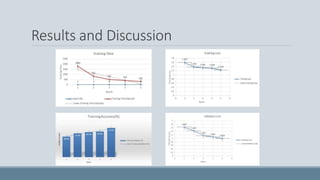
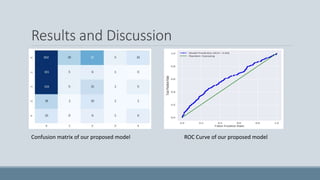
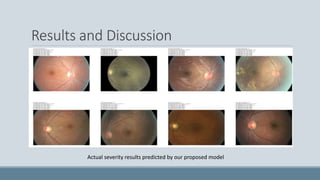
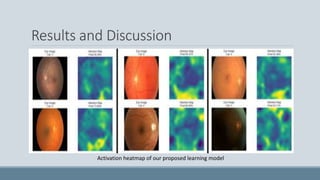
This document summarizes a study that developed an attention-based deep learning model to detect diabetic retinopathy from fundus images. The proposed model used an InceptionV3 architecture with additional convolutional layers and an attention mechanism. On a dataset of 35,000 fundus images, the model achieved 94.3% validation accuracy, an improvement over previous models. Activation heatmaps showed the model learned important retinal features. The study demonstrated that deep learning can effectively detect diabetic retinopathy from images and may help with early diagnosis.




![Related Work
Nursel Yalçin et al. [1] proposed a deep learning approach for DR disease classification.
Omer Deperlioglu et al. [2] proposed a CNN based deep learning model.
Darshit Doshi et al [3] proposed a CNN model.
Arkadiusz Kwasigroch et al [4] proposed CNN based decision support system for DR disease
classification.
Fully connected convolutional neural network was proposed by Manaswini Jena et al [5].
XiaoliangWang et al [6] used deep learning model with 63.23% validation accuracy. The
proposed model was based on pre-trained model inceptionNetV3.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deepdrimageguideddiabeticretinopathydetectionusingattentionbaseddeeplearningscheme-research-article-240304083042-c2d60513/85/DeepDRImageGuidedDiabeticRetinopathyDetectionUsingAttentionBasedDeepLearningScheme-Research-Article-pptx-5-320.jpg)
![Related Work
Hai Quan Chen et al [7] obtained validation accuracy up to 80.0%. Deep neural network model
was discussed in his paper.
Abhay Shah et al [8] described a CNN model with 53.57% accuracy.
IgiArdiyanto et al [9] proposed a Deep learning model for assessment DR disease in embedded
system.
Hanung Adi Nugroho [10] discussed the three different approaches. First approach was based
on pathologies. Second approach was based on foveal avascular zone (FAZ) structure. In third
approach, deep learning was proposed with more than 95% validation accuracy.
FengLiYu et al. [11] obtained 95.42% validation accuracy using deep learning model.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deepdrimageguideddiabeticretinopathydetectionusingattentionbaseddeeplearningscheme-research-article-240304083042-c2d60513/85/DeepDRImageGuidedDiabeticRetinopathyDetectionUsingAttentionBasedDeepLearningScheme-Research-Article-pptx-6-320.jpg)
![Related Work
Bhavani Sambaturu et al [12] achieved 91% validation accuracy via deep learning techniques.
Yashal Shakti Kanungo et al. [13] discussed deep learning model with 88% training accuracy.
Syahidahizza Rufaida et al. [14] achieved 51.05% accuracy using CNN deep learning model.
Ratul Ghosh et al. [15] proposed two deep learning techniques for two DR stages. 95% and 85%
validation accuracy were achieved respectively.
Roye [16] explained a model based on fuzzy C mean based technique to extract the features and
support vector machine to classify the feature.
Dong et al. [17] proposed a wavelet based feature classification techniques with up to 84% validation
accuracy.
S. Choudhury et al. [18] extracted features using Fuzzy C mean based feature extraction technique.
These extracted features were classified using support vector machines.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deepdrimageguideddiabeticretinopathydetectionusingattentionbaseddeeplearningscheme-research-article-240304083042-c2d60513/85/DeepDRImageGuidedDiabeticRetinopathyDetectionUsingAttentionBasedDeepLearningScheme-Research-Article-pptx-7-320.jpg)
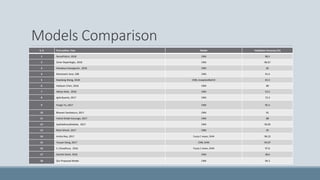
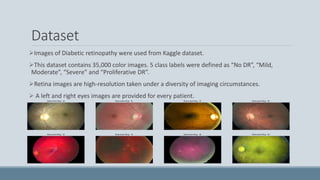



![Description of Proposed CNN Architecture
Layer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to
input_3 (InputLayer) (None, 512, 512, 3) 0
xception (Model) (None, 16, 16, 2048) 20861480 input_3[0][0]
batch_normalization_10 (BatchNo (None, 16, 16,
2048)
8192 xception[1][0]
dropout_4 (Dropout) (None, 16, 16, 2048) 0 batch_normalization_10[0][0]
conv2d_15 (Conv2D) (None, 16, 16, 64) 131136 dropout_4[0][0]
conv2d_16 (Conv2D) (None, 16, 16, 16) 1040 conv2d_15[0][0]
conv2d_17 (Conv2D) (None, 16, 16, 8) 136 conv2d_16[0][0]
conv2d_18 (Conv2D) (None, 16, 16, 4) 36 conv2d_17[0][0]
conv2d_19 (Conv2D) (None, 16, 16, 1) 5 conv2d_18[0][0]
conv2d_20 (Conv2D) (None, 16, 16, 2048) 2048 conv2d_19[0][0]
multiply_2 (Multiply) (None, 16, 16, 2048) 0 conv2d_20[0][0]
batch_normalization_10[0][0]
global_average_pooling2d_3 (GAP) (None, 2048) 0 multiply_2[0][0]
global_average_pooling2d_4 (GAP) (None, 2048) 0 conv2d_20[0][0]
RescaleGAP (Lambda) (None, 2048) 0 global_average_pooling2d_3[0][0]
global_average_pooling2d_4[0][0]
dropout_5 (Dropout) (None, 2048) 0 RescaleGAP[0][0]
dense_4 (Dense) (None, 128) 262272 dropout_5[0][0]
dropout_6 (Dropout) (None, 128) 0 dense_4[0][0]
dense_5 (Dense) (None, 64) 8256 dropout_6[0][0]
dense_6 (Dense) (None, 5) 325 dense_5[0][0]
Total params: 21,274,926
Trainable params: 407,302
Non-trainable params: 20,867,624](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deepdrimageguideddiabeticretinopathydetectionusingattentionbaseddeeplearningscheme-research-article-240304083042-c2d60513/85/DeepDRImageGuidedDiabeticRetinopathyDetectionUsingAttentionBasedDeepLearningScheme-Research-Article-pptx-13-320.jpg)