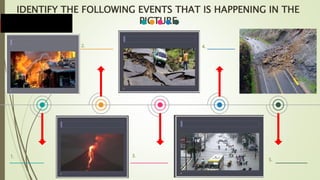
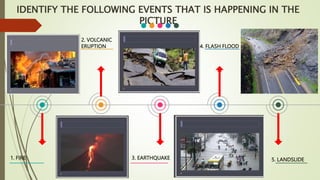
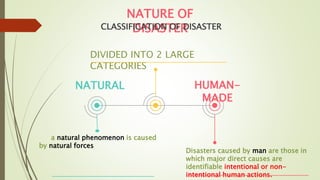
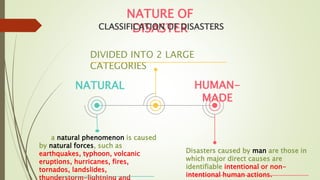
The document contains classroom rules for students which include turning off electronic devices during class, using polite speech and body language, speaking only when permitted by raising your hand, and asking for help if confused by asking the teacher or other students. It also contains an agenda for a presentation on disaster readiness and risk reduction which includes reviewing important elements of the fire triangle, causes of fire incidents, proper use of fire extinguishers, and actions to take in a fire. The presentation identifies different types of disasters in pictures such as fires, volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, floods, and defines key terms like disaster, storm surge, natural disasters, and classifications of disasters as natural or human-made.