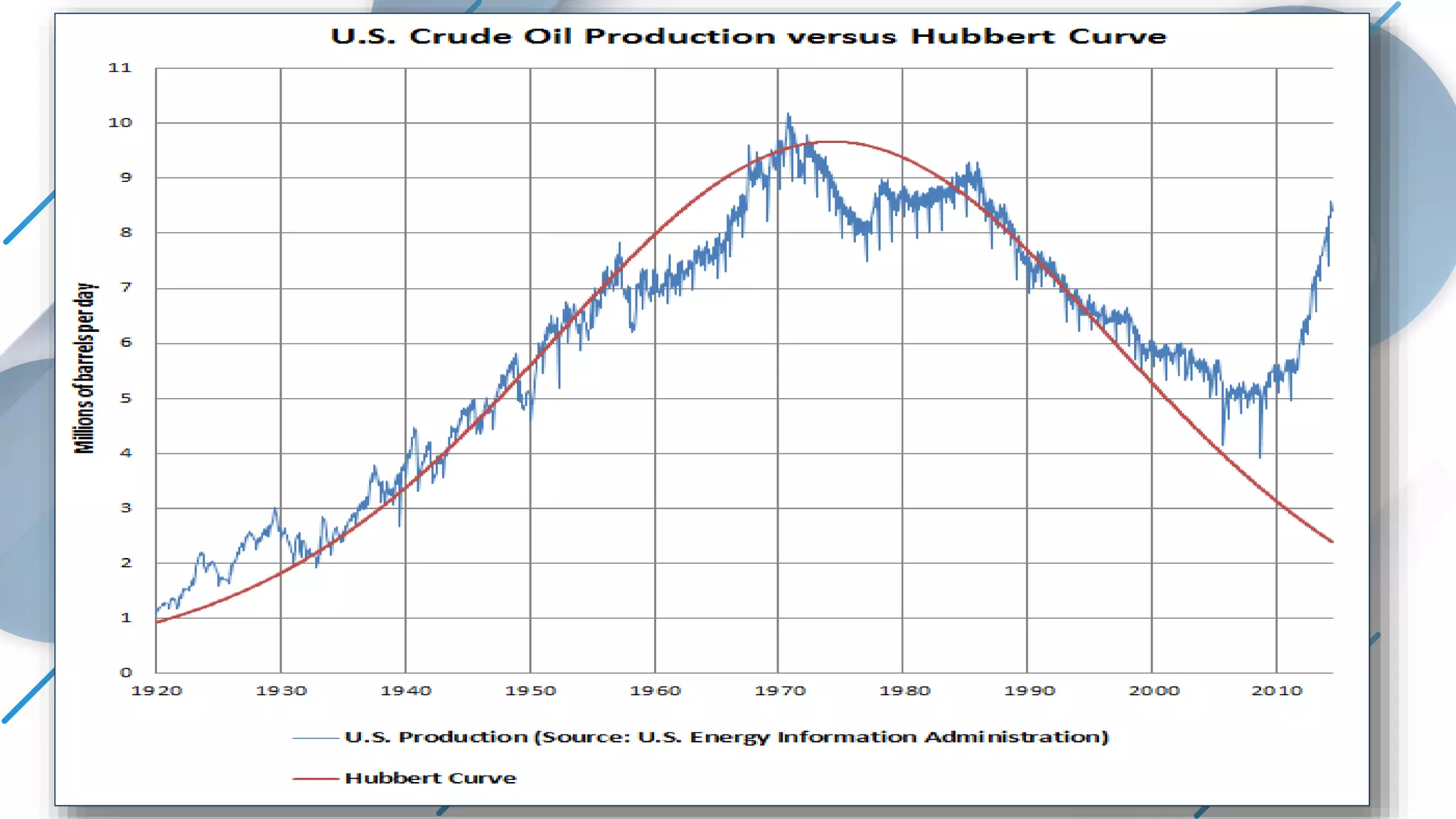
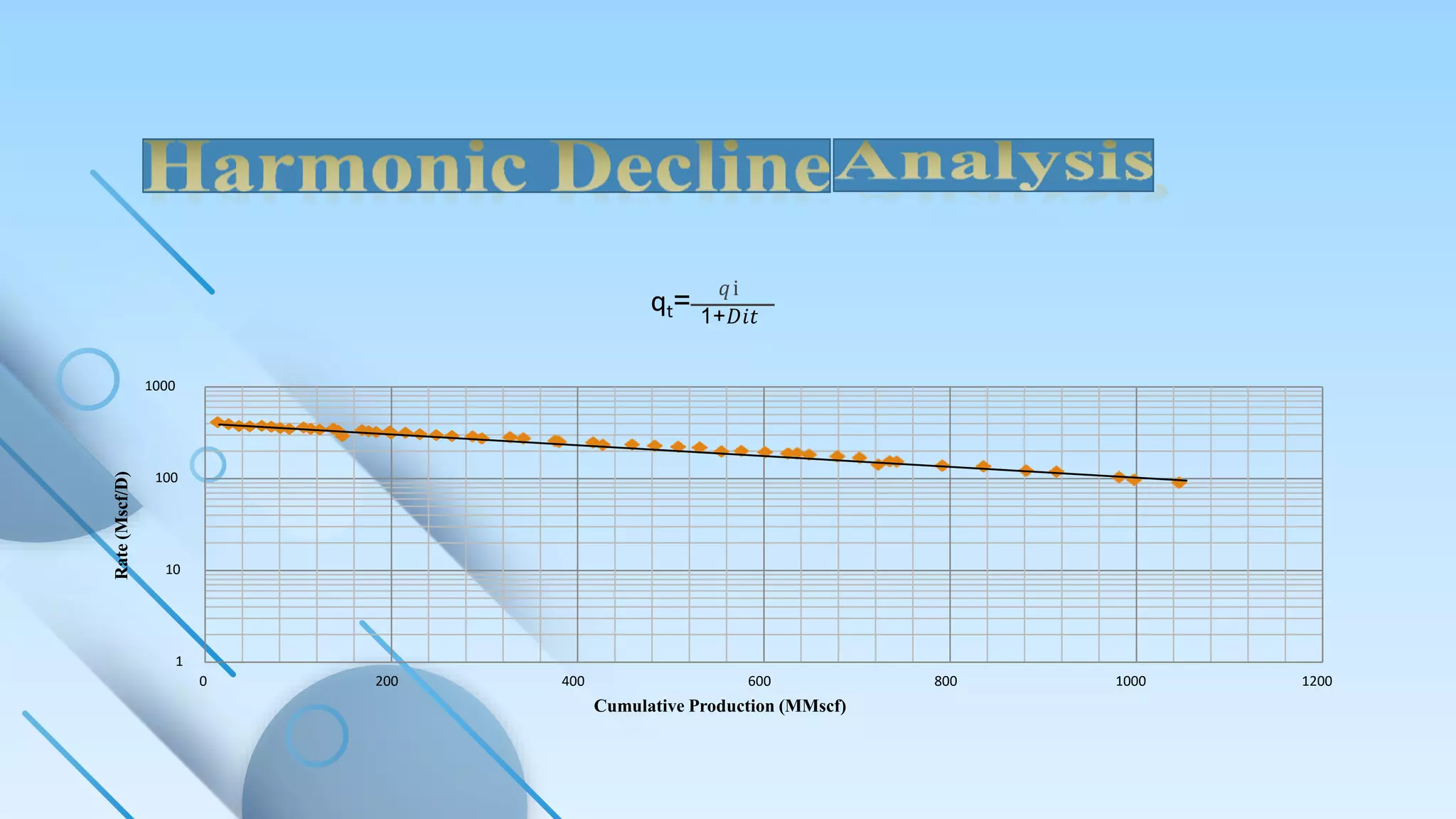
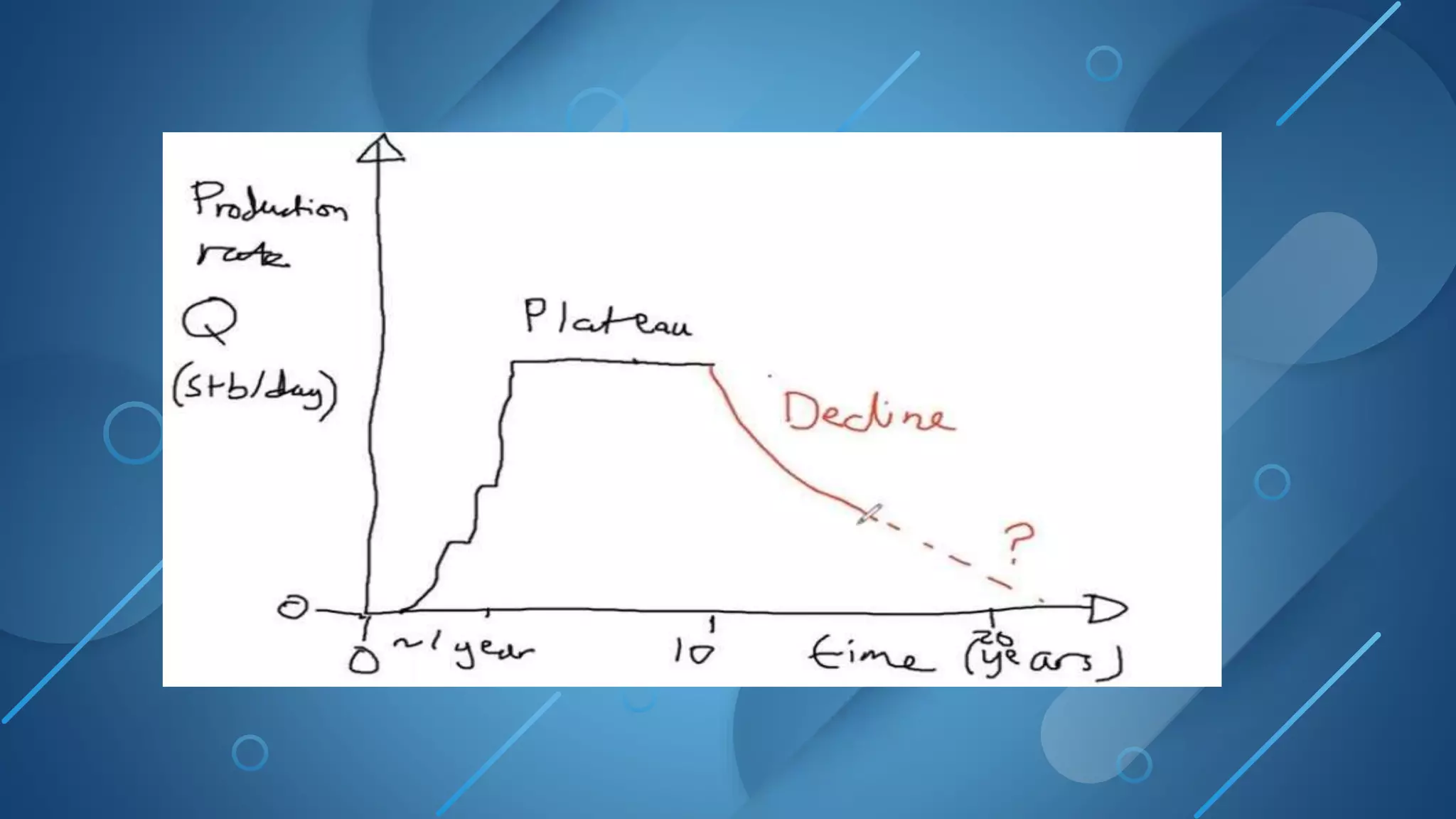
This document discusses decline curve analysis for predicting the depletion of natural resources like oil. It presents Hubbert's peak theory, which models the production rate of a resource over time as demand increases and peaks before dropping off. The objective of decline curve analysis is to predict production declines based on past data by fitting curves like exponential, harmonic, or hyperbolic models. Different curve types can model production declines for individual wells, fields, or groups of fields.







![References:
M. King Hubbert. " (PDF). Drilling and Production Practice (1956)
American Petroleum Institute & Shell Development Co. Publication No. 95, See Pp 9-11, 21-
22. Archived from (PDF) on 2008-05-27.^
Ugo Bardi and Leigh Yaxley. ] Proceedings of the 4th Workshop, Lisbon 2005^ Jean
Laherrere. . July, 1997.^ Patzek, Tad (2008-05-17).
" ". Archives
of Mining Sciences. 53 (2): 131–159. Retrieved 2018-11-17.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/declinecurvepresentations-230613094041-890e301d/75/decline-curve-presentations-pptx-11-2048.jpg)
