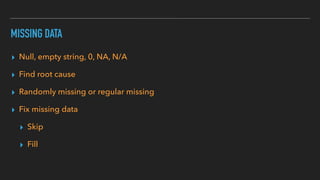
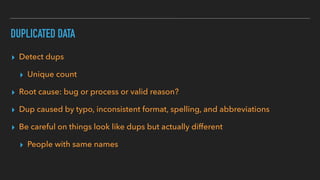
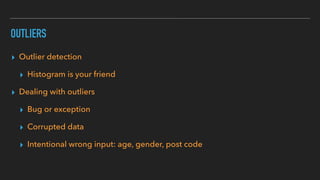
This document discusses various data quality issues that can arise such as missing data, duplicated data, outliers, and subtle problems. It provides examples of each issue and recommends approaches for detecting and resolving them. A wide range of tools are also presented for exploratory and production data cleansing using technologies like R, Python, OpenRefine, and Hadoop/Spark. Machine learning techniques can also be applied to help with data cleansing. General best practices emphasized include following a data pipeline, keeping raw data immutable, and making processes reproducible.