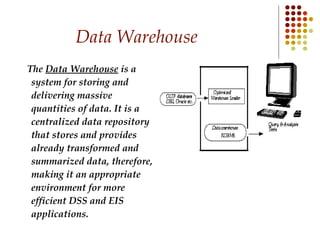
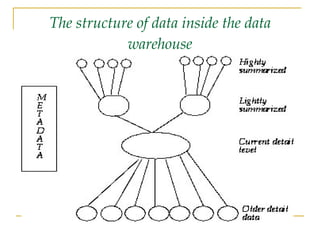
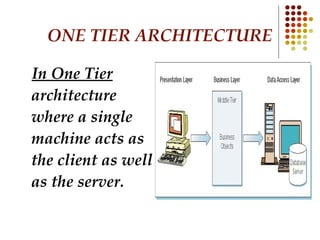
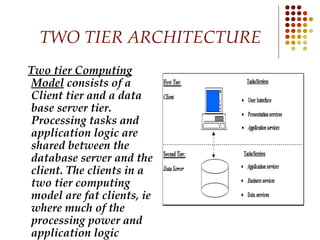
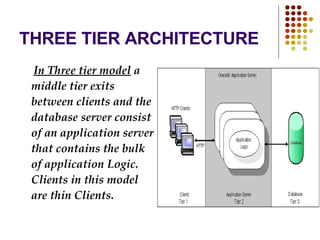
Databases are systems that contain objects used together to facilitate fast access to data. A data warehouse stores and provides already transformed and summarized data, making it suitable for decision support systems. Metadata is data about data that describes source data elements. Data mining refers to extracting hidden patterns from large databases.