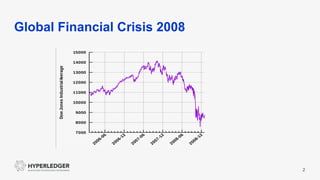
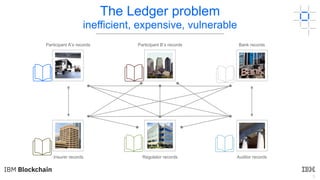
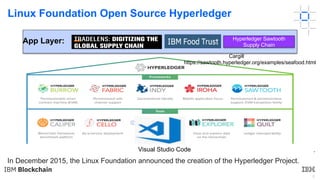
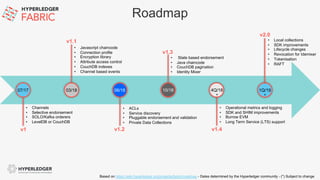
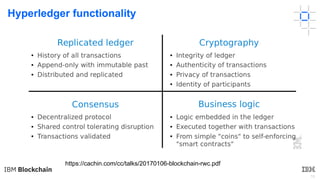
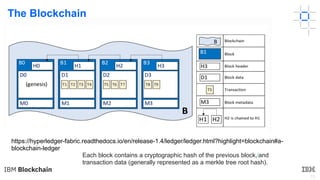
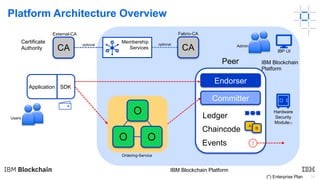
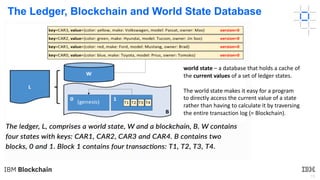
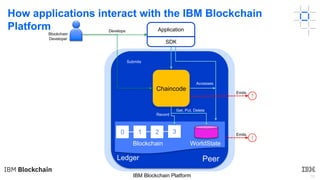
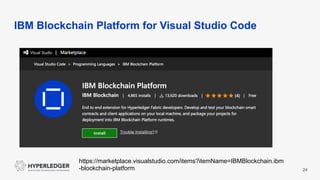
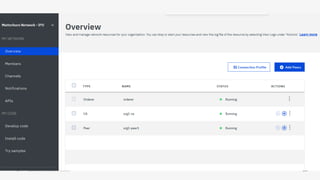
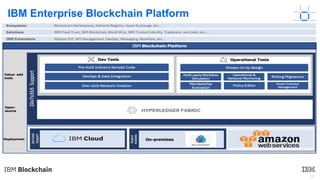
This document provides an introduction to blockchain and Hyperledger. It discusses how Hyperledger addresses issues with traditional ledgers by providing a shared, replicated ledger with consensus. It describes key Hyperledger components like membership services, ordering service, and peers. It also outlines the development process for building apps on Hyperledger, highlighting code patterns, frameworks, and using Visual Studio Code with IBM's blockchain plugin.