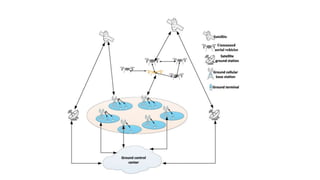
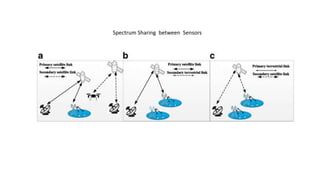
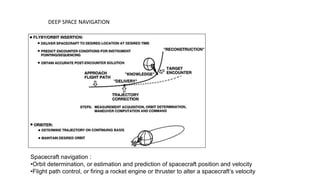
Space data comes from sensors on satellites and contains unique properties. It requires specialized processing techniques due to its large size. Data analytics and artificial intelligence are increasingly being used to analyze space data and extract useful information. For example, NASA uses AI to optimize data downloading from the Mars Express spacecraft to prevent data loss. In the future, AI may enable more autonomous spacecraft navigation and coordinated control of multiple spacecraft.