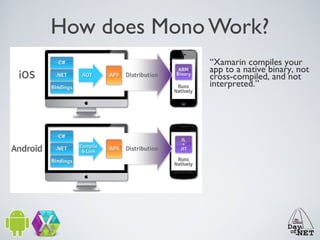
1) This document provides an overview of Xamarin and building Android apps. It discusses components like Xamarin.Mobile that allow writing code once across platforms.
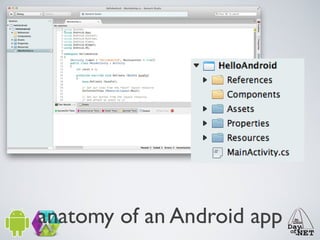
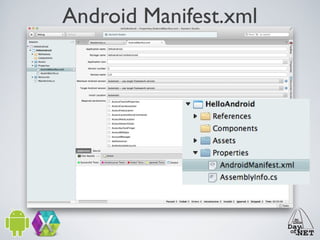
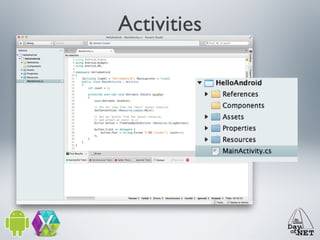
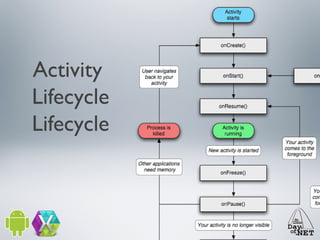
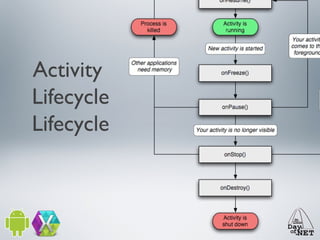
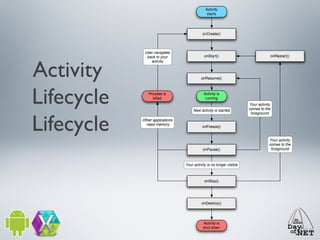
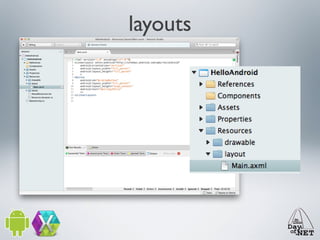
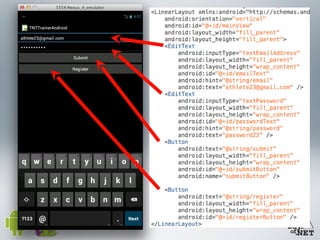
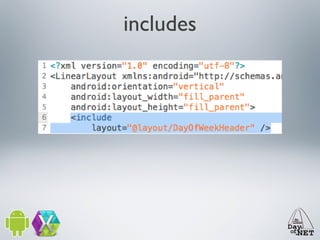
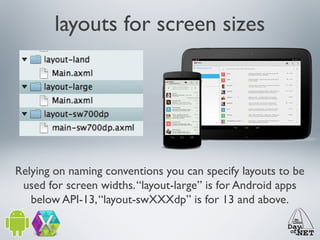
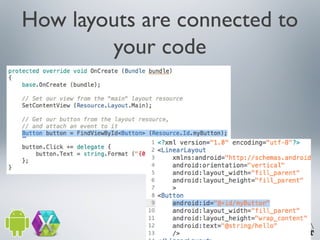
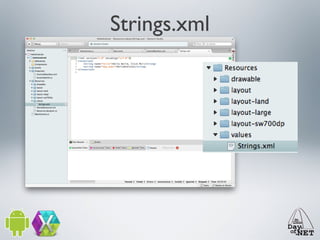
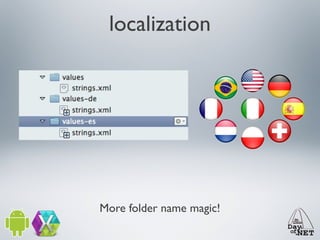
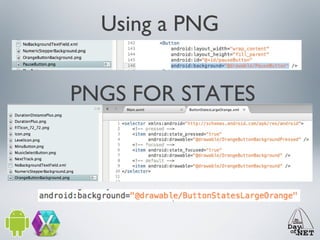
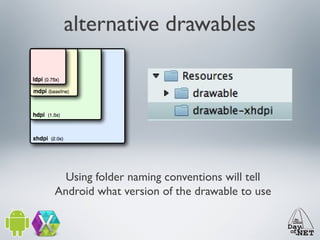
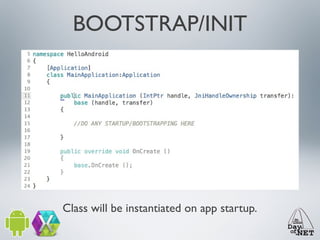
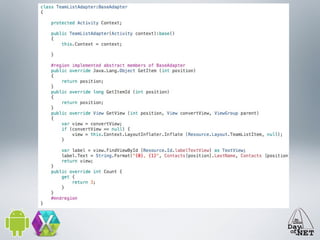
2) It describes the anatomy of an Android app including activities, layouts, strings, styles, and the main application class.
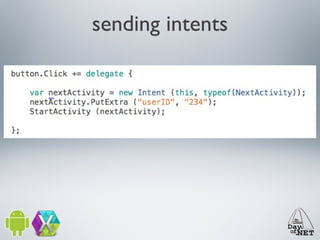
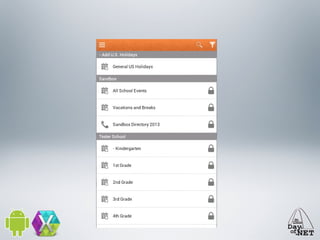
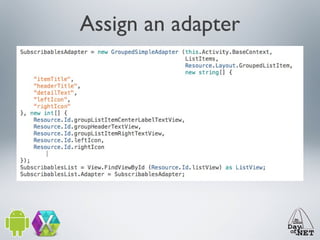
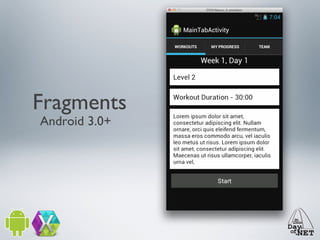
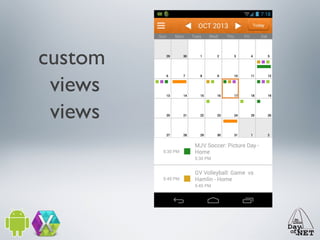
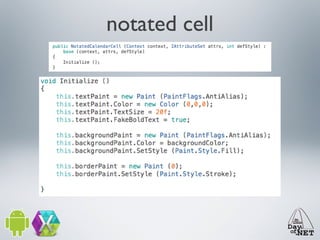
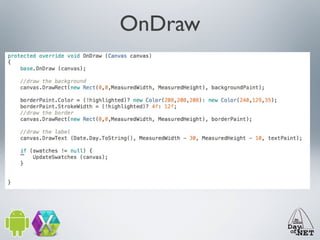
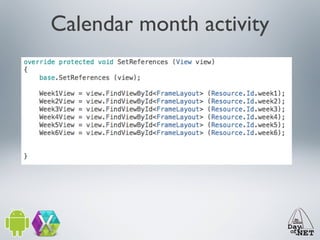
3) The document demonstrates how to create custom views like a calendar and handle intents, fragments, lists, and drawing. It provides best practices for testing on devices due to emulator limitations.