Recommended
PPTX
PPTX
Data compression techniques
PPTX
PPTX
Data-Compression-Technique(communication).pptx
PDF
10lecture10datacompression-171023182241.pdf
PPT
lecture on data compression
PPTX
Unit 3 Image Compression and Segmentation.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
loss less compression in data compression
PDF
Data Communication & Computer network: Data compression
PDF
How GZIP works... in 10 minutes
PPTX
Fundamentals of Data compression
PPTX
data compression for information technology.pptx
PPTX
PPT
111111111111111111111111111111111789.ppt
PPTX
multimedia and design data compression techniques
PPTX
PPTX
Data compression & Classification
PPT
PPT
Grade 8 WK 14 Calculating File Transfer Speeds .ppt
PDF
2019188026 Data Compression (1) (1).pdf
PDF
The Language of Compression
PDF
The Language of Compression - Leif Walsh
PPTX
PPT
End-to-End Data representation in network.ppt
PPT
PPTX
image compression using html css js .pptx
PPTX
Image ppt using tmlcss ani js javascrit.pptx
PPTX
Organizational Structure and Design Topic 4
PDF
Analysis of Union Budget 2026-27: Major Announcements and their Impact
More Related Content
PPTX
PPTX
Data compression techniques
PPTX
PPTX
Data-Compression-Technique(communication).pptx
PDF
10lecture10datacompression-171023182241.pdf
PPT
lecture on data compression
PPTX
Unit 3 Image Compression and Segmentation.pptx
PPTX
Similar to Data_Compression_Application_Layer .
PPTX
loss less compression in data compression
PDF
Data Communication & Computer network: Data compression
PDF
How GZIP works... in 10 minutes
PPTX
Fundamentals of Data compression
PPTX
data compression for information technology.pptx
PPTX
PPT
111111111111111111111111111111111789.ppt
PPTX
multimedia and design data compression techniques
PPTX
PPTX
Data compression & Classification
PPT
PPT
Grade 8 WK 14 Calculating File Transfer Speeds .ppt
PDF
2019188026 Data Compression (1) (1).pdf
PDF
The Language of Compression
PDF
The Language of Compression - Leif Walsh
PPTX
PPT
End-to-End Data representation in network.ppt
PPT
PPTX
image compression using html css js .pptx
PPTX
Image ppt using tmlcss ani js javascrit.pptx
Recently uploaded
PPTX
Organizational Structure and Design Topic 4
PDF
Analysis of Union Budget 2026-27: Major Announcements and their Impact
PDF
10 Best Sites To Buy iCloud Email Accounts.pdf
PPTX
Blue and Yellow Education Technology Keynote Presentation.pptx
PDF
"Streamline Project Management with Trello + Butler Automation | CA Suvidha C...
PDF
US Digital Fan Engagement Index 2026: Benchmarking Online Demand for Sports T...
PPTX
Top Institute for Data Analyst Course in Navi Mumbai
PDF
chapter one introduction to Probability theory.pdf
PPTX
End to End Supply Chain Management- Analytics Case Study.
PDF
Trustworthy AI : Governance of AI through Ethics
PDF
AI Data Analyst for Real Estate Reporting & Insights | Leni Analytics
PDF
Columbus Data and Analytics Wednesday - People Analytics 101: Making Sense of...
PDF
WORLD-LITERATURE-2ND-SEMESTER2025-2026.pdf
DOCX
What Are Buy Verified Apple Pay Accounts and Why Do You Need Them_.docx
PDF
Purdue CS592_ Databases for AI_ Vector Databases (Spring 2026)
PDF
Unlocking the Future of Logistics & Supply Chain
PDF
Understanding Data Analytics: Concepts, Types, and Use Cases
PPTX
How to Find Sources Wisely for Academic Writing.pptx
PPTX
AI IN CYBERSECURITY Best Practices for IT
PPTX
Big Data Anaytics ..................................(3).pptx
Data_Compression_Application_Layer . 1. 2. What is Data Compression?
• Data compression reduces the size of data to
save bandwidth and speed up transmission.
• It helps in efficient communication over
networks.
3. Why is Compression Needed?
• - Faster transmission
• - Saves bandwidth
• - Reduces storage
• - Optimizes app performance (email, web, file
transfer)
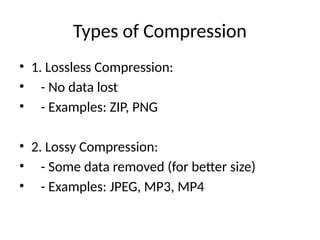
4. Types of Compression
• 1. Lossless Compression:
• - No data lost
• - Examples: ZIP, PNG
• 2. Lossy Compression:
• - Some data removed (for better size)
• - Examples: JPEG, MP3, MP4
5. How Does It Work?
• Common Techniques:
• - Run-Length Encoding (RLE)
• - Huffman Coding
• - LZW (Lempel-Ziv-Welch)
• Each method reduces repeated or common
data patterns.
6. Real-World Examples
• - Web pages use GZIP
• - Email attachments as ZIP files
• - Video streaming with MP4
• - FTP file transfers
• - Cloud storage compression
7. Advantages & Limitations
• ✅ Advantages:
• - Smaller file sizes
• - Faster data transfer
• - Saves data and bandwidth
• ⚠️Limitations:
• - May take time to compress/decompress
• - Lossy compression may reduce quality
8. Role in Application Layer
• - Used in HTTP (web), FTP, SMTP (email),
Telnet/SSH
• - Makes communication faster and more
efficient
• - Important for sending large data over the
internet