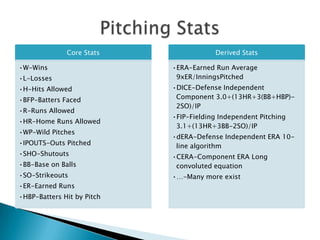
The document discusses using data mining techniques to analyze baseball player and pitcher statistics from the 2010 regular season. Decision tree models identified several key stats that were associated with teams winning their divisions that year, such as keeping strikeouts high and walks low for pitchers. Counterintuitively, having too many home runs was linked to losing the division. Data mining provided more insights than traditional statistical analyses by revealing complex, nonlinear relationships between performance metrics.