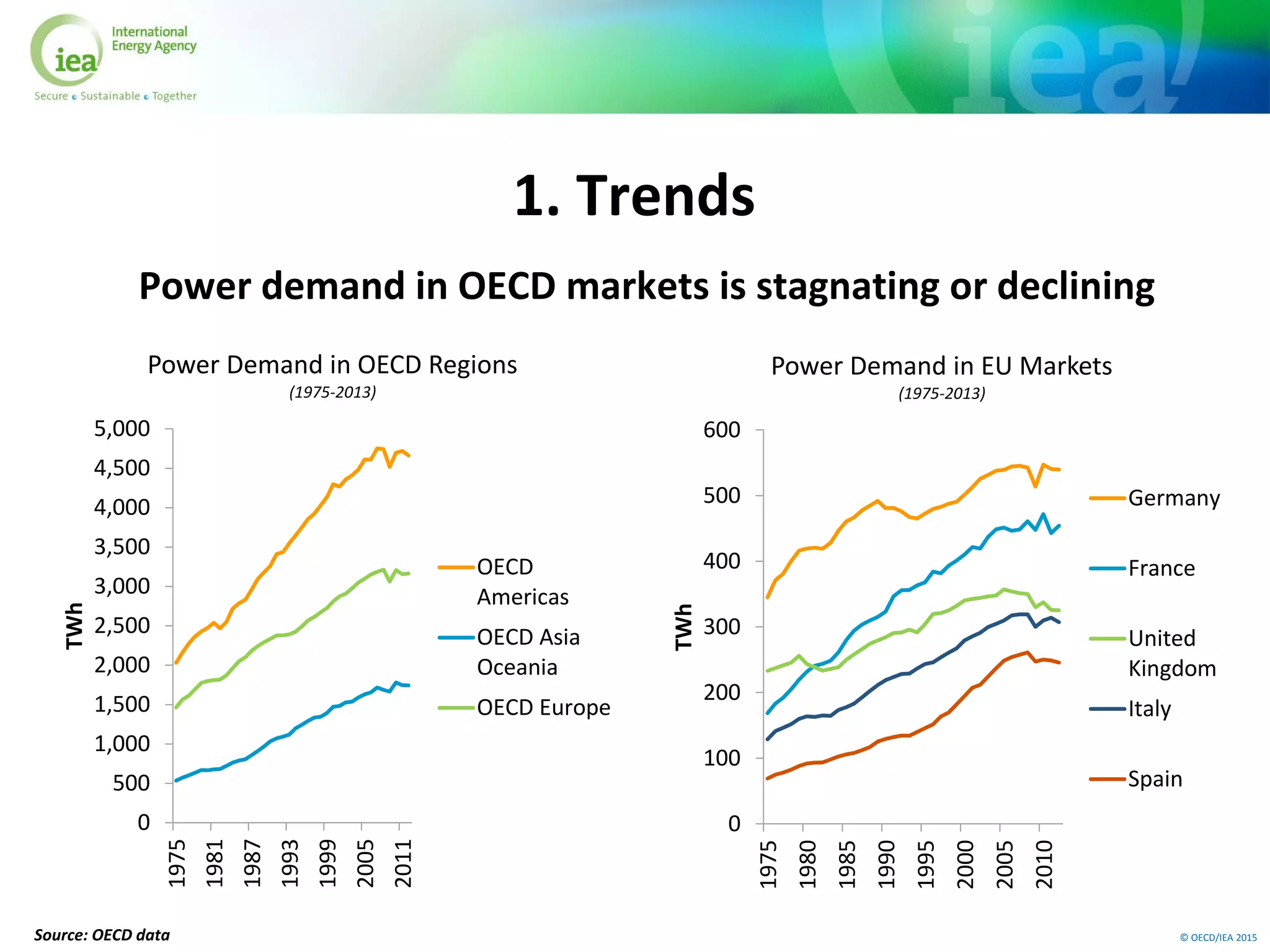
The document discusses trends and challenges in decarbonizing the EU power sector. It summarizes that power demand growth has declined since the 1990s and fossil fuels are being squeezed by rising renewable generation. A key challenge is that most coal and nuclear plants are over 30 years old. Meeting long-term decarbonization goals will require a large shift to renewable and low-carbon sources. However, integrating high shares of variable renewables poses economic and technical challenges to maintaining grid stability. Reforming the EU Emissions Trading System will also be important to provide a stronger carbon price signal to encourage needed investment in cleaner technologies.