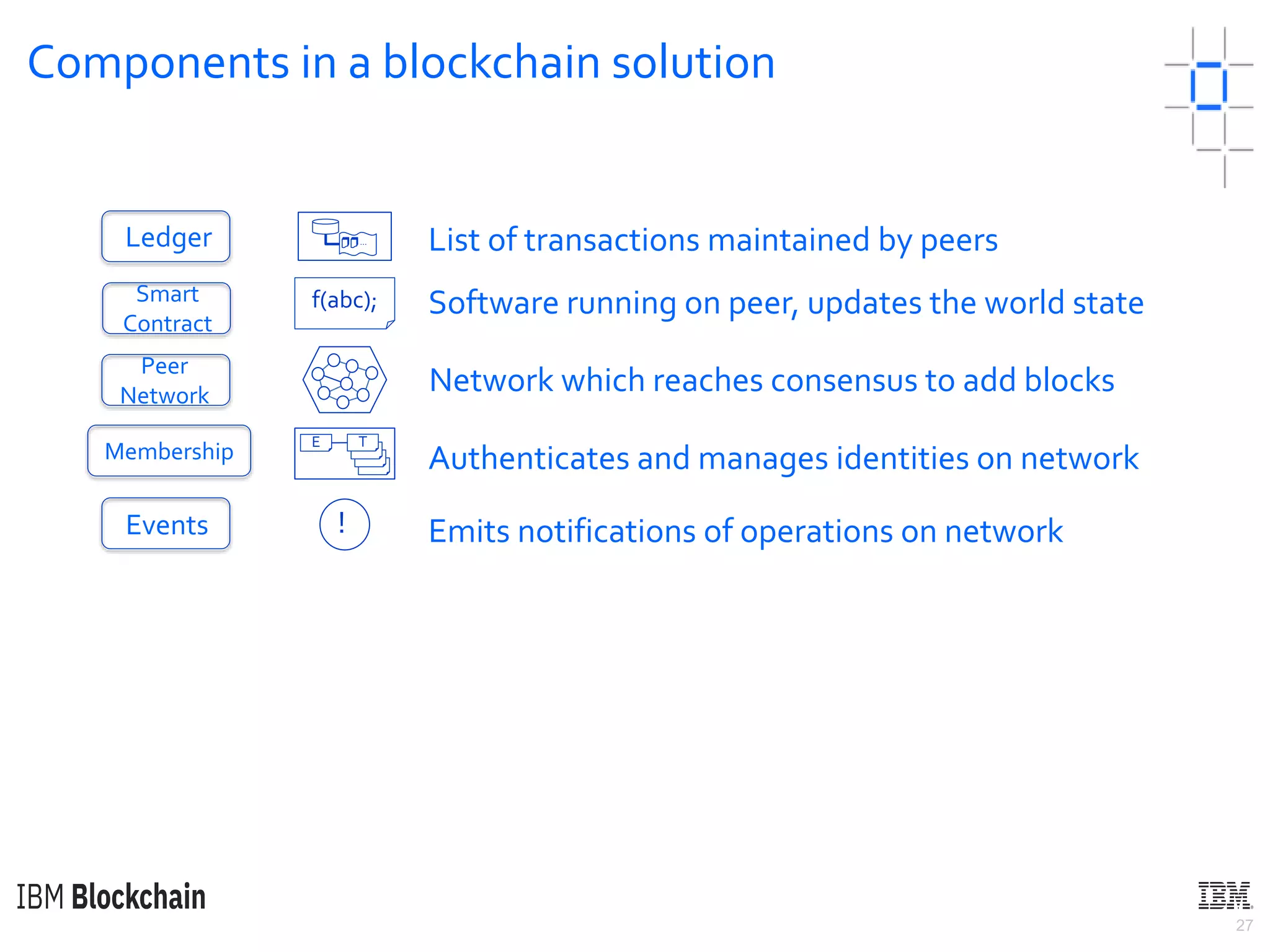
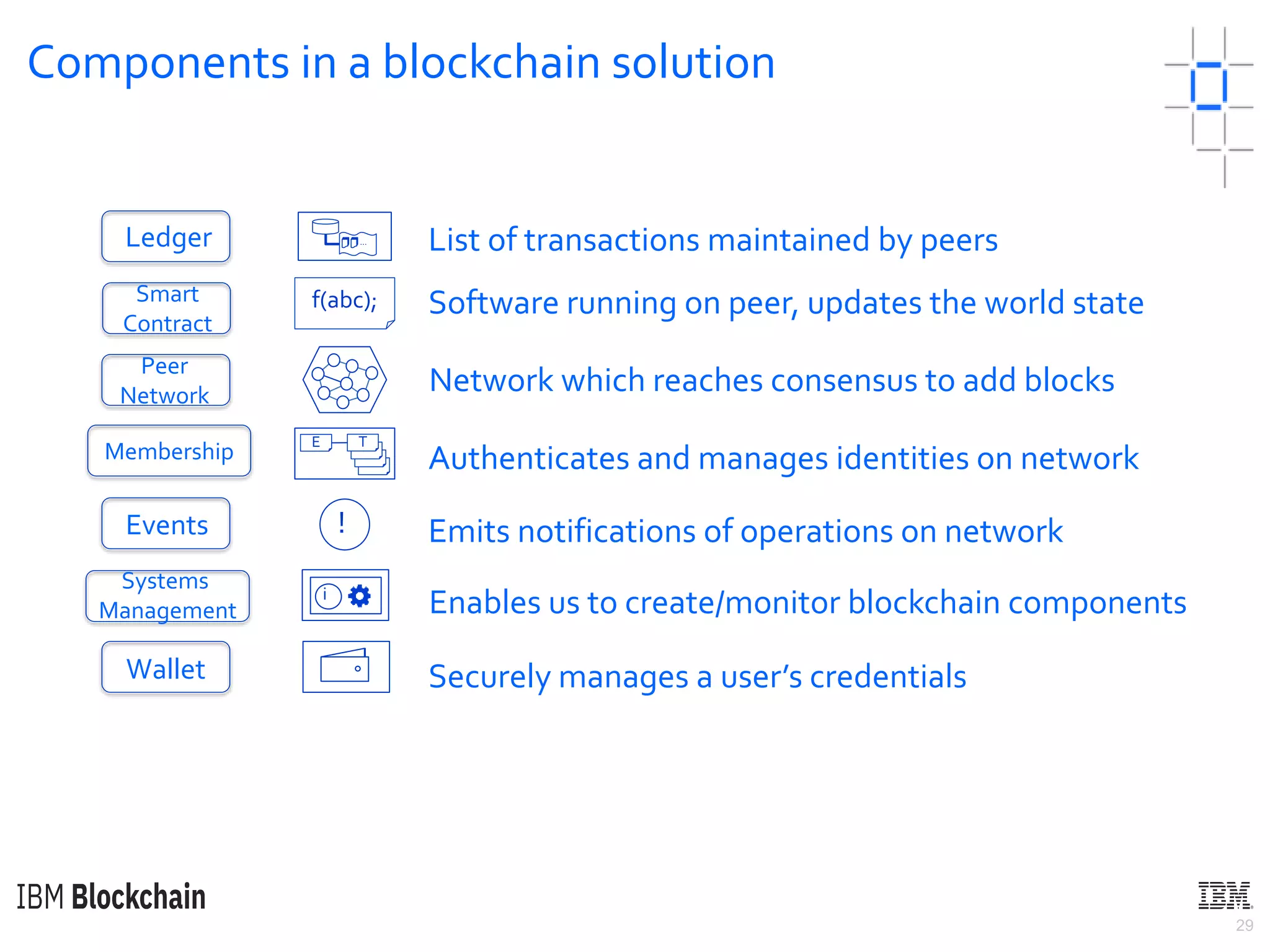
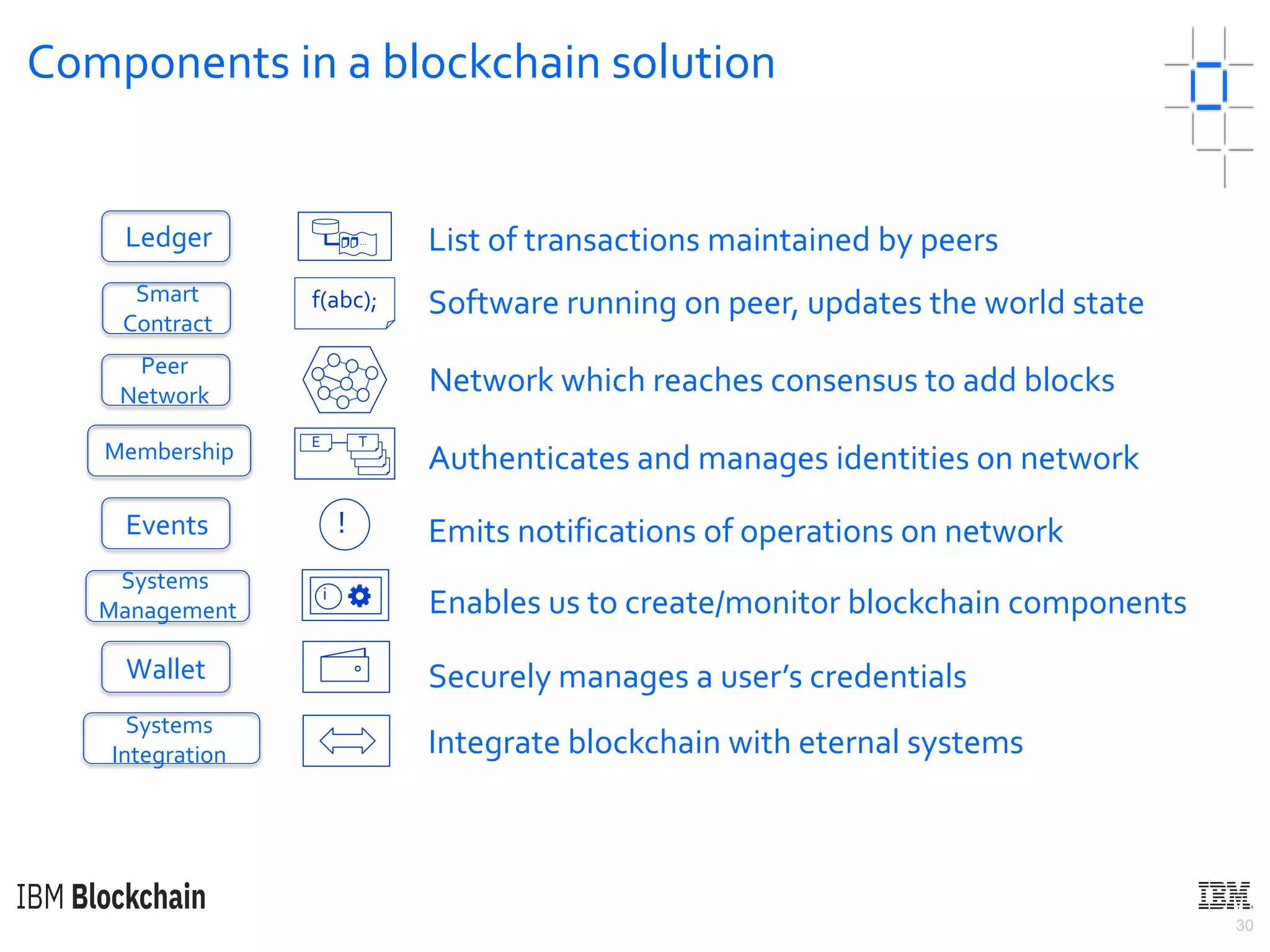
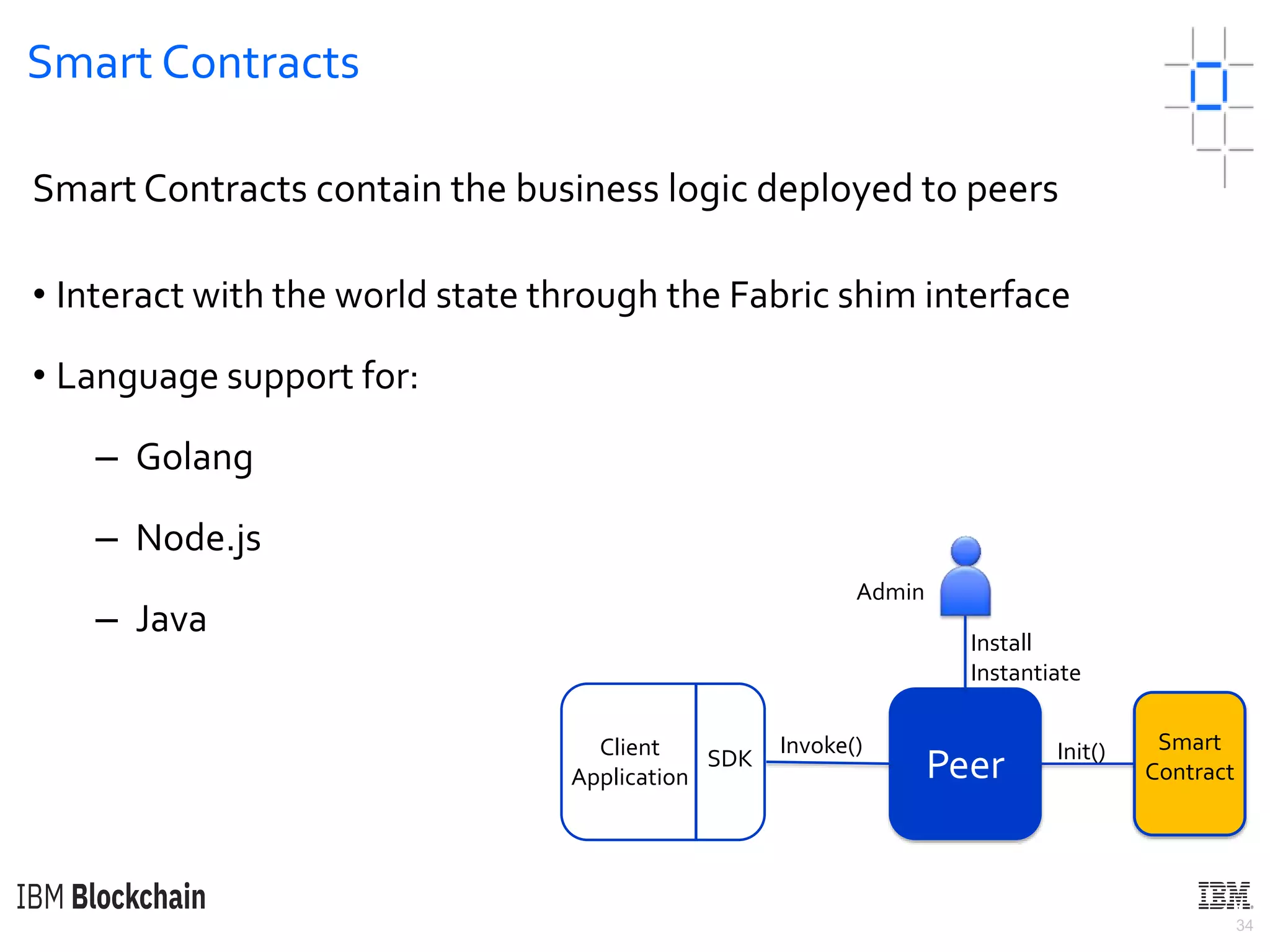
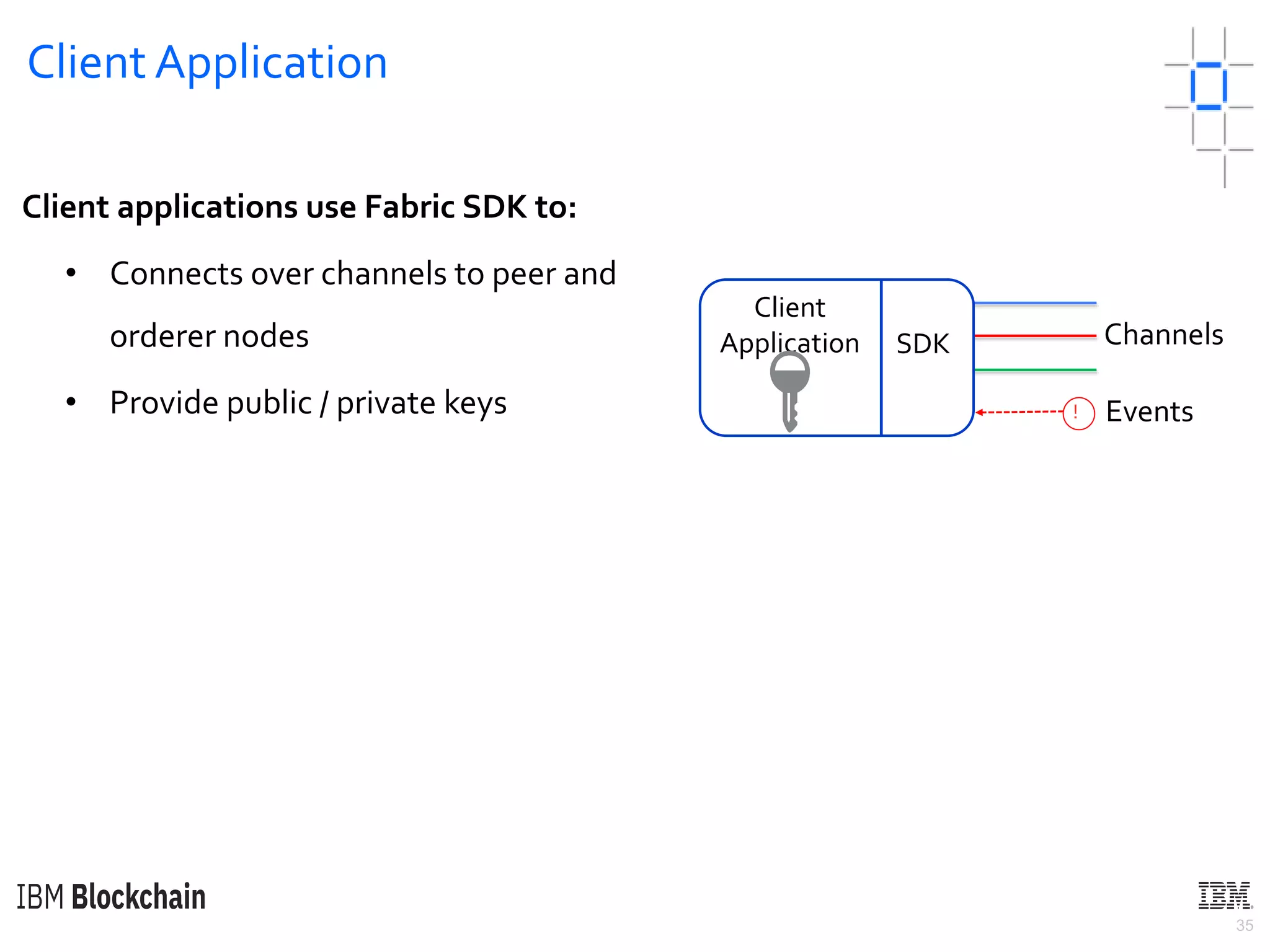
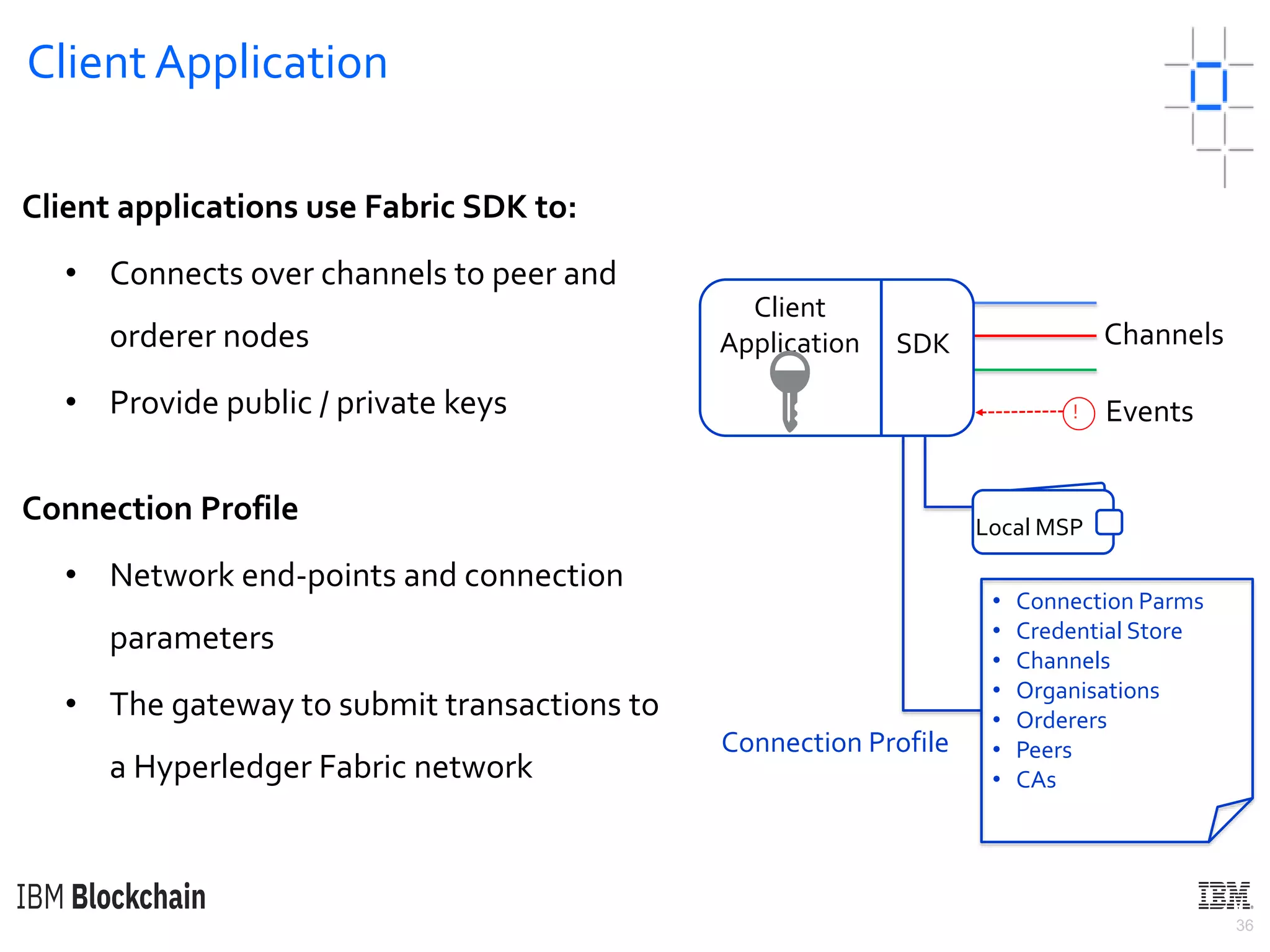
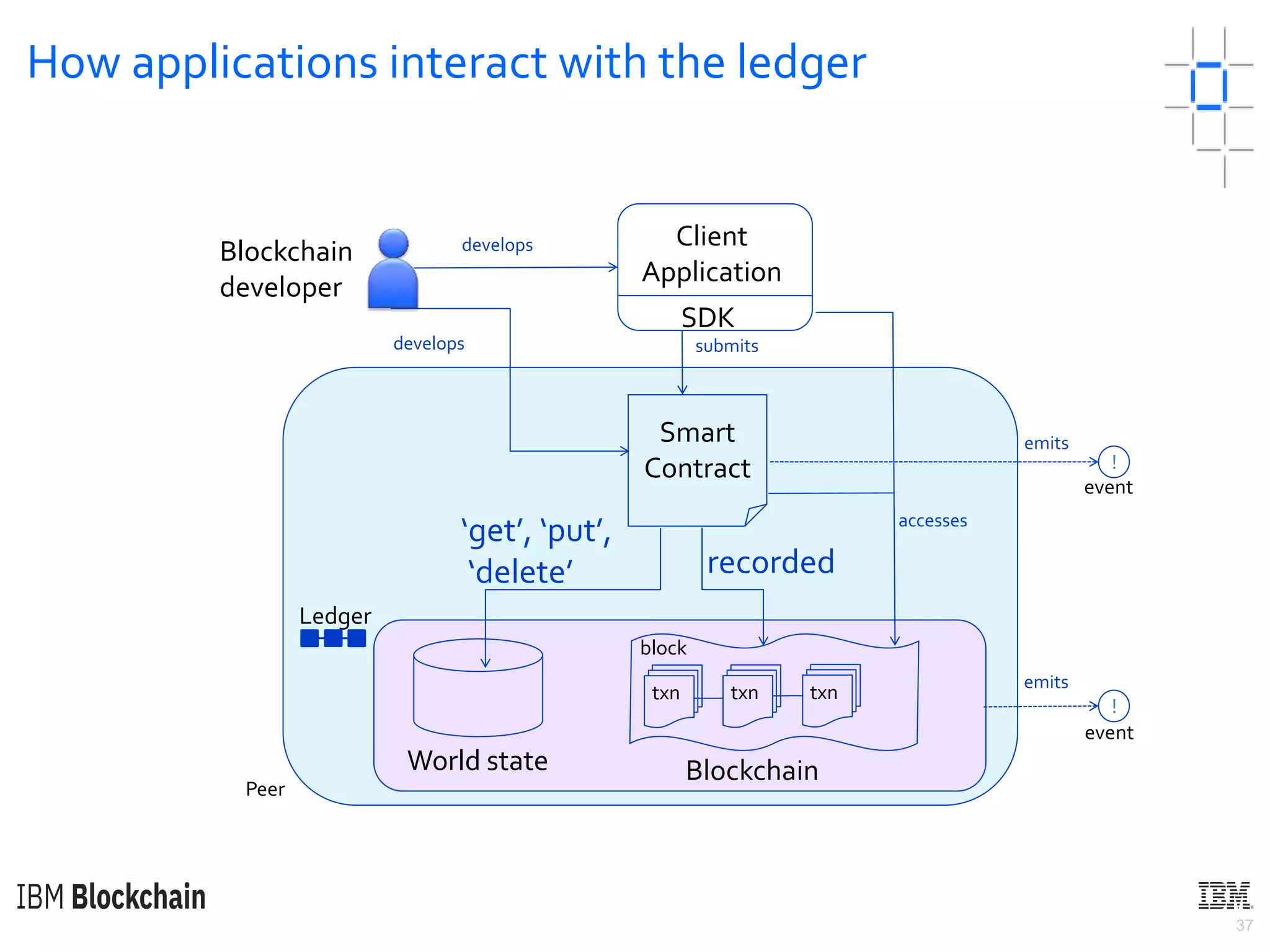
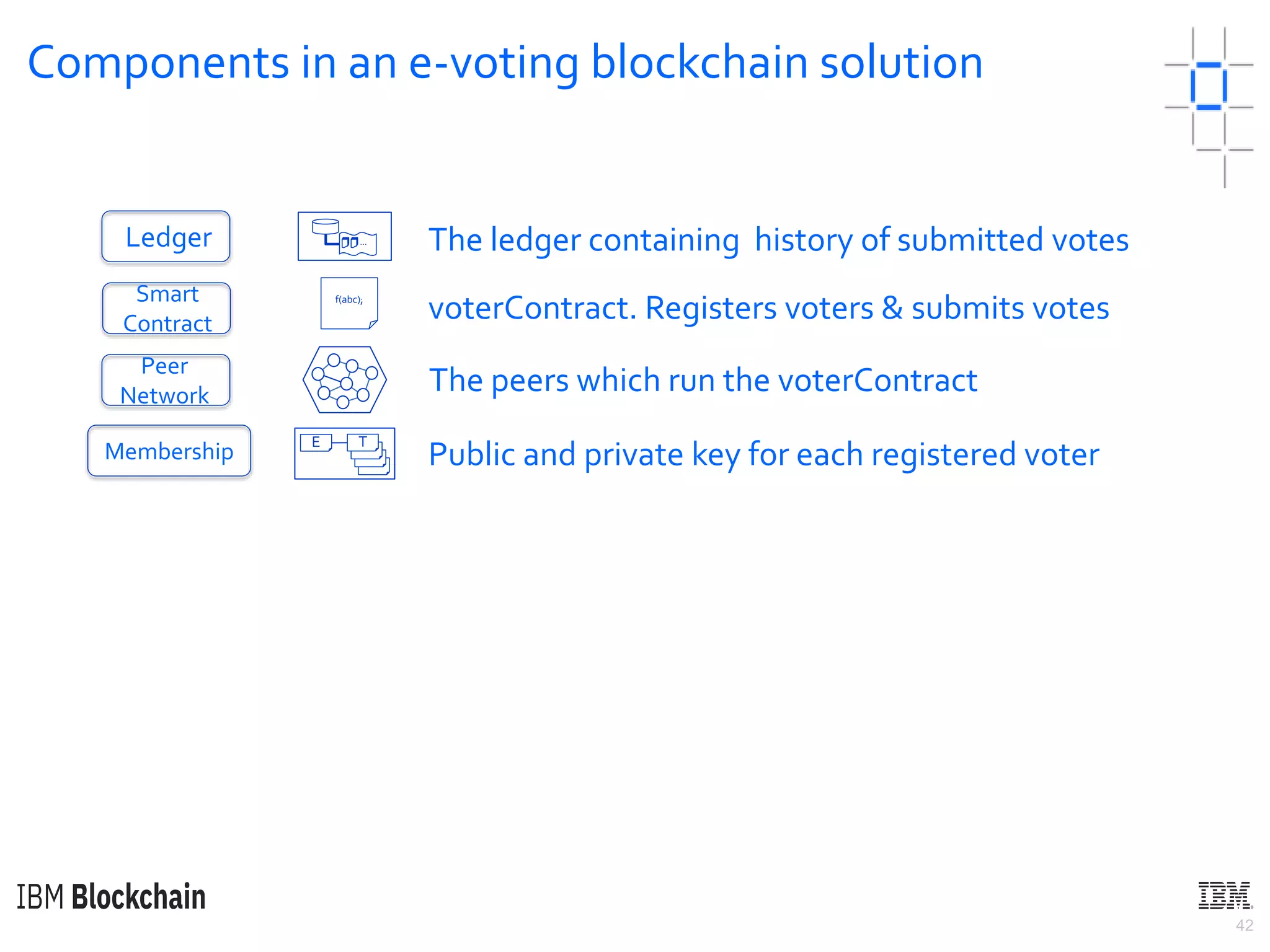
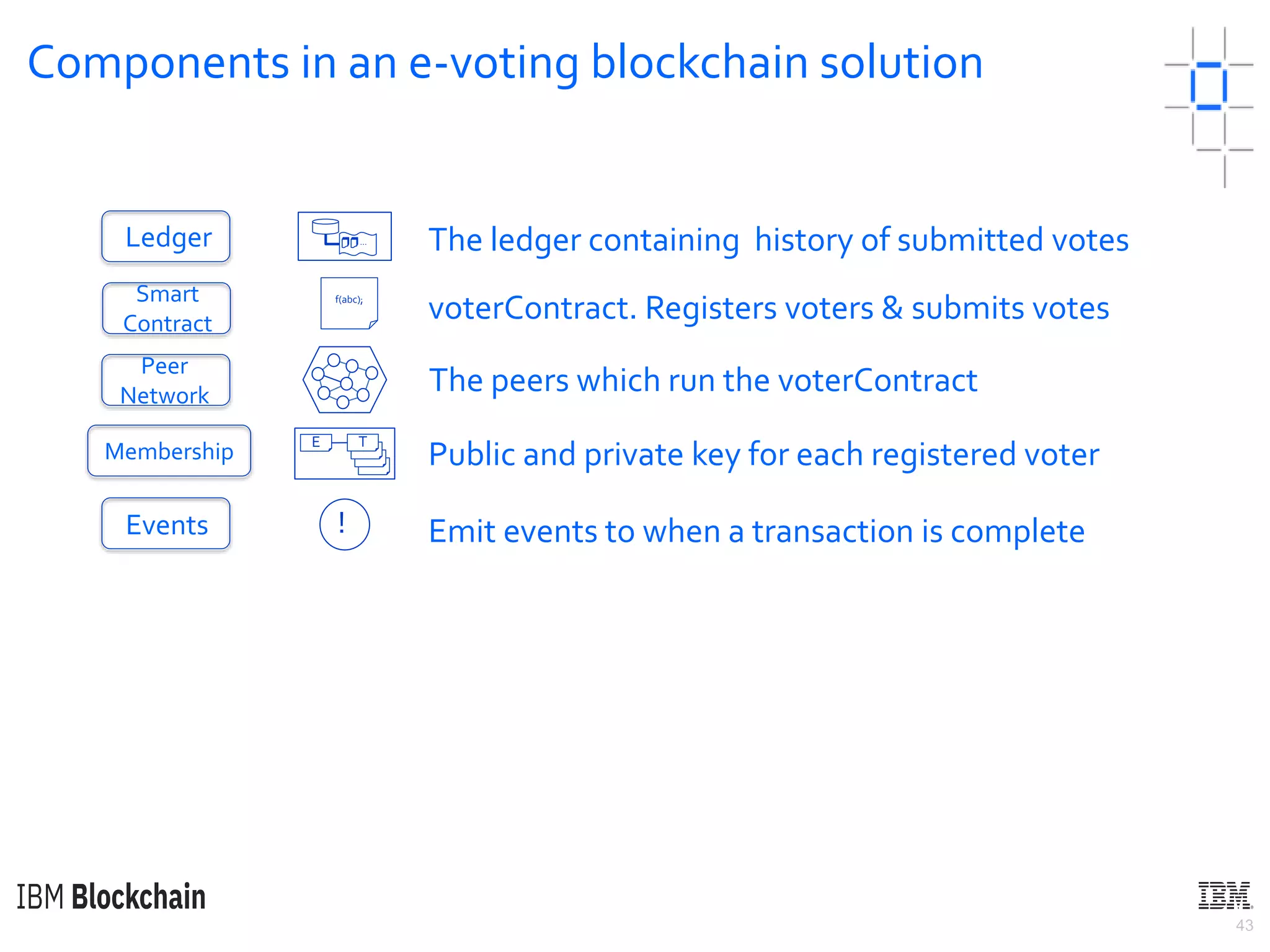
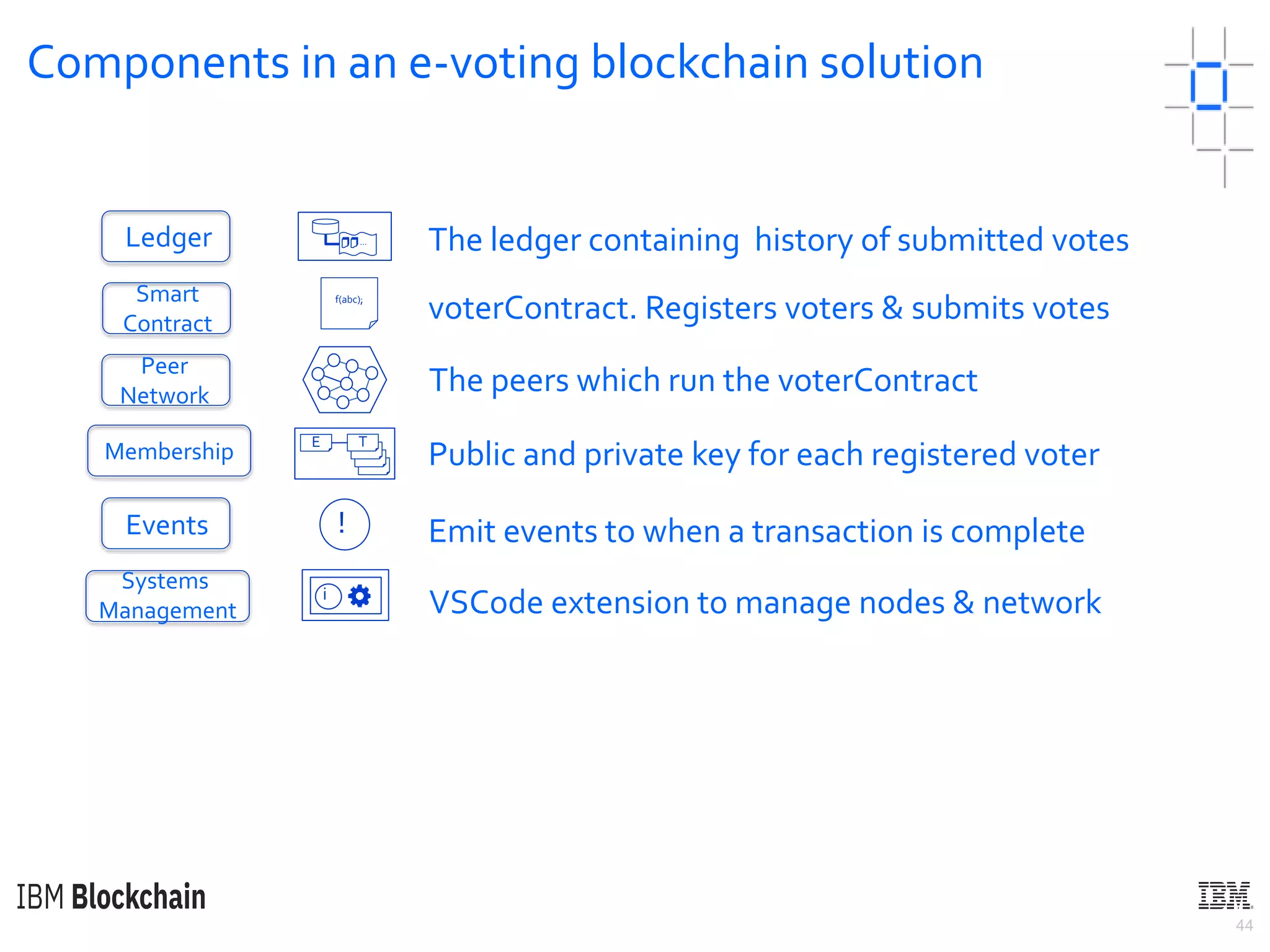
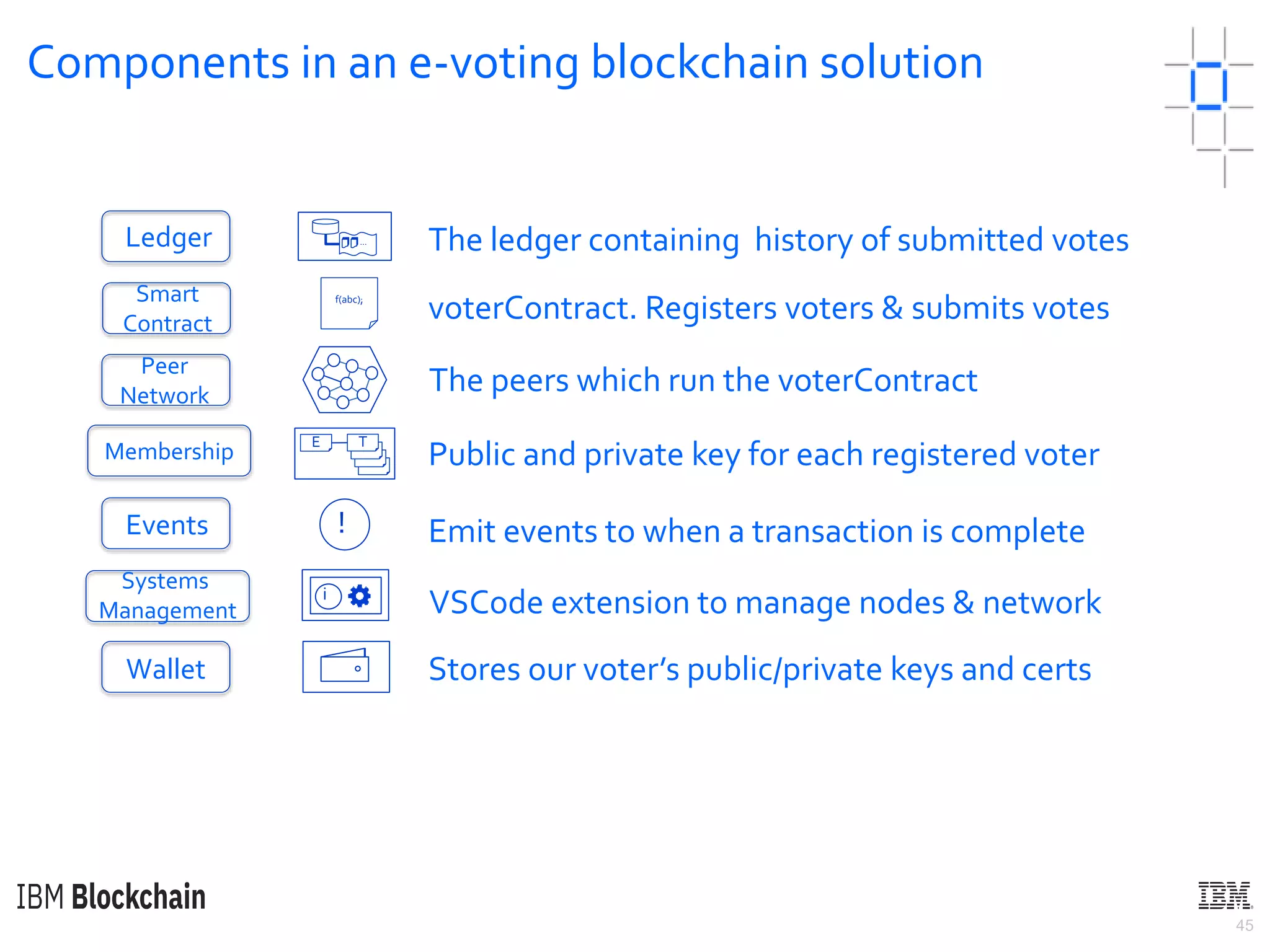
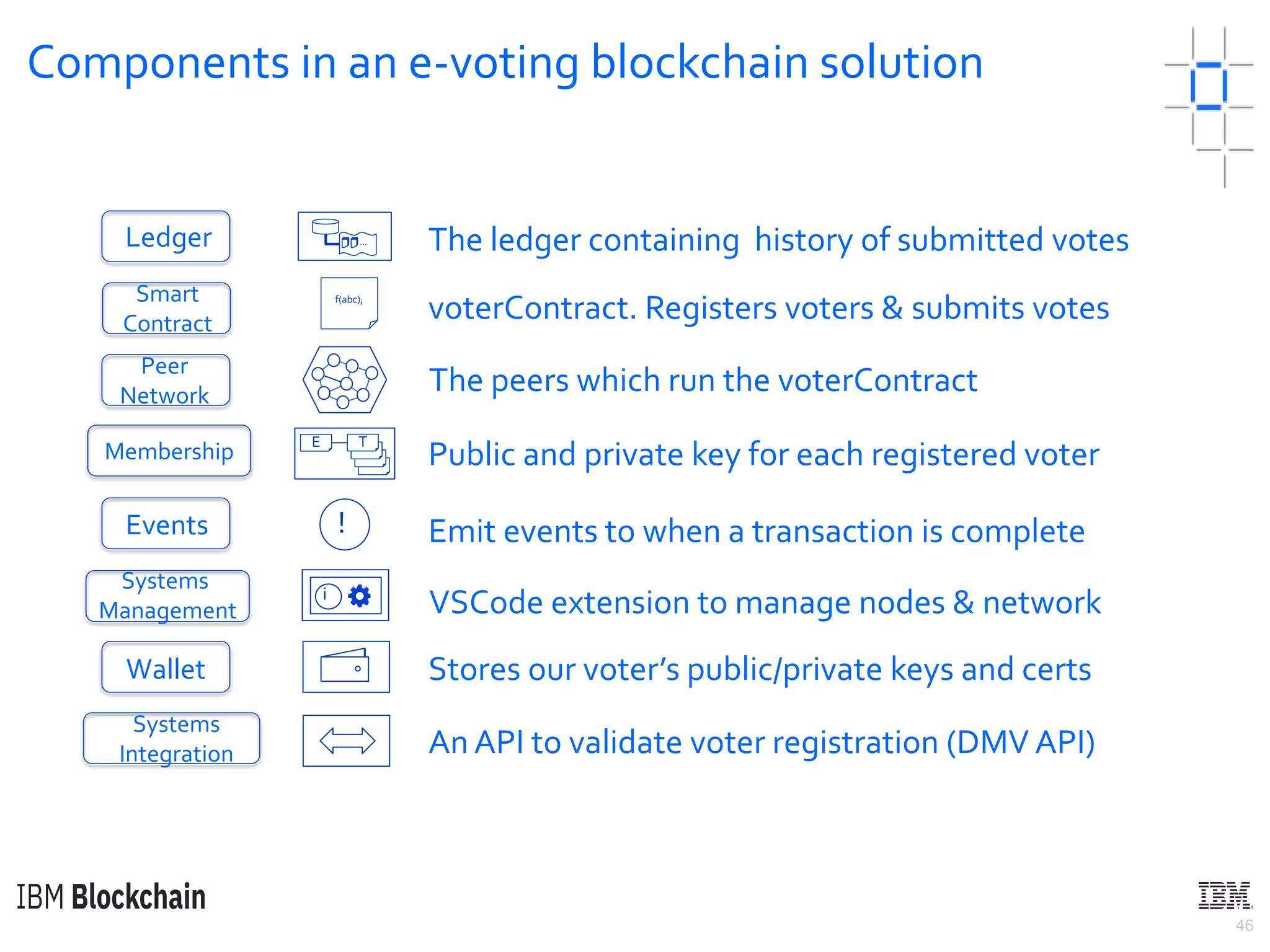
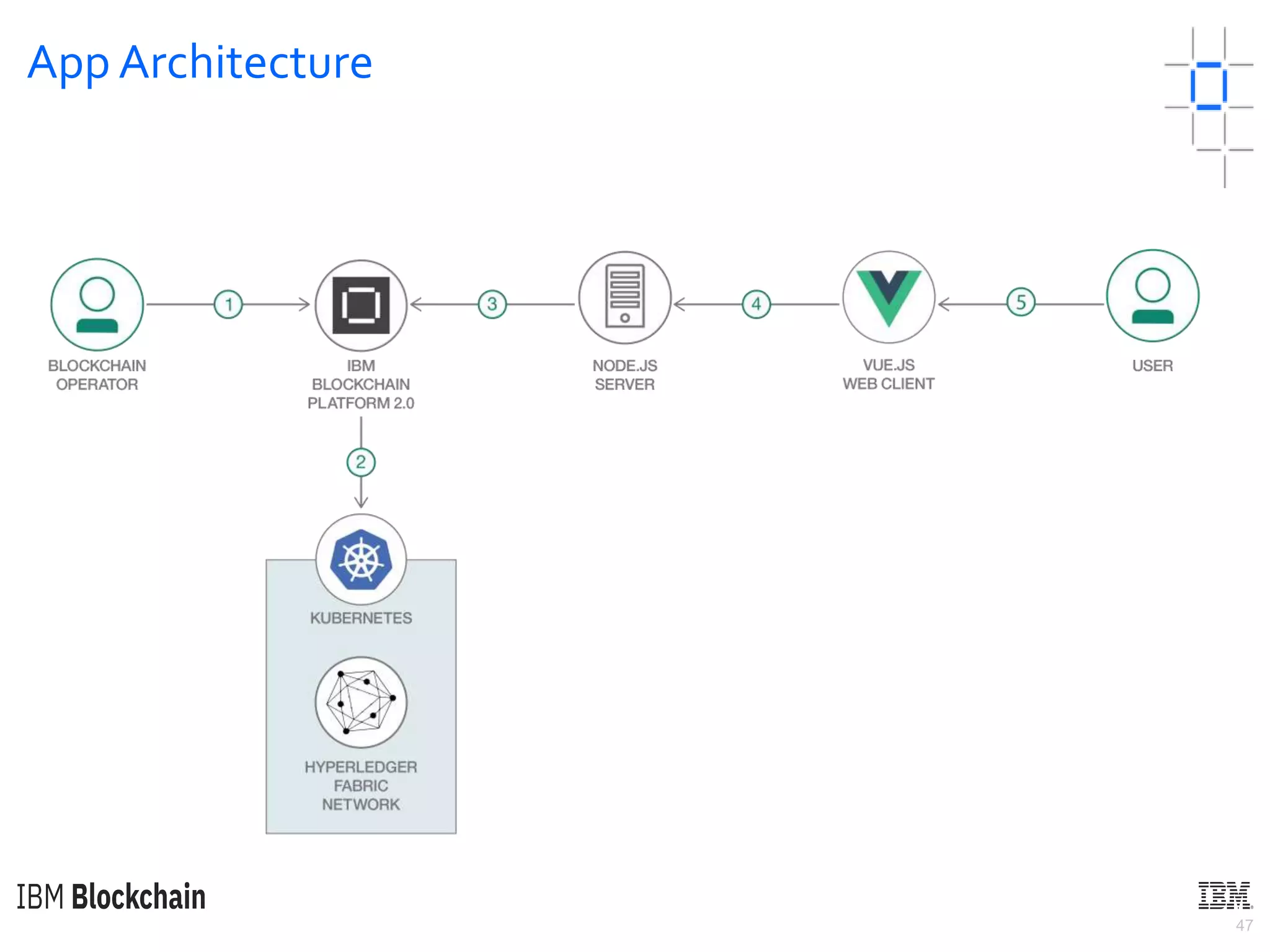
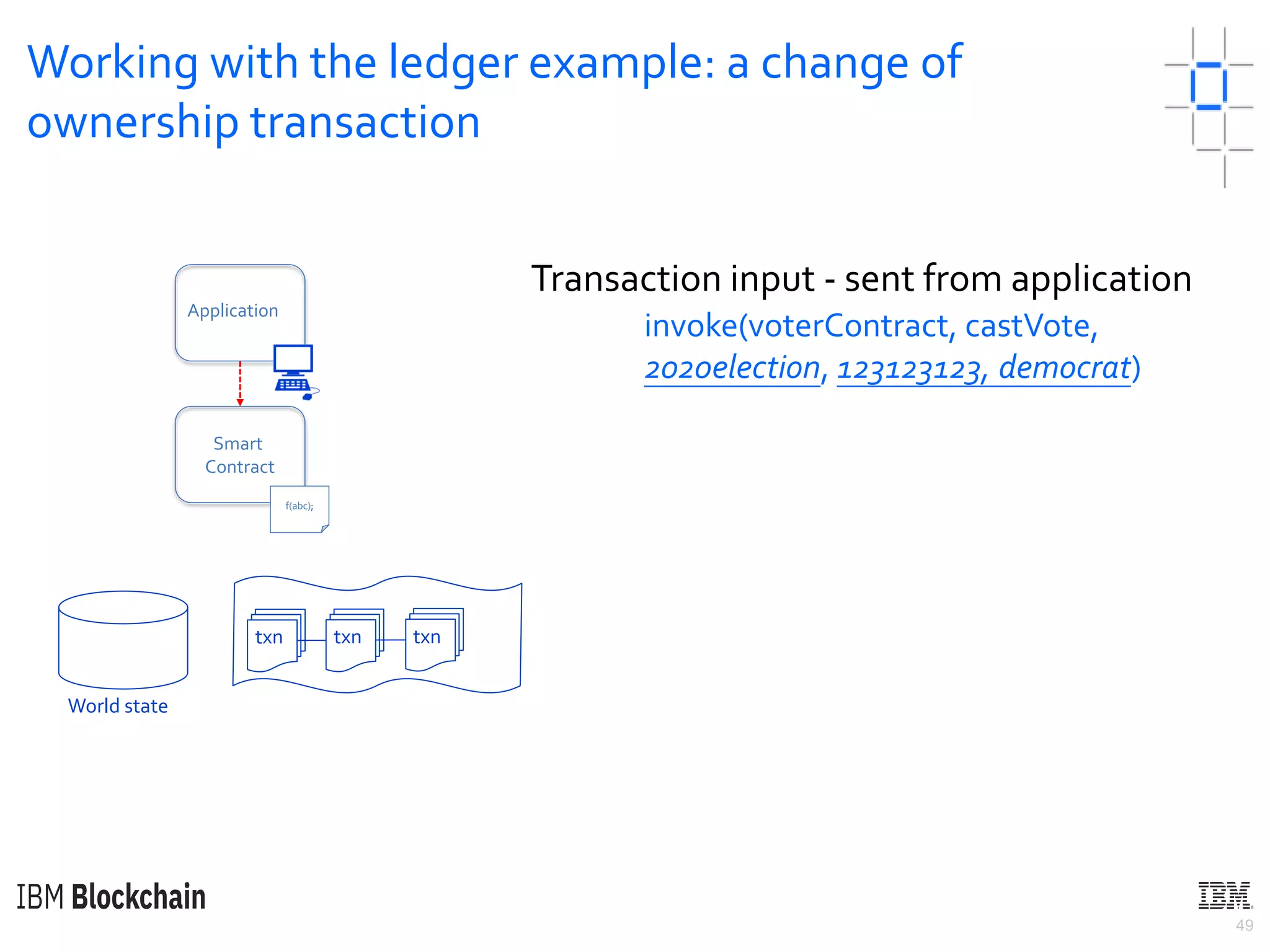
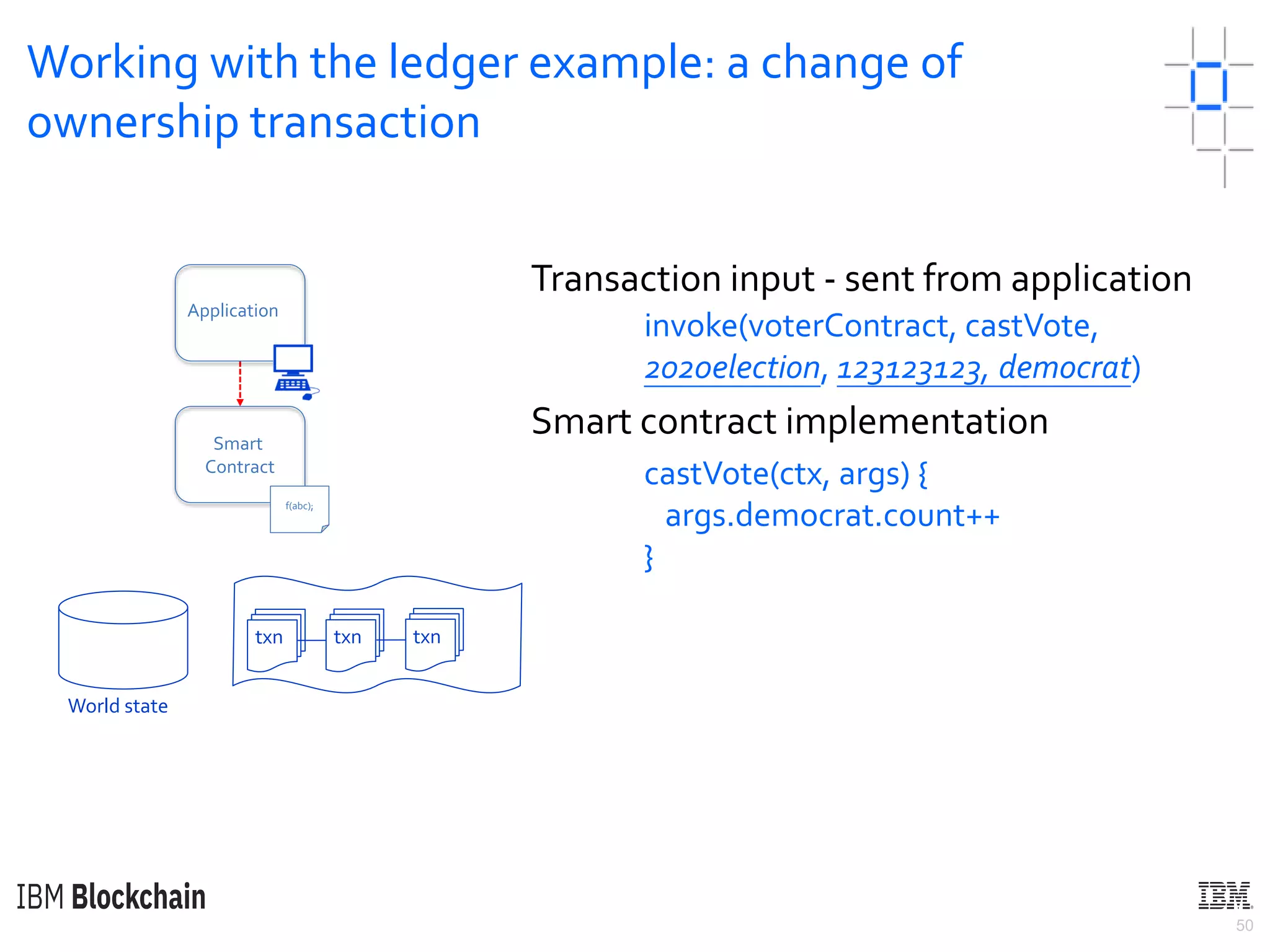
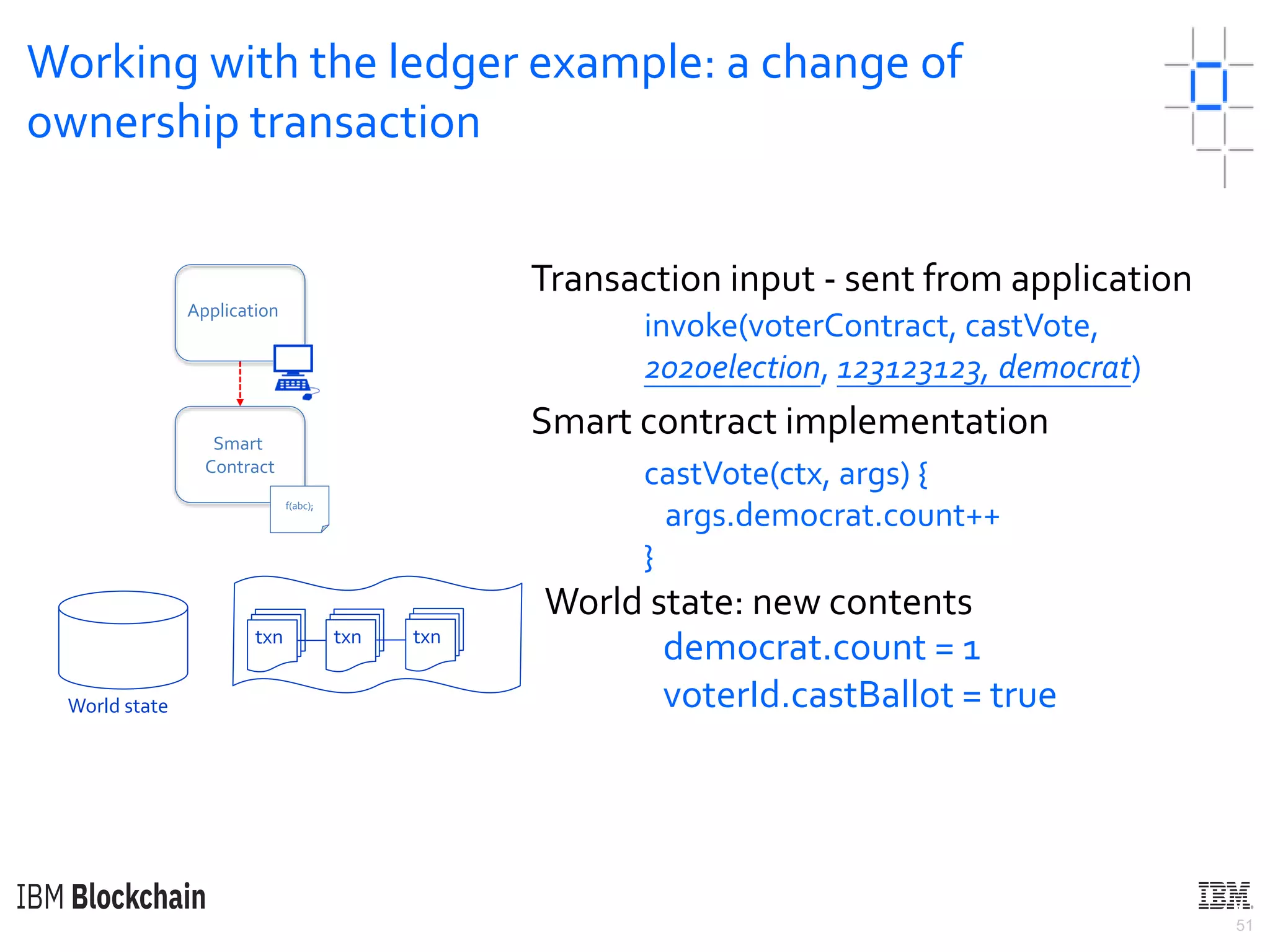
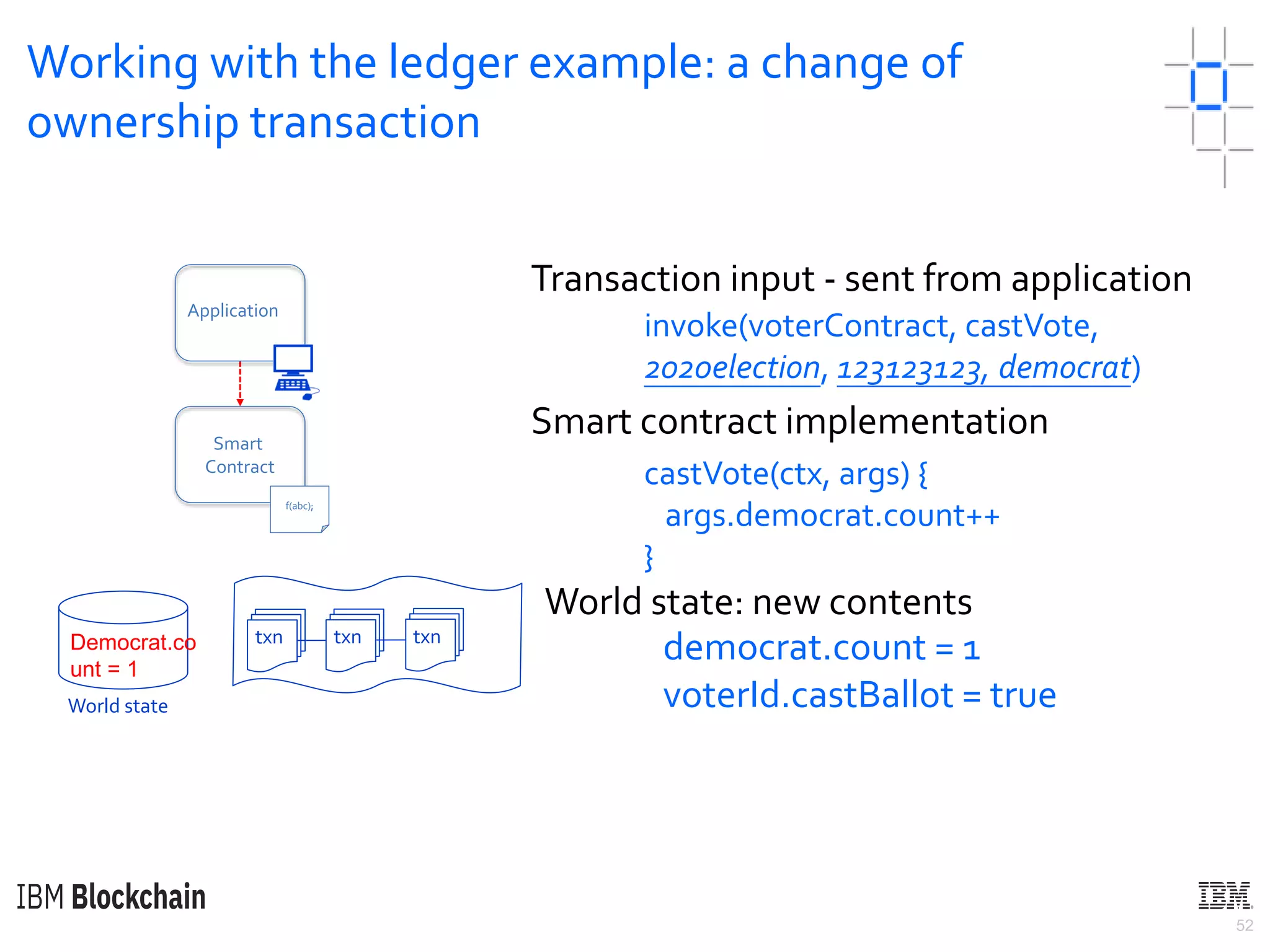
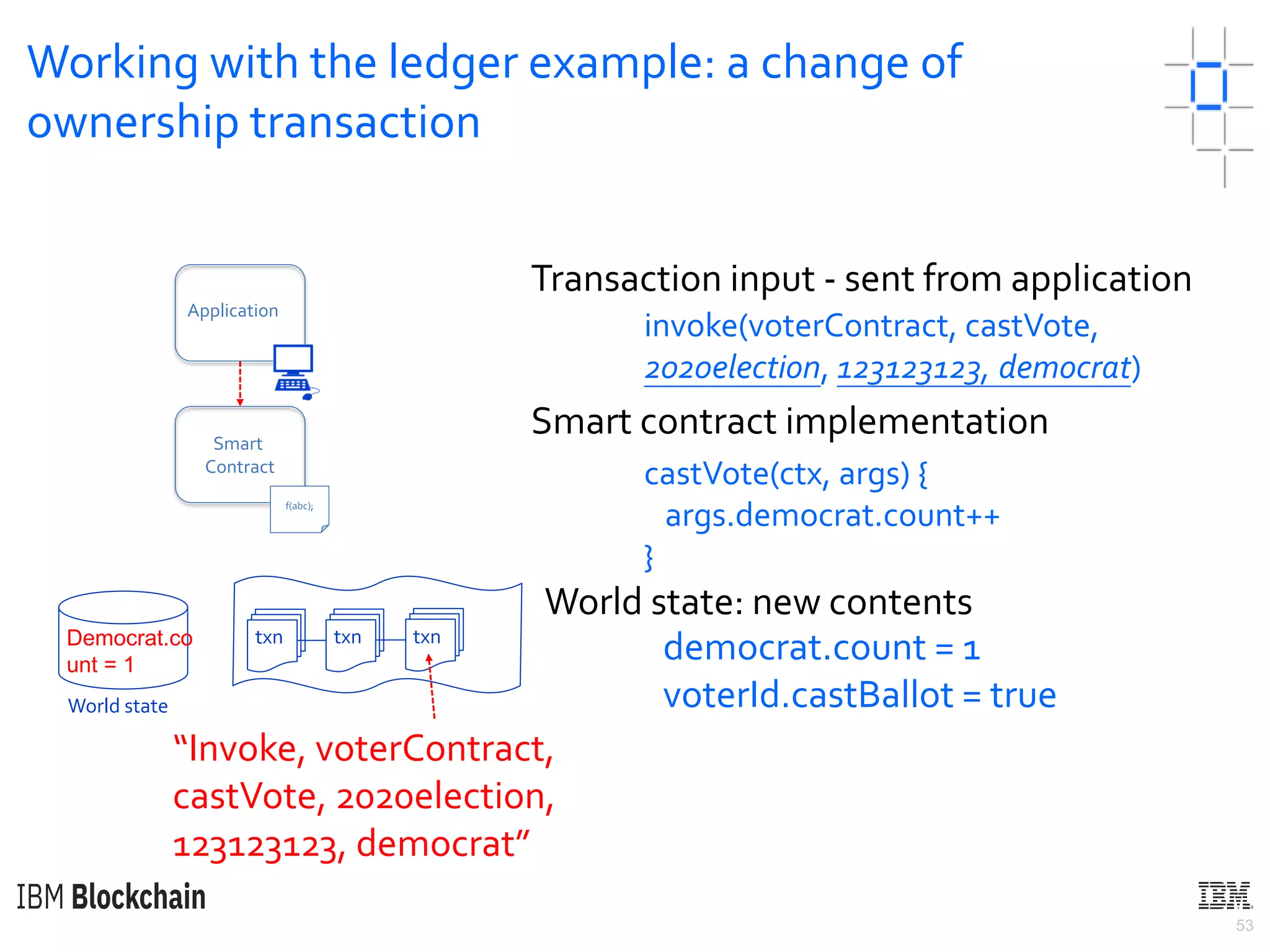
The document discusses deploying a blockchain web application using Hyperledger Fabric. It begins by introducing key concepts like blockchain vocabulary, the difference between public and private blockchains, and the architecture of a Hyperledger Fabric solution. It then covers the components of a Hyperledger Fabric network, including peers, smart contracts, the ledger, and client applications. It provides an example of how a smart contract updates the world state and an example use case of an e-voting application on the blockchain.