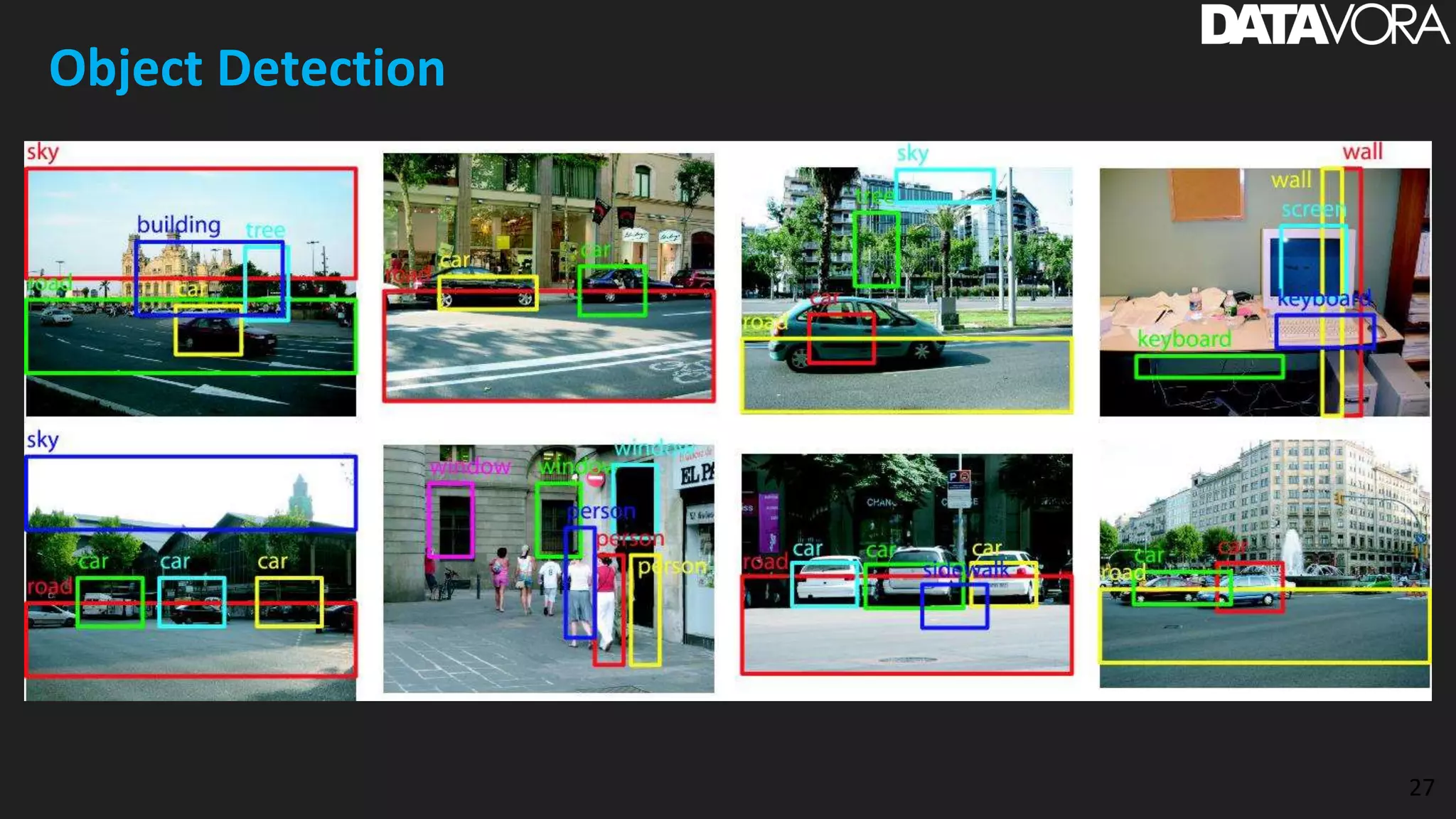
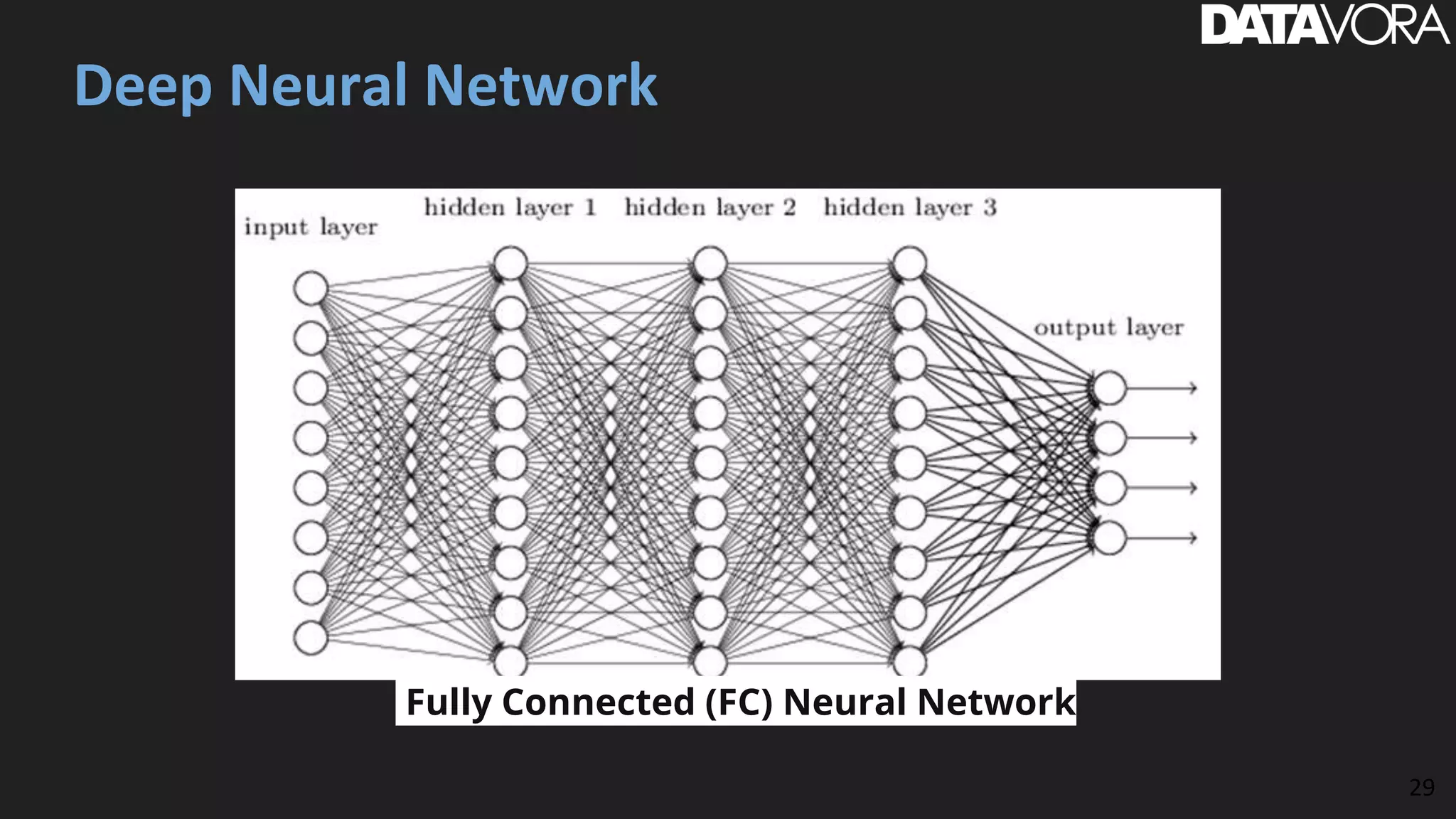
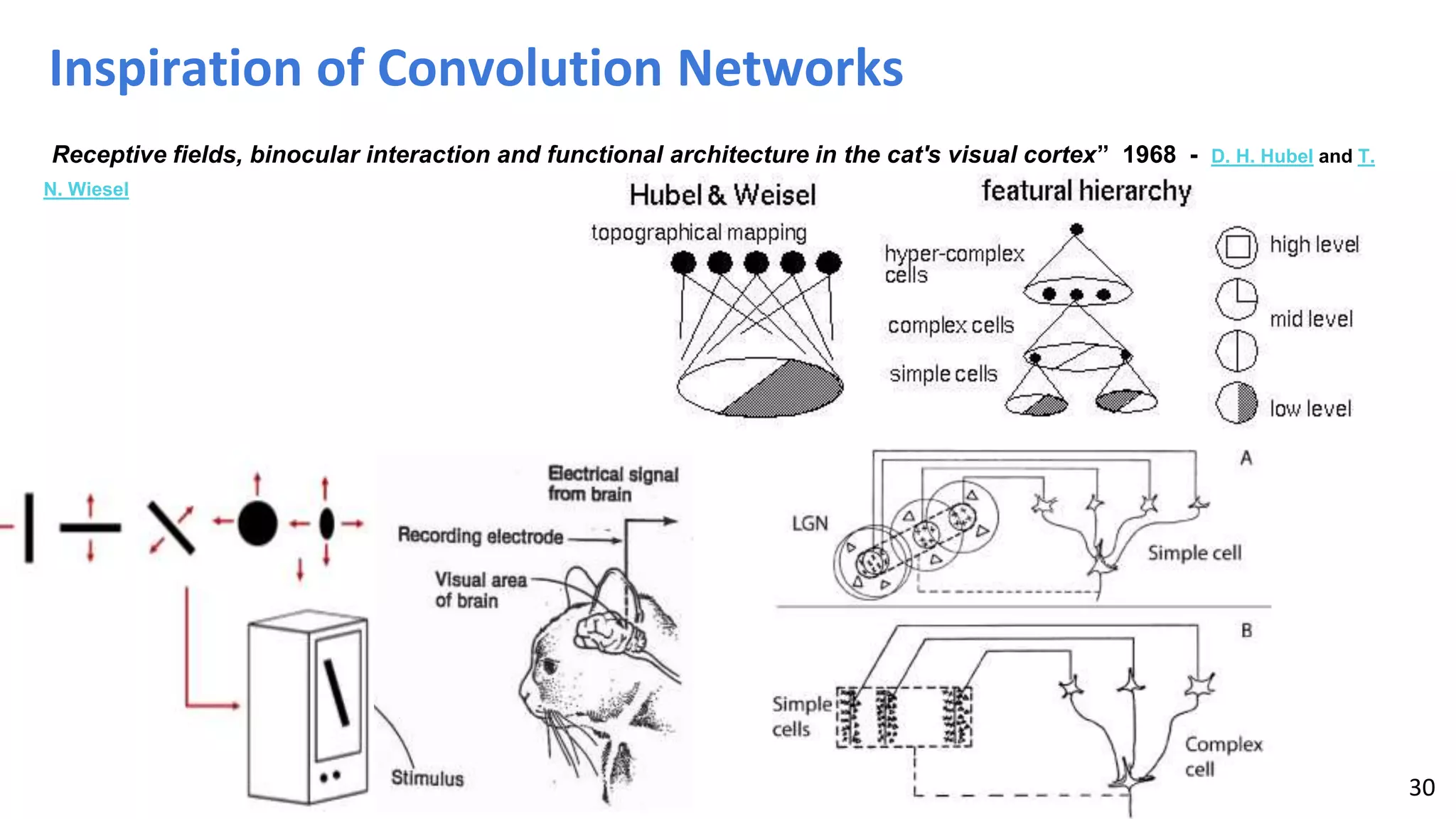
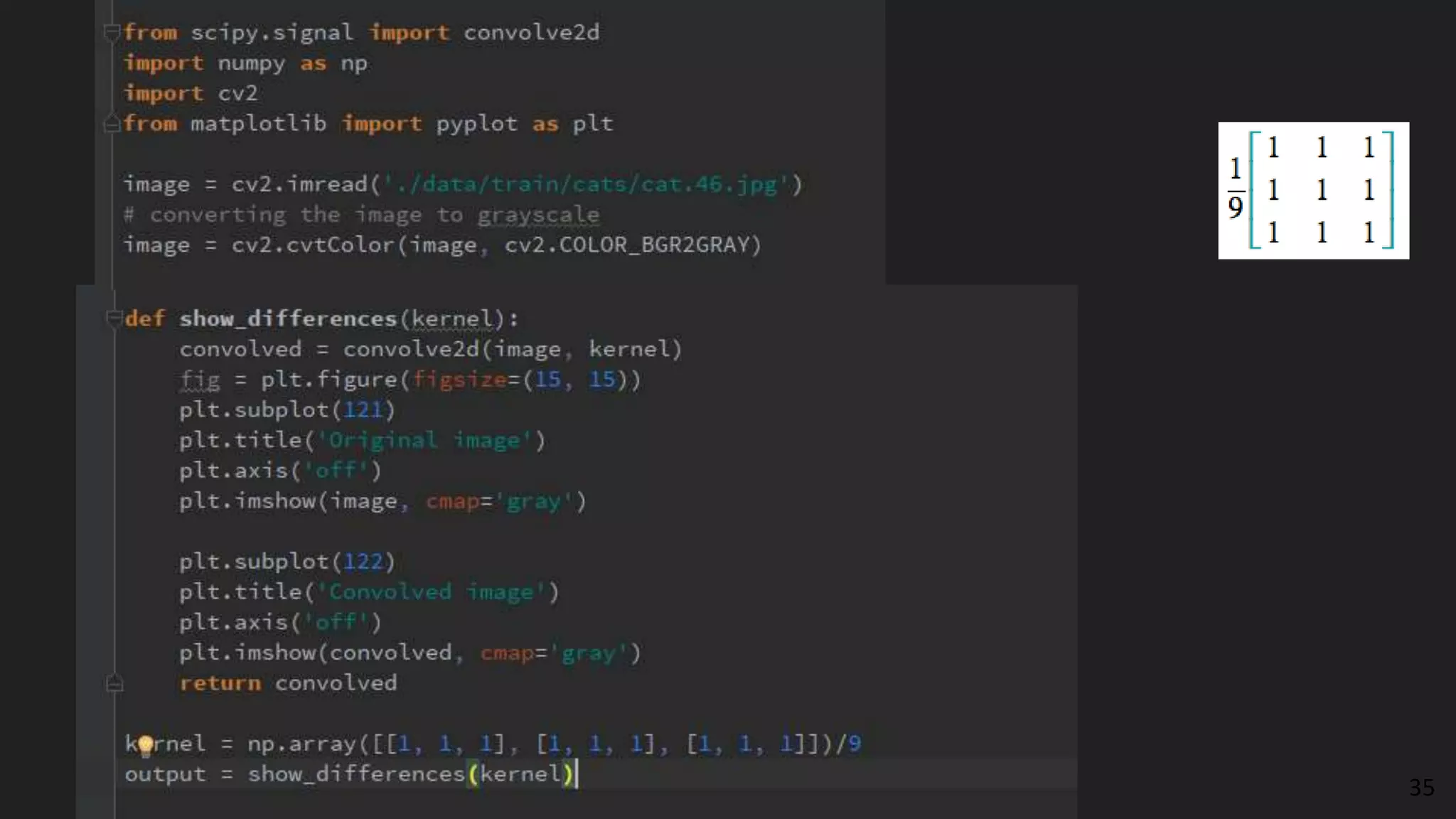
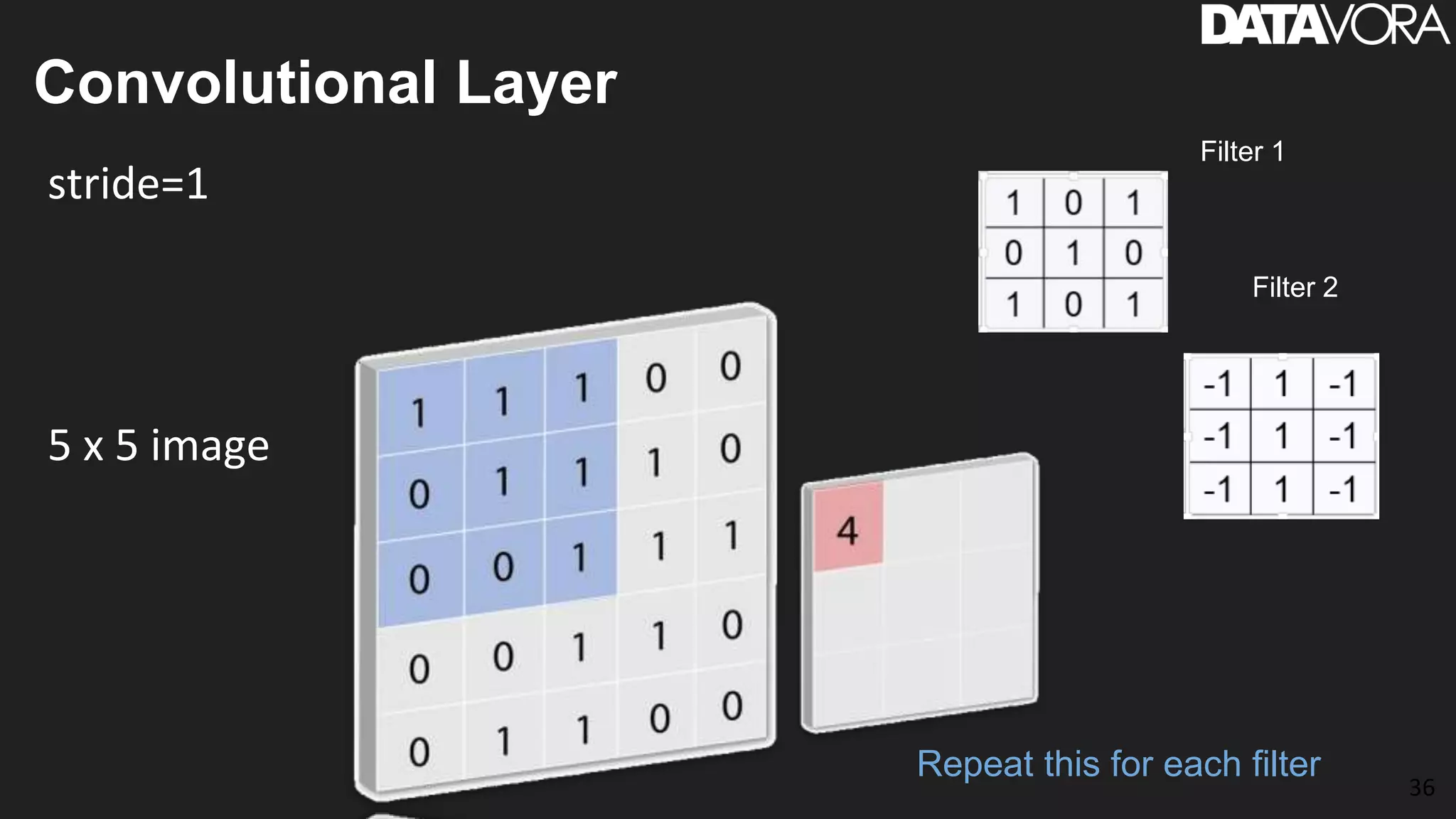
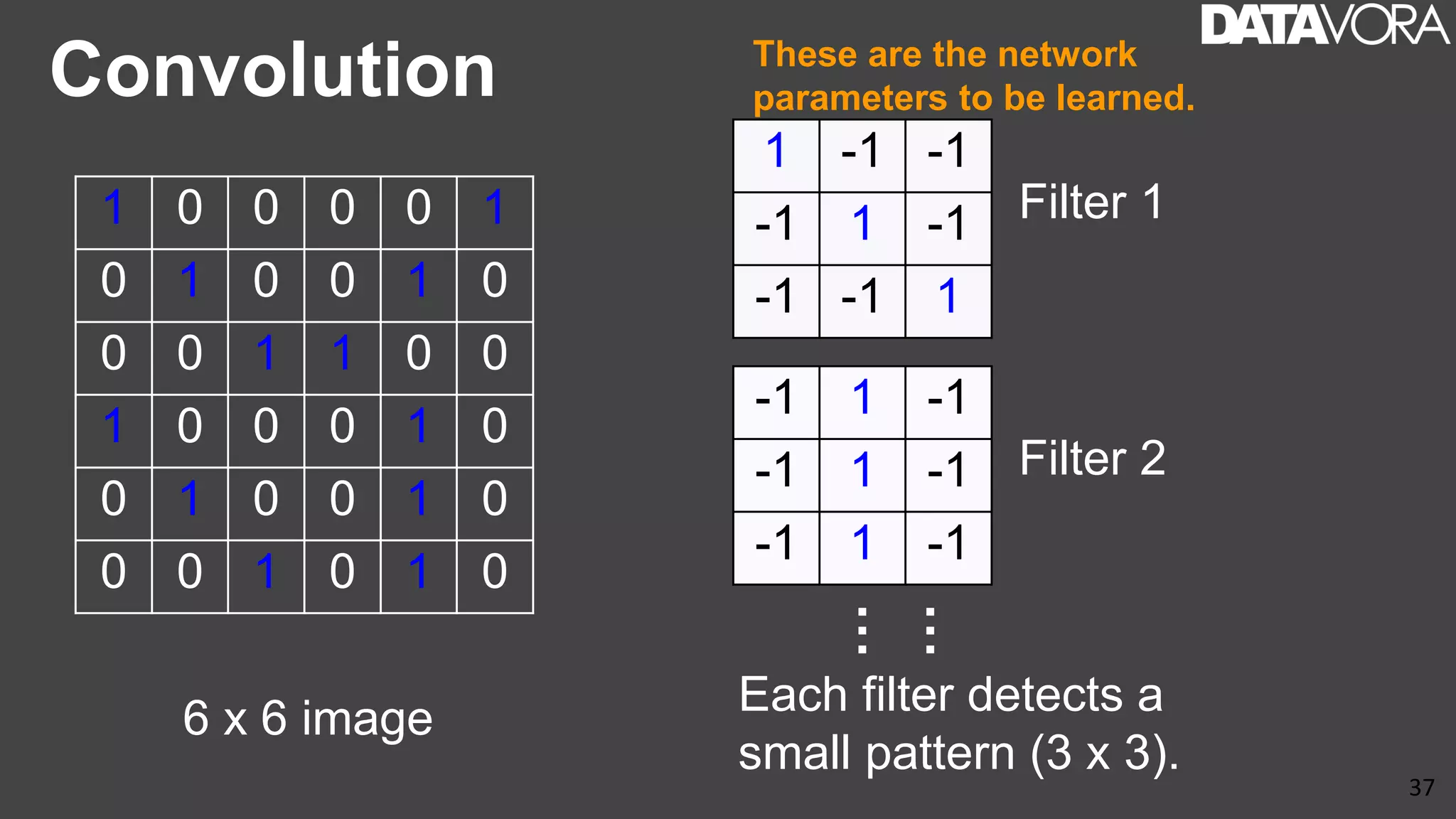
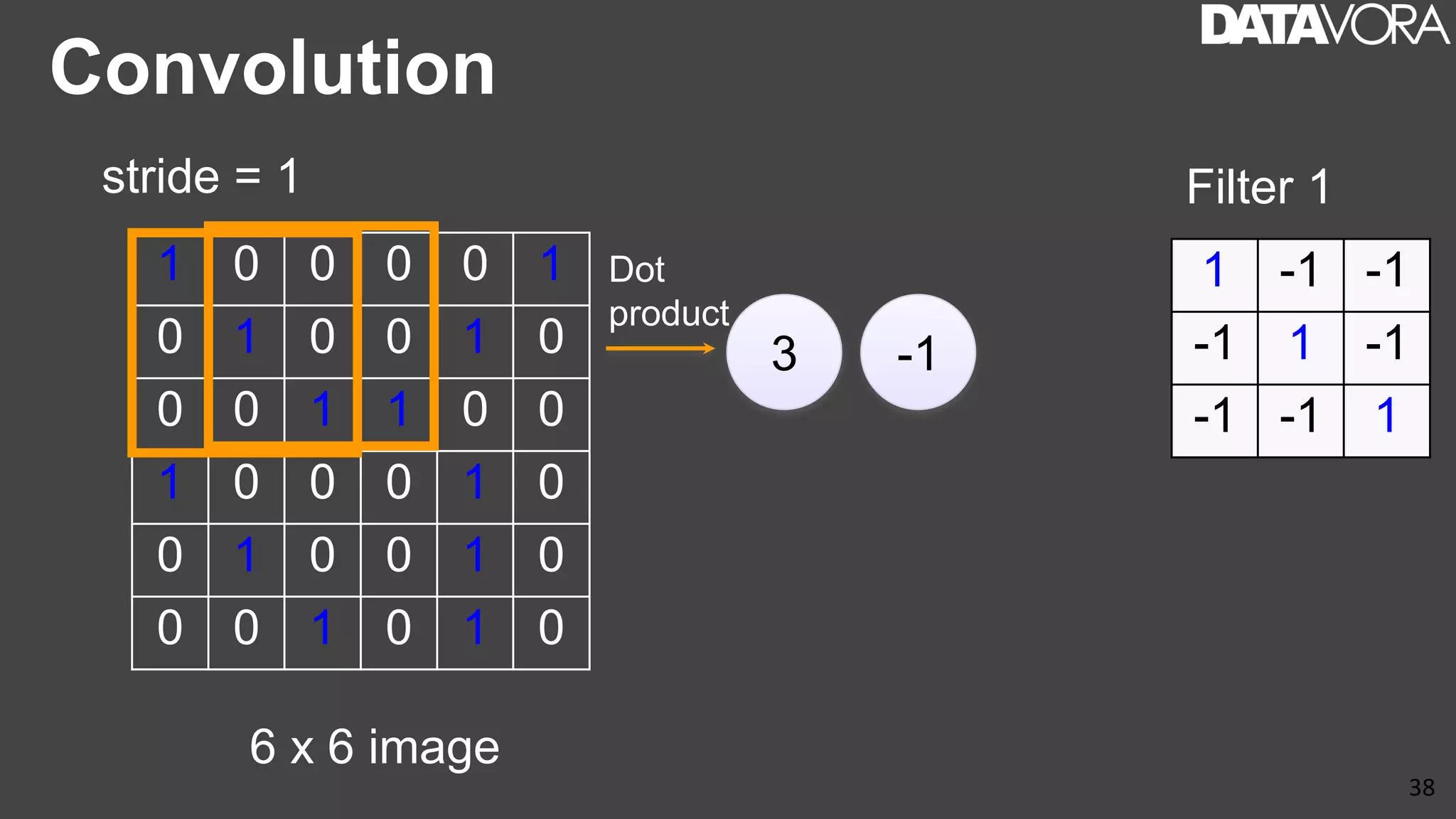
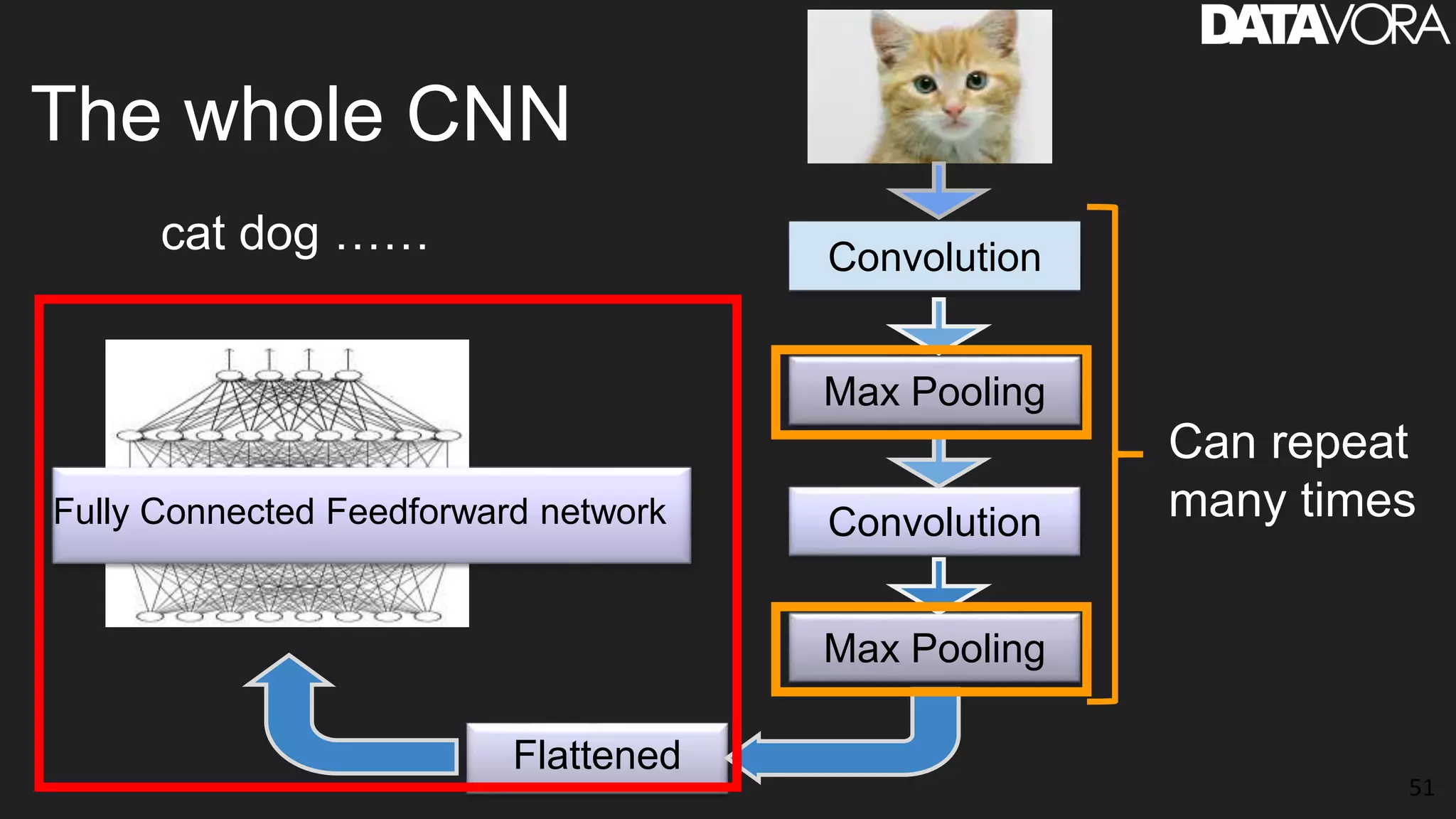
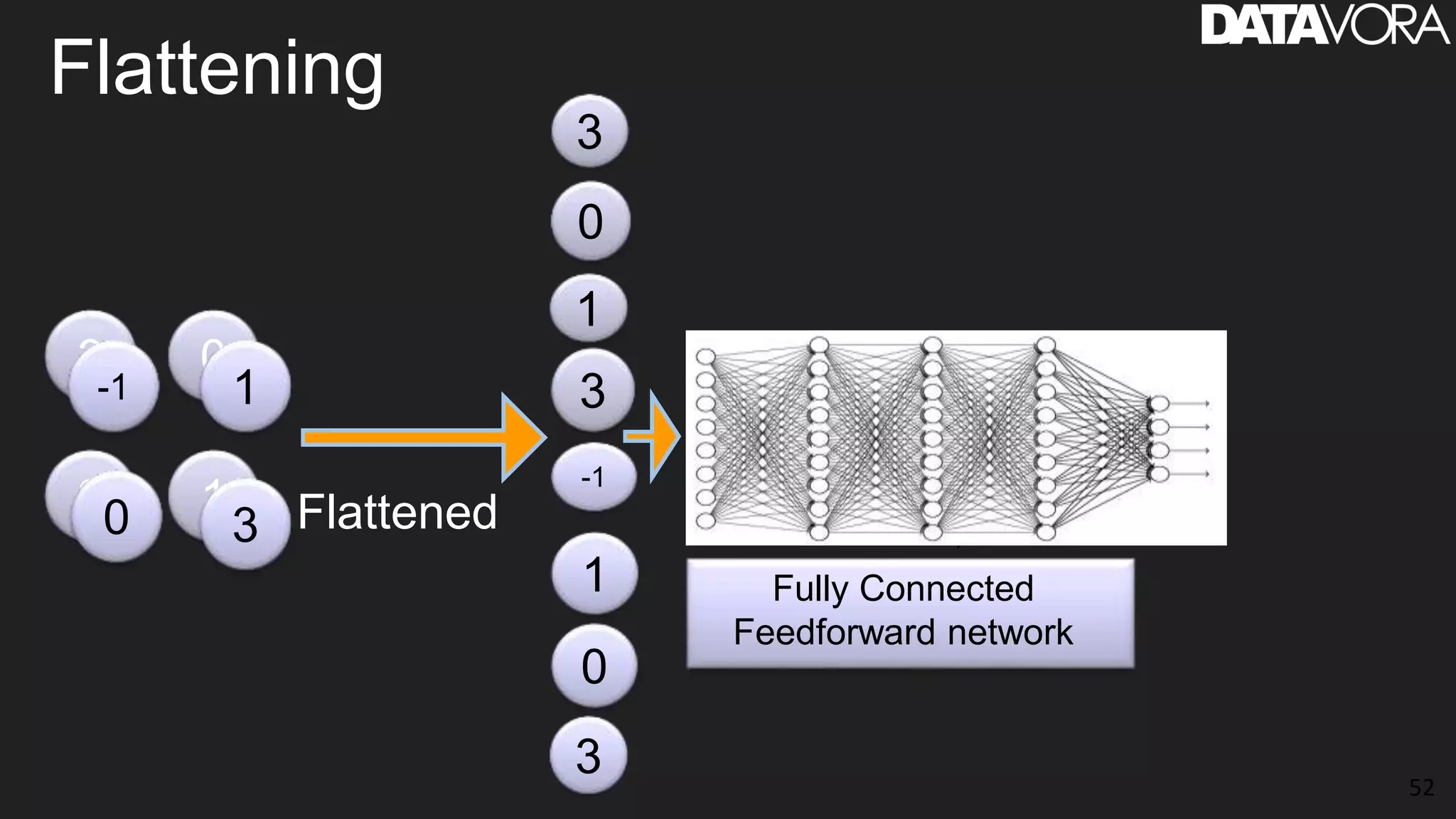
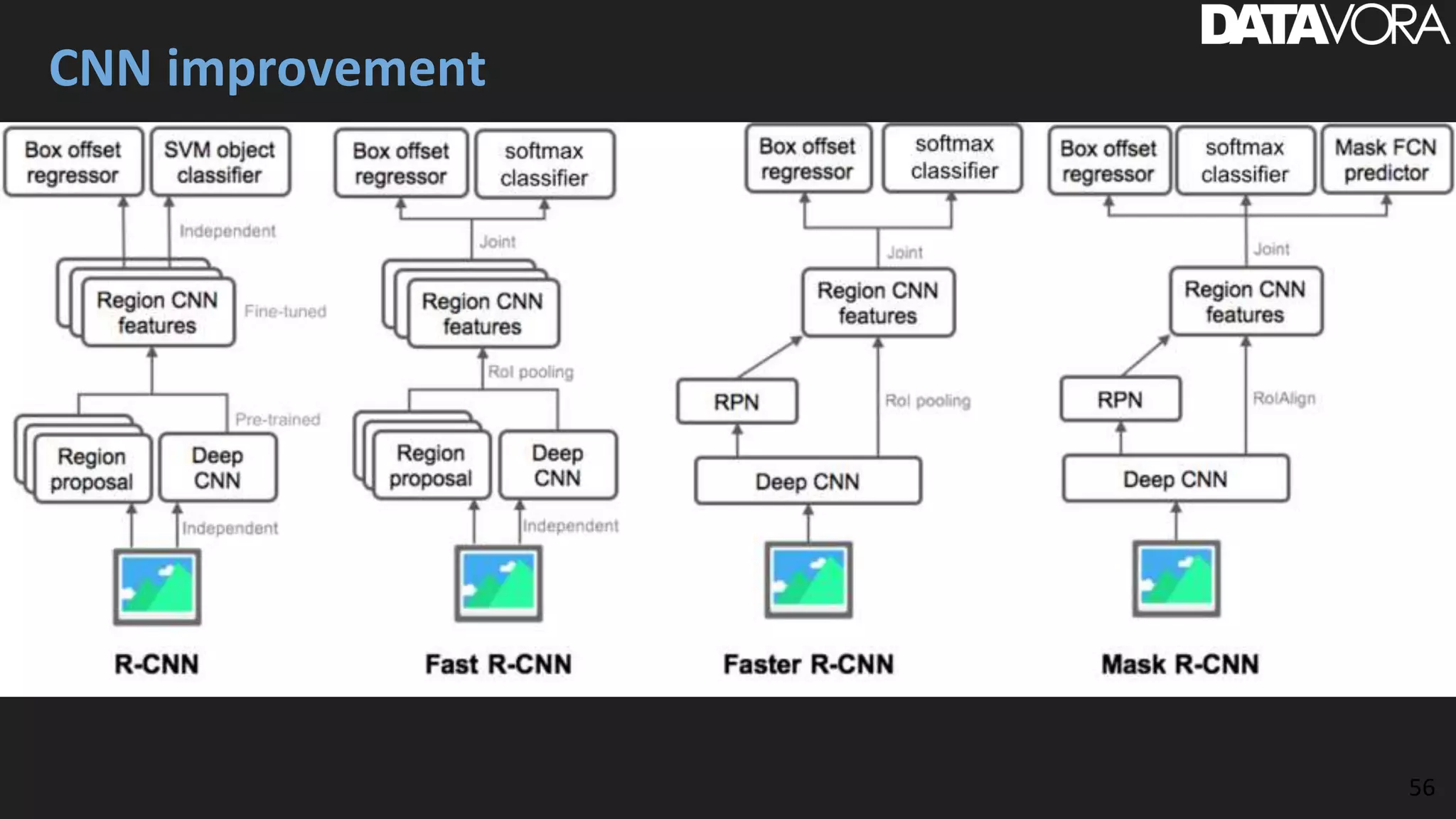
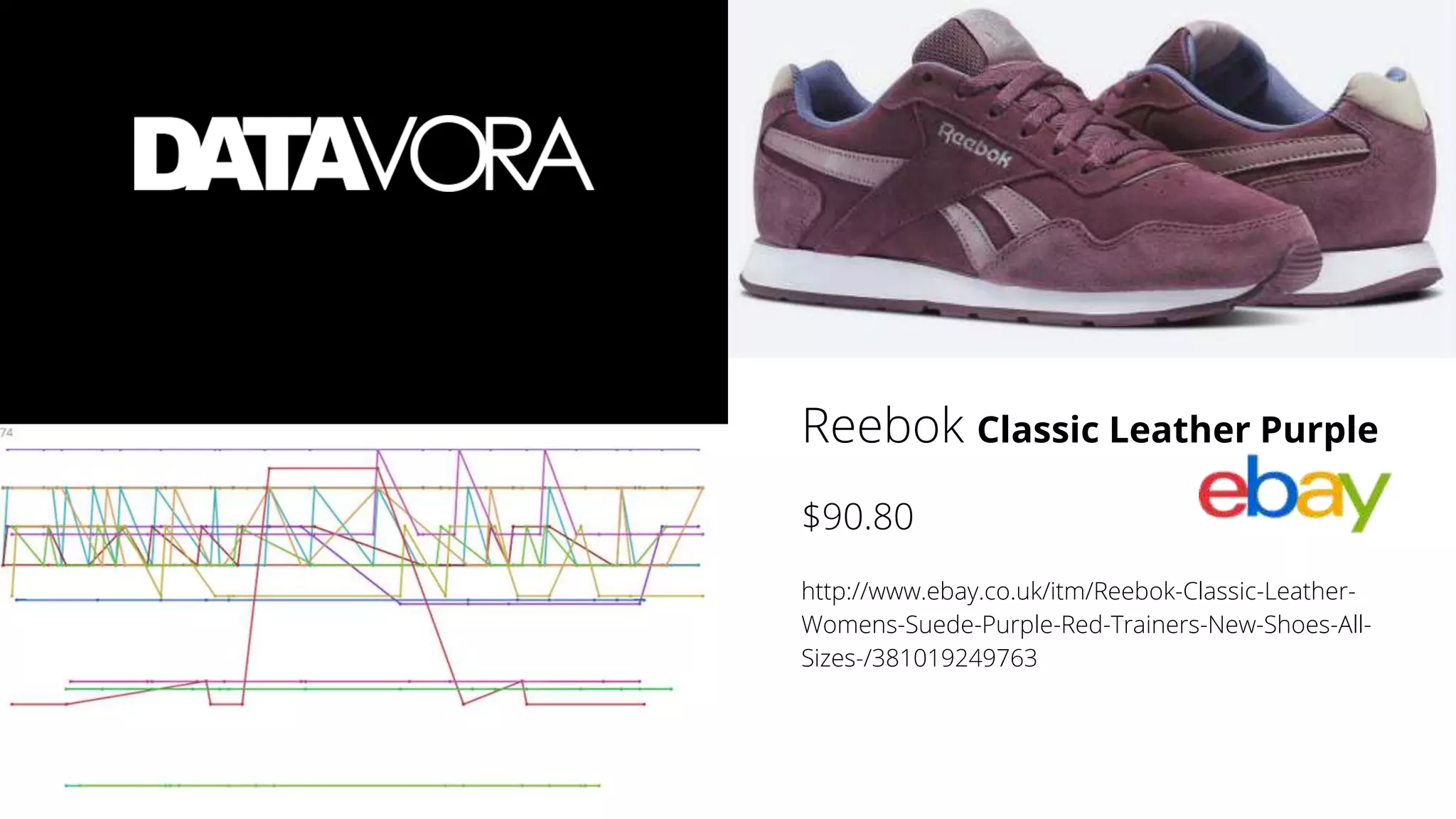
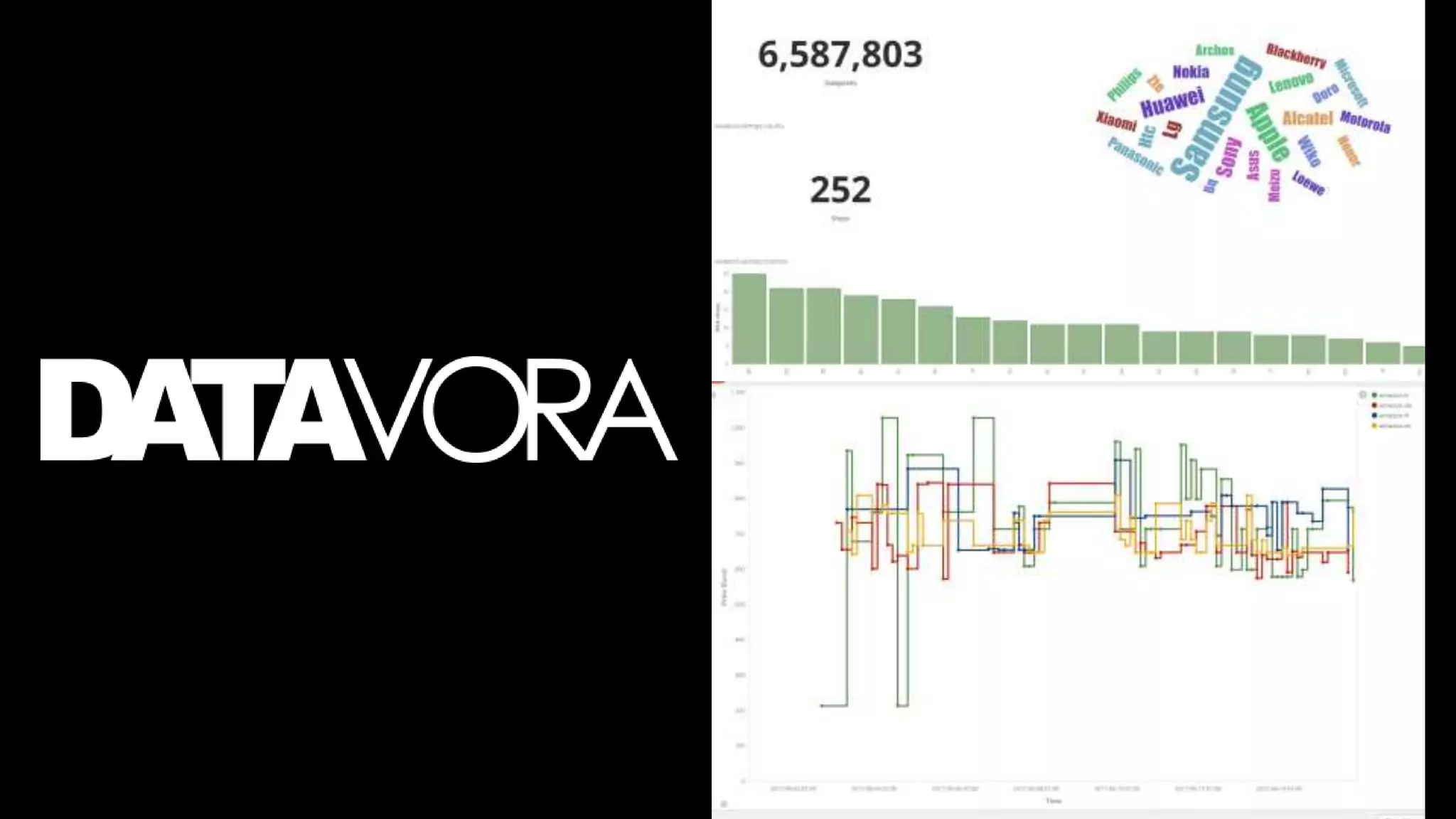
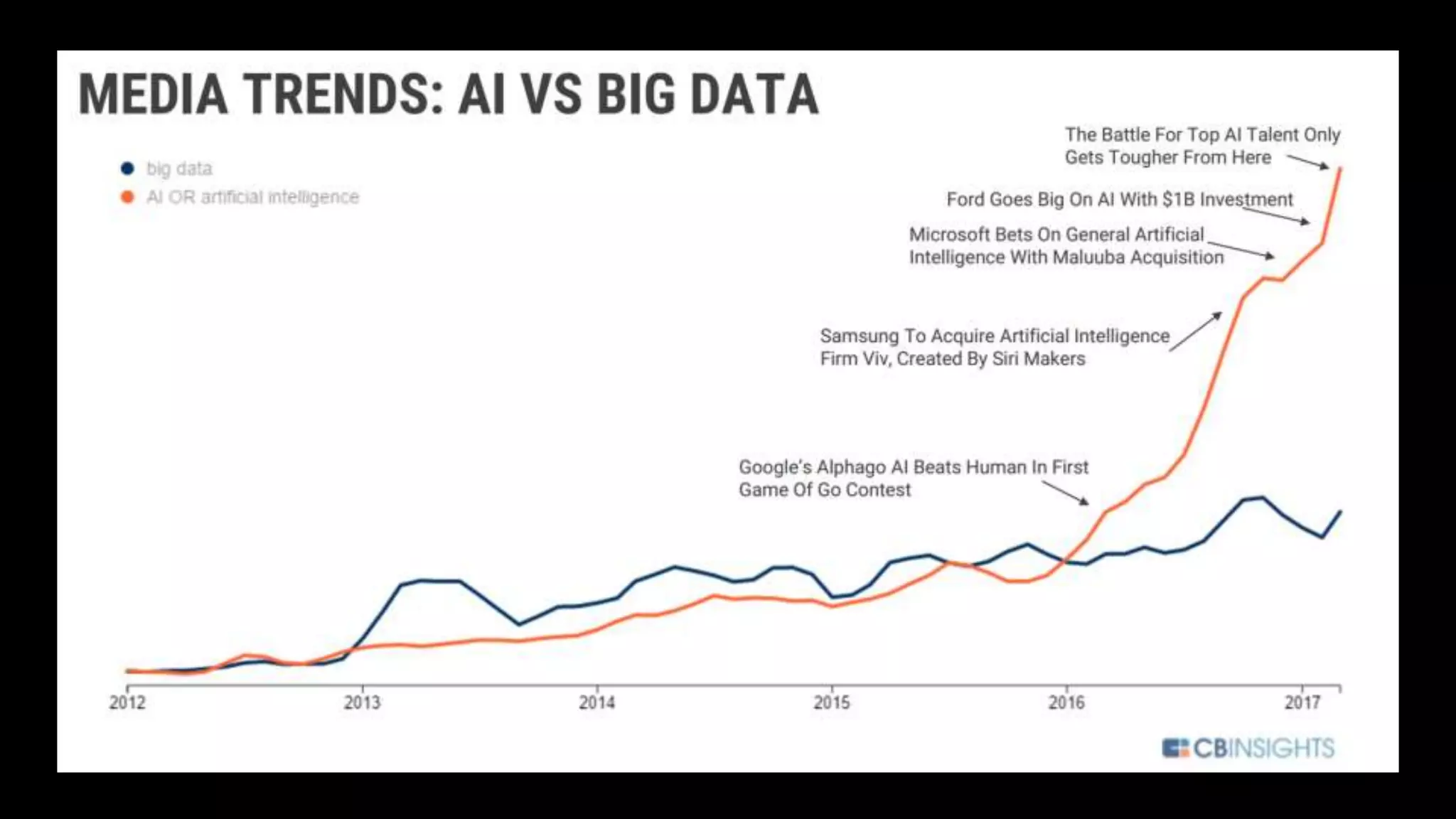
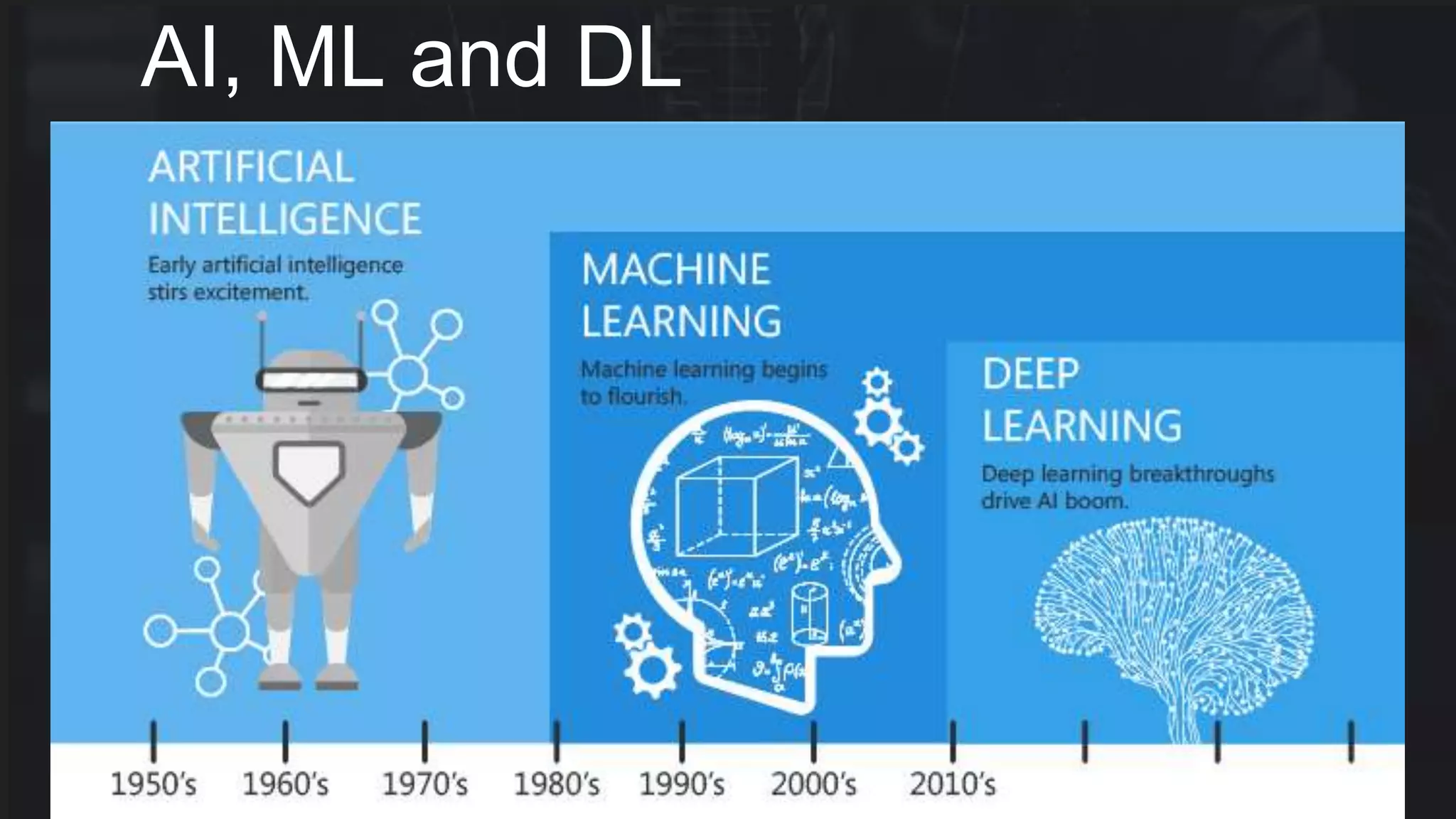
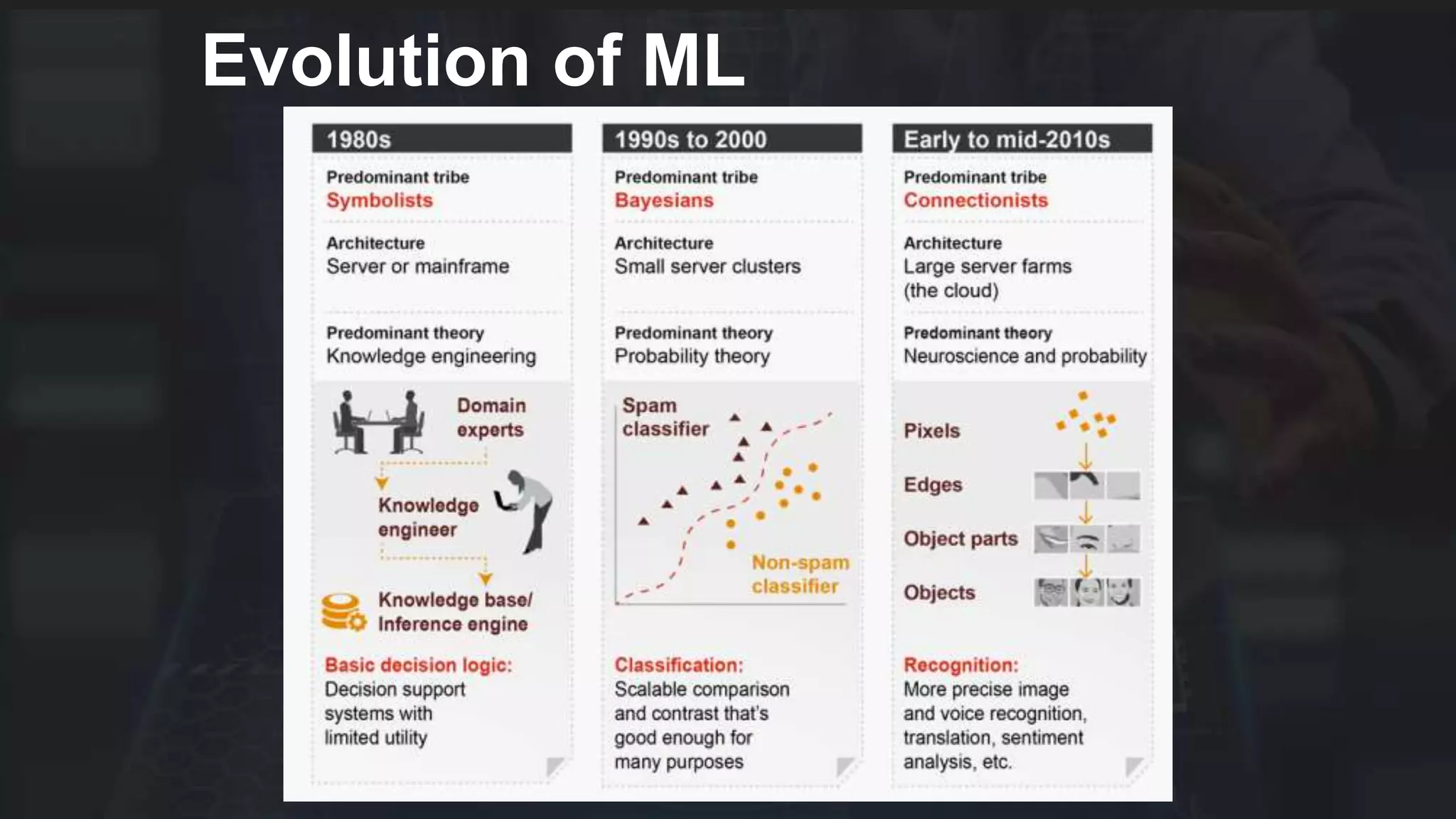
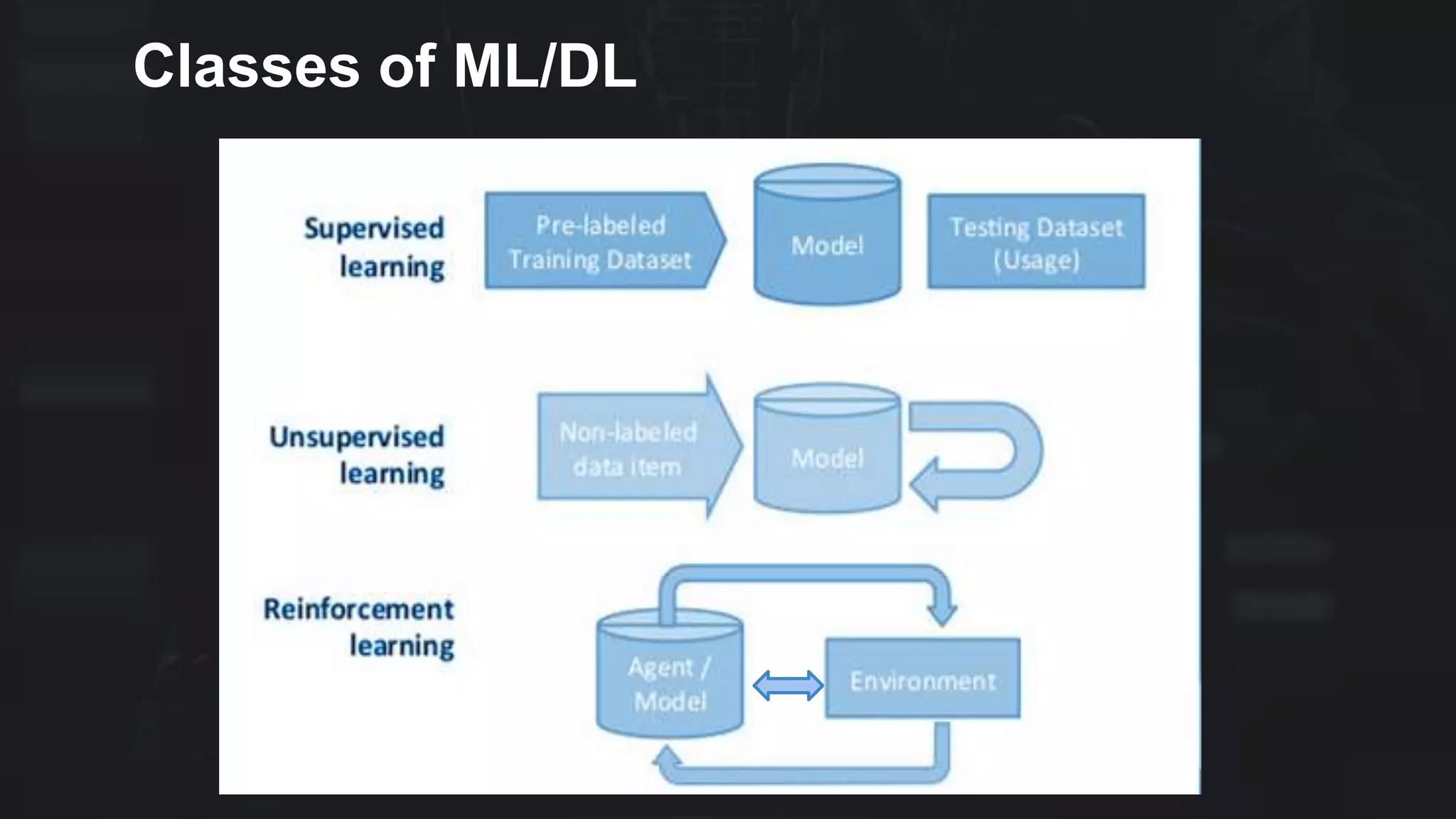
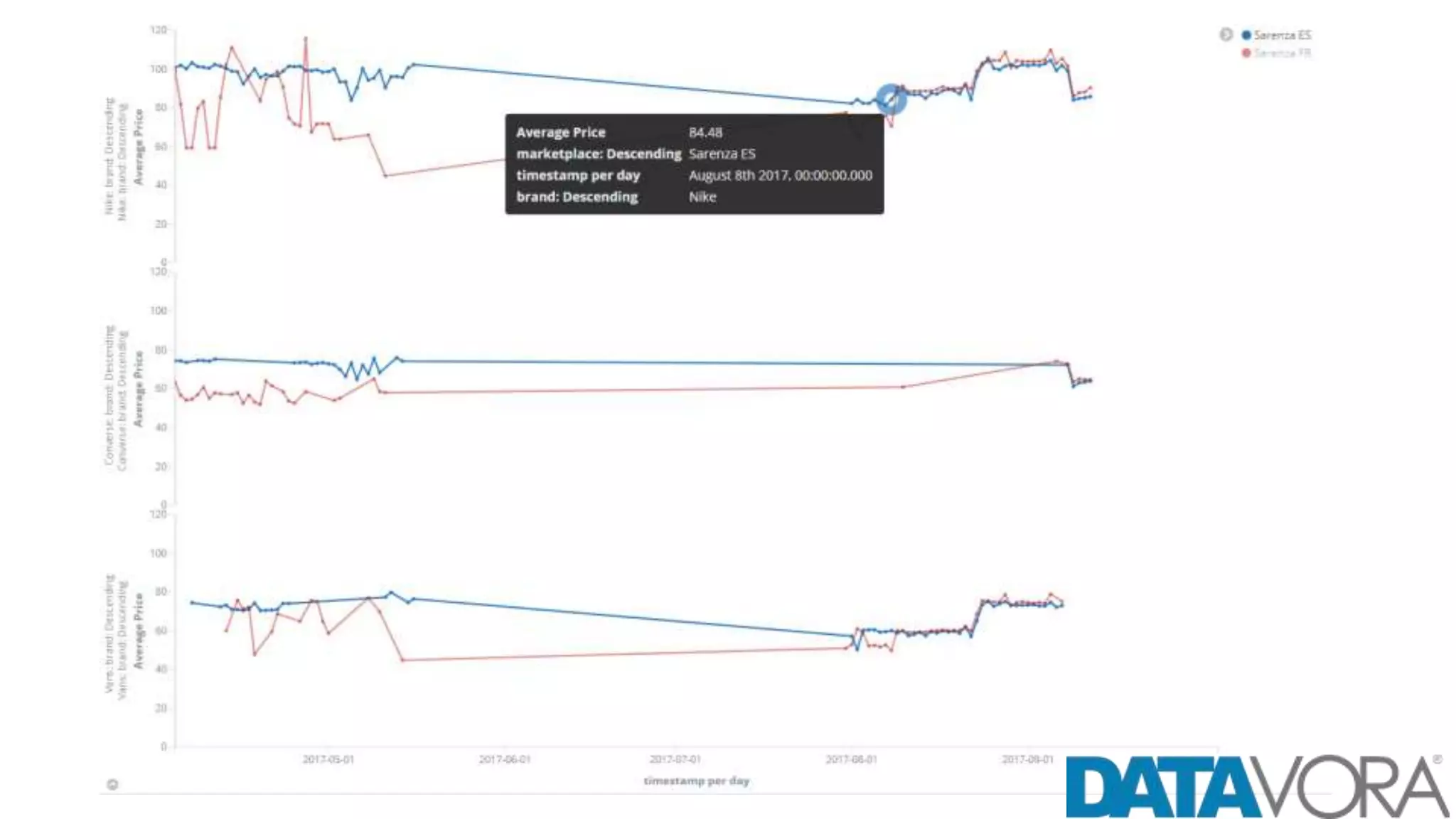
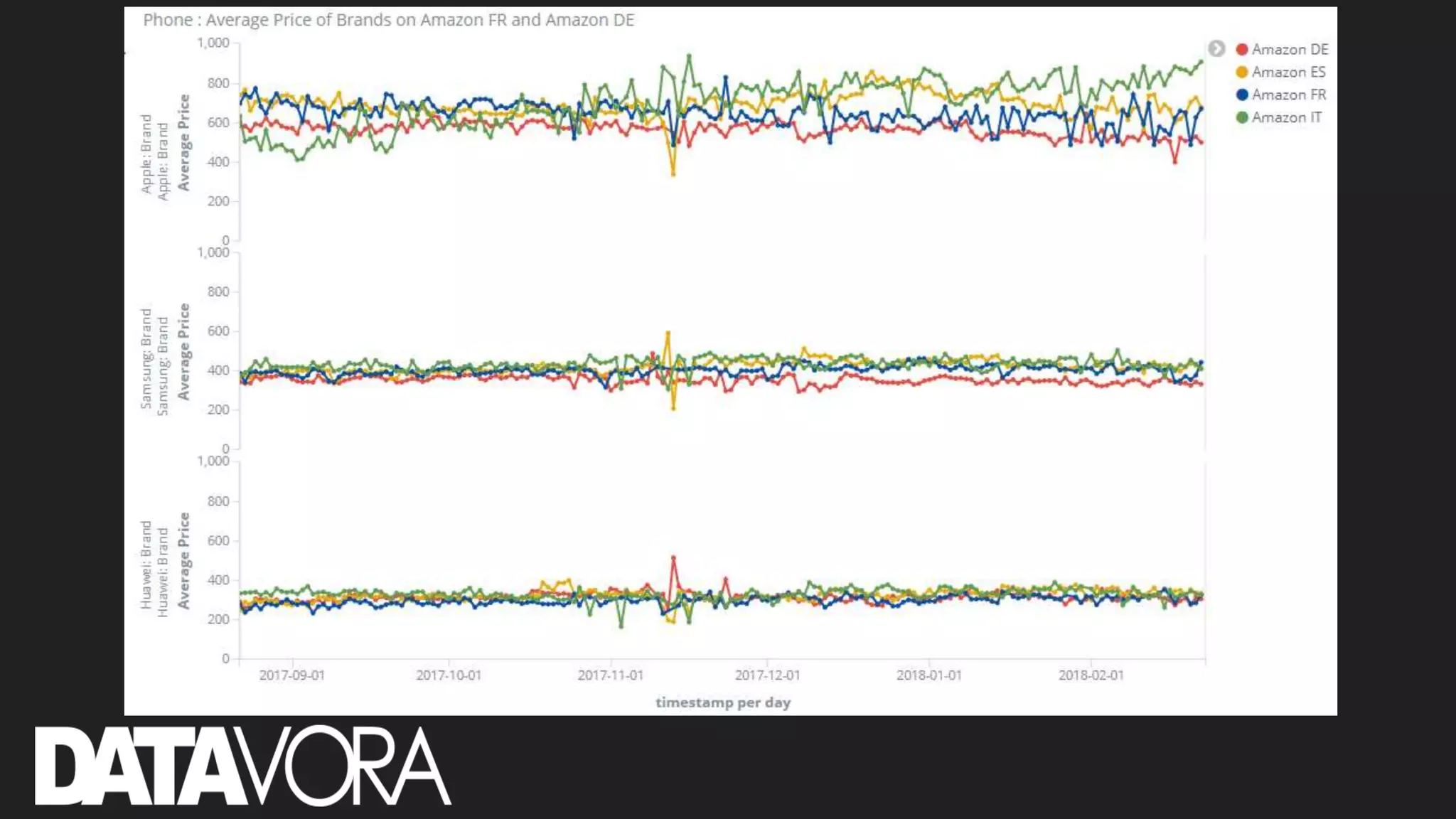
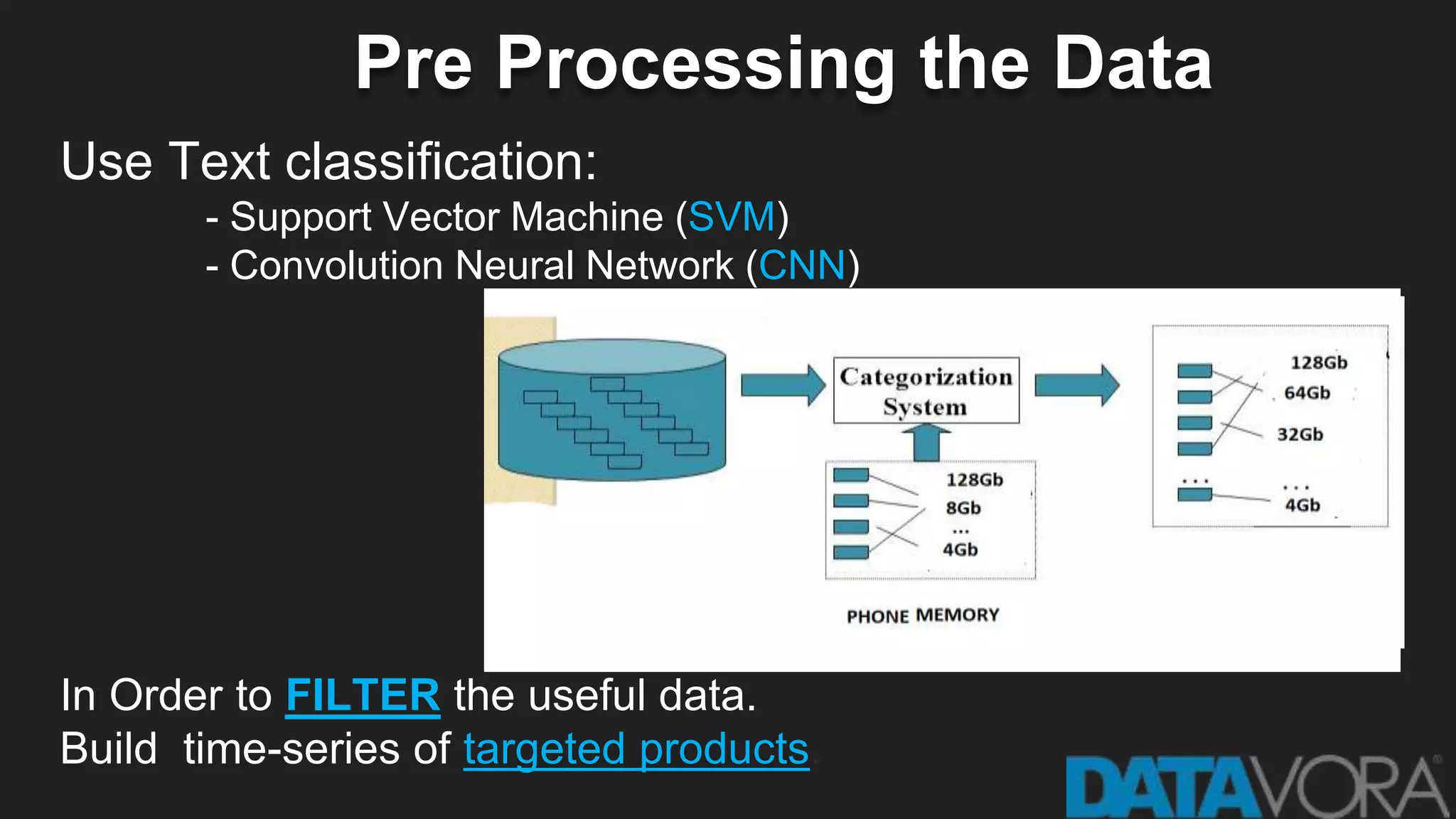
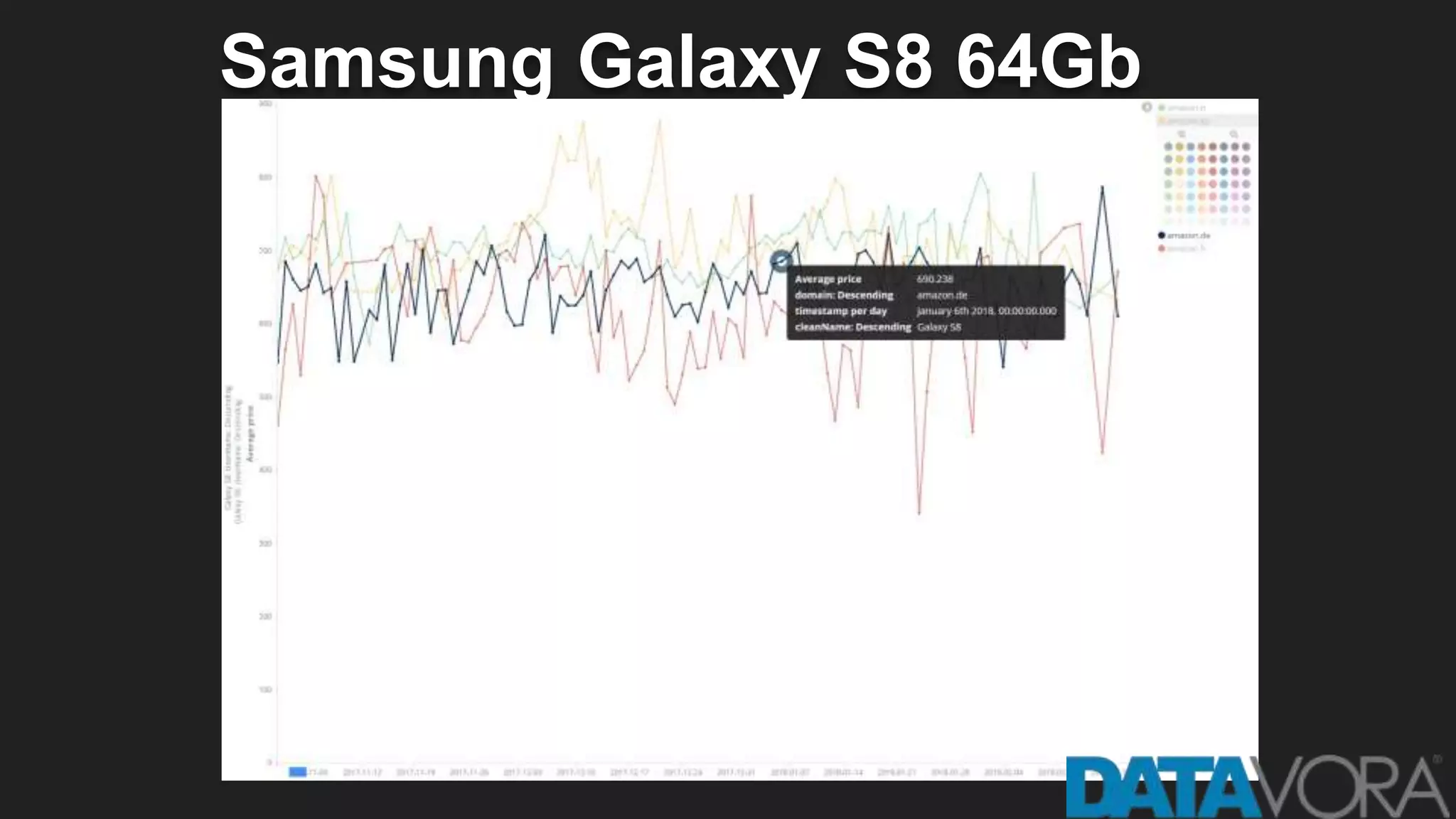
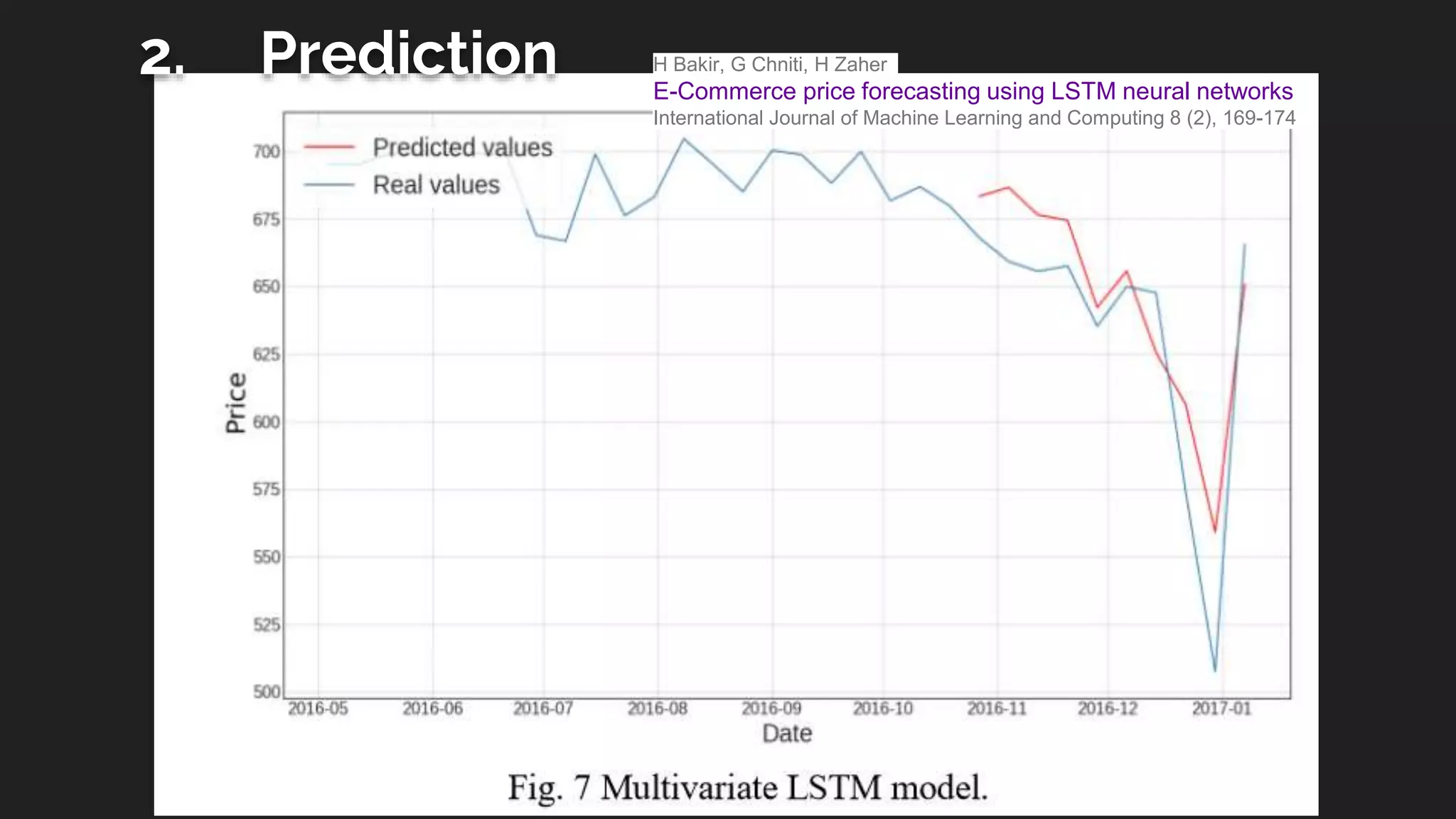
The document provides an overview of deep learning applications in e-commerce, emphasizing techniques like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for product classification and price forecasting. It discusses the architecture and functionality of CNNs, their implementation using frameworks like TensorFlow and Keras, and outlines various loss functions for different learning scenarios. Additionally, practical use cases and challenges in deploying these technologies for product matching are addressed.





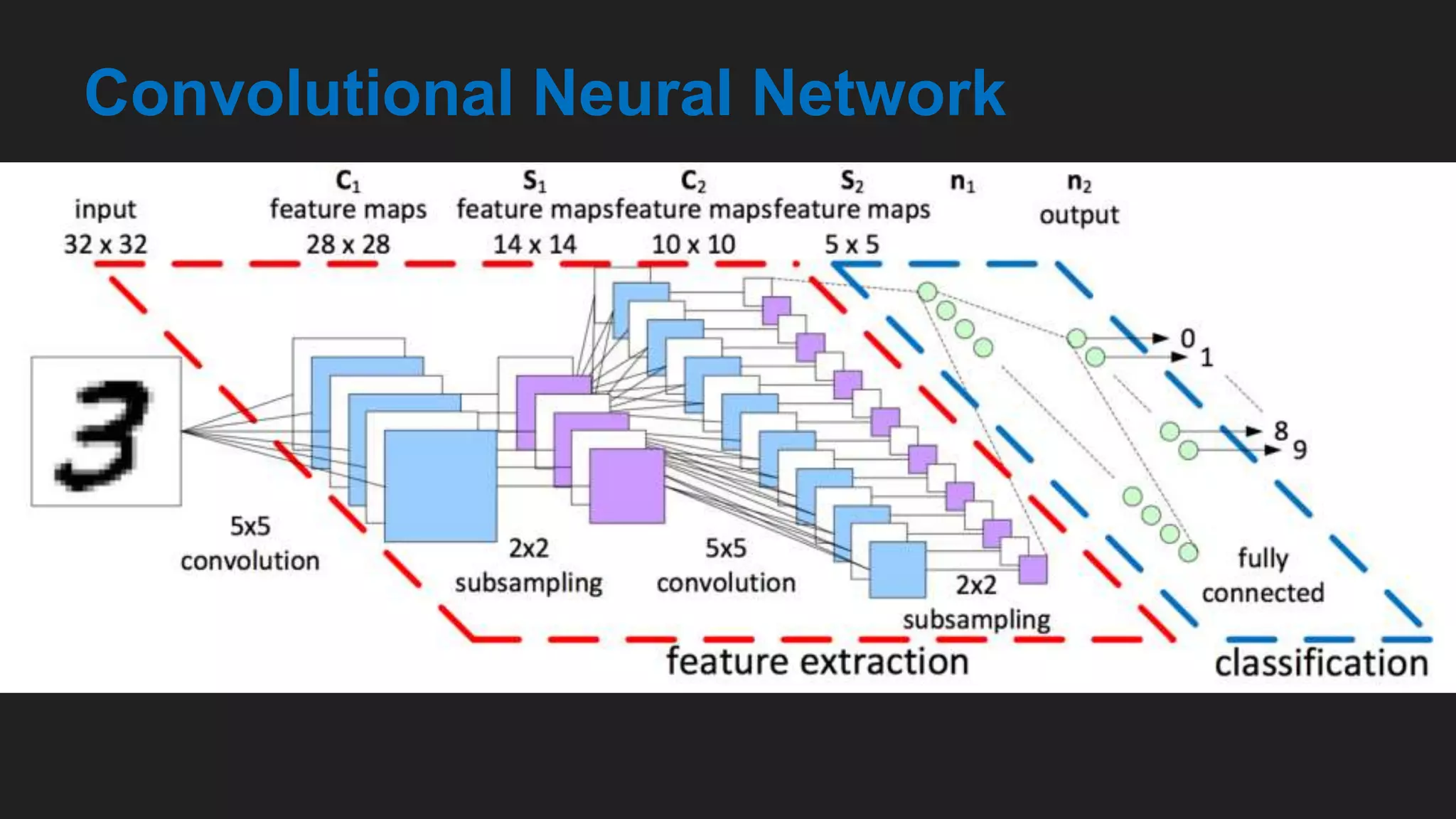
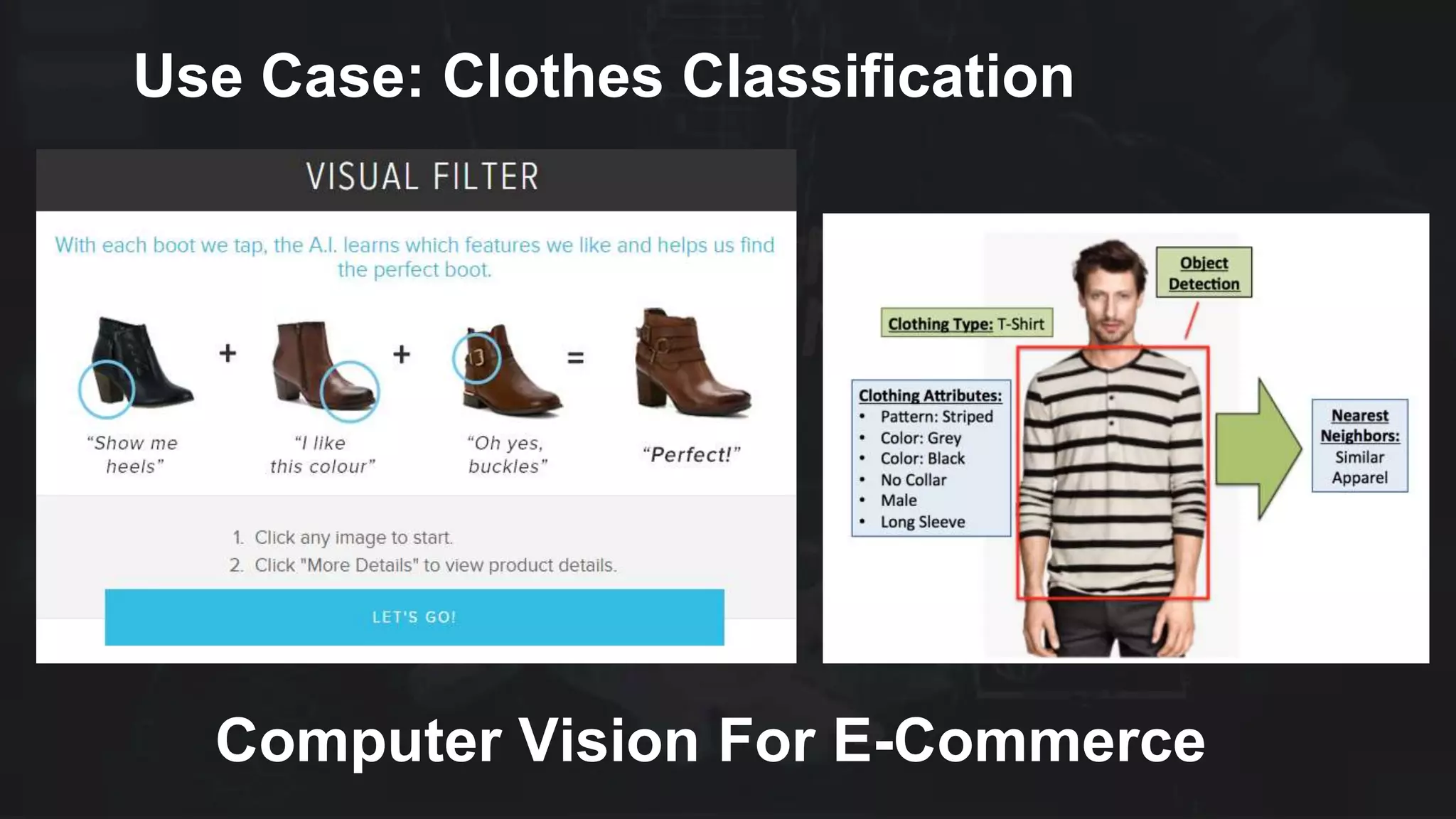
![Clothes Classification
[Convolutional Neural Networks for Clothes Categories September
2015 doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-48570-5_12 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningcnn-181012140922/75/Deep-learning-in-E-Commerce-Applications-and-Challenges-CNN-21-2048.jpg)