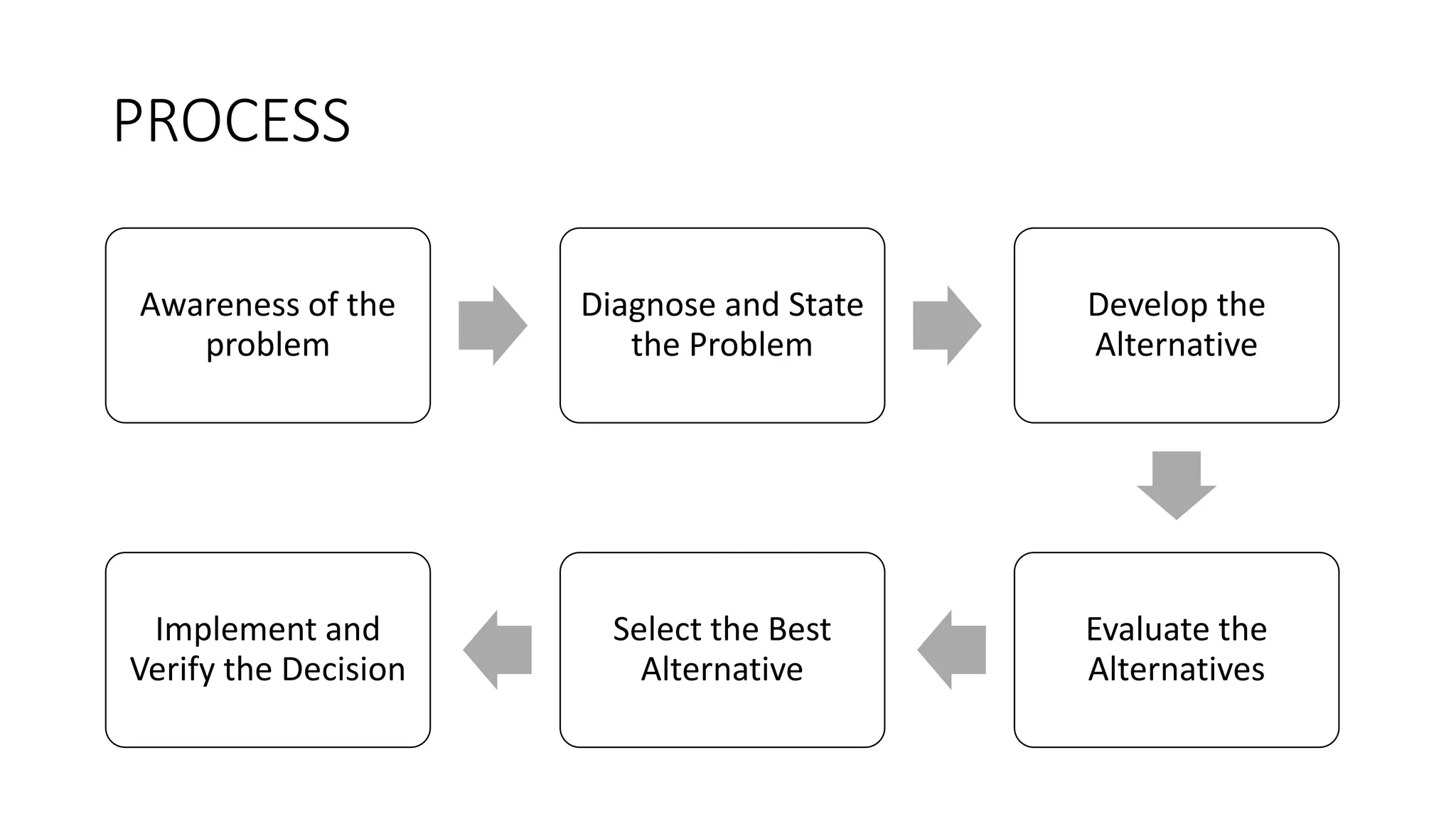
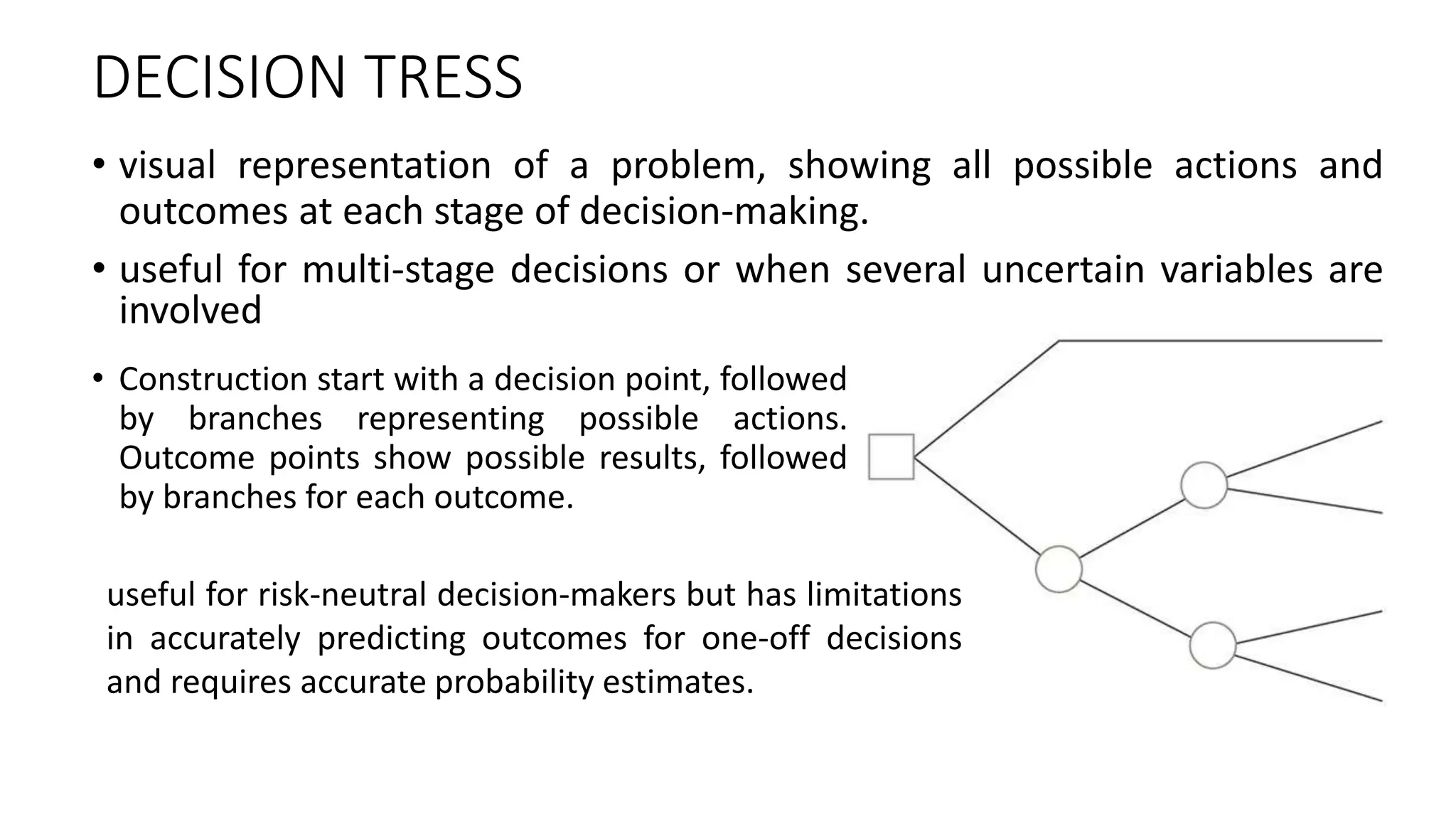
Decision-making is the cognitive process of selecting a course of action from multiple alternatives, aimed at achieving organizational goals. It is characterized by being goal-oriented, analytical, and a continuous activity involving risk and uncertainty. Various types and processes of decision-making exist, with tools like decision trees and SWOT analysis aiding in effective choices.