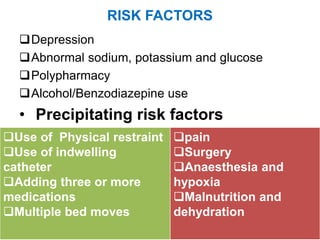
Delirium is a serious disturbance in mental abilities characterized by confused thinking and reduced awareness. It involves disturbances in attention, consciousness, cognition, as well as hallucinations and perceptual disturbances. It is common in hospitalized older patients and is triggered by medical illnesses, medications, electrolyte imbalances, and lack of sleep. Signs include reduced awareness, cognitive impairments, behavioral changes like agitation, and emotional disturbances like anxiety or depression. Diagnosis involves mental status exams and tests to check for underlying causes. Treatment focuses on treating the underlying medical condition and managing symptoms.