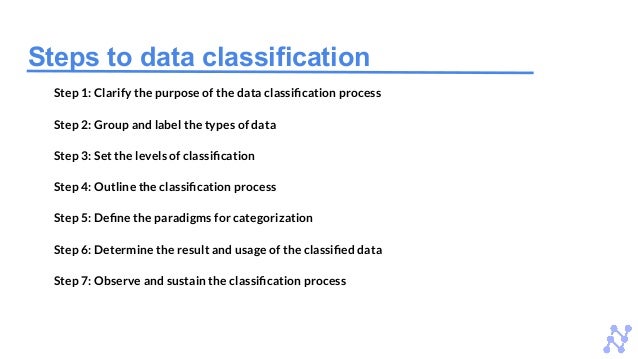
Data classification is the process of categorizing structured and unstructured data based on various criteria, enhancing data organization and searchability for organizations. There are four types of data classification based on sensitivity levels: public access, internal, confidential, and restricted access data. The document outlines the steps for effective data classification and emphasizes the importance of selecting appropriate data classification tools to ensure data security.