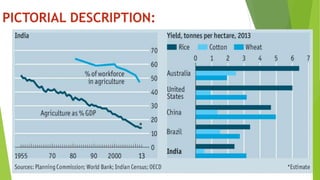
Indian agriculture has its origins in the Indus Valley Civilization. Agriculture involves growing crops and raising livestock. India's main agricultural crops are rice and wheat. Agriculture makes up a quarter of India's economy and employs 60% of its workforce. There are two main types of agriculture in India - industrialized agriculture which uses industrial techniques to mass produce crops and livestock for sale, and subsistence agriculture where small family farms produce enough only for their own consumption. Farming systems vary across India's different regions depending on climate and geography. India is heavily dependent on its monsoon rains for agricultural production.